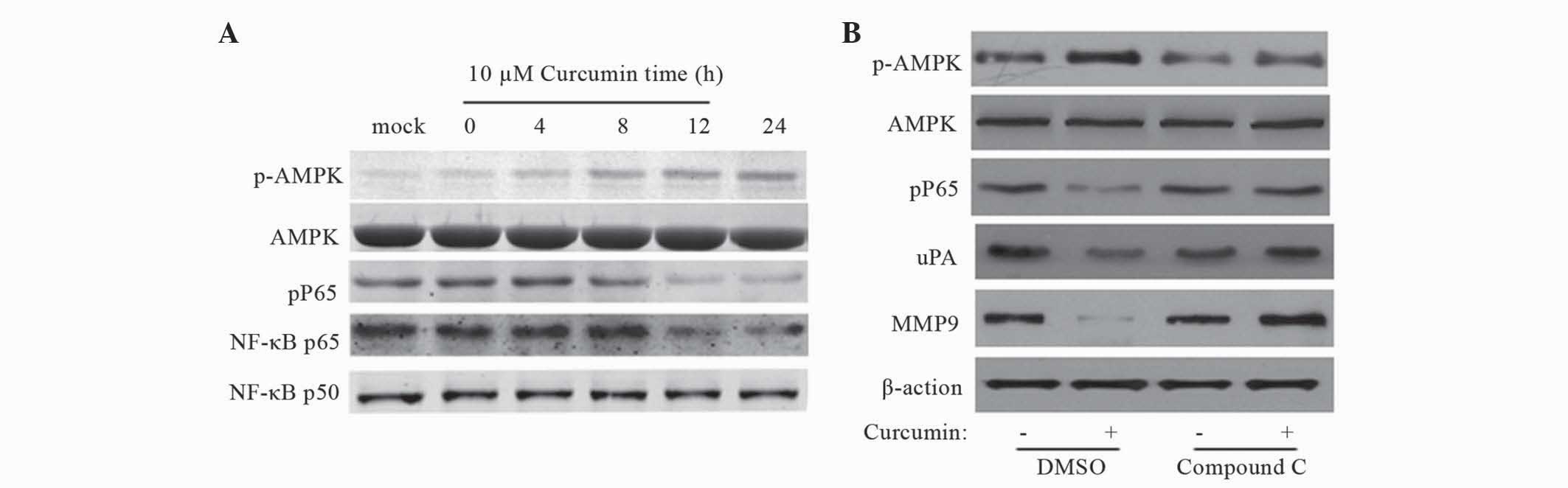
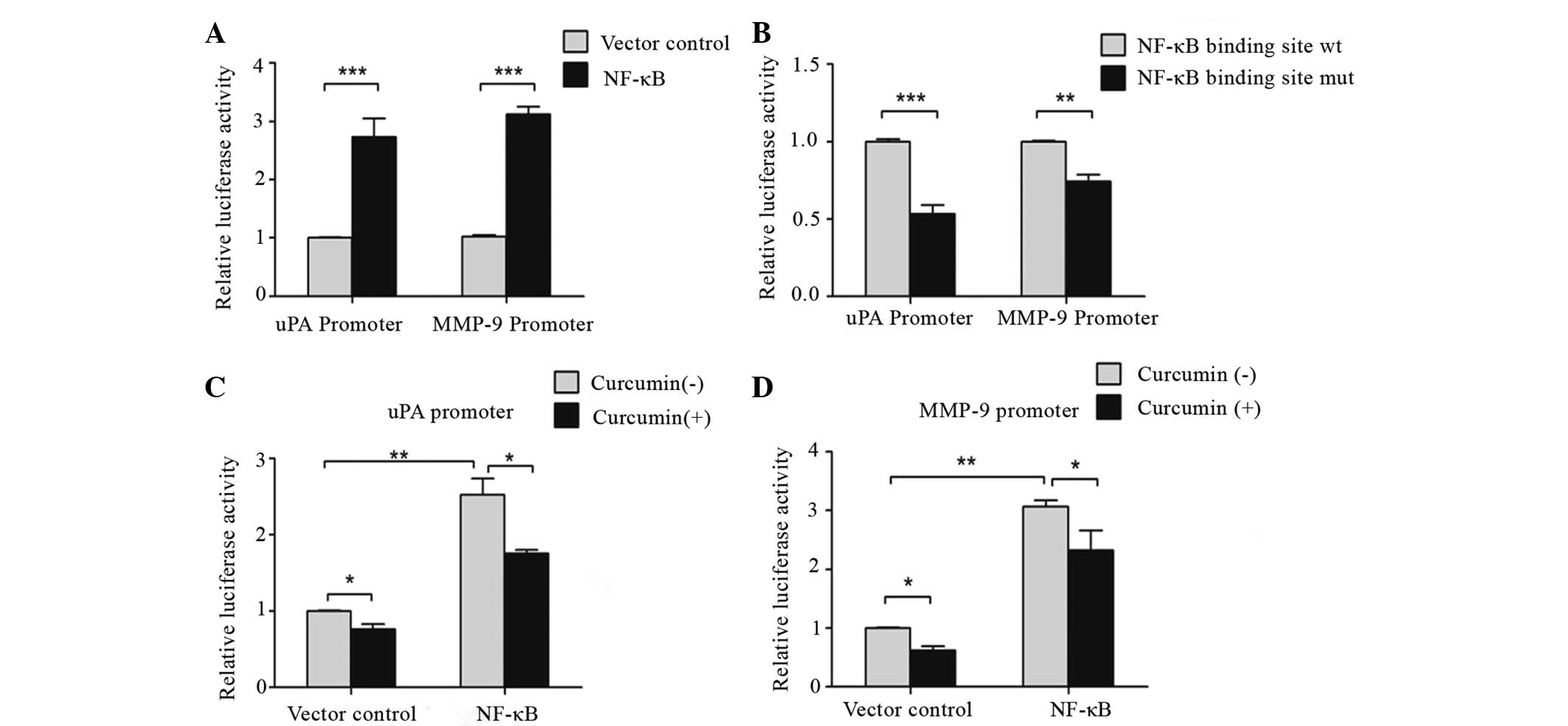
|
1
|
Fearon ER and Vogelstein B: A genetic
model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 61:759–767. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brooks SA, Lomax-Browne HJ, Carter TM,
Kinch CE and Hall DM: Molecular interactions in cancer cell
metastasis. Acta Histochem. 112:3–25. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Raghu H, Sodadasu PK, Malla RR, Gondi CS,
Estes N and Rao JS: Localization of uPAR and MMP-9 in lipid rafts
is critical for migration, invasion and angiogenesis in human
breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 10:6472010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Andreasen PA, Egelund R and Petersen HH:
The plasminogen activation system in tumor growth, invasion, and
metastasis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 57:25–40. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vihinen P, Ala-aho R and Kähäri VM: Matrix
metalloproteinases as therapeutic targets in cancer. Curr Cancer
Drug Targets. 5:203–220. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hildenbrand R, Gandhari M, Stroebel P,
Marx A, Allgayer H and Arens N: The urokinase-system - role of cell
proliferation and apoptosis. Histol Histopathol. 23:227–236.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Andreasen PA, Kjøller L, Christensen L and
Duffy MJ: The urokinase-type plasminogen activator system in cancer
metastasis: A review. Int J Cancer. 72:1–22. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Visse R and Nagase H: Matrix
metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases:
Structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ Res. 92:827–839. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Newell KJ, Witty JP, Rodgers WH and
