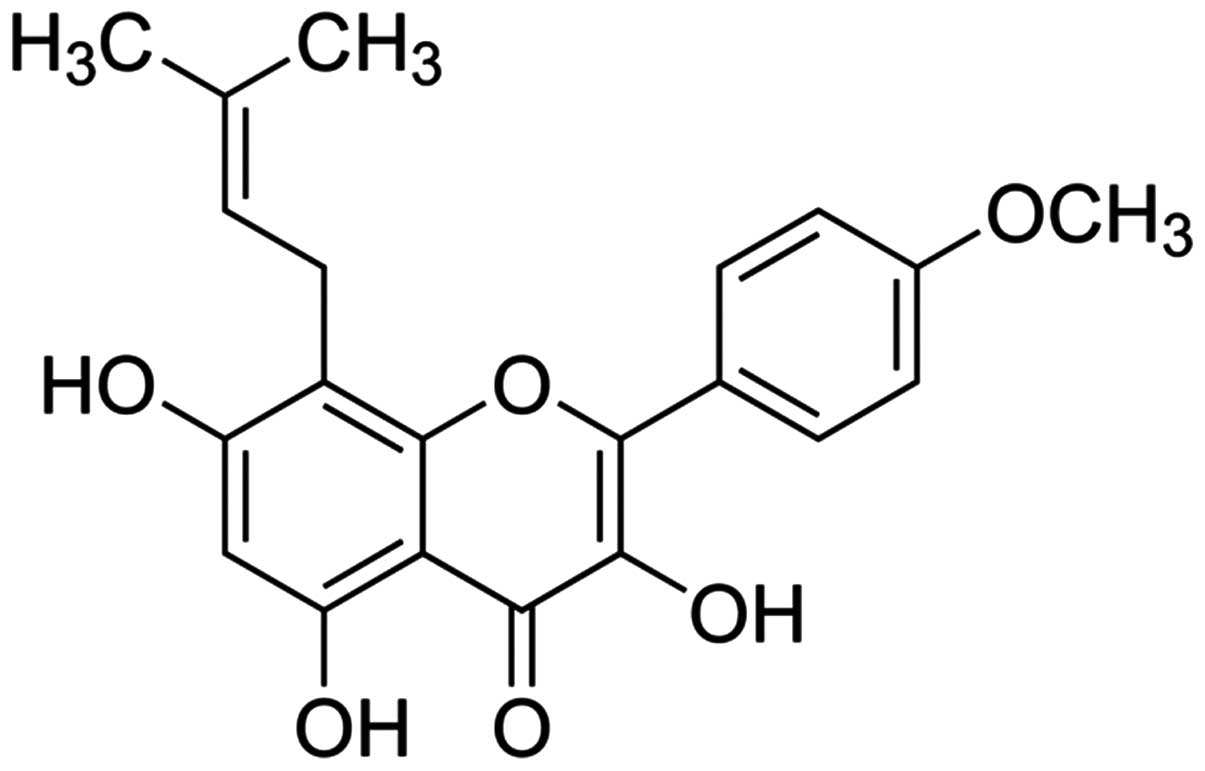
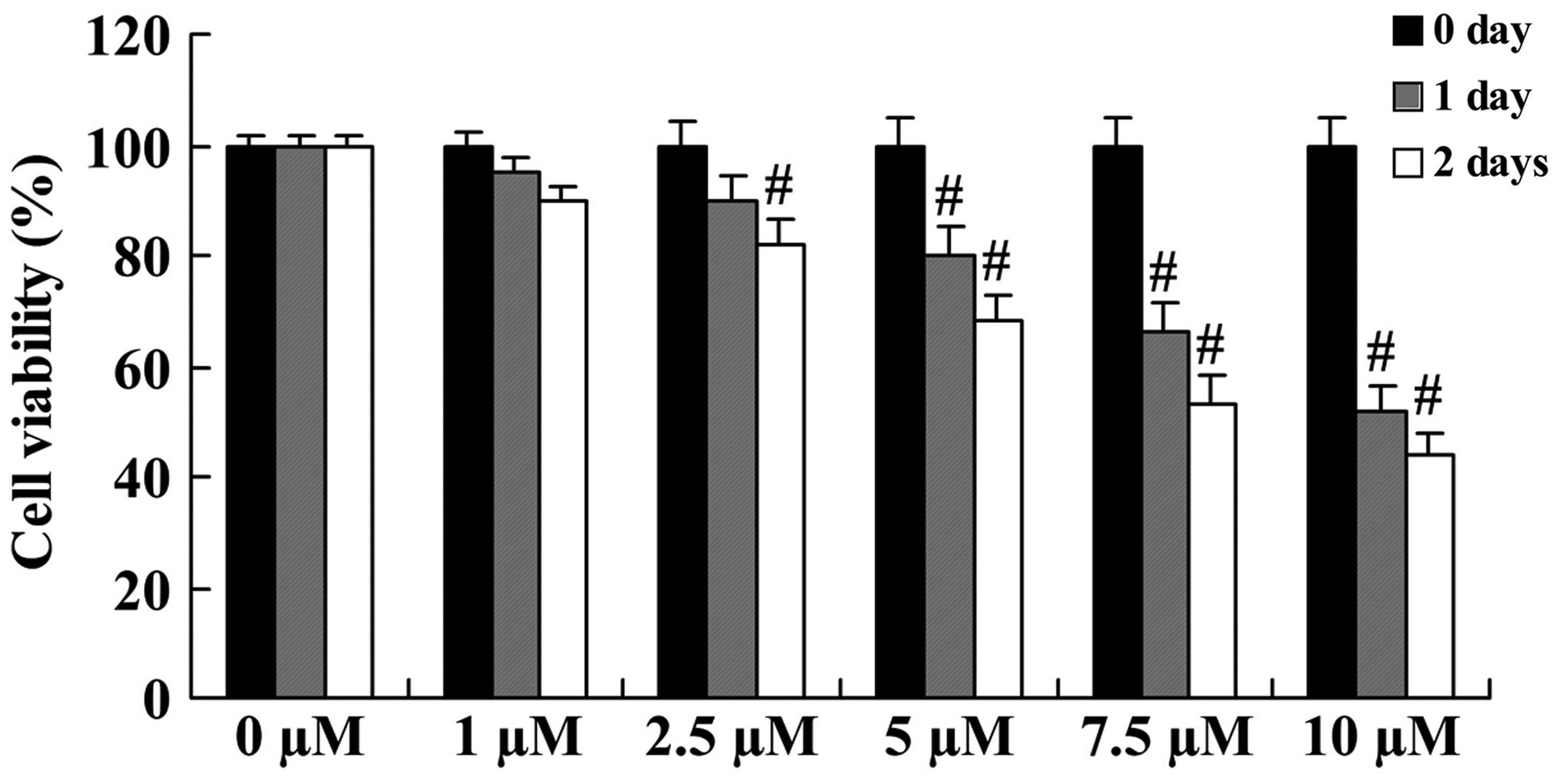
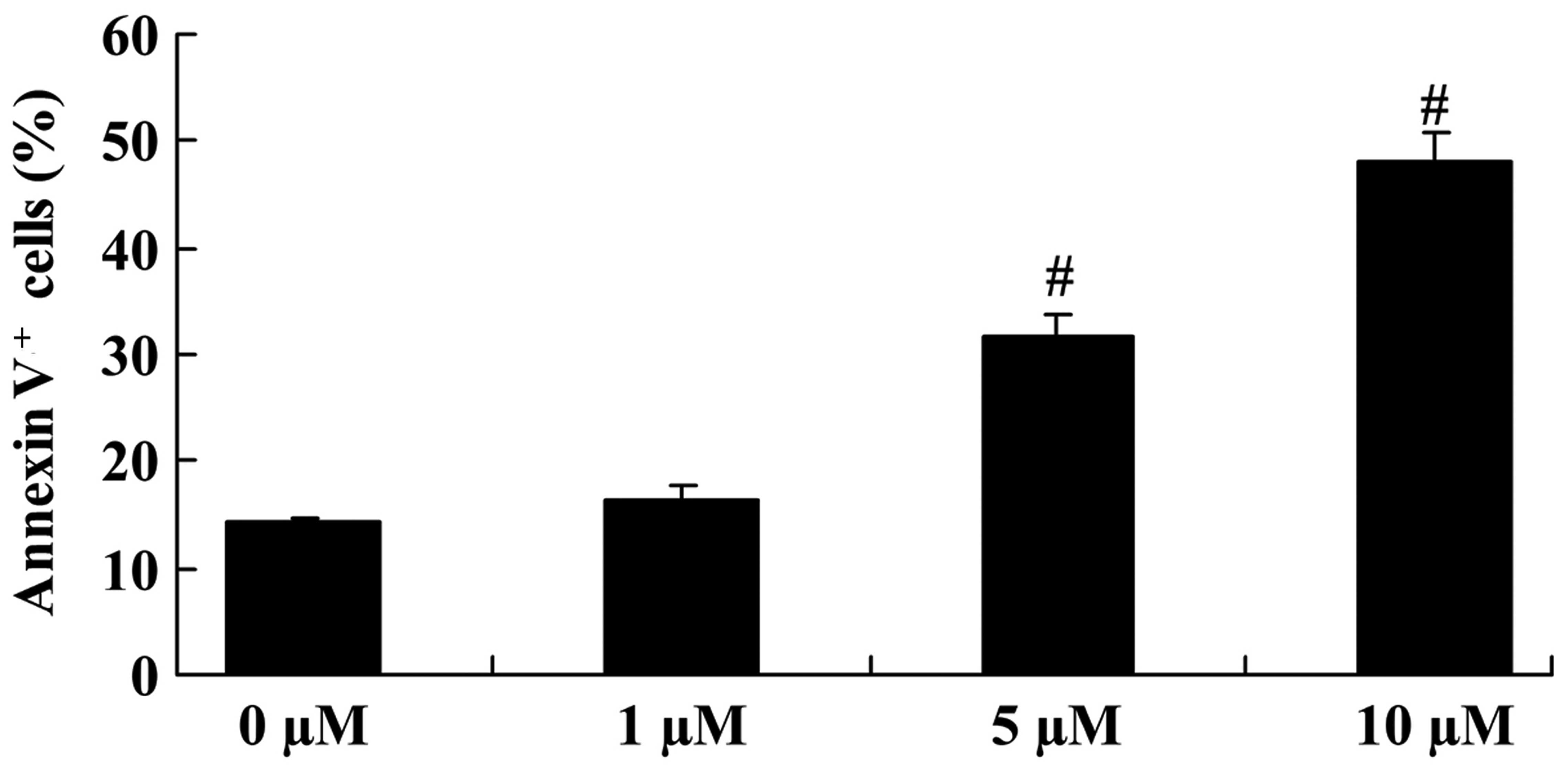
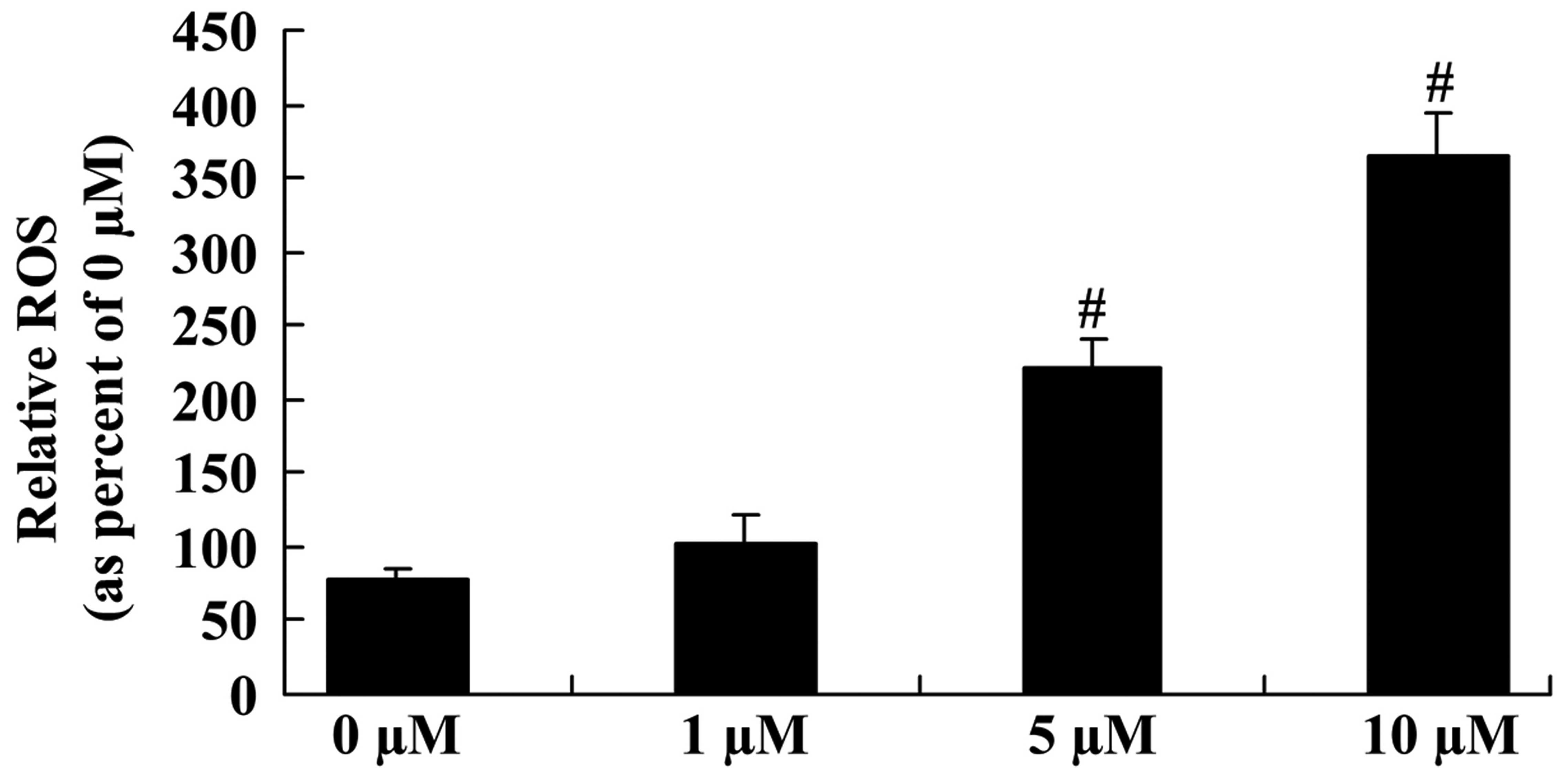
|
1
|
Lee WS, Yun JW, Nagappan A, Park HS, Lu
JN, Kim HJ, Chang SH, Kim DC, Lee JH, Jung JM, et al: Tetraarsenic
hexoxide demonstrates anticancer activity at least in part through
suppression of NF-kB activity in SW620 human colon cancer cells.
Oncol Rep. 33:2940–2946. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Quaglia A, Tavilla A, Shack L, Brenner H,
Janssen-Heijnen M, Allemani C, Colonna M, Grande E, Grosclaude P
and Vercelli M: EUROCARE Working Group: The cancer survival gap
between elderly and middle-aged patients in Europe is widening. Eur
J Cancer. 45:1006–1016. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chang W, Wei Y, Ren L, Zhong Y, Yu Y, Chen
J, Zhu D, Ye L, Qin C, Zhao N, et al: Randomized controlled trial
of intraportal chemotherapy combined with adjuvant chemotherapy
(mFOLFOX6) for stage II and III colon cancer. Ann Surg.
263:434–439. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Aleksandrova K, Pischon T, Buijsse B, May
AM, Peeters PH, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, Jenab M, Fedirko V, Dahm CC,
Siersema PD, et al: Adult weight change and risk of colorectal
cancer in the European prospective investigation into cancer and
nutrition. Eur J Cancer. 49:3526–3536. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li F, Chen Z, Yang Y, Yi X, Yang Y and
Zhang L: Characterization of the pathologic and endoscopic
measurements of colorectal polyp sizes with a focus on sessile
serrated adenoma and high-grade dysplasia. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:1635–1643. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sahm M, Wesselmann S, Kube R, Schöffel N,
Pross M, Lippert H and Kahl S: The development process of colon
cancer centres. Zentralbl Chir. 138:33–37. 2013.(In German).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rivoltini L, Chiodoni C, Squarcina P,
Tortoreto M, Villa A, Vergani B, Bürdek M, Botti L, Arioli I, Cova
A, et al: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-armed
exosomes deliver proapoptotic signals to tumor site. Clin Cancer
Res. 22:3499–3512. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bhattacharyya S, Pal PB and Sil PC: A 35
kD Phyllanthus niruri protein modulates iron mediated oxidative
impairment to hepatocytes via the inhibition of ERKs, p38 MAPKs and
activation of PI3k/Akt pathway. Food Chem Toxicol. 56:119–130.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Arts WF, Scholte HR, Loonen MC, Przyrembel
H, Fernandes J, Trijbels JM and Luyt-Houwen IE: Cytochrome c
oxidase deficiency in subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy. J
Neurol Sci. 77:103–115. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Araki K and Nagata K: Functional in vitro
analysis of the ERO1 protein and protein-disulfide isomerase
pathway. J Biol Chem. 286:32705–32712. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Satapathy SR, Mohapatra P, Das D,
Siddharth S and Kundu CN: The apoptotic effect of plant based
nanosilver in colon cancer cells is a p53 dependent process
involving ROS and JNK cascade. Pathol Oncol Res. 21:405–411. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Peng X and Gandhi V: ROS-activated
anticancer prodrugs: A new strategy for tumor-specific damage. Ther
Deliv. 3:823–833. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou Y, Liu QH, Liu CL and Lin L:
Calycosin induces apoptosis in human ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells by
activating caspases and Bcl-2 family proteins. Tumour Biol.
36:5333–5339. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Alibek K, Irving S, Sautbayeva Z,
Kakpenova A, Bekmurzayeva A, Baiken Y, Imangali N, Shaimerdenova M,
Mektepbayeva D, Balabiyev A and Chinybayeva A: Disruption of Bcl-2
and Bcl-xL by viral proteins as a possible cause of cancer. Infect
Agent Cancer. 9:442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li Q, Huai L, Zhang C, Wang C, Jia Y, Chen
Y, Yu P, Wang H, Rao Q, Wang M and Wang J: Icaritin induces AML
cell apoptosis via the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signal pathways. Int J
Hematol. 97:617–623. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Guo Y, Zhang X, Meng J and Wang ZY: An
anticancer agent icaritin induces sustained activation of the
extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway and inhibits
growth of breast cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 658:114–122. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tong JS, Zhang QH, Huang X, Fu XQ, Qi ST,
Wang YP, Hou Y, Sheng J and Sun QY: Icaritin causes sustained
ERK1/2 activation and induces apoptosis in human endometrial cancer
cells. PLoS One. 6:e167812011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
He J, Wang Y, Duan F, Jiang H, Chen MF and
Tang SY: Icaritin induces apoptosis of HepG2 cells via the JNK1
signaling pathway independent of the estrogen receptor. Planta Med.
