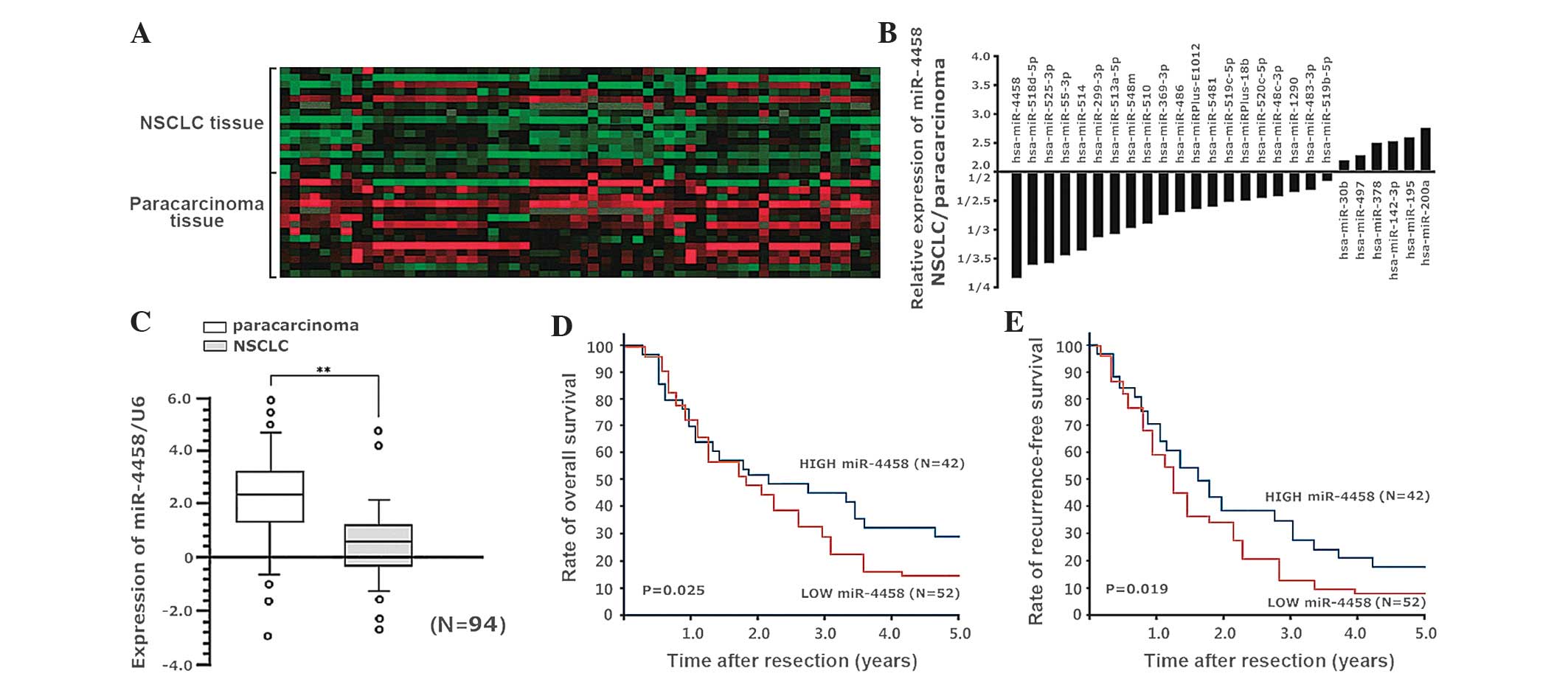
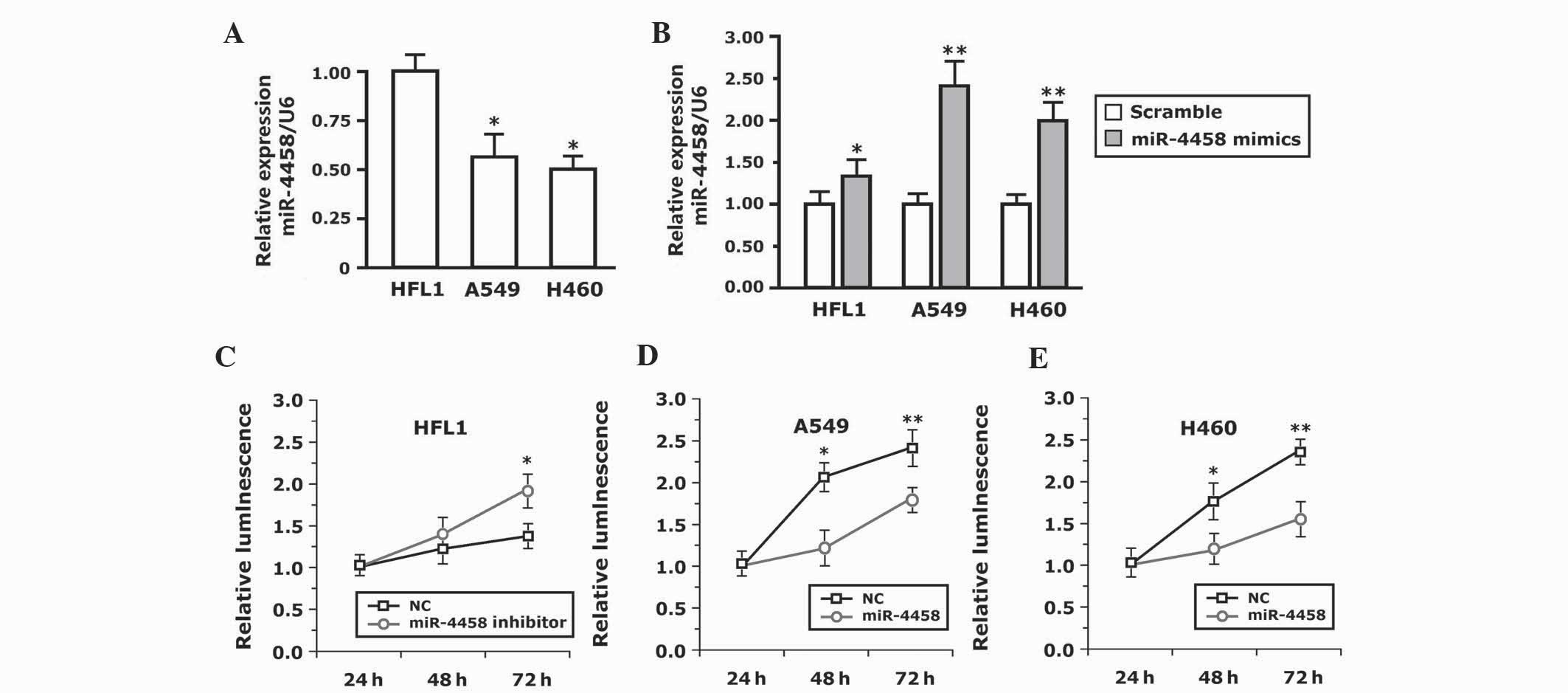
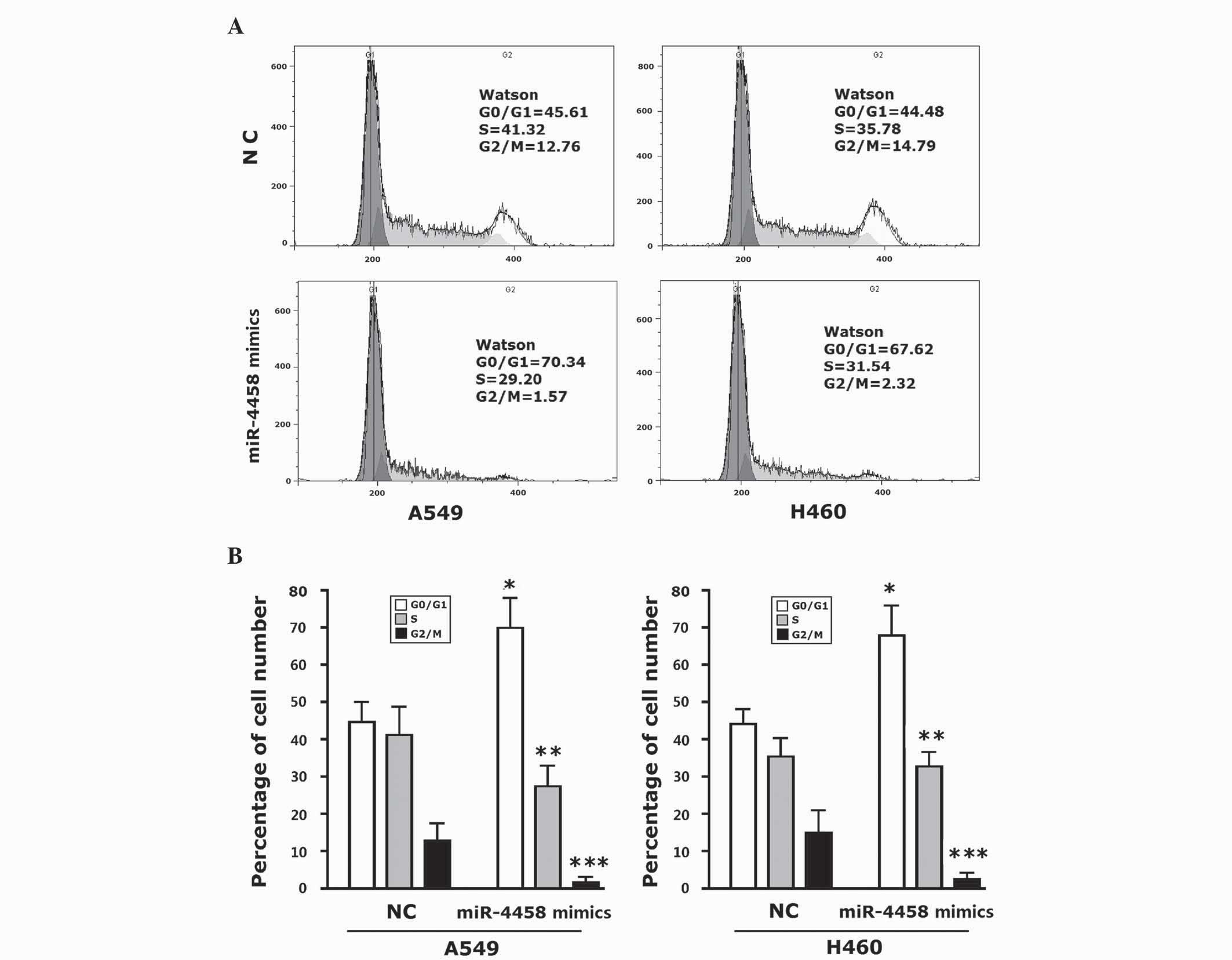
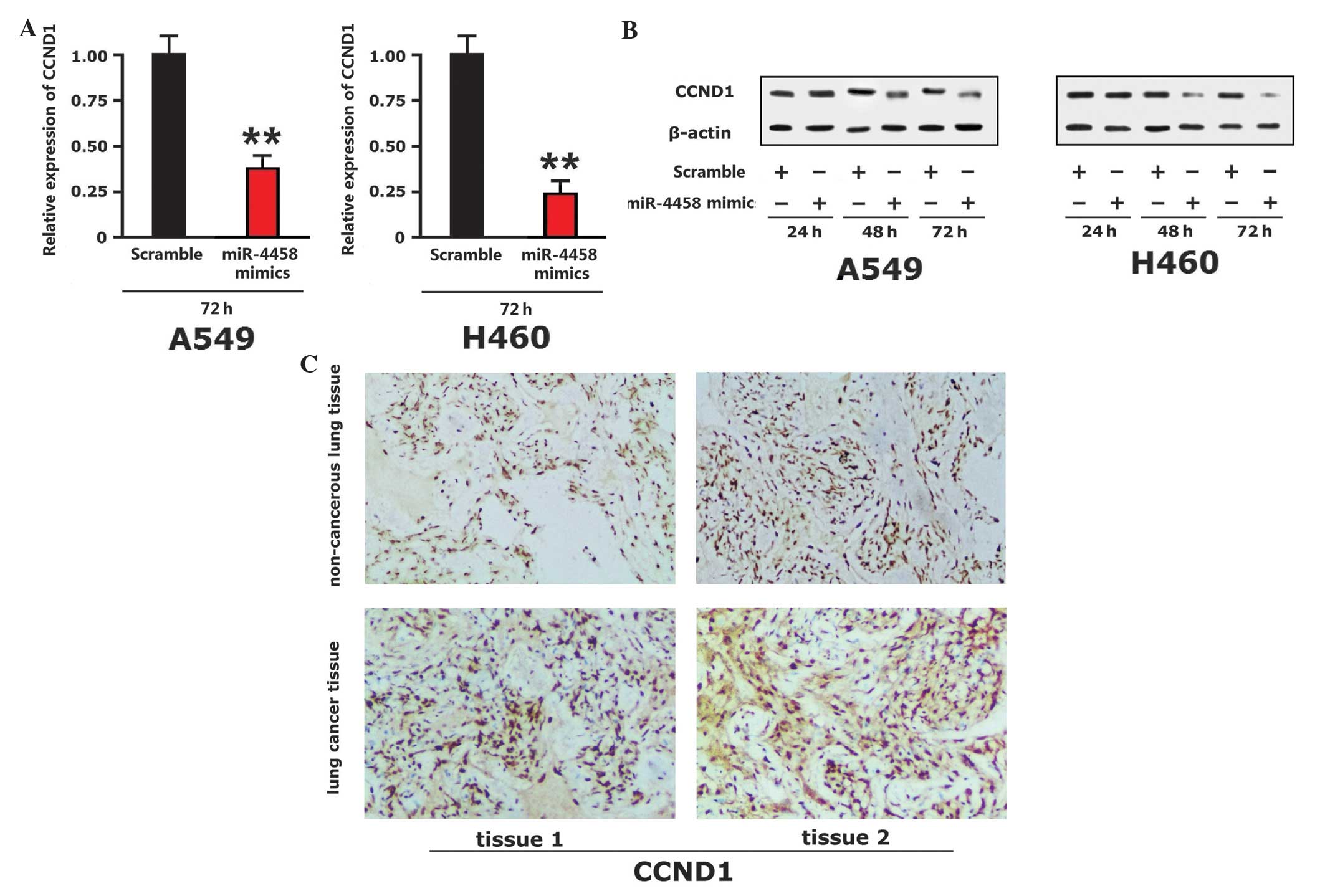
|
1
|
Stepanenko AA and Dmitrenko VV: HEK293 in
cell biology and cancer research: Phenotype, karyotype,
tumorigenicity, and stress-induced genome-phenotype evolution.
Gene. 569:182–190. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ma MZ, Li CX, Zhang Y, Weng MZ, Zhang MD,
Qin YY, Gong W and Quan ZW: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR, a c-Myc
activated driver of malignancy, negatively regulates miRNA-130a in
gallbladder cancer. Mol Cancer. 13:1562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Verma M, Khoury MJ and Ioannidis JP:
Opportunities and challenges for selected emerging technologies in
cancer epidemiology: Mitochondrial, epigenomic, metabolomic and
