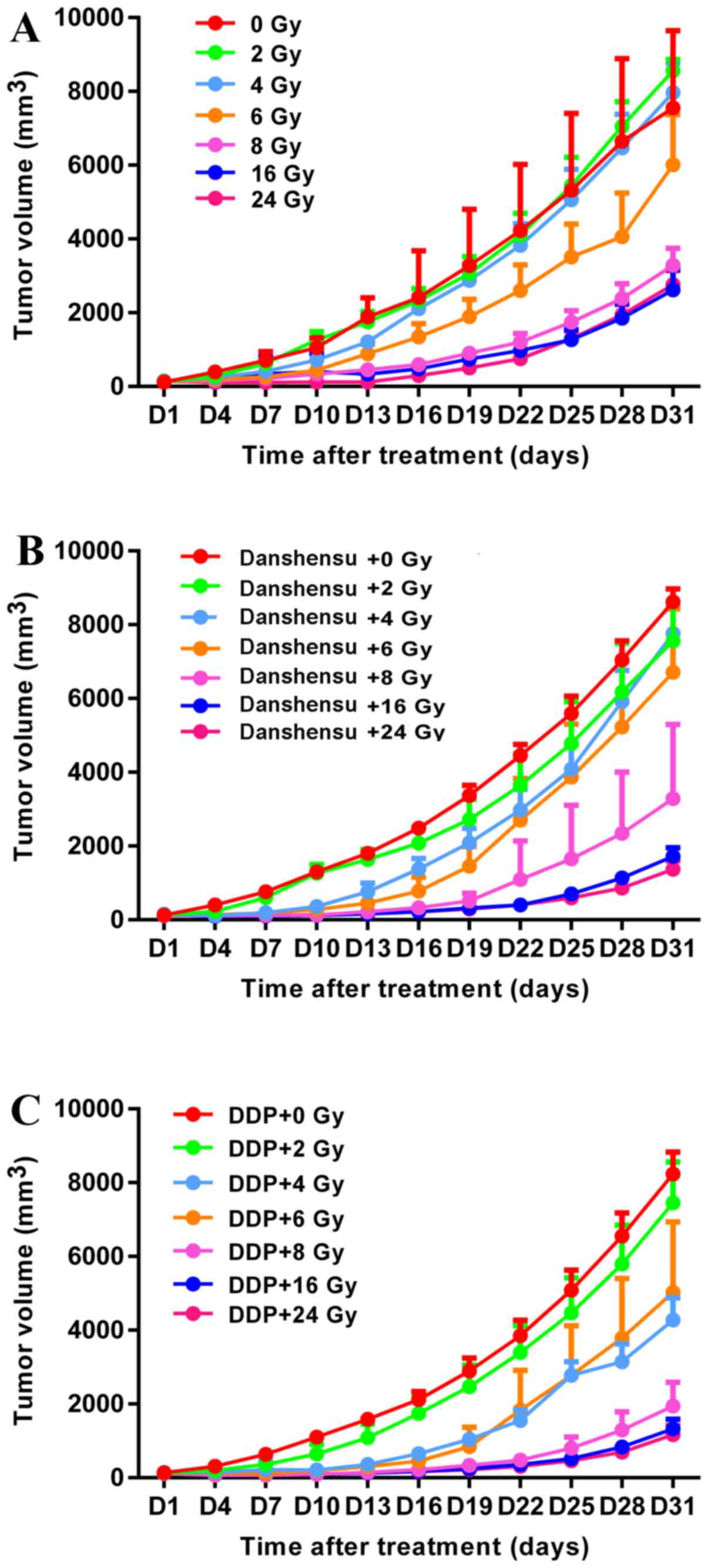
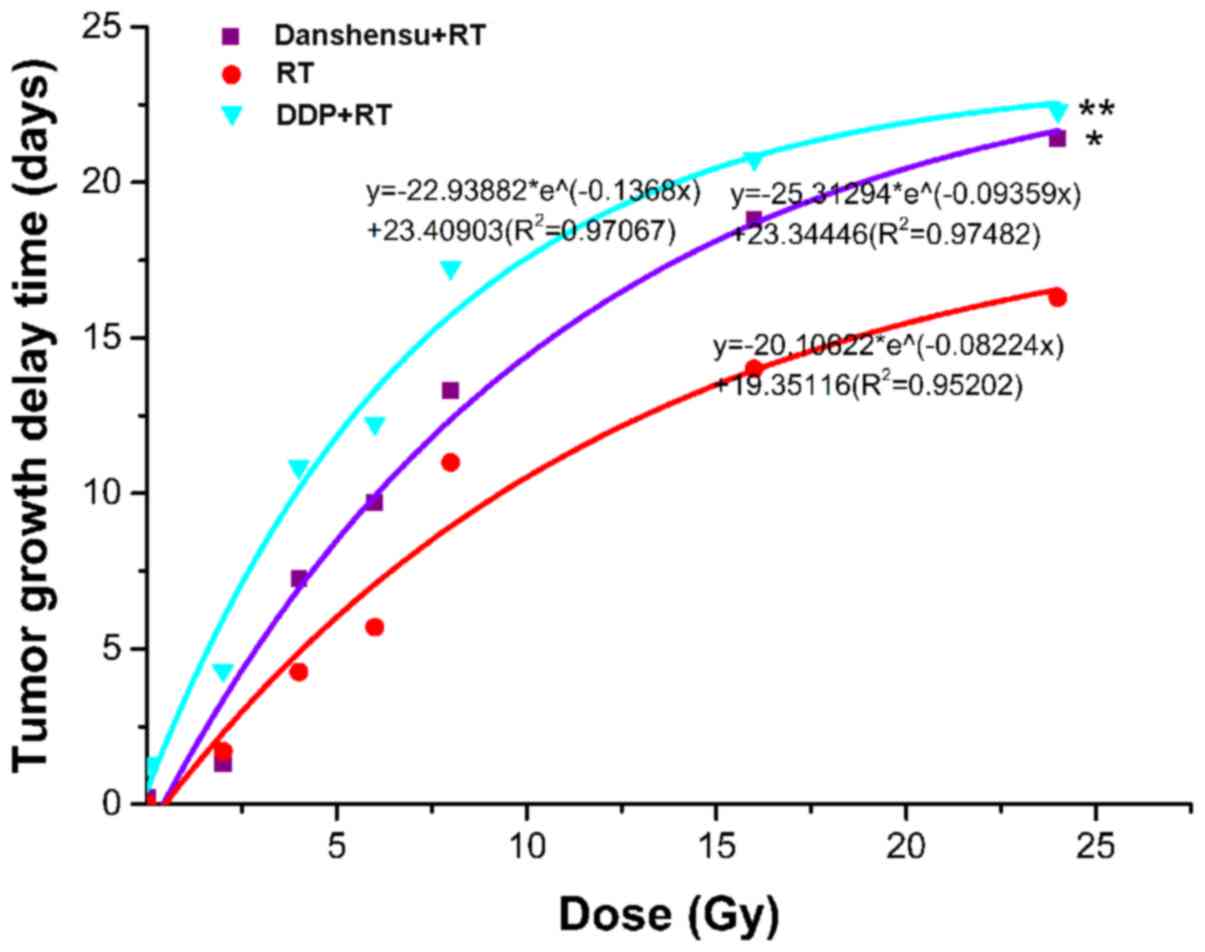
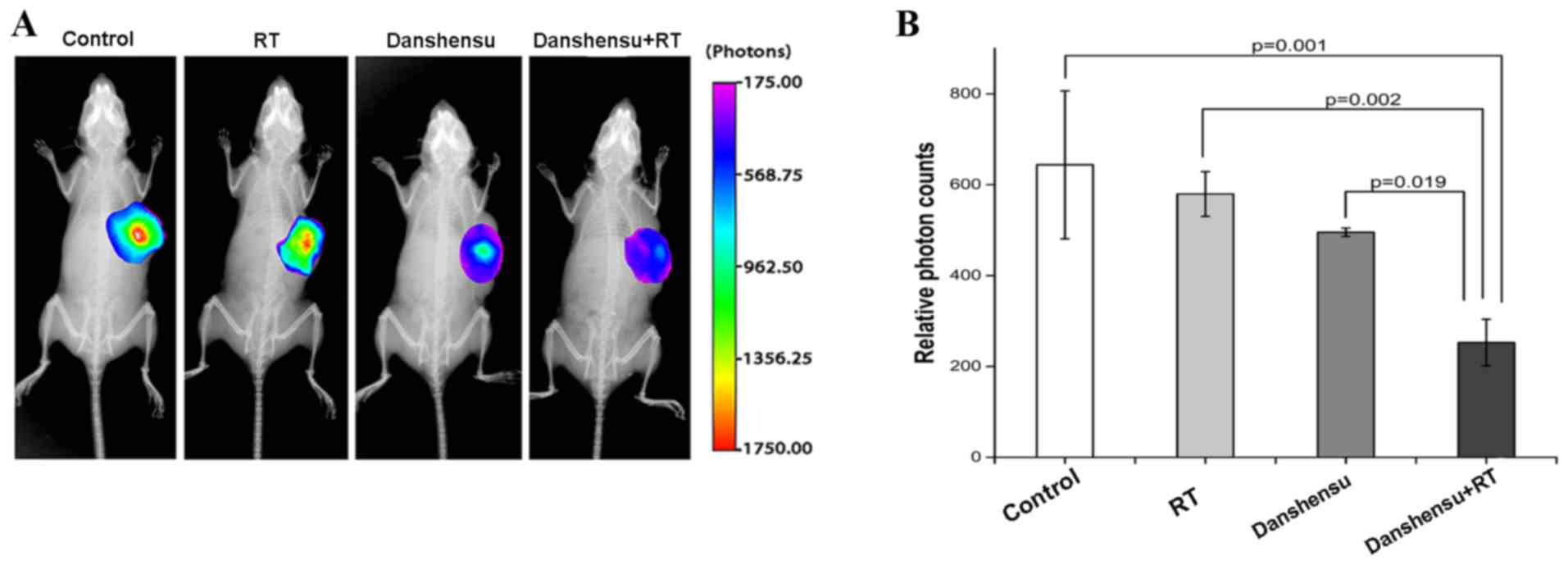
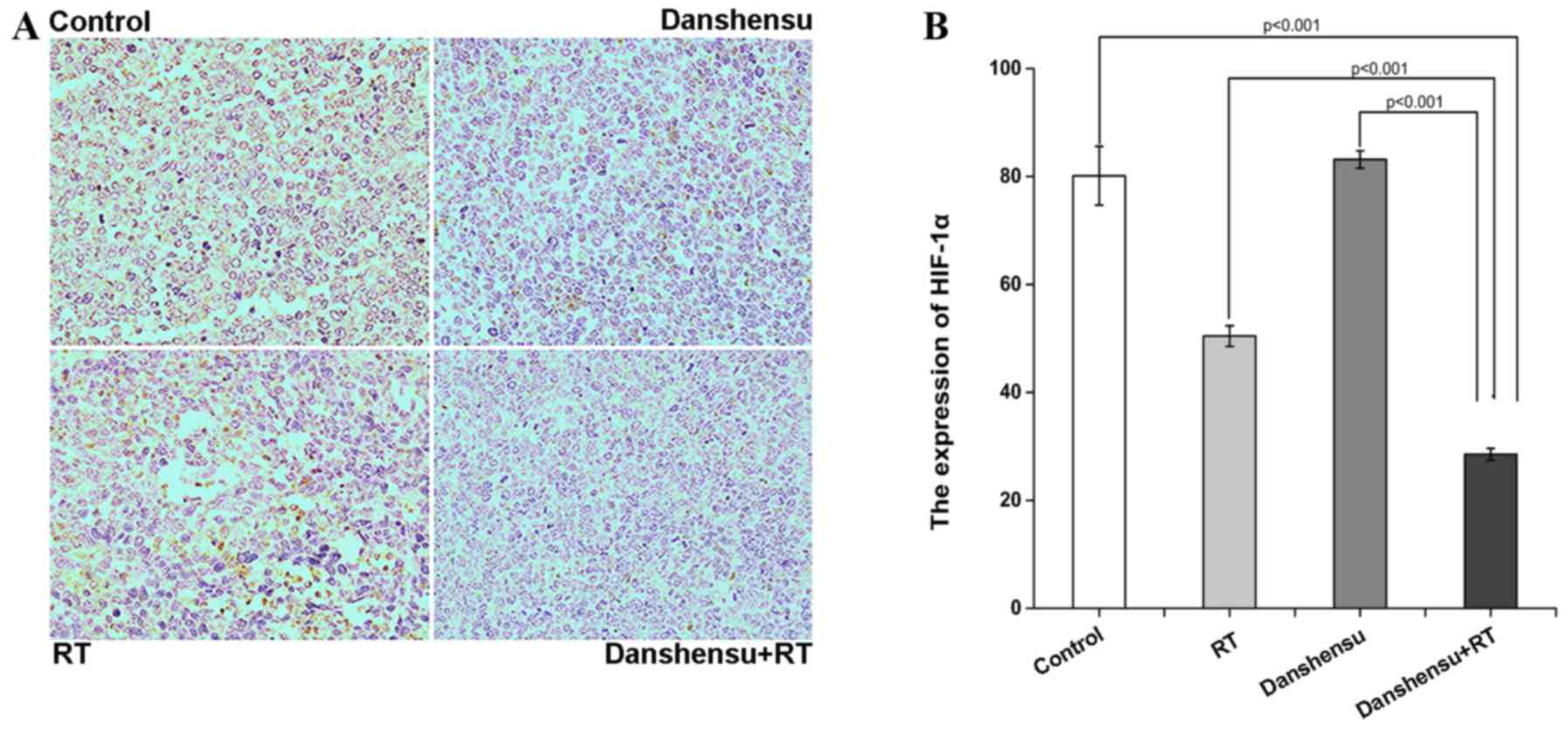
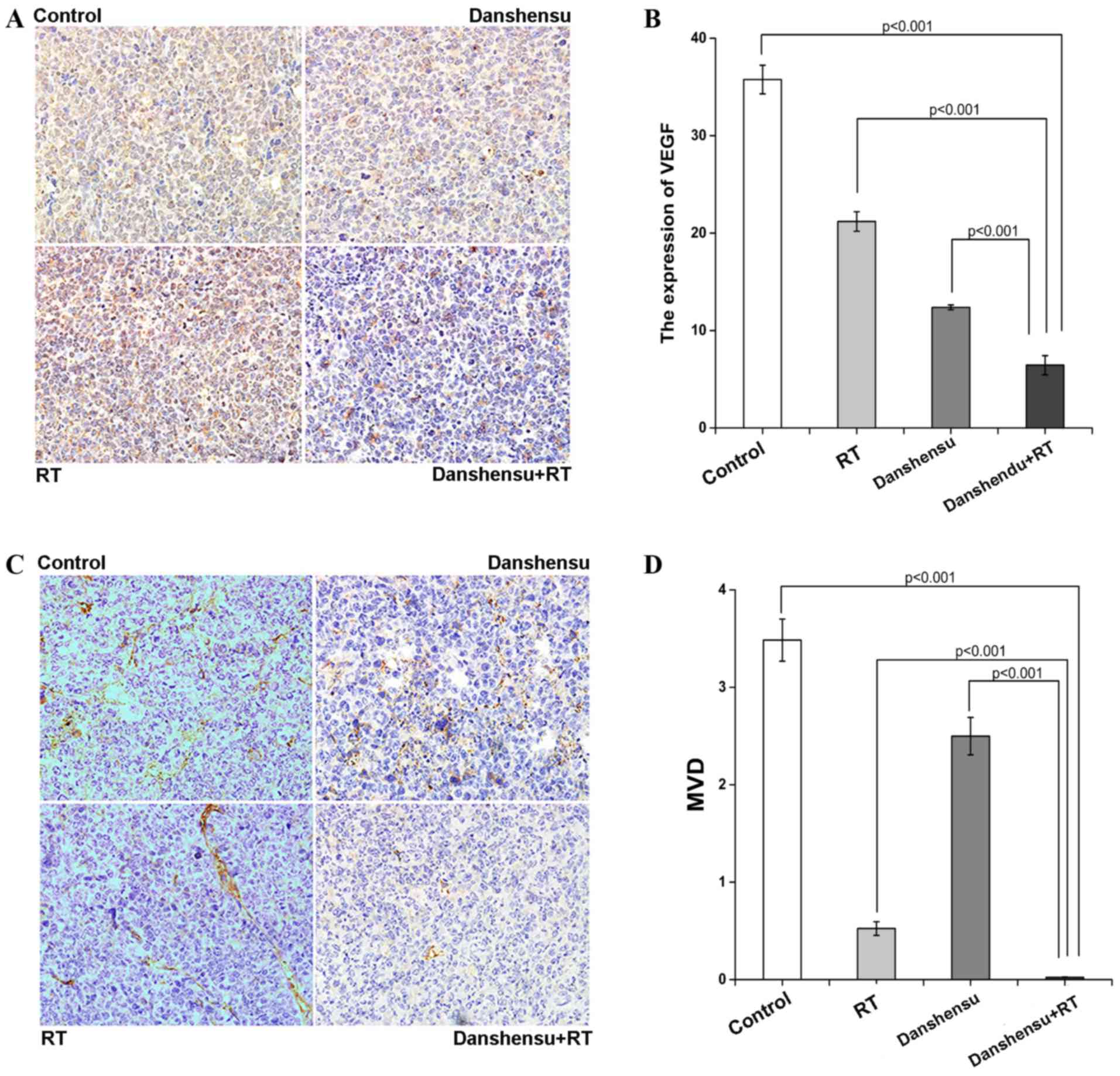
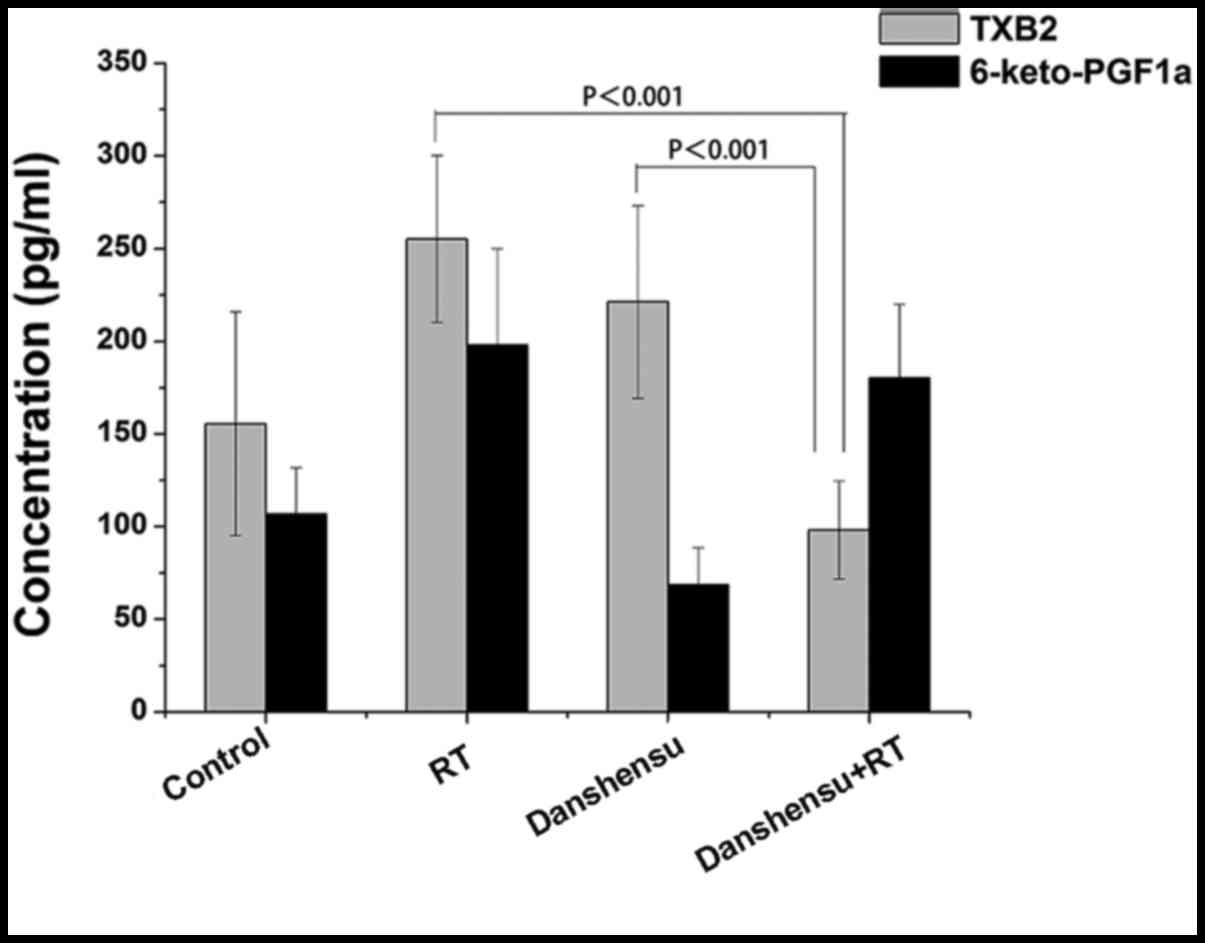
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zhao P, Zeng H,
Zou X and He J: Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2010.
Chin J Cancer Res. 26:48–58. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tyldesley S, Boyd C, Schulze K, Walker H
and Mackillop WJ: Estimating the need for radiotherapy for lung
cancer: An evidence-based, epidemiologic approach. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 49:973–985. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jain RK: Normalizing tumor
microenvironment to treat cancer: Bench to bedside to biomarkers. J
Clin Oncol. 31:2205–2218. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vaupel P: Tumor microenvironmental
physiology and its implications for radiation oncology. Semin
Radiat Oncol. 14:198–206. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Winkler F, Kozin SV, Tong RT, Chae SS,
Booth MF, Garkavtsev I, Xu L, Hicklin DJ, Fukumura D, di Tomaso E,
et al: Kinetics of vascular normalization by VEGFR2 blockade
governs brain tumor response to radiation: Role of oxygenation,
angiopoietin-1, and matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Cell.
6:553–563. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Meng MB, Jiang XD, Deng L, Na FF, He JZ,
Xue JX, Guo WH, Wen QL, Lan J, Mo XM, et al: Enhanced radioresponse
with a novel recombinant human endostatin protein via tumor
vasculature remodeling: Experimental and clinical evidence.
Radiother Oncol. 106:130–137. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dey N, De P and Brian LJ: Evading
anti-angiogenic therapy: Resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy in
solid tumors. Am J Transl Res. 7:1675–1698. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen SJ and Ren JL: Identification of a
potential anticancer target of danshensu by inverse docking. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:111–116. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang RX, Huang SY, Yan FF, Lu XT, Xing YF,
Liu Y, Liu YF and Zhao YX: Danshensu protects vascular endothelia
in a rat model of hyperhomocysteinemia. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
31:1395–1400. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang N, Zou H, Jin L, Wang J, Zhong MF,
Huang P, Gu BQ, Mao SL, Zhang C and Chen H: Biphasic effects of
sodium danshensu on vessel function in isolated rat aorta. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 31:421–428. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ding M, Ye TX, Zhao GR, Yuan YJ and Guo
ZX: Aqueous extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza attenuates increased
endothelial permeability induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
Int Immunopharmacol. 5:1641–1651. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang LJ, Chen L, Lu Y, Wu JM, Xu B, Sun
ZG, Zheng SZ and Wang AY: Danshensu has anti-tumor activity in
B16F10 melanoma by inhibiting angiogenesis and tumor cell invasion.
Eur J Pharmacol. 643:195–201. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu T, Wei G, Xi M, Yan J, Wu X, Wang Y,
Zhu Y, Wang C and Wen A: Synergistic cardioprotective effects of
Danshensu and hydroxysafflor yellow A against myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury are mediated through the Akt/Nrf2/HO-1
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 38:83–94. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen YC, Cao WW, Cao Y, Zhang L, Chang BB,
Yang WL and Liu XQ: Using neural networks to determine the
contribution of danshensu to its multiple cardiovascular activities
in acute myocardial infarction rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 138:126–134.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gu MJ and Kwon KW: Carbonic anhydrase IX
expression is associated with favorable prognostic factors in small
intestinal carcinoma. J Histochem Cytochem. 62:205–210. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Akudugu JM and Slabbert JP: Modulