Article
Open Access
Evaluation of 3D-CPA, HR-HPV, and TCT joint detection on cervical disease screening
- Authors:
- Hui Liang
- Min Fu
- Jian Zhou
- Lei Song
-
View Affiliations / Copyright
Affiliations:
Maternal and Child Care Service Center of Xuzhou, Xuzhou Maternal and Child Care Service Center of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou, Jiangsu 221009, P.R. China
-
Pages:
887-892
|
Published online on:
June 2, 2016
https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2016.4677
- Expand metrics +
Metrics:
Total
Views: 0
(Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics:
)
Metrics:
Total PDF Downloads: 0
(Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics:
)
This article is mentioned in:
Abstract
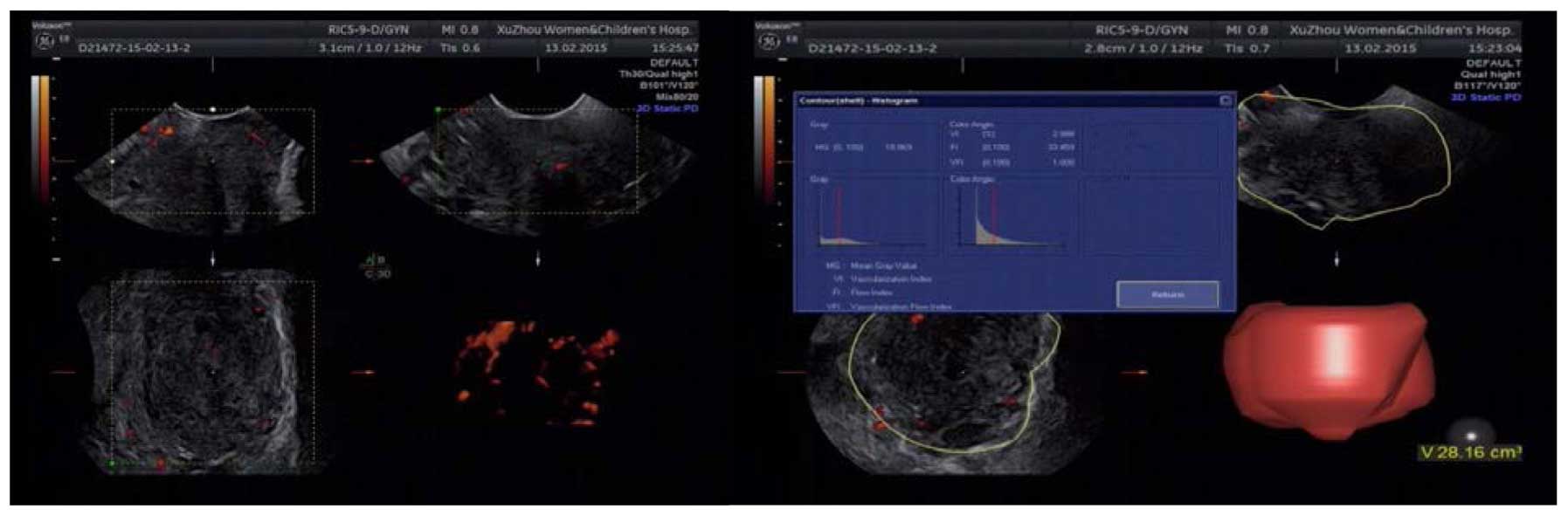
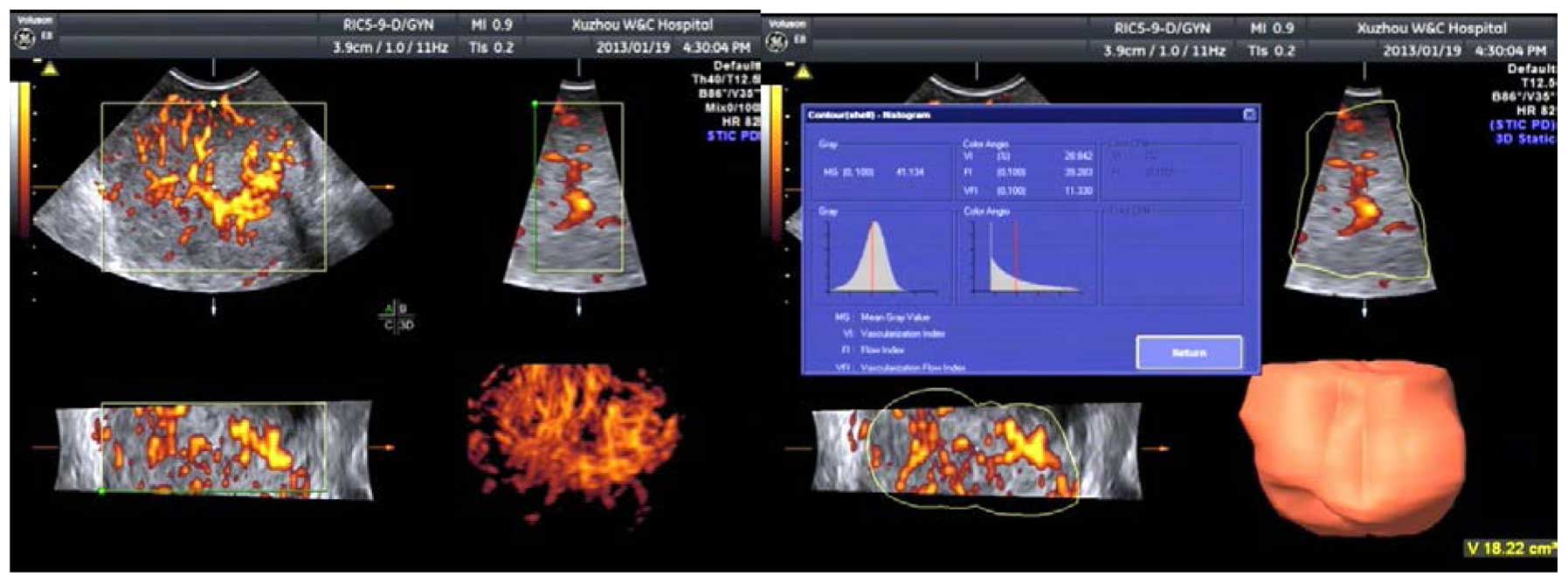
The application value of three-dimensional color power angiography (3D-CPA), high-risk human papillomavirus (HR-HPV), ThinPrep cytology test (TCT) joint detection on cervical disease screening was investigated. In total, 1,900 patients that were examined in Gynecological and Cervix Clinic of Maternal and Child Care Service Center of Xuzhou from June 2012 to March 2015 were enrolled in the present study. After admission, the patients underwent TCT, HR-HPV and 3D-CPA examinations, and vascular morphology and typing, vascularization index (VI) were recorded. Colposcopic biopsy was performed in patients with a positive outcome of any of the three indices. Pathological diagnosis was taken as the golden standard