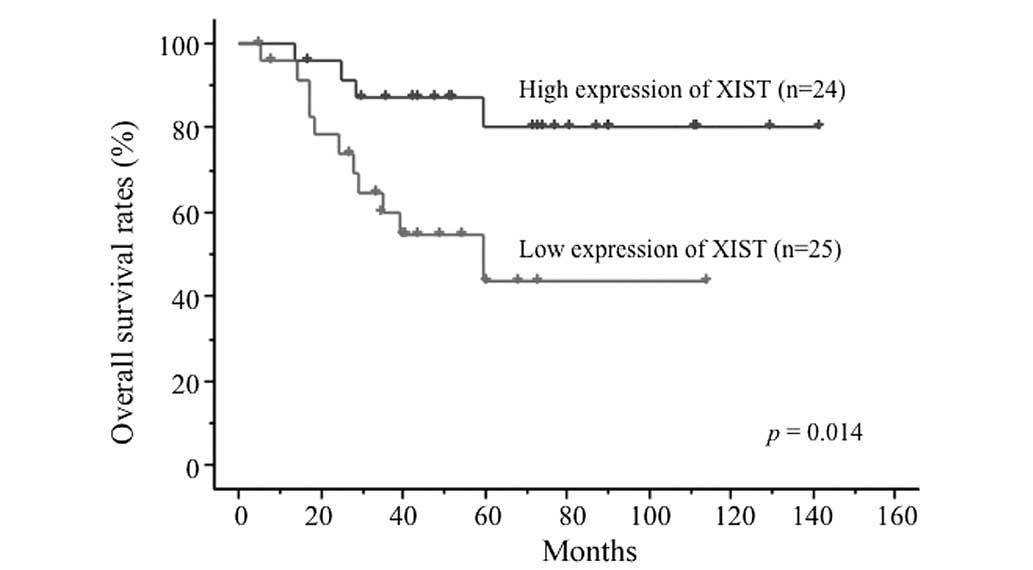
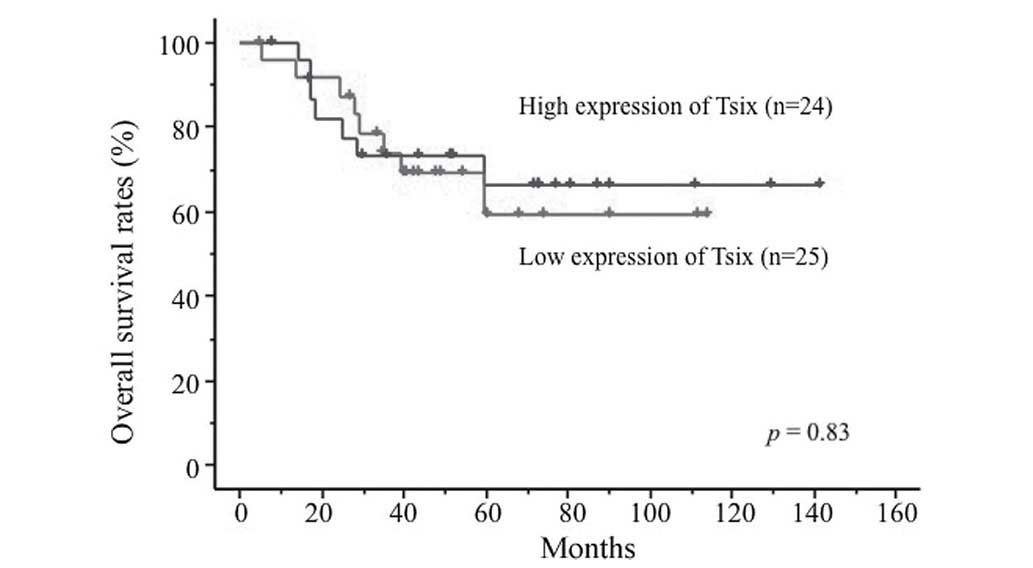
|
1
|
NCI Press Office, . NCI issues clinical
announcement on cervical cancer: Chemotherapy plus radiation
improves survival. http://www.nih.gov/news/pr/feb99/nci-22.htmAccessed.
