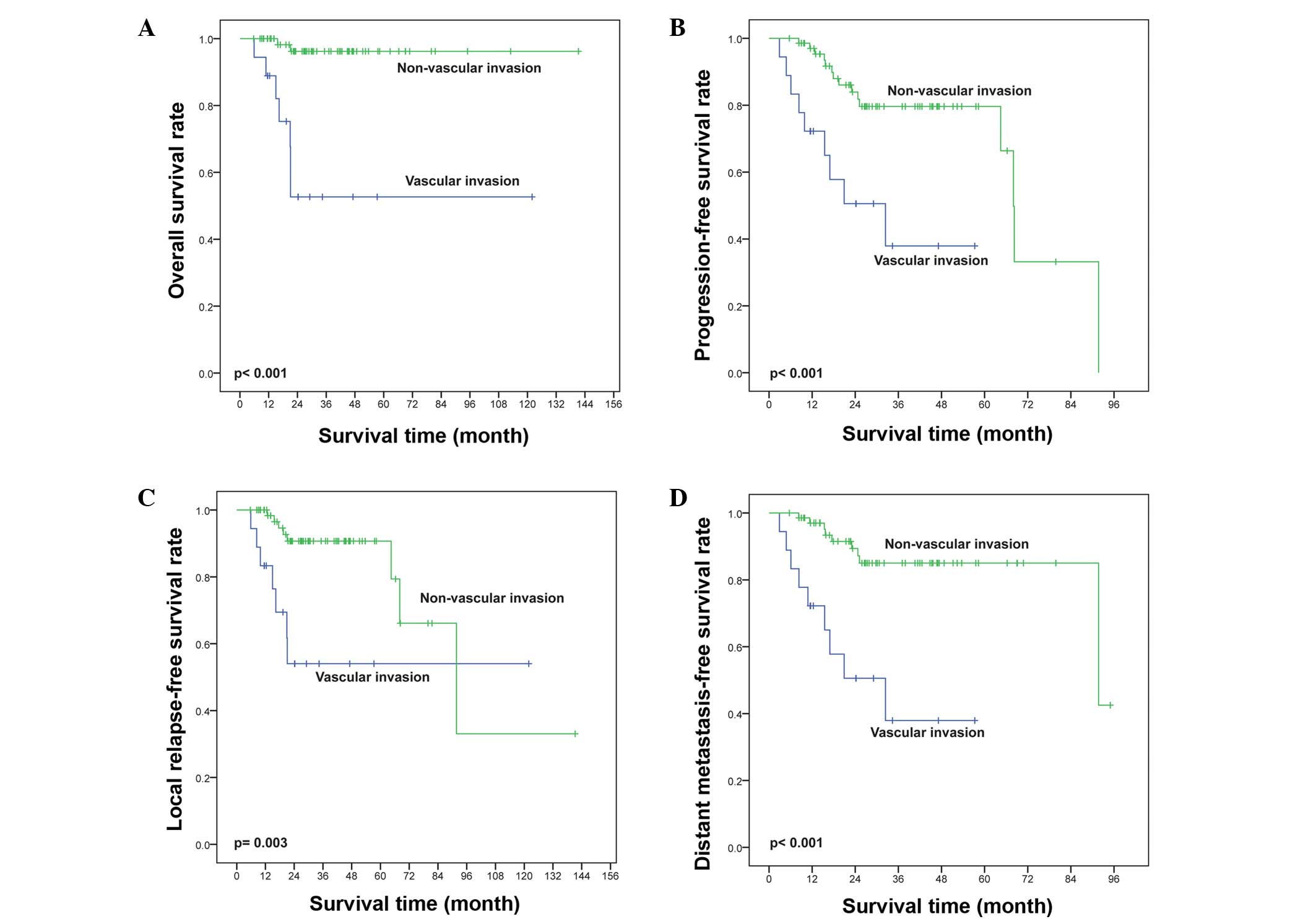
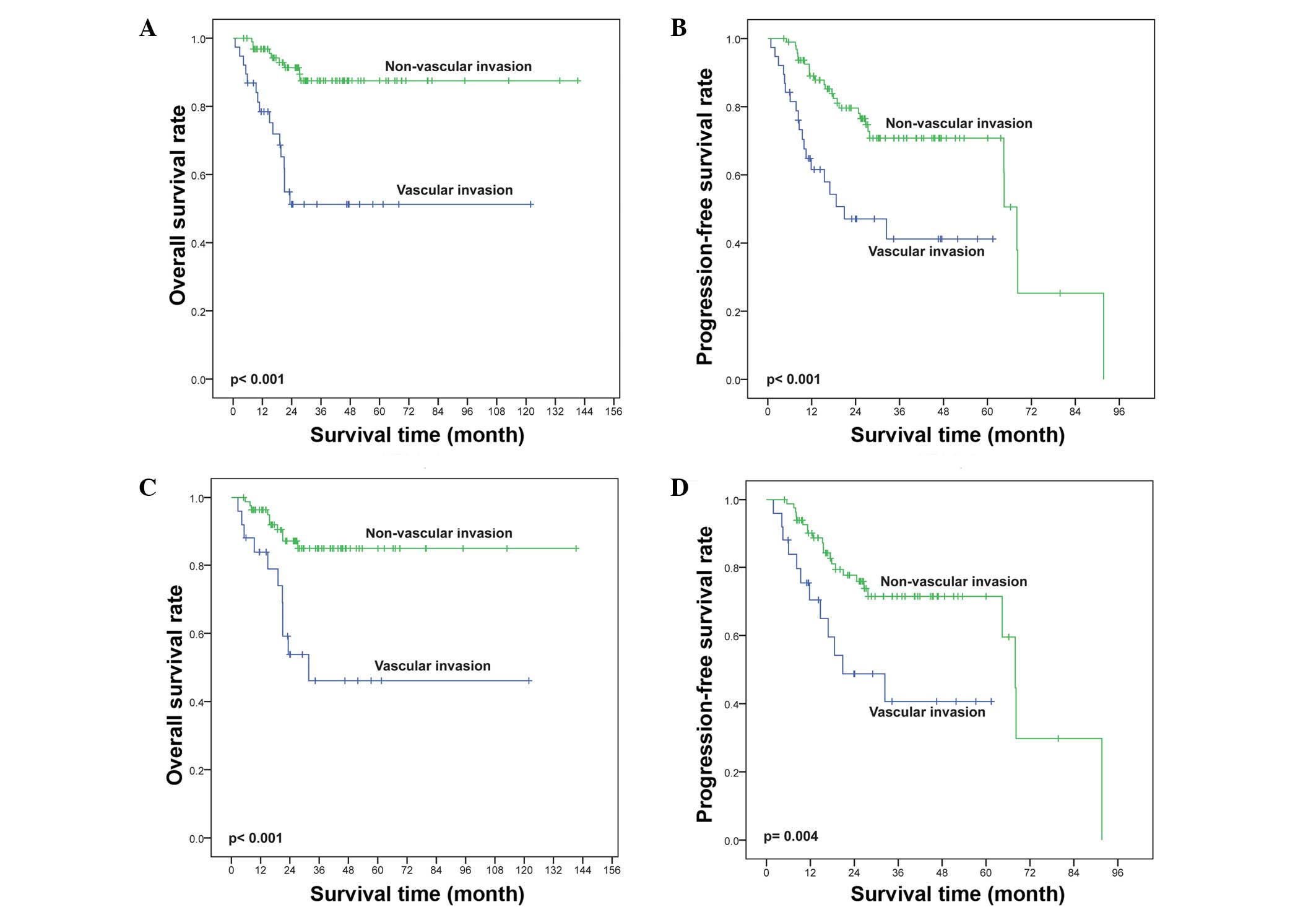
|
1
|
Vose J, Armitage J and Weisenburger D:
International T-Cell Lymphoma Project: International peripheral
T-cell and natural killer/T-cell lymphoma study: Pathology findings
and clinical outcomes. J Clin Oncol. 26:4124–4130. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Au WY, Ma SY, Chim CS, et al:
Clinicopathologic features and treatment outcome of mature T-cell
and natural killer-cell lymphomas diagnosed according to the World
Health Organization classification scheme: A single center
experience of 10 years. Ann Oncol. 16:206–214. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li YX, Liu QF, Fang H, Qi SN, Wang H, Wang
WH, Song YW, Lu J, Jin J, Wang SL, et al: Variable clinical
presentations of nasal and Waldeyer ring natural killer/T-cell
lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:2905–2912. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kwong YL, Kim WS, Lim ST, Kim SJ, Tang T,
Tse E, Leung AY and Chim CS: SMILE for natural killer/T-cell
lymphoma: Analysis of safety and efficacy from the Asia Lymphoma
Study Group. Blood. 120:2973–2980. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang L, Xia ZJ, Huang HQ, Lu Y and Zhang
YJ: Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone
(CHOP) in the treatment of stage IE/IIE extranodal natural killer/T
cell lymphoma, nasal type: 13-year follow-up in 135 patients. Int J
Hematol. 96:617–623. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee J, Suh C, Park YH, Ko YH, Bang SM, Lee
JH, Lee DH, Huh J, Oh SY, Kwon HC, et al: Extranodal natural killer
T-cell lymphoma, nasal-type: A prognostic model from a
retrospective multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 24:612–618. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nishida T, Katayama S and Tsujimoto M: The
clinicopathological significance of histologic vascular invasion in
differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Am J Surg. 183:80–86. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Straume O and Akslen LA: Independent
prognostic importance of vascular invasion in nodular melanomas.