76:1834–1839. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li S, Priceman SJ, Xin H, Zhang W, Deng J,
Liu Y, Huang J, Zhu W, Chen M, Hu W, et al: Icaritin inhibits
JAK/STAT3 signaling and growth of renal cell carcinoma. PLoS One.
8:e816572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vemulapalli R, Lara LF, Sreenarasimhaiah
J, Harford WV and Siddiqui AA: A comparison of palliative stenting
or emergent surgery for obstructing incurable colon cancer. Dig Dis
Sci. 55:1732–1737. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Haghighi MM, Vahedi M, Mohebbi SR,
Pourhoseingholi MA, Fatemi SR and Zali MR: Comparison of survival
between patients with hereditary non polyposis colorectal cancer
(HNPCC) and sporadic colorectal cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
10:209–212. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zheng Q, Liu WW, Li B, Chen HJ, Zhu WS,
Yang GX, Chen MJ and He GY: Anticancer effect of icaritin on human
lung cancer cells through inducing S phase cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 34:497–503. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang XF and Wang J: Icaritin suppresses
the proliferation of human osteosarcoma cells in vitro by
increasing apoptosis and decreasing MMP expression. Acta Pharmacol
Sin. 35:531–539. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Trachootham D, Zhou Y, Zhang H, Demizu Y,
Chen Z, Pelicano H, Chiao PJ, Achanta G, Arlinghaus RB, Liu J and
Huang P: Selective killing of oncogenically transformed cells
through a ROS-mediated mechanism by beta-phenylethyl
isothiocyanate. Cancer Cell. 10:241–252. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gong EY, Shin YJ, Hwang IY, Kim JH, Kim
SM, Moon JH, Shin JS, Lee DH, Hur DY, Jin DH, et al: Combined
treatment with vitamin C and sulindac synergistically induces p53-
and ROS-dependent apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Toxicol
Lett. 258:126–133. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Park KW, Kundu J, Chae IG, Bachar SC, Bae
JW and Chun KS: Methanol extract of Flacourtia indica aerial parts
induces apoptosis via generation of ROS and activation of caspases
in human colon cancer HCT116 cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:7291–7296. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhai W, Xu YF, Peng B, Zhang HM, Huang JH,
Liu M, Wang GC and Zheng JH: Effect of free radical scavenger on
c-jun activation in rats with crush syndrome. Int J Clin Pharmacol
Ther. 51:600–605. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gopalakrishnan N, Saravanakumar M,
Madankumar P, Thiyagu M and Devaraj H: Colocalization of β-catenin
with Notch intracellular domain in colon cancer: A possible role of
Notch1 signaling in activation of CyclinD1-mediated cell
proliferation. Mol Cell Biochem. 396:281–293. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qin A, Yu Q, Gao Y, Tan J, Huang H, Qiao Z
and Qian W: Inhibition of STAT3/cyclinD1 pathway promotes
chemotherapeutic sensitivity of colorectal caner. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 457:681–687. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Prosnitz RG, Patwardhan MB, Samsa GP,
Mantyh CR, Fisher DA, McCrory DC, Cline KE, Gray RN and Morse MA:
Quality measures for the use of adjuvant chemotherapy and radiation
therapy in patients with colorectal cancer: A systematic review.
Cancer. 107:2352–2360. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Patwardhan MB, Samsa GP, McCrory DC,
Fisher DA, Mantyh CR, Morse MA, Prosnitz RG, Cline KE and Gray RN:
Cancer care quality measures: Diagnosis and treatment of colorectal
cancer. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 1–116. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rahmutulla B, Matsushita K, Satoh M,
Seimiya M, Tsuchida S, Kubo S, Shimada H, Ohtsuka M, Miyazaki M and
Nomura F: Alternative splicing of FBP-interacting repressor
coordinates c-Myc, P27Kip1/cyclinE and Ku86/XRCC5 expression as a
molecular sensor for bleomycin-induced DNA damage pathway.
Oncotarget. 5:2404–2417. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|