August 28–2014
|
|
2
|
NCCN Guidelines®, . NCCN clinical practice
guidelines in oncology: Cervical cancer version 1, 2016. National
Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc.; Fort Washington, PA, USA:
2015
|
|
3
|
Chemoradiotherapy for Cervical Cancer
Meta-Analysis Collaboration, . Reducing uncertainties about the
effects of chemoradiotherapy for cervical cancer: A systematic
review and meta-analysis of individual patient data from 18
randomized trials. J Clin Oncol. 26:5802–5812. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nakano T, Ohno T, Ishikawa H, Suzuki Y and
Takahashi T: Current advancement in radiation therapy for uterine
cervical cancer. J Radiat Res. 51:1–8. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hauspy J, Harley I and Fyles AW: Uterine
cervix cancerPrognostic Factors in Cancer. Gospodarowicz MK,
O'Sullivan B and Sobin LH: 3rd. John Wiley & Sons Inc.;
Hoboken, NJ: pp. 219–222. 2006
|
|
6
|
Noordhuis MG, Eijsink JJ, Roossink F, de
Graeff P, Pras E, Schuuring E, Wisman GB, de Bock GH and van der
Zee AG: Prognostic cell biological markers in cervical cancer
patients primarily treated with (chemo)radiation: A systematic
review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 79:325–334. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Harima Y, Ikeda K, Utsunomiya K, Komemushi
A, Kanno S, Shiga T and Tanigawa N: Apolipoprotein C-II is a
potential serum biomarker as a prognostic factor of locally
advanced cervical cancer after chemoradiation therapy. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 87:1155–1161. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cech TR and Steitz JA: The noncoding RNA
revolution-trashing old rules to forge new ones. Cell. 157:77–94.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Elgar G and Vavouri T: Tuning in to the
signals: Noncoding sequence conservation in vertebrate genomes.
Trends Genet. 24:344–352. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang Y, Yang L and Chen LL: Life without
A tail: New formats of long noncoding RNAs. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 54:338–349. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hu X, Schwarz JK, Lewis JS Jr, Huettner
PC, Rader JS, Deasy JO, Grigsby PW and Wang XA: A microRNA
expression signature for cervical cancer prognosis. Cancer Res.
70:1441–1448. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hauptman N and Glavač D: Long non-coding
RNA in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 14:4655–4669. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Spizzo R, Almeida MI, Colombatti A and
Calin GA: Long non-coding RNAs and cancer: A new frontier of
translational research? Oncogene. 31:4577–4587. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cheetham SW, Gruhl F, Mattick JS and
Dinger ME: Long noncoding RNAs and the genetics of cancer. Br J
Cancer. 108:2419–2425. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ismailov S, Rashitov M, Kobayashi M,
Shibata N, Kato Y, Omi Y, Iihara M and Okamoto T: Trefoil factor 3
(TFF3) mRNA expression level in follicular thyroid tumors using
formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) blocks. O J Pathol.
3:78–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
von Ahlfen S, Missel A, Bendrat K and
Schlumpberger M: Determinants of RNA quality from FFPE samples.
PLoS One. 2:e12612007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sánchez-Navarro I, Gámez-Pozo A,
González-Barón M, Pinto-Marín A, Hardisson D, López R, Madero R,
Cejas P, Mendiola M, Espinosa E and Vara JA: Comparison of gene
expression profiling by reverse transcription quantitative PCR
between fresh frozen and formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded breast
cancer tissues. Biotechniques. 48:389–397. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mittempergher L, de Ronde JJ, Nieuwland M,
Kerkhoven RM, Kerkhoven RM, Simon I, Rutgers EJ, Wessels LF and
Van't Veer LJ: Gene expression profiles from formalin fixed
paraffin embedded breast cancer tissue are largely comparable to
fresh frozen matched tissue. PLoS One. 6:e171632011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Martianov I, Ramadass A, Barros A Serra,
Chow N and Akoulitchev A: Repression of the human dihydrofolate
reductase gene by a non-coding interfering transcript. Nature.