telomerase profiling. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 22:189–200.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang L, Wei P, Shen X, Zhang Y, Xu B,
Zhou J, Fan S, Hao Z, Shi H, Zhang X, et al: MicroRNA expression
profile in penile cancer revealed by next-generation small RNA
sequencing. PloS One. 10:e01313362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mo W, Zhang J, Li X, Meng D, Gao Y, Yang
S, Wan X, Zhou C, Guo F, Huang Y, et al: Identification of novel
AR-targeted microRNAs mediating androgen signalling through
critical pathways to regulate cell viability in prostate cancer.
PLoS One. 8:e565922013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hsiao SH, Chung CL, Lee CM, Chen WY, Chou
YT, Wu ZH, Chen YC and Lin SE: Suitability of computed
tomography-guided biopsy specimens for subtyping and genotyping of
non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 14:719–725. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ramnath N, Dilling TJ, Harris LJ, Kim AW,
Michaud GC, Balekian AA, Diekemper R, Detterbeck FC and Arenberg
DA: Treatment of stage III non-small cell lung cancer: Diagnosis
and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest
Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest.
143(Suppl 5): e314S–e340S. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhong KZ, Chen WW, Hu XY, Jiang AL and
Zhao J: Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of
microRNA-107 in human non small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 7:4545–4551. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chatterjee A, Chattopadhyay D and
Chakrabarti G: miR-17-5p downregulation contributes to paclitaxel
resistance of lung cancer cells through altering beclin1
expression. PLoS One. 9:e957162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Okudela K, Tateishi Y, Umeda S, Mitsui H,
Suzuki T, Saito Y, Woo T, Tajiri M, Masuda M, Miyagi Y and Ohashi
K: Allelic imbalance in the miR-31 host gene locus in lung
cancer-its potential role in carcinogenesis. PLoS One.
9:e1005812014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu B, Wu X, Liu B, Wang C, Liu Y, Zhou Q
and Xu K: miR-26a enhances metastasis potential of lung cancer
cells via AKT pathway by targeting PTEN. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1822:1692–1704. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang Z, Zhang L, Yin ZY, Fan XL, Hu B,
Wang LQ and Zhang D: miR-107 regulates cisplatin chemosensitivity
of A549 non small cell lung cancer cell line by targeting cyclin
dependent kinase 8. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:7236–7241.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Takahashi Y, Forrest AR, Maeno E,
Hashimoto T, Daub CO and Yasuda J: miR-107 and miR-185 can induce
cell cycle arrest in human non small cell lung cancer cell lines.
