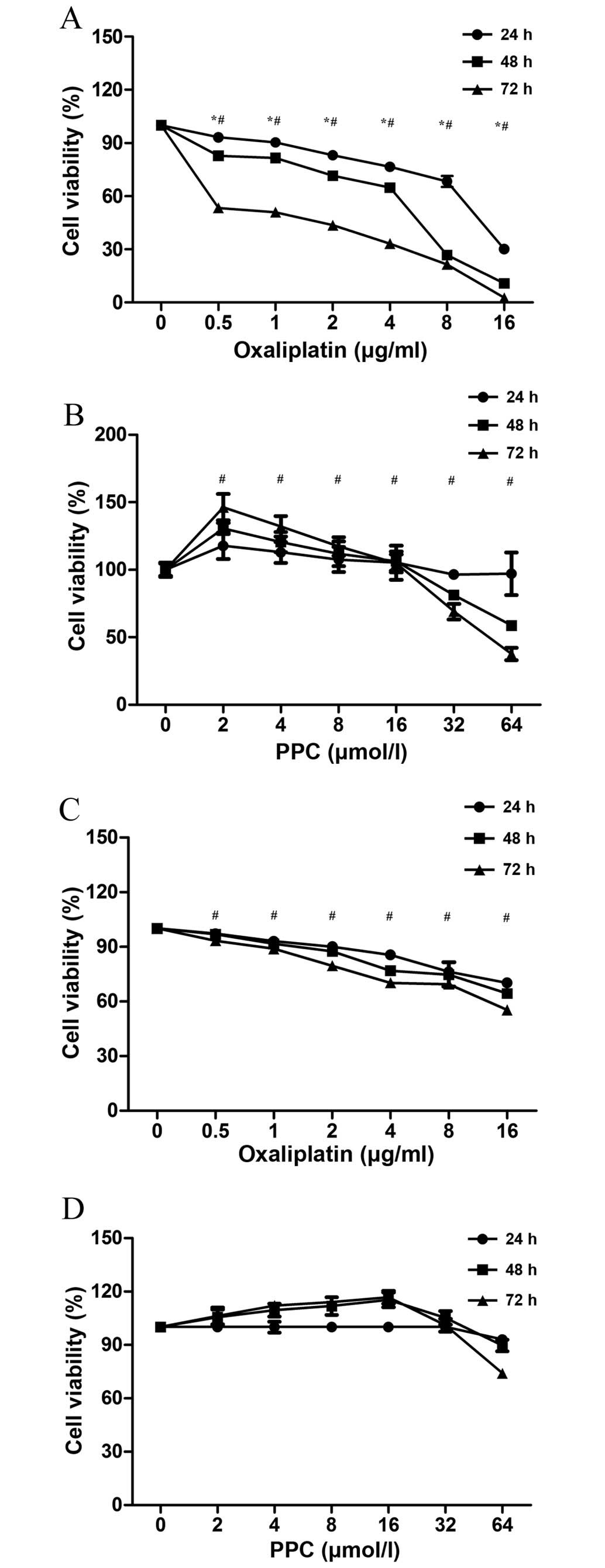
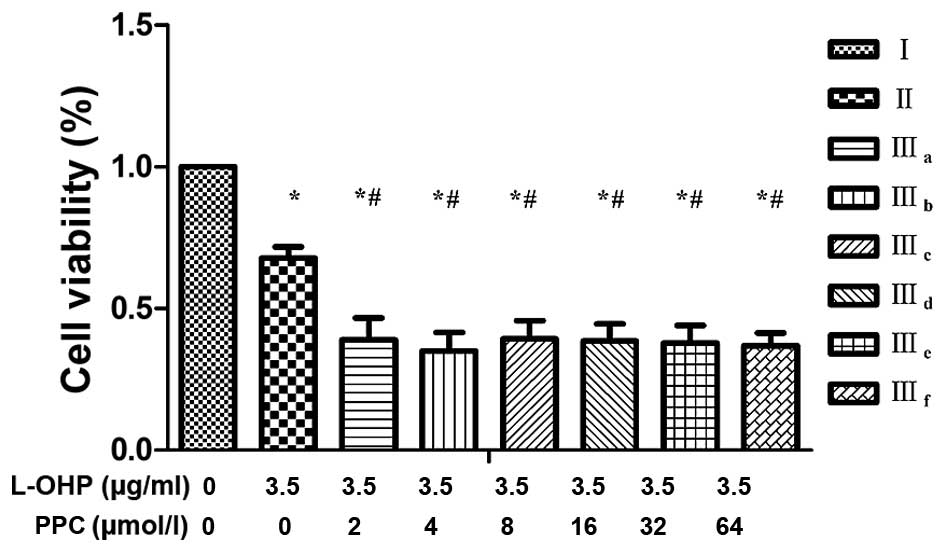
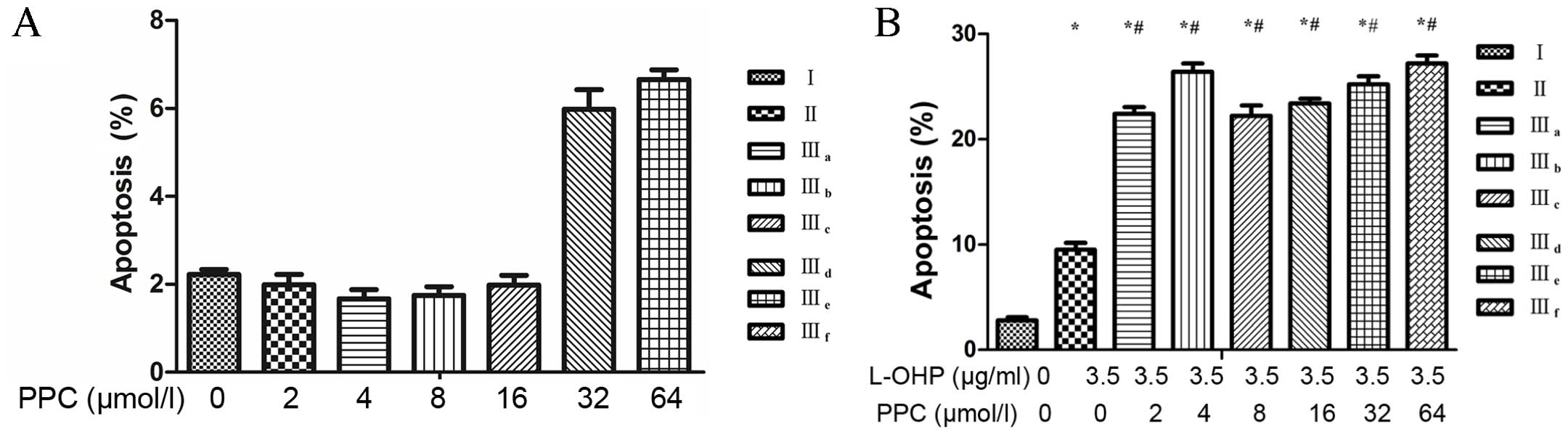
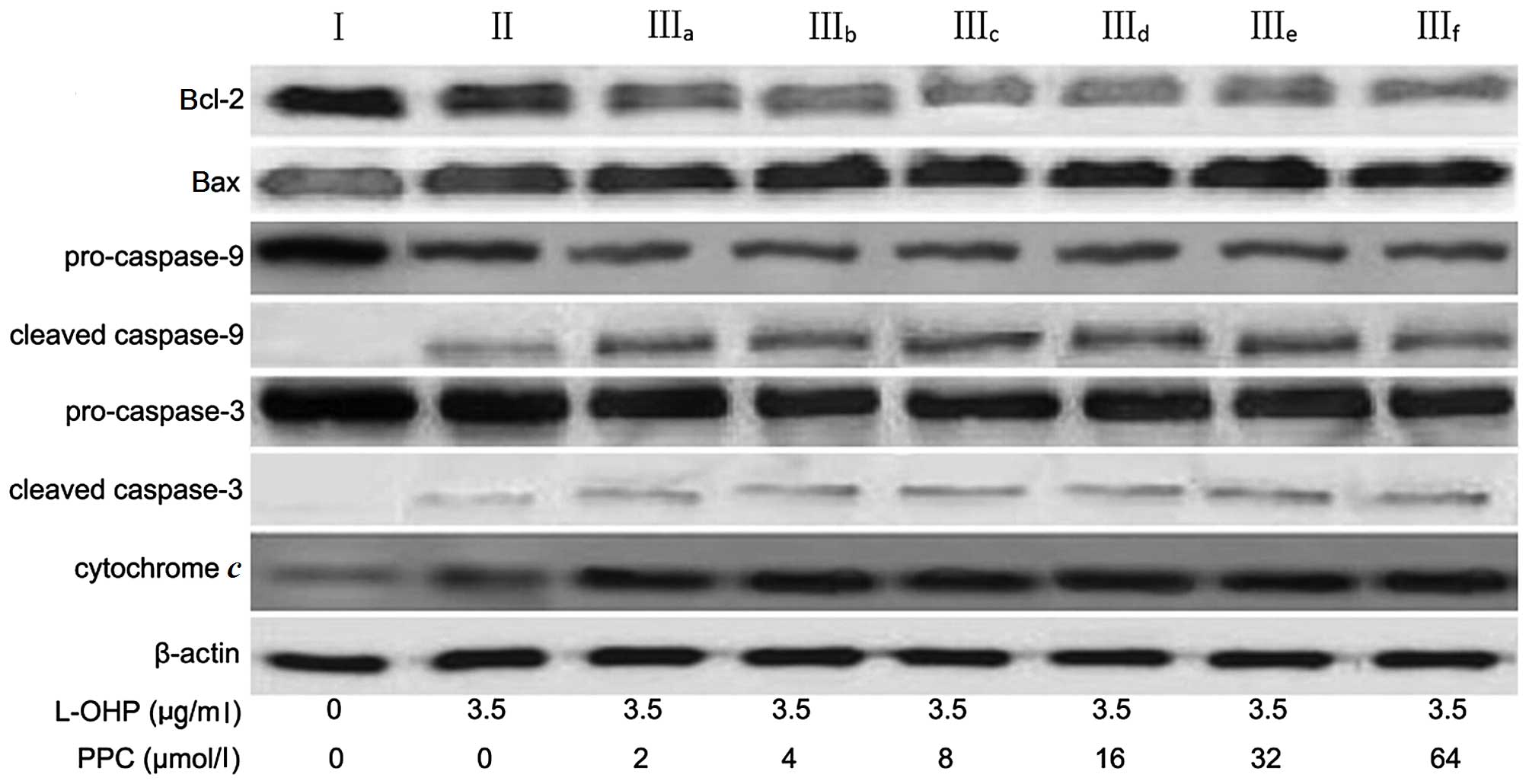
|
1
|
Dong CX, Fu JF, Ye XY, Li XF, Zhong X and
Yuan Y: Surgical resection of advanced gastric cancer following
trastuzumab/oxaliplatin/capecitabine combination therapy. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:12355–12358. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Choi IJ, Lee JH, Kim YI, Kim CG, Cho SJ,
Lee JY, Ryu KW, Nam BH, Kook MC and Kim YW: Long-term outcome
comparison of endoscopic resection and surgery inearly gastric
cancer meeting the absolute indication for endoscopic resection.
Gastro intest Endosc. 81:333.e1–341.e1. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fiteni F, Nguyen T, Vernerey D, Paillard
MJ, Kim S, Demarchi M, Fein F, Borg C, Bonnetain F and Pivot X:
Cisplatin/gemcitabine or oxaliplatin/gemcitabine in the treatment
of advanced biliary tract cancer: A systematic review. Cancer Med.
3:1502–1511. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schumacher JD and Guo GL: Mechanistic
review of drug-induced steatohepatitis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
289:40–47. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang Tao, Song Hao, Zhao Yuan-Yuan, Liang
Jun, Zhang Hong-Jun and Liu Xi-Guang: Effect of oxaliplatin
combined with polyenephosphatidylcholine on proliferation of
gastric cancer cells. Chinese Journal of Cancer Prevention and
Treatment. 13:41–44. 2014.
|
|
7
|
Cao M, Li X, Zhang B, Han S, Yang Y, Zhou
B and Zhang Y: The effect of polyene phosphatidyl choline
intervention on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and related mechanism.
Am J Transl Res. 8:2325–2330. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim HS, Kim JH, Kim HJ, Jang HJ, Kim JB,
Kim JW, Jung SY, Kim BC, Yang DH, Park S, et al: Oxaliplatin,
5-fluorouracil and leucovorin (modified FOLFOX-6) as first-line
chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer patients with poor
performance status. Oncol Lett. 3:425–428. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rosati G, Ferrara D and Manzione L: New
perspectives in the treatment of advanced or metastatic gastric
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 15:2689–2692. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Koizumi W, Takiuchi H, Yamada Y, Boku N,
Fuse N, Muro K, Komatsu Y and Tsuburaya A: Phase II study of
oxaliplatin plus S-1 as first-line treatment for advanced gastric
cancer (G-SOX study). Ann Oncol. 21:1001–1005. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Park I, Lee JL, Ryu MH, Chang HM, Kim TW,
Sym SJ, Lee SS, Jang G, Yoo C, Bae KS and Kang YK: Phase I/II and
pharmacokinetic study of S-1 and oxaliplatin in previously
untreated advanced gastric cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
65:473–480. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Choti MA: Chemotherapy-associated
hepatotoxicity: Do we need to be concerned? Ann Surg Oncol.
16:2391–2394. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Malaguarnera M, Di RM, Nicoletti F and
Malaguarnera L: Molecular mechanisms involved in NAFLD progression.
J Mol Med (Berl). 87:679–695. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Okyama W, Tanaka N, Nakajima T, Tanaka E,
Kiyosawa K, Gonzalez FJ and Aoyama T: Polyenephosphatidylcholine
prevents alcoholic liver disease in PPARalpha-null mice through
attenuation of increases in oxidative stress. J Hepatol.
50:1236–1246. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lieber CS, Robins SJ, Li J, DeCarli LM,
Mak KM, Fasulo JM and Leo MA: Phosphatidylcholine protects against
fibrosis and cirrhosis in the baboon. Gastroenterology.
106:152–159. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cao Q, Mak KM and Lieber CS:
Dilinoleoylphosphatidylcholine decreases acetaldehyde-induced
TNF-alpha generation in Kupffer cells of ethanol-fed rats. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 299:459–464. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cao Q, Mak KM and Lieber CS: DLPC and SAMe
combined prevent leptin-stimulated TIMP-1 production in LX-2 human
hepatic stellate cells by inhibiting HO-mediated signal
transduction. Liver Int. 26:221–231. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chou TC: Drug combination studies and
their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer
Res. 70:440–446. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Esmaeili MA, Abagheri-Mahabadi N,
Hashempour H, Farhadpour M, Gruber CW and Ghassempour A: Viola
plant cyclotide vigno 5 induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis
viacytochrome C release and caspases activation in cervical cancer
cells. Fitoterapia. 109:162–168. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Brentnall M, Rodriguez-Menocal L, De
Guevara RL, Cepero E and Boise LH: Caspase-9, caspase-3 and
caspase-7 have distinct roles during intrinsic apoptosis. BMC Cell
Biol. 14:322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Saito H, Osaki T, Murakami D, Sakamoto T,
Kanaji S, Tatebe S, Tsujitani S and Ikeguchi M: Effect of age on
prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. ANZ J Surg. 76:458–461.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yoon H and Kim N: Diagnosis and management
of high risk group for gastric cancer. Gut Liver. 9:5–17. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Glimelius B, Ekström K, Hoffman K, Graf W,
Sjödén PO, Haglund U, Svensson C, Enander LK, Linné T, Sellström H
and Heuman R: Randomized comparison between chemotherapy plus best
supportive care with best supportive care in advanced gastric
cancer. Ann Oncol. 8:163–168. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Oba K, Paoletti X, Bang YJ, Bleiberg H,
Burzykowski T, Fuse N, Michiels S, Morita S, Ohashi Y, Pignon JP,
et al: Role of chemotherapy for advanced/recurrent gastric cancer:
An individual-patient-data meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer.