445:666–670. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Miyagawa R, Tano K, Mizuno R, Nakamura Y,
Ijiri K, Rakwal R, Shibato J, Masuo Y, Mayeda A, Hirose T and
Akimitsu N: Identification of cis- and trans-acting factors
involved in the localization of MALAT-1 noncoding RNA to nuclear
speckles. RNA. 18:738–751. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kumamoto T and Oshio S: Effect of fetal
exposure to bisphenol A on brain mediated by X-chromosome
inactivation. J Toxicol Sci. 38:485–494. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Latos PA, Pauler FM, Koerner MV, et al:
Airn transcriptional overlap, but not its lncRNA products, induces
imprinted Igf2r silencing. Science. 338:1469–1472. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ganesan S, Silver DP, Greenberg RA, Avni
D, Drapkin R, Miron A, Mok SC, Randrianarison V, Brodie S, Salstrom
J, et al: BRCA1 supports XIST RNA concentration on the inactive X
chromosome. Cell. 111:393–405. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pageau GJ, Hall LL and Lawrence JB: BRCA1
does not paint the inactive X to localize XIST RNA but may
contribute to broad changes in cancer that impact XIST and Xi
heterochromatin. J Cell Biochem. 100:835–850. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Richardson AL, Wang ZC, De Nicolo A, Lu X,
Brown M, Miron A, Liao X, Iglehart JD, Livingston DM and Ganesan S:
X chromosomal abnormalities in basal-like human breast cancer.
Cancer Cell. 9:121–132. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Silver DP, Dimitrov SD, Feunteun J, Gelman
R, Drapkin R, Lu SD, Shestakova E, Velmurugan S, Denunzio N,
Dragomir S, et al: Further evidence for BRCA1 communication with
the inactive X chromosome. Cell. 128:991–1002. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sirchia SM, Ramoscelli L, Grati FR,
Barbera F, Coradini D, Rossella F, Porta G, Lesma E, Ruggeri A,
Radice P, et al: Loss of the inactive X chromosome and replication
of the active X in BRCA1-defective and wild-type breast cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 65:2139–2146. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sirchia SM, Tabano S, Monti L, Recalcati
MP, Gariboldi M, Grati FR, Porta G, Finelli P, Radice P and Miozzo
M: Misbehaviour of XIST RNA in breast cancer cells. PLoS One.
4:e55592009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vincent-Salomon A, Ganem-Elbaz C, Manié E,
Raynal V, Sastre-Garau X, Stoppa-Lyonnet D, Stern MH and Heard E: X
inactive-specific transcript RNA coating and genetic instability of
the X chromosome in BRCA1 breast tumors. Cancer Res. 67:5134–5140.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Benoît MH, Hudson TJ, Maire G, Squire JA,
Arcand SL, Provencher D, Mes-Masson AM and Tonin PN: Global
analysis of chromosome X gene expression in primary cultures of
normal ovarian surface epithelial cells and epithelial ovarian
cancer cell lines. Int J Oncol. 30:5–17. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kawakami T, Zhang C, Taniguchi T, Kim CJ,
Okada Y, Sugihara H, Hattori T, Reeve AE, Ogawa O and Okamoto K:
Characterization of loss-of-inactive X in Klinefelter syndrome and
female-derived cancer cells. Oncogene. 23:6163–6169. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Huang KC, Rao PH, Lau CC, Heard E, Ng SK,
Brown C, Mok SC, Berkowitz RS and Ng SW: Relationship of XIST
expression and responses of ovarian cancer to chemotherapy. Mol
Cancer Ther. 1:769–776. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee JT, Davidow LS and Warshawsky D: Tsix,
a gene antisense to Xist at the X-inactivation centre. Nat Genet.
21:400–404. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Feng J, Funk WD, Wang SS, Weinrich SL,
Avilion AA, Chiu CP, Adams RR, Chang E, Allsopp RC, Yu J, et al:
The RNA component of human telomerase. Science. 269:1236–1241.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cao Y, Bryan TM and Reddel RR: Increased
copy number of the TERT and TERC telomerase subunit genes in cancer
cells. Cancer Sci. 99:1092–1099. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tu Z, Zhang A, Wu R, Jiang J, Li Y, Wulan
N, Li J, Zhang Y, Li Y, Chen Z and Wei L: Genomic amplification of
the human telomerase RNA gene for differential diagnosis of
cervical disorders. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 191:10–16. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hitchings GH Jr: Nobel lecture in
physiology or medicine - 1988. Selective inhibitors of
dihydrofolate reductase. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 25:303–310. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
El-Shewy HM and Luttrell LM: Insulin-like
growth factor-2/mannose-6 phosphate receptors. Vitam Horm.
80:667–697. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nagano T, Mitchell JA, Sanz LA, Pauler FM,
Ferguson-Smith AC, Feil R and Fraser P: The Air noncoding RNA
epigenetically silences transcription by targeting G9a to
chromatin. Science. 322:1717–1720. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mohammad F, Mondal T and Kanduri C:
Epigenetics of imprinted long noncoding RNAs. Epigenetics.
4:277–286. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings
HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chisholm KM, Wan Y, Li R, Montgomery KD,
Chang HY and West RB: Detection of long non-coding RNA in archival
tissue: Correlation with polycomb protein expression in primary and
metastatic breast carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e479982012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen FJ, Sun M, Li SQ, Wu QQ, Ji L, Liu
ZL, Zhou GZ, Cao G, Jin L, Xie HW, et al: Upregulation of the long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
metastasis and poor prognosis. Mol Carcinog. 52:908–915. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu XH, Liu ZL, Sun M, Liu J, Wang ZX and
De W: The long non-coding RNA HOTAIR indicates a poor prognosis and
promotes metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer.
13:4642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yang Z, Zhou L, Wu LM, Lai MC, Xie HY,
Zhang F and Zheng SS: Overexpression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR
predicts tumor recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma patients
following liver transplantation. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:1243–1250.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Geng YJ, Xie SL, Li Q, Ma J and Wang GY:
Large intervening non-coding RNA HOTAIR is associated with
hepatocellular carcinoma progression. J Int Med Res. 39:2119–2128.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
He X, Bao W, Li X, Chen Z, Che Q, Wang H
and Wan XP: The long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is upregulated in
endometrial carcinoma and correlates with poor prognosis. Int J Mol
Med. 33:325–332. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Brown CJ, Ballabio A, Rupert JL,
Lafreniere RG, Grompe M, Tonlorenzi R and Willard HF: A gene from
the region of the human X inactivation centre is expressed
exclusively from the inactive X chromosome. Nature. 349:38–44.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Weakley SM, Wang H, Yao Q and Chen C:
Expression and function of a large non-coding RNA gene XIST in
human cancer. World J Surg. 35:1751–1756. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liu Y, Wang L and Zheng P: X-linked tumor
suppressors: Perplexing inheritance, a unique therapeutic
opportunity. Trends Genet. 26:260–265. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Spatz A, Borg C and Feunteun J:
X-chromosome genetics and human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:617–629.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yildirim E, Kirby JE, Brown DE, Mercier
FE, Sadreyev RI, Scadden DT and Lee JT: Xist RNA is a potent
suppressor of hematologic cancer in mice. Cell. 152:727–742. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Froberg JE, Yang L and Lee JT: Guided by
RNAs: X-inactivation as a model for lncRNA function. J Mol Biol.
425:3698–3706. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|