Cancer. 78:1211–1219. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ouchi K, Sugawara T, Ono H, Fujiya T,
Kamiyama Y, Kakugawa Y, Mikuni J and Tateno H: Histologic features
and clinical significance of venous invasion in colorectal
carcinoma with hepatic metastasis. Cancer. 78:2313–2317. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Maehara Y, Kabashima A, Koga T, Tokunaga
E, Takeuchi H, Kakeji Y and Sugimachi K: Vascular invasion and
potential for tumor angiogenesis and metastasis in gastric
carcinoma. Surgery. 128:408–416. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chau GY, Lui WY and Wu CW: Spectrum and
significance of microscopic vascular invasion in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 12:25–34, viii. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Van Poppel H, Vandendriessche H, Boel K,
Mertens V, Goethuys H, Haustermans K, Van Damme B and Baert L:
Microscopic vascular invasion is the most relevant prognosticator
after radical nephrectomy for clinically nonmetastatic renal cell
carcinoma. J Urol. 158:45–49. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schoppmann SF, Bayer G, Aumayr K, Taucher
S, Geleff S, Rudas M, Kubista E, Hausmaninger H, Samonigg H, Gnant
M, et al: Prognostic value of lymphangiogenesis and lymphovascular
invasion in invasive breast cancer. Ann Surg. 240:306–312. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang JJ, Jiang WQ, Lin TY, Huang Y, Xu
RH, Huang HQ and Li ZM: Absolute lymphocyte count is a novel
prognostic indicator in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma,
nasal type. Ann Oncol. 22:149–155. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Conill C, Verger E and Salamero M:
Performance Status Assessment in Cancer Patients. Cancer.
65:1864–1866. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Musshoff K and Schmidt-Vollmer H:
Proceedings: Prognosis of non-Hodgkin's lymphomas with special
emphasis on the staging classification. Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
83:323–341. 1975.
|
|
17
|
Lin ZX, Bai B, Cai QC, Cai QQ, Wang XX, Wu
XY and Huang HQ: High numbers of tumor-associated macrophages
correlate with poor prognosis in patients with mature T- and
natural killer cell lymphomas. Med Oncol. 29:3522–3528. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang L, Xia ZJ, Huang HQ, Lu Y and Zhang
YJ: Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone
(CHOP) in the treatment of stage IE/IIE extranodal natural killer/T
cell lymphoma, nasal type: 13 year follow up in 135 patients. Int J
Hematol. 96:617–623. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huijgens PC, Ossenkoppele GJ, Van Der
Lelie J, Thomas LL, Wijngaarden MJ and Slaper CM: IMVP-16 followed
by high dose chemotherapy and autologous bone marrow
transplantation as salvage treatment for malignant lymphoma.
Hematol Oncol. 9:245–251. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Velasquez WS, Cabanillas F, Salvador P,
McLaughlin P, Fridrik M, Tucker S, Jagannath S, Hagemeister FB,
Redman JR and Swan F: Effective salvage therapy for lymphoma with
cisplatin in combination with high-dose Ara-C and dexamethasone
(DHAP). Blood. 71:117–122. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang H, Wuxiao ZJ, Zhu J, Wang Z, Wang KF,
Li S, Chen X, Lu Y and Xia ZJ: Comparison of gemcitabine,
oxaliplatin and L-asparaginase and etoposide, vincristine,
doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide and prednisone as firstline
chemotherapy in patients with stage IE to IIE extranodal natural
killer/Tcell lymphoma: A multicenter retrospective study. Leuk
Lymphoma. 56:971–977. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cheson BD, Horning SJ, Coiffier B, et al:
Report of an international workshop to standardize response
criteria for non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. NCI sponsored international
working group. J Clin Oncol. 17:12441999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang L, Li P, Wang H, Liu J, Zhang X, Qiu
H and Zhang B: Prognostic significance of Ki-67 antigen expression
in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Med
Oncol. 31:2182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bossard C, Belhadj K, Reyes F,
Martin-Garcia N, Berger F, Kummer JA, Brière J, Baglin AC, Cheze S,
Bosq J, et al: Expression of the granzyme B inhibitor PI9 predicts
outcome in nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma: Results of a Western series of
48 patients treated with first-line polychemotherapy within the
Groupe d'Etude des Lymphomes de l'Adulte (GELA) trials. Blood.