49:1565–1577. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Falcone A, Ricci S, Brunetti I, Pfanner E,
Allegrini G, Barbara C, Crinò L, Benedetti G, Evangelista W,
Fanchini L, et al: Phase III trial of infusional fluorouracil,
leucovorin, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan (FOLFOXIRI) compared with
infusional fluorouracil, leucovorin, and irinotecan (FOLFIRI) as
first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: The Gruppo
Oncologico Nord Ovest. J Clin Oncol. 25:1670–1676. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Al-Batran SE, Hartmann JT, Probst S,
Schmalenberg H, Hollerbach S, Hofheinz R, Rethwisch V, Seipelt G,
Homann N, Wilhelm G, et al: Phase III trial in metastatic
gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma with fluorouracil, leucovorin plus
either oxaliplatin or cisplatin: A study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft
Internistische Onkologie. J Clin Oncol. 26:1435–1442. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nordberg J and Arnér ES: Reactive oxygen
species, antioxidants and the mammalian thioredoxin system. Free
Radic Biol Med. 31:1287–1312. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zeng L, Li Y, Li T, Cao W, Yi Y, Geng W,
Sun Z and Xu H: Selenium-platinum coordination compounds as novel
anticancer drugs: Selectively killing cancer cells via a reactive
oxygen species (ROS)-mediated apoptosis route. Chem Asian J.
9:2295–2302. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee DJ and Kang SW: Reactive oxygen
species and tumor metastasis. Mol Cells. 35:93–98. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Atmaca M, Kuloglu M, Tezcan E and Ustundag
B: Antioxidant enzyme and malondialdehyde levels in patients with
social phobia. Psychiatry Res. 159:95–100. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Singh N, Zaidi D, Shyam H, Sharma R and
Balapure AK: Polyphenols sensitization potentiates susceptibility
of MCF-7 and MDA MB-231 cells to Centchroman. PLoS One.
7:e377362012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Culy CR, Clemett D and Wiseman LR:
Oxaliplatin. A review of its pharmacological properties and
clinical efficacy in metastatic colorectal cancer and its potential
in other malignancies. Drugs. 60:895–924. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fernandez FG, Ritter J, Goodwin JW,
Linehan DC, Hawkins WG and Strasberg SM: Effect of steatohepatitis
associated with irinotecan or oxaliplatin pretreatment on
resectability of hepatic colorectal metastases. J Am Coll Surg.
200:845–853. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Horejsová M and Urban J: The effect of
polyene phosphatidylcholine (Essentiale forte) in the treatment of
liver steatosis and ultrasound findings-preliminary study. Cas Lek
Cesk. 133:366–369. 1994.(In Czech). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Su HL, Zhu YX, Gao ZJ, Dong XY, Zhu JY,
Lei WR, Zhang Y and Han Y: Efficacy comparison between bicyclol and
polyene phosphatidylcholine treatments for the patients with
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi.
9:552–553. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
36
|
Dragovich T, Rudin CM and Thompson CB:
Signal transduction pathways that regulate cell survival and cell
death. Oncogene. 17:3207–3213. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gross A, McDonnell JM and Korsmeyer SJ:
BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev.
13:1899–1911. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu X, Kim CN, Yang J, Jemmerson R and
Wang X: Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts:
Requirement for dATP and cytochrome c. Cell. 86:147–157. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zou H, Henzel WJ, Liu X, Lutschg A and
Wang X: Apaf-1, a human protein homologous to C. elegans CED-4,
participates in cytochrome c-dependent activation of caspase-3.
Cell. 90:405–413. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Enari M, Sakahira H, Yokoyama H, Okawa K,
Iwamatsu A and Nagata S: A caspase-activated DNase that degrades
DNA during apoptosis, and its inhibitor ICAD. Nature. 391:43–50.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Almeida A: Regulation of APC/C-Cdh1 and
its function in neuronal survival. Mol Neurobiol. 46:547–554. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang K and Kumar R: Interferon-alpha
inhibits cyclin E- and cyclin D1-dependent CDK-2 kinase activity
associated with RB protein and E2F in Daudi cells. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 200:522–528. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hossain Z, Konishi M, Hosokawa M and
Takahashi K: Effect of polyunsaturated fatty acid-enriched
phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine on butyrate-induced
growth inhibition, differentiation and apoptosis in Caco-2 cells.
Cell Biochem Funct. 24:159–165. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Raffy S and Teissié J: Control of lipid
membrane stability by cholesterol content. Biophys J. 76:2072–2080.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|