Matrisian LM: Expression and localization of matrix-degrading
metalloproteinases during colorectal tumorigenesis. Mol Carcinog.
10:199–206. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Crowley CW, Cohen RL, Lucas BK, Liu G,
Shuman MA and Levinson AD: Prevention of metastasis by inhibition
of the urokinase receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 90:5021–5025.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Roy R, Yang J and Moses MA: Matrix
metalloproteinases as novel biomarkers and potential therapeutic
targets in human cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:5287–5297. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Baichwal VR: Activate NF-kappa B or die?
Curr Biol. 7:R94–R96. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Beg AA and Baltimore D: An essential role
for NF-kappaB in preventing TNF-alpha-induced cell death. Science.
274:782–784. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Verma IM and Stevenson J: IkappaB kinase:
Beginning, not the end. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:11758–11760.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen ZJ, Parent L and Maniatis T:
Site-specific phosphorylation of IkappaBalpha by a novel
ubiquitination-dependent protein kinase activity. Cell. 84:853–862.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shishodia S and Aggarwal BB: Nuclear
factor-kappaB activation: A question of life or death. J Biochem
Mol Biol. 35:28–40. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hatcher H, Planalp R, Cho J, Torti FM and
Torti SV: Curcumin: From ancient medicine to current clinical
trials. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:1631–1652. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Aggarwal BB, Kumar A and Bharti AC:
Anticancer potential of curcumin: Preclinical and clinical studies.