109:2183–2189. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim WY, Jeon YK, Kim TM, Kim JE, Kim YA,
Lee SH, Kim DW, Heo DS and Kim CW: Increased quantity of
tumor-infiltrating FOXP3-positive regulatory T cells is an
independent predictor for improved clinical outcome in extranodal
NK/T-cell lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 20:1688–1696. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shim SJ, Yang WI, Shin E, Koom WS, Kim YB,
Cho JH, Suh CO, Kim JH and Kim GE: Clinical significance of
cyclooxygenase-2 expression in extranodal natural killer
(NK)/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
67:31–38. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hong J, Park S, Baek HL, Jung JH, Kang IG,
Sym SJ, Park J, Ahn JY, Cho EK, Kim ST, et al: Tumor cell nuclear
diameter and CD30 expression as potential prognostic parameter in
patients with extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 5:939–947. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cuadra-Garcia I, Proulx GM, Wu CL, Wang
CC, Pilch BZ, Harris NL and Ferry JA: Sinonasal lymphoma: A
clinicopathologic analysis of 58 cases from the Massachusetts
General Hospital. Am J Surg Pathol. 23:1356–1369. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Seki D, Ueno K, Kurono Y and Eizuru Y:
Clinicopathological features of Epstein-Barr virus-associated nasal
T/NK cell lymphomas in southern Japan. Auris Nasus Larynx.
28:61–70. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wróbel T, Poreba M, Mazur G, Poreba R,
Pyszel A, Beck B, Steinmetz-Beck A, Andrzejak R and Kuliczkowski K:
Angiogenic and coagulation-fibrinolysis factors in non Hodgkin's
lymphoma. Neoplasma. 53:253–258. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tan KL, Scott DW, Hong F, Kahl BS, Fisher
RI, Bartlett NL, Advani RH, Buckstein R, Rimsza LM, Connors JM, et
al: Tumor-associated macrophages predict inferior outcomes in
classic Hodgkin lymphoma: A correlative study from the E2496
intergroup trial. Blood. 120:3280–3287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Siveen KS and Kuttan G: Role of
macrophages in tumour progression. Immunol Lett. 123:97–102. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Allavena P, Sica A, Solinas G, Porta C and
Mantovani A: The inflammatory micro-environment in tumor
progression: The role of tumor-associated macrophages. Crit Rev
Oncol Hematol. 66:1–9. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li YX, Yao B, Jin J, Wang WH, Liu YP, Song
YW, Wang SL, Liu XF, Zhou LQ, He XH, et al: Radiotherapy as primary
treatment for stage IE and IIE nasal natural killer/T-cell
lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 24:181–189. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim GE, Cho JH, Yang WI, Chung EJ, Suh CO,
Park KR, Hong WP, Park IY, Hahn JS, Roh JK and Kim BS: Angiocentric
lymphoma of the head and neck: Patterns of systemic failure after
radiation treatment. J Clin Oncol. 18:54–63. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Koom WS, Chung EJ, Yang WI, Shim SJ, Suh
CO, Roh JK, Yoon JH and Kim GE: Angiocentric T-cell and NK/T-cell
lymphomas: Radiotherapeutic viewpoints. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 59:1127–1137. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li CC, Tien HF, Tang JL, Yao M, Chen YC,
Su IJ, Hsu SM and Hong RL: Treatment outcome and pattern of failure
in 77 patients with sinonasal natural killer/T-cell or T-cell
lymphoma. Cancer. 100:366–375. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang H, Wuxiao ZJ, Zhu J, Wang Z, Wang KF,
Li S, Chen X, Lu Y and Xia ZJ: Comparison of gemcitabine,
oxaliplatin and L-asparaginase and etoposide, vincristine,
doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide and prednisone as first-line
chemotherapy in patients with stage IE to IIE extranodal natural
killer/T-cell lymphoma: A multicenter retrospective study. Leuk
Lymphoma. 56:971–977. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim SJ, Yang DH, Kim JS, Kwak JY, Eom HS,
Hong DS, Won JH, Lee JH, Yoon DH, Cho J, et al: Concurrent
chemoradiotherapy followed by L-asparaginase-containing
chemotherapy, VIDL, for localized nasal extranodal NK/T cell
lymphoma: CISL08-01 phase II study. Ann Hematol. 93:1895–1901.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|