PLoS One. 4:e66772009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou C, Chen H, Han L, Wang A and Chen LA:
Identification of featured biomarkers in different types of lung
cancer with DNA microarray. Mol Biol Rep. 41:6357–6363. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jakopovic M, Thomas A, Balasubramaniam S,
Schrump D, Giaccone G and Bates SE: Targeting the epigenome in lung
cancer: Expanding approaches to epigenetic therapy. Front Oncol.
3:2612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gray BP, McGuire MJ and Brown KC: A
liposomal drug platform overrides peptide ligand targeting to a
cancer biomarker, irrespective of ligand affinity or density. PloS
One. 8:e729382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gao CZ, Zhang Y, Chen J, Fei F, Wang TS,
Yang B, Dong P and Zhang YJ: Research progress of the drug delivery
system of antitumor platinum drugs with macrocyclic compounds. Yao
Xue Xue Bao. 50:650–657. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee WH, Liu HE, Chang JY, Liou JP and
Huang HM: MPT0B169, a new tubulin inhibitor, inhibits cell growth
and induces G2/M arrest in nonresistant and paclitaxel-resistant
cancer cells. Pharmacology. 92:90–98. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gailhouste L, Gomez-Santos L and Ochiya T:
Potential applications of miRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic
markers in liver cancer. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 18:199–223.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Song T, Zhang X, Yang G, Song Y and Cai W:
Decrement of miR-199a-5p contributes to the tumorigenesis of
bladder urothelial carcinoma by regulating MLK3/NF-κB pathway. Am J
Transl Res. 7:2786–2794. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fesler A, Xu X, Zheng X, Li X, Jiang J,
Russo JJ and Ju J: Identification of miR-215 mediated
targets/pathways via translational immunoprecipitation expression
analysis (TrIP-chip). Oncotarget. 6:24463–24473. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ochieng J, Ecuru J, Nakwagala F and
Kutyabami P: Research site monitoring for compliance with ethics
regulatory standards: Review of experience from Uganda. BMC Med
Ethics. 14:232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Marchetti D, Spagnolo A, Cicerone M,
Cascini F, La Monaca G and Spagnolo AG: Research ethics committee
auditing: The experience of a university hospital. HEC Forum.
25:257–268. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jhun BW, Lee KJ, Jeon K, Suh GY, Chung MP,
Kim H, Kwon OJ, Sun JM, Ahn JS, Ahn MJ, et al: Clinical
applicability of staging small cell lung cancer according to the
seventh edition of the TNM staging system. Lung Cancer. 81:65–70.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee DS, Kim YS, Kay CS, Kim SH, Yeo CD,
Kim JW, Kim SJ, Kim YK, Ko YH, Kang JH and Lee KY: Distinctive
patterns of initially presenting metastases and clinical outcomes
according to the histological subtypes in stage IV non-small cell
lung cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e27952016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sokolenko S and Aucoin MG: A correction
method for systematic error in (1)H-NMR time-course data validated
through stochastic cell culture simulation. BMC Syst Biol.
9:512015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ying H, Lyu J, Ying T, Li J, Jin S, Shao
J, Wang L and Xu H: Risk miRNA screening of ovarian cancer based on
miRNA functional synergistic network. J Ovarian Res. 7:92014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kumarathasan P, Breznan D, Das D, Salam
MA, Siddiqui Y, Mackinnon-Roy C, Guan J, de Silva N, Simard B and
Vincent R: Cytotoxicity of carbon nanotube variants: A comparative
in vitro exposure study with A549 epithelial and J774 macrophage
cells. Nanotoxicology. 9:148–161. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bao L, Zhao J, Dai X, Wang Y, Ma R, Su Y,
Cui H, Niu J, Bai S, Xiao Z, et al: Correlation between miR-23a and
onset of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol.
38:318–330. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ji H, Yang Z, Jiang W, Geng C, Gong M,
Xiao H, Wang Z and Cheng L: Antiviral activity of nano carbon
fullerene lipidosome against influenza virus in vitro. J Huazhong
Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 28:243–246. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak and Schmittgen, . Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu XH, Sun M, Nie FQ, Ge YB, Zhang EB,
Yin DD, Kong R, Xia R, Lu KH, Li JH, et al: Lnc RNA HOTAIR
functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate HER2 expression
by sponging miR-331-3p in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 13:922014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Paul S and Giri AK: Epimutagenesis: A
prospective mechanism to remediate arsenic-induced toxicity.