Anticancer Res. 23:363–398. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Singh S and Aggarwal BB: Activation of
transcription factor NF-kappa B is suppressed by curcumin
(diferuloylmethane) [corrected]. J Biol Chem. 270:24995–25000.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kumar A, Dhawan S, Hardegen NJ and
Aggarwal BB: Curcumin (Diferuloylmethane) inhibition of tumor
necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated adhesion of monocytes to endothelial
cells by suppression of cell surface expression of adhesion
molecules and of nuclear factor-kappaB activation. Biochem
Pharmacol. 55:775–783. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shi M, Cai Q, Yao L, Mao Y, Ming Y and
Ouyang G: Antiproliferation and apoptosis induced by curcumin in
human ovarian cancer cells. Cell Biol Int. 30:221–226. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kawamori T, Lubet R, Steele VE, Kelloff
GJ, Kaskey RB, Rao CV and Reddy BS: Chemopreventive effect of
curcumin, a naturally occurring anti-inflammatory agent, during the
promotion/progression stages of colon cancer. Cancer Res.
59:597–601. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mukhopadhyay A, Bueso-Ramos C, Chatterjee
D, Pantazis P and Aggarwal BB: Curcumin downregulates cell survival
mechanisms in human prostate cancer cell lines. Oncogene.
20:7597–7609. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bharti AC, Donato N and Aggarwal BB:
Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) inhibits constitutive and
IL-6-inducible STAT3 phosphorylation in human multiple myeloma
cells. J Immunol. 171:3863–3871. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kunnumakkara AB, Anand P and Aggarwal BB:
Curcumin inhibits proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis and
metastasis of different cancers through interaction with multiple
cell signaling proteins. Cancer Lett. 269:199–225. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Plummer SM, Holloway KA, Manson MM, Munks
RJ, Kaptein A, Farrow S and Howells L: Inhibition of
cyclo-oxygenase 2 expression in colon cells by the chemopreventive
agent curcumin involves inhibition of NF-kappaB activation via the
NIK/IKK signalling complex. Oncogene. 18:6013–6020. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mohan R, Sivak J, Ashton P, Russo LA, Pham
BQ, Kasahara N, Raizman MB and Fini ME: Curcuminoids inhibit the
angiogenic response stimulated by fibroblast growth factor-2,
including expression of matrix metalloproteinase gelatinase B. J
Biol Chem. 275:10405–10412. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pan MH, Lin-Shiau SY and Lin JK:
Comparative studies on the suppression of nitric oxide synthase by
curcumin and its hydrogenated metabolites through down-regulation
of IkappaB kinase and NFkappaB activation in macrophages. Biochem
Pharmacol. 60:1665–1676. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jobin C, Bradham CA, Russo MP, Juma B,
Narula AS, Brenner DA and Sartor RB: Curcumin blocks
cytokine-mediated NF-kappaB activation and proinflammatory gene
expression by inhibiting inhibitory factor I-kappa B kinase
activity. J Immunol. 163:3474–3483. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cheng AL, Hsu CH, Lin JK, Hsu MM, Ho YF,
Shen TS, Ko JY, Lin JT, Lin BR, Ming-Shiang W, et al: Phase I
clinical trial of curcumin, a chemopreventive agent, in patients
with high-risk or pre-malignant lesions. Anticancer Res.
21:2895–2900. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Al-Tubuly AA: SDS-PAGE and western
blotting. Methods Mol Med. 40:391–405. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KI and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sandur SK, Deorukhkar A, Pandey MK, Pabón
AM, Shentu S, Guha S, Aggarwal BB and Krishnan S: Curcumin
modulates the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells by
suppressing constitutive and inducible NF-kappaB activity. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 75:534–542. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Killeen SD, Wang JH, Andrews EJ and
Redmond HP: Bacterial endotoxin enhances colorectal cancer cell
adhesion and invasion through TLR-4 and NF-kappaB-dependent
activation of the urokinase plasminogen activator system. Br J
Cancer. 100:1589–1602. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sliva D, English D, Lyons D and Lloyd FP
Jr: Protein kinase C induces motility of breast cancers by
upregulating secretion of urokinase-type plasminogen activator
through activation of AP-1 and NF-kappaB. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 290:552–557. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tsunoda K, Kitange G, Anda T, Shabani HK,
Kaminogo M, Shibata S and Nagata I: Expression of the
constitutively activated RelA/NF-kappaB in human astrocytic tumors
and the in vitro implication in the regulation of urokinase-type
plasminogen activator, migration, and invasion. Brain Tumor Pathol.
