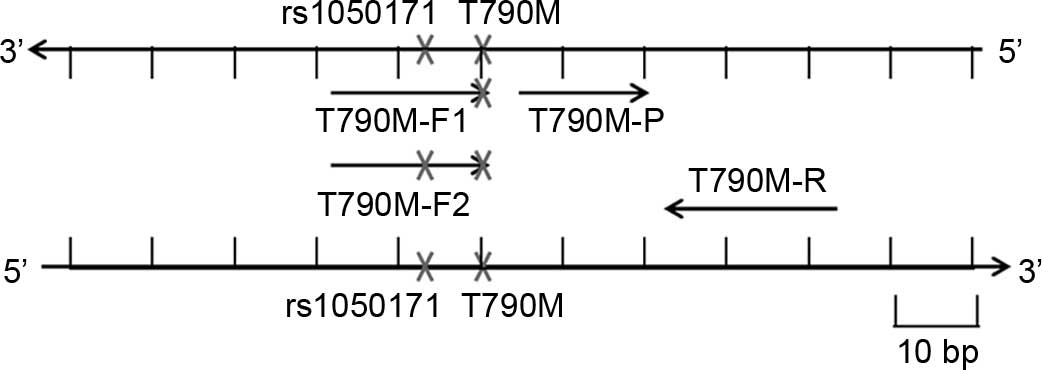
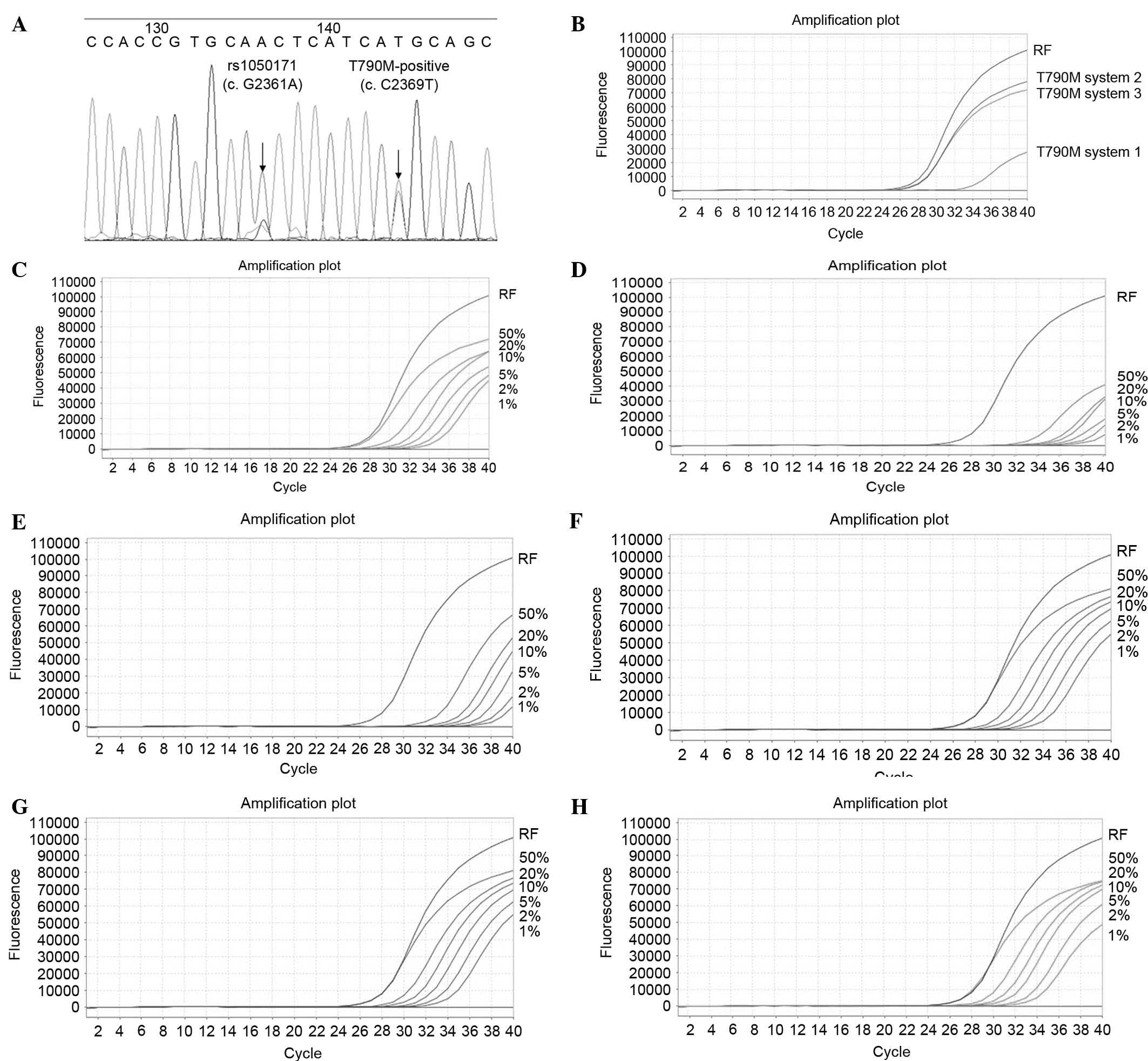
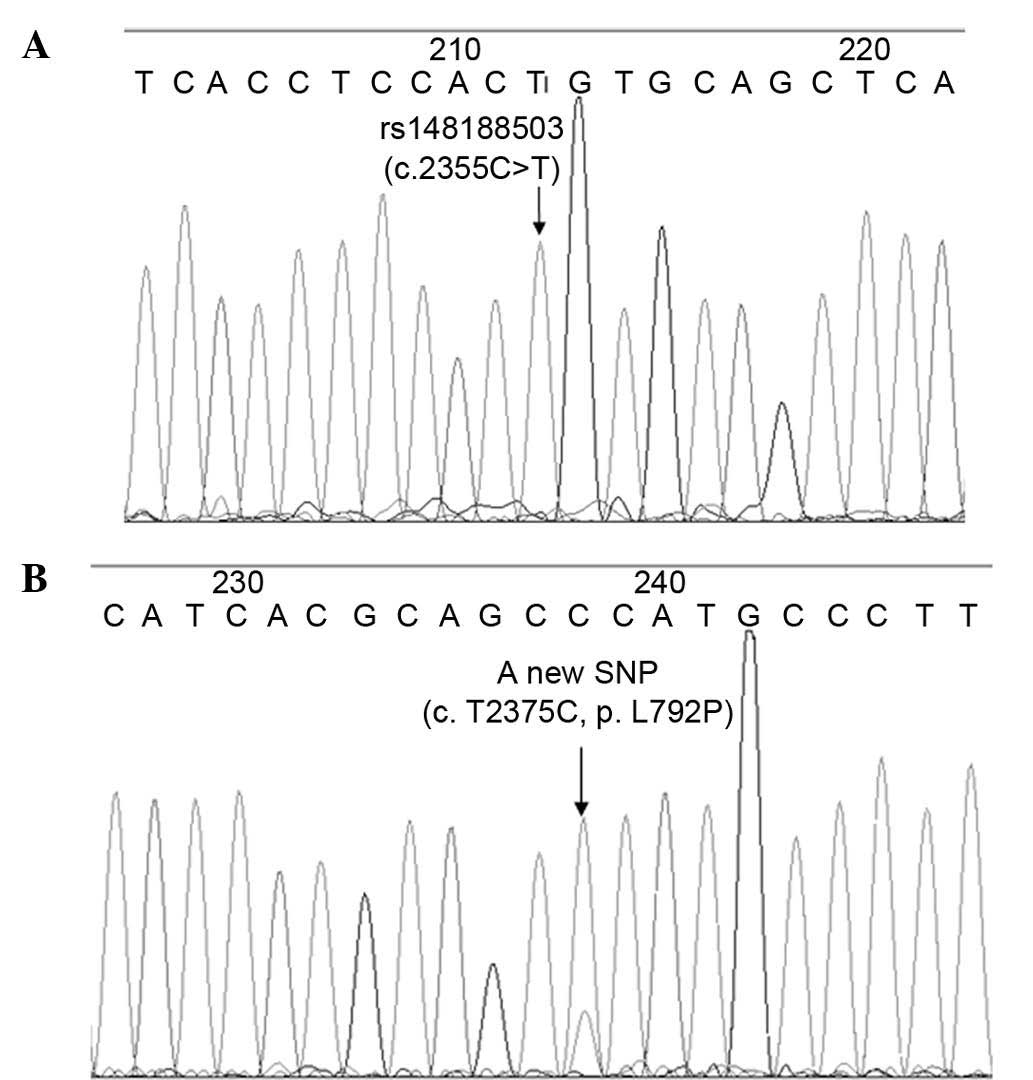
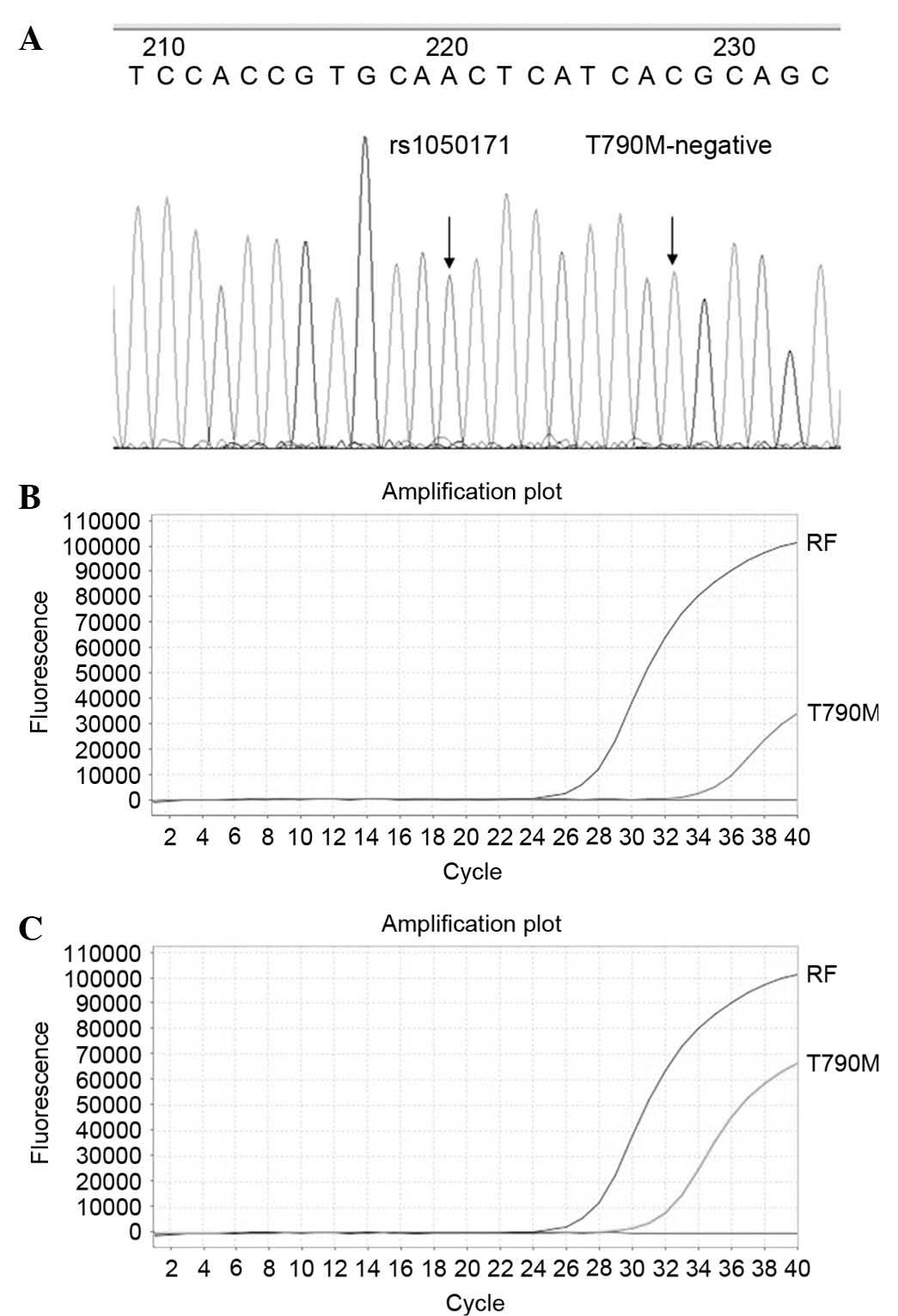
|
1
|
Wang J, Ramakrishnan R, Tang Z, Fan W,
Kluge A, Dowlati A, Jones RC and Ma PC: Quantifying EGFR
alterations in the lung cancer genome with nanofluidic digital PCR
arrays. Clini Chem. 56:623–632. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kim Y, Ko J, Cui Z, Abolhoda A, Ahn JS, Ou
SH, Ahn MJ and Park K: The EGFR T790M mutation in acquired
resistance to an irreversible second-generation EGFR inhibitor. Mol
Cancer Ther. 11:784–791. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Jänne
PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M, Johnson BE, Eck MJ, Tenen DG and Halmos
B: EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to
gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 352:786–792. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kuang Y, Rogers A, Yeap BY, Wang L,
Makrigiorgos M, Vetrand K, Thiede S, Distel RJ and Jänne PA:
Noninvasive detection of EGFR T790M in gefitinib or erlotinib
resistant non-small cell lung cancer. Clinical cancer research: An
official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
15:2630–2636. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun JM, Ahn MJ, Choi YL, Ahn JS and Park
K: Clinical implications of T790M mutation in patients with
acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Lung
Cancer. 82:294–298. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yamada T, Azuma K, Muta E, Kim J, Sugawara
S, Zhang GL, Matsueda S, Kasama-Kawaguchi Y, Yamashita Y, Yamashita
T, et al: EGFR T790M mutation as a possible target for
immunotherapy; identification of HLA-A*0201-restricted T cell
epitopes derived from the EGFR T790M mutation. PloS One.
8:e783892013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Denis MG, Vallée A and Théoleyre S: EGFR
T790M resistance mutation in non small-cell lung carcinoma. Clin
Chim Acta. 444:81–85. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lin L and Bivona TG: Mechanisms of
resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors and novel
therapeutic strategies to overcome resistance in NSCLC patients.
Chemother Res Pract. 2012:8172972012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou W, Ercan D, Chen L, Yun CH, Li D,
Capelletti M, Cortot AB, Chirieac L, Iacob RE, Padera R, et al:
Novel mutant-selective EGFR kinase inhibitors against EGFR T790M.
Nature. 462:1070–1074. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yung TK, Chan KC, Mok TS, Tong J, To KF
and Lo YM: Single-molecule detection of epidermal growth factor
receptor mutations in plasma by microfluidics digital PCR in
non-small cell lung cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 15:2076–2084.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Thomas RK, Nickerson E, Simons JF, Jänne
PA, Tengs T, Yuza Y, Garraway LA, LaFramboise T, Lee JC, Shah K, et
al: Sensitive mutation detection in heterogeneous cancer specimens
by massively parallel picoliter reactor sequencing. Nat Med.
