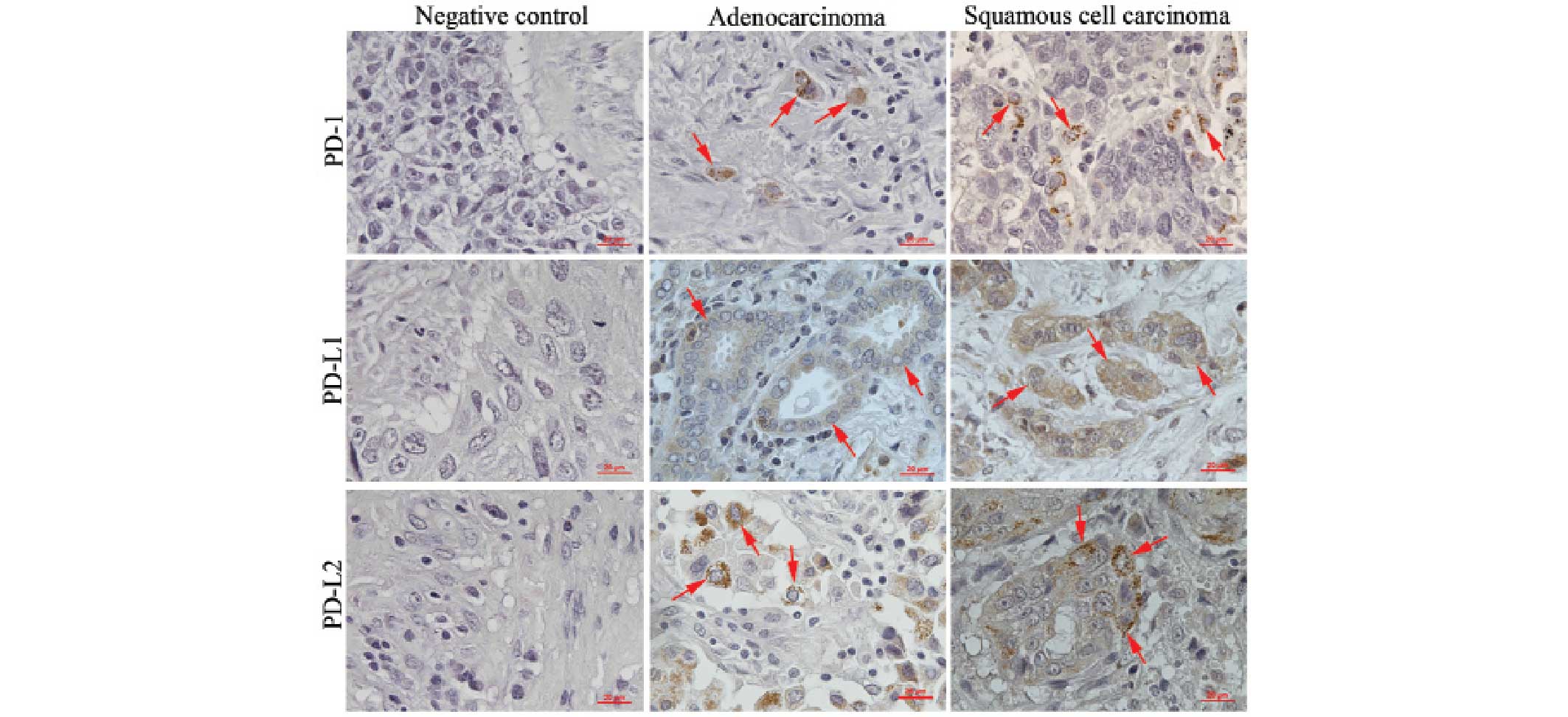
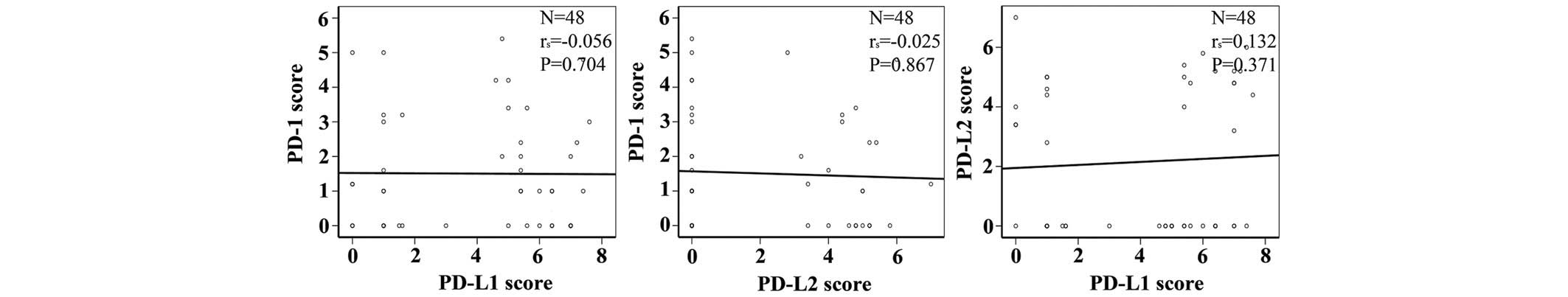
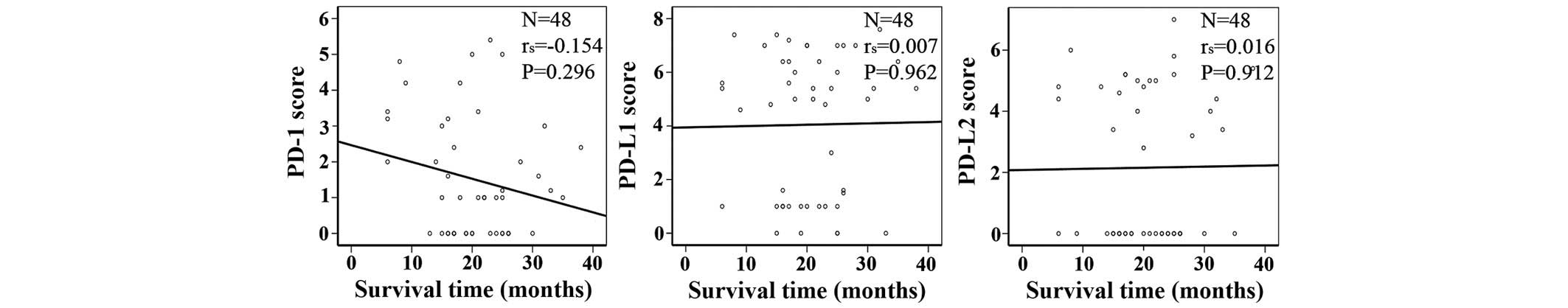
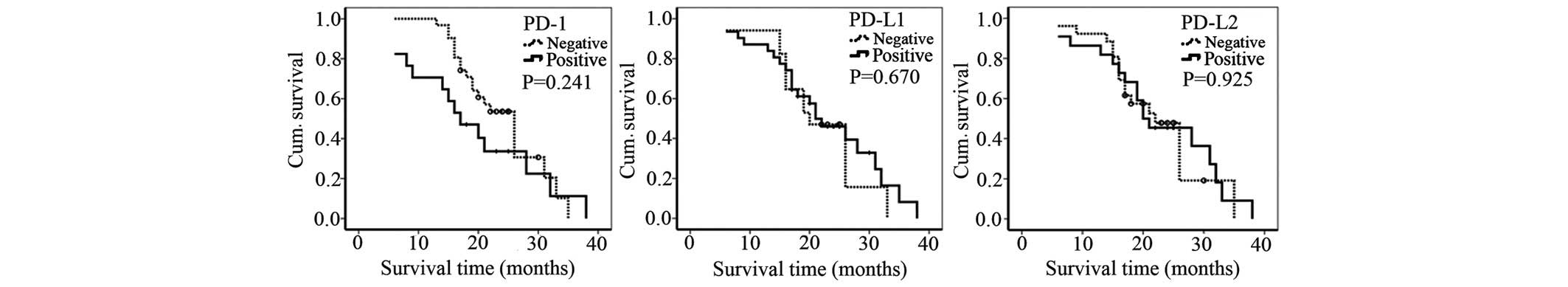
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zhang S and Zou X: Evaluation on
the incidence, mortality and tendency of lung cancer in China.
Thoracic Cancer. 1:35–40. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ledford H: Cancer treatment: The killer
within. Nature. 508:24–26. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kantoff PW, Higano CS, Shore ND, Berger
ER, Small EJ, Penson DF, Redfern CH, Ferrari AC, Dreicer R, Sims
RB, et al: Sipuleucel-T immunotherapy for castration-resistant
prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:411–422. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hodi FS, O'Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW,
Sosman JA, Haanen JB, Gonzalez R, Robert C, Schadendorf D, Hassel
JC, et al: Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with
metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 363:711–723. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Harvey RD Immunologic and clinical effects
of targeting of pd-1 in lung cancer. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2014.
|
|
8
|
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR,
Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Carvajal RD,
Sosman JA, Atkins MB, et al: Safety, activity, and immune
correlates of anti-pd-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med.