to assess the sensitivity, specificity, diagnostic rate, and Youden index of the three methods being used independently or jointly. Of the 1,900 patients, 276 cases (14.53%) were HR-HPV-positive, 214 cases (11.26%) were VI-positive and 164 cases (8.63%) were TCT-positive. A total of 418 cases were confirmed with a positive outcome of any of the three indices and a cervical biopsy was obtained. Of the 418 cases, 162 cases (38.75%) were diagnosed with chronic cervicitis, 146 cases with low-level cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) (34.93%), 104 cases (24.88%) with high level CIN, 6 cases (1.44%) with cervical cancer. Histology more than low level CIN was defined as positive: i) screening results when the three methods were used independently: HPV was confirmed with the highest sensitivity (90.63%), VI with the highest specificity (83.95%), and HPV with the highest diagnostic accuracy (83.73%); ii) screening results under HPV+TCT and HPV+TCT+VI: HPV+TCT+VI was confirmed with the highest sensitivity and specificity: sensitivity (94.53%), specificity (81.48%), diagnosis coincidence rate (89.47%) and the highest Youden index of 0.760; and iii) vascular morphology and grading were significantly different in the early stage cervical carcinoma, high level CIM, and cervicitis groups. In conclusion, the joint detection of 3D-CPA, HR-HPV, and TCT improved the sensitivity and accuracy of cervical disease screening. 3D-CPA technology may therefore be used as an auxiliary screening method for cervical cancer.