Environ Int. 81:8–17. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yu X, Song H, Xia T, Han S, Xiao B, Luo L,
Xi Y and Guo J: Growth inhibitory effects of three miR-129 family
members on gastric cancer. Gene. 532:87–93. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Du B, Wang Z, Zhang X, Feng S, Wang G, He
J and Zhang B: MicroRNA-545 suppresses cell proliferation by
targeting cyclin D1 and CDK4 in lung cancer cells. PLoS One.
9:e880222014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li Z, Li X, Li C, Su Y, Fang W, Zhong C,
Ji W, Zhang Q and Su C: Transcription factor OCT4 promotes cell
cycle progression by regulating CCND1 expression in esophageal
carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 354:77–86. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wong L, Power N, Miles A and Tropepe V:
Mutual antagonism of the paired-type homeobox genes, vsx2 and
dmbx1, regulates retinal progenitor cell cycle exit upstream of
ccnd1 expression. Dev Biol. 402:216–228. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Komori T: Regulation of Rb family proteins
by Cdk6/Ccnd1 in growth plates. Cell Cycle. 12:2161–2162. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Junk DJ, Cipriano R, Stampfer M and
Jackson MW: Constitutive CCND1/CDK2 activity substitutes for p53
loss, or MYC or oncogenic RAS expression in the transformation of
human mammary epithelial cells. PLoS One. 8:e537762013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jensen LB, Bartlett JM, Witton CJ,
Kirkegaard T, Brown S, Müller S, Campbell F, Cooke TG and Nielsen
KV: Frequent amplifications and deletions of G1/S-phase transition
genes, CCND1 and MYC in early breast cancers: A potential role in
G1/S escape. Cancer Biomark. 5:41–49. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Choi YJ, Li X, Hydbring P, Sanda T,
Stefano J, Christie AL, Signoretti S, Look AT, Kung AL, von Boehmer
H and Sicinski P: The requirement for cyclin D function in tumor
maintenance. Cancer Cell. 22:438–451. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu X, Lv XB, Wang XP, Sang Y, Xu S, Hu K,
Wu M, Liang Y, Liu P, Tang J, et al: MiR-138 suppressed
nasopharyngeal carcinoma growth and tumorigenesis by targeting the
CCND1 oncogene. Cell Cycle. 11:2495–2506. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cao L, Li C, Shen S, Yan Y, Ji W, Wang J,
Qian H, Jiang X, Li Z, Wu M, et al: OCT4 increases BIRC5 and CCND1
expression and promotes cancer progression in hepatocellular
carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 13:822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhong Z, Yeow WS, Zou C, Wassell R, Wang
C, Pestell RG, Quong JN and Quong AA: Cyclin D1/cyclin-dependent
kinase 4 interacts with filamin A and affects the migration and
invasion potential of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
70:2105–2114. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Achiwa Y, Hasegawa K and Udagawa Y: Effect
of ursolic acid on MAPK in cyclin D1 signaling and RING-type E3
ligase (SCF E3s) in two endometrial cancer cell lines. Nutr Cancer.
65:1026–1033. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang JC, Thiere M, Henne-Bruns D,
Knippschild U and Kornmann M: Inhibition of pancreatic cancer cell
growth in vivo using a tetracycline-inducible cyclin D1 antisense
expression system. Pancreas. 42:141–148. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Schonbrunn E, Betzi S, Alam R, Martin MP,
Becker A, Han H, Francis R, Chakrasali R, Jakkaraj S, Kazi A, et
al: Development of highly potent and selective diaminothiazole
inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinases. J Med Chem. 56:3768–3782.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sewify EM, Afifi OA, Mosad E, Zaki AH and
El Gammal SA: Cyclin D1 amplification in multiple myeloma is
associated with multidrug resistance expression. Clin Lymphoma
Myeloma Leuk. 14:215–222. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ikeda Y, Oda K, Hiraike-Wada O, Koso T,
Miyasaka A, Kashiyama T, Tanikawa M, Sone K, Nagasaka K, Maeda D,
et al: Cyclin D1 harboring the T286I mutation promotes oncogenic
activation in endometrial cancer. Oncol Rep. 30:584–588.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|