366:2443–2454. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LQ, Hwu WJ,
Topalian SL, Hwu P, Drake CG, Camacho LH, Kauh J, Odunsi K, et al:
Safety and activity of anti-pd-l1 antibody in patients with
advanced cancer. N Engl J Med. 366:2455–2465. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lipson EJ, Sharfman WH, Drake CG, Wollner
I, Taube JM, Anders RA, Xu H, Yao S, Pons A, Chen L, et al: Durable
cancer regression off-treatment and effective reinduction therapy
with an anti-pd-1 antibody. Clin Cancer Res. 19:462–468. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hamid O, Robert C, Daud A, Hodi FS, Hwu
WJ, Kefford R, Wolchok JD, Hersey P, Joseph RW, Weber JS, et al:
Safety and tumor responses with lambrolizumab (anti-pd-1) in
melanoma. N Engl J Med. 369:134–144. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wolchok JD, Kluger H, Callahan MK, Postow
MA, Rizvi NA, Lesokhin AM, Segal NH, Ariyan CE, Gordon RA, Reed K,
et al: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J
Med. 369:122–133. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Robert C, Schachter J, Long GV, Arance A,
Grob JJ, Mortier L, Daud A, Carlino MS, McNeil C, Lotem M, et al:
Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med.
372:2521–2532. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Garon EB, Rizvi NA, Hui R, Leighl N,
Balmanoukian AS, Eder JP, Patnaik A, Aggarwal C, Gubens M, Horn L,
et al: Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 372:2018–2028. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Herbst RS, Soria JC, Kowanetz M, Fine GD,
Hamid O, Gordon MS, Sosman JA, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Gettinger
SN, et al: Predictive correlates of response to the anti-pd-l1
antibody mpdl3280a in cancer patients. Nature. 515:563–567. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cha E, Wallin J and Kowanetz M: Pd-l1
inhibition with mpdl3280a for solid tumors. Semin Oncol.
42:484–487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ishida Y, Agata Y, Shibahara K and Honjo
T: Induced expression of pd-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin
gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 11:3887–3895.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nishimura H, Minato N, Nakano T and Honjo
T: Immunological studies on pd-1 deficient mice: Implication of
pd-1 as a negative regulator for b cell responses. Int Immunol.
10:1563–1572. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nishimura H, Nose M, Hiai H, Minato N and
Honjo T: Development of lupus-like autoimmune diseases by
disruption of the pd-1 gene encoding an itim motif-carrying
immunoreceptor. Immunity. 11:141–151. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, Bourque K,
Chernova T, Nishimura H, Fitz LJ, Malenkovich N, Okazaki T, Byrne
MC, et al: Engagement of the pd-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a
novel b7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte
activation. J Exp Med. 192:1027–1034. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K and Chen L: B7-h1,
a third member of the b7 family, co-stimulates t-cell proliferation
and interleukin-10 secretion. Nat Med. 5:1365–1369. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Latchman Y, Wood CR, Chernova T, Chaudhary
D, Borde M, Chernova I, Iwai Y, Long AJ, Brown JA, Nunes R, et al:
Pd-l2 is a second ligand for pd-1 and inhibits t cell activation.
Nat Immunol. 2:261–268. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tseng SY, Otsuji M, Gorski K, Huang X,
Slansky JE, Pai SI, Shalabi A, Shin T, Pardoll DM and Tsuchiya H:
B7-dc, a new dendritic cell molecule with potent costimulatory
properties for t cells. J Exp Med. 193:839–846. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Okazaki T and Honjo T: Pd-1 and pd-1
ligands: From discovery to clinical application. Int Immunol.
19:813–824. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dong H, Strome SE, Salomao DR, Tamura H,
Hirano F, Flies DB, Roche PC, Lu J, Zhu G, Tamada K, et al:
Tumor-associated b7-h1 promotes t-cell apoptosis: A potential
mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med. 8:793–800. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ and Sharpe
AH: Pd-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev
Immunol. 26:677–704. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sharpe AH and Freeman GJ: The b7-cd28
superfamily. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:116–126. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Muller-Hermelink
HK and Harris CC: World Health Organization Classification of
Tumours. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura,
Thymus and Heart. Lyon, IARC Press. pp9–11. 2004.
|
|
29
|
Allred DC, Clark GM, Elledge R, Fuqua SA,
Brown RW, Chamness GC, Osborne CK and McGuire WL: Association of
p53 protein expression with tumor cell proliferation rate and
clinical outcome in node-negative breast cancer. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 85:200–206. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim MY, Koh J, Kim S, Go H, Jeon YK and
Chung DH: Clinicopathological analysis of pd-l1 and pd-l2
expression in pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma: Comparison with
tumor-infiltrating t cells and the status of oncogenic drivers.
Lung Cancer. 88:24–33. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pan ZK, Ye F, Wu X, An HX and Wu JX:
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of programmed cell
death ligand1 (pd-l1) expression in patients with non-small cell
lung cancer: A meta-analysis. J Thorac Dis. 7:462–470.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|