22:79–87. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bharti AC, Donato N, Singh S and Aggarwal
BB: Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) down-regulates the constitutive
activation of nuclear factor-kappa B and IkappaBalpha kinase in
human multiple myeloma cells, leading to suppression of
proliferation and induction of apoptosis. Blood. 101:1053–1062.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zong H, Wang F, Fan QX and Wang LX:
Curcumin inhibits metastatic progression of breast cancer cell
through suppression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator by
NF-kappa B signaling pathways. Mol Biol Rep. 39:4803–4808. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shishodia S, Amin HM, Lai R and Aggarwal
BB: Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) inhibits constitutive NF-kappaB
activation, induces G1/S arrest, suppresses proliferation, and
induces apoptosis in mantle cell lymphoma. Biochem Pharmacol.
70:700–713. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shishodia S, Potdar P, Gairola CG and
Aggarwal BB: Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) down-regulates cigarette
smoke-induced NF-kappaB activation through inhibition of
IkappaBalpha kinase in human lung epithelial cells: Correlation
with suppression of COX-2, MMP-9 and cyclin D1. Carcinogenesis.
24:1269–1279. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Johnson SM, Gulhati P, Arrieta I, Wang X,
Uchida T, Gao T and Evers BM: Curcumin inhibits proliferation of
colorectal carcinoma by modulating Akt/mTOR signaling. Anticancer
Res. 29:3185–3190. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen H, Zhang ZS, Zhang YL and Zhou DY:
Curcumin inhibits cell proliferation by interfering with the cell
cycle and inducing apoptosis in colon carcinoma cells. Anticancer
Res. 19:3675–3680. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Baeuerle PA and Baichwal VR: NF-kappa B as
a frequent target for immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory
molecules. Adv Immunol. 65:111–137. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Garg A and Aggarwal BB: Nuclear
transcription factor-kappaB as a target for cancer drug
development. Leukemia. 16:1053–1068. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang S, Pettaway CA, Uehara H, Bucana CD
and Fidler IJ: Blockade of NF-kappaB activity in human prostate
cancer cells is associated with suppression of angiogenesis,
invasion, and metastasis. Oncogene. 20:4188–4197. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hideshima T, Chauhan D, Richardson P,
Mitsiades C, Mitsiades N, Hayashi T, Munshi N, Dang L, Castro A,
Palombella V, et al: NF-kappa B as a therapeutic target in multiple
myeloma. J Biol Chem. 277:16639–16647. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ghosh S and Karin M: Missing pieces in the
NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell. 109 Suppl:S81–S96. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Salminen A, Hyttinen JM and Kaarniranta K:
AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits NF-kappaB signaling and
inflammation: Impact on healthspan and lifespan. J Mol Med (Berl).
89:667–676. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bai A, Ma AG, Yong M, Weiss CR, Ma Y, Guan
Q, Bernstein CN and Peng Z: AMPK agonist downregulates innate and
adaptive immune responses in TNBS-induced murine acute and
relapsing colitis. Biochem Pharmacol. 80:1708–1717. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yang Z, Kahn BB, Shi H and Xue BZ:
Macrophage alpha1 AMP-activated protein kinase (alpha1AMPK)
antagonizes fatty acid-induced inflammation through SIRT1. J Biol
Chem. 285:19051–19059. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sag D, Carling D, Stout RD and Suttles J:
Adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase promotes
macrophage polarization to an anti-inflammatory functional
phenotype. J Immunol. 181:8633–8641. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang S, Zhang M, Liang B, Xu J, Xie Z, Liu
C, Viollet B, Yan D and Zou MH: AMPKalpha2 deletion causes aberrant
expression and activation of NAD(P)H oxidase and consequent
endothelial dysfunction in vivo: Role of 26S proteasomes. Circ Res.
106:1117–1128. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wu X, Mahadev K, Fuchsel L, Ouedraogo R,
Xu SQ and Goldstein BJ: Adiponectin suppresses IkappaB kinase
activation induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha or high glucose
in endothelial cells: Role of cAMP and AMP kinase signaling. Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 293:E1836–E1844. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hattori Y, Suzuki K, Hattori S and Kasai
K: Metformin inhibits cytokine-induced nuclear factor kappaB
activation via AMP-activated protein kinase activation in vascular
endothelial cells. Hypertension. 47:1183–1188. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Cantó C and Auwerx J: AMP-activated
protein kinase and its downstream transcriptional pathways. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 67:3407–3423. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhong H, Voll RE and Ghosh S:
Phosphorylation of NF-kappa B p65 by PKA stimulates transcriptional
activity by promoting a novel bivalent interaction with the
coactivator CBP/p300. Mol Cell. 1:661–671. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|