View References
|
1
|
Castellsagué X, de Sanjosé S, Aguado T,
Louie L..Bruni KS, Muñoz J, Diaz M, Irwin K, Gacic M, Beauvais O,
et al: HPV and Cervical Cancer in the World 2007 Report.
25:2007.http://www.hpvcentre.net/link_media/HPVReport2007.pdf
|
|
2
|
PAHO publication: Estrategia y Plan de
Acción Regionales sobre la Prevención y el Control del Cáncer
Cervicouterino. Washington DC: 2008.https://www.rho.org/files/PAHO_Regional_Strategy_2010_sp.pdf(In
Spanish).
|
|
3
|
Sherman SM, Moss E and Redman CW: The
invasive cervical cancer review: Psychological issues surrounding
disclosure. Cytopathol. 24:77–80. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jiao G, Xu H and Ren L: The diagnostic
value of three-dimensional ultrasound in invasive cervical
tuberculosis. J Tongji Univ. 31:85–87. 2010.(Medical edition).
|
|
5
|
Johnston EI and Logani S: Cytologic
diagnosis of atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance
in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women: lessons learned from
human Papillomavirus DNA testing. Cancer. 111:160–165. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tjalma W, Van Marck E, Weyler J, Dirix L,
Van Daele A, Goovaerts G, Albertyn G and van Dam P: Quantification
and prognostic relevance of angiogenic parameters in invasive
cervical cancer. Br J Cancer. 78:170–174. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Meijer CJ, Snijders PJ and van den Brule
AJ: Screening for cervical cancer: Should we test for infection
with high-risk HPV? CMAJ. 163:535–538. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Landt S, Mordelt K, Schwidde I, Barinoff
J, Korlach S, Stöblen F, Lichtenegger W, Sehouli J and Kümmel S:
Prognostic significance of the angiogenic factors angiogenin,
endoglin and endostatin in cervical cancer. Anticancer Res.
31:2651–2655. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pairleitner H, Steiner H, Hasenoehrl G and
Staudach A: Three-dimensional power Doppler sonography: imaging and
quantifying blood flow and vascularization. Ultrasound Obstet
Gynecol. 14:139–143. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li P, Wang X and Zhang Y: Correlation
between the blood flow of cervical cancer and MVD, VEGF under
three-dimensional energy doppler ultrasound detection. J China Med
Univ. 38:8462009.
|
|
11
|
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR and Folkman
J: Tumor angiogenesis and metastases correlation in invasive breast
carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 324:1–8. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hsu KF, Su JM, Huang SC, Cheng YM, Kang
CY, Shen MR, Chang FM and Chou CY: Three-dimensional power Doppler
imaging of early-stage cervical cancer. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol.
24:664–671. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liang H, Fu-Min L, Lei S, Peng L and Jian
Z: Transvaginal three-dimensional color power Doppler ultrasound
and cervical MVD measurement in the detection of cervical
intraepithelial neoplasia. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 18:1979–1984.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Saslow D, Castle PE, Cox JT, Davey DD,
Einstein MH, Ferris DG, Goldie SJ, Harper DM, Kinney W, Moscicki
AB, et al: American Cancer Society Guideline for human
papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine use to prevent cervical cancer and its
precursors. CA Cancer J Clin. 57:7–28. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|