12:852–855. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guha M, Castellanos-Rizaldos E and
Makrigiorgos GM: DISSECT method using PNA-LNA clamp improves
detection of T790M mutation. PloS One. 8:e677822013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bai H, Wang Z, Wang Y, Zhuo M, Zhou Q,
Duan J, Yang L, Wu M, An T, Zhao J and Wang J: Detection and
clinical significance of intratumoral EGFR mutational heterogeneity
in Chinese patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. PloS
One. 8:e541702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Board RE, Ellison G, Orr MC, Kemsley KR,
McWalter G, Blockley LY, Dearden SP, Morris C, Ranson M, Cantarini
MV, et al: Detection of BRAF mutations in the tumour and serum of
patients enrolled in the AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) advanced melanoma
phase II study. Br J Cancer. 101:1724–1730. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chu H, Zhong C, Xue G, Liang X, Wang J,
Liu Y, Zhao S, Zhou Q and Bi J: Direct sequencing and amplification
refractory mutation system for epidermal growth factor receptor
mutations in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep.
30:2311–2315. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ellison G, Donald E, McWalter G, Knight L,
Fletcher L, Sherwood J, Cantarini M, Orr M and Speake G: A
comparison of ARMS and DNA sequencing for mutation analysis in
clinical biopsy samples. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 29:1322010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Franklin WA, Haney J, Sugita M, Bemis L,
Jimeno A and Messersmith WA: KRAS mutation: Comparison of testing
methods and tissue sampling techniques in colon cancer. J Mol
Diagn. 12:43–50. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fukuoka M, Wu YL, Thongprasert S,
Sunpaweravong P, Leong SS, Sriuranpong V, Chao TY, Nakagawa K, Chu
DT, Saijo N, et al: Biomarker analyses and final overall survival
results from a phase III, randomized, open-label, first-line study
of gefitinib versus carboplatin/paclitaxel in clinically selected
patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer in Asia (IPASS).
J Clin Oncol. 29:2866–2874. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hamfjord J, Stangeland AM, Skrede ML,
Tveit KM, Ikdahl T and Kure EH: Wobble-enhanced ARMS method for
detection of KRAS and BRAF mutations. Diagn Mol Pathol. 20:158–165.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Harlé A, Lion M, Lozano N, Husson M,
Harter V, Genin P and Merlin JL: Analysis of PIK3CA exon 9 and 20
mutations in breast cancers using PCR-HRM and PCR-ARMS: Correlation
with clinicopathological criteria. Oncol Rep. 29:1043–1052.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang T, Zhuge J and Zhang WW: Sensitive
detection of BRAF V600E mutation by amplification refractory
mutation system (ARMS)-PCR. Biomark Res. 1:32013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu Y, Liu B, Li XY, Li JJ, Qin HF, Tang
CH, Guo WF, Hu HX, Li S, Chen CJ, et al: A comparison of ARMS and
direct sequencing for EGFR mutation analysis and tyrosine kinase
inhibitors treatment prediction in body fluid samples of
non-small-cell lung cancer patients. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
30:1112011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Machnicki MM, Glodkowska-Mrowka E,
Lewandowski T, Ploski R, Wlodarski P and Stoklosa T: ARMS-PCR for
detection of BRAF V600E hotspot mutation in comparison with
real-time PCR-based techniques. Acta Biochim Pol. 60:57–64.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ogasawara N, Bando H, Kawamoto Y, Yoshino
T, Tsuchihara K, Ohtsu A and Esumi H: Feasibility and robustness of
amplification refractory mutation system (ARMS)-based KRAS testing
using clinically available formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded
samples of colorectal cancers. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 41:52–56. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang B, Xu CW, Shao Y, Wang HT, Wu YF,
Song YY, Li XB, Zhang Z, Wang WJ, Li LQ and Cai CL: Comparison of
droplet digital PCR and conventional quantitative PCR for measuring
gene mutation. Exp Ther Med. 9:1383–1388. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pettersson M, Bylund M and Alderborn A:
Molecular haplotype determination using allele-specific PCR and
pyrosequencing technology. Genomics. 82:390–396. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vlassov VV, Laktionov PP and Rykova EY:
Circulating nucleic acids as a potential source for cancer
biomarkers. Curr Mol Med. 10:142–165. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ye S, Dhillon S, Ke X, Collins AR and Day
IN: An efficient procedure for genotyping single nucleotide
polymorphisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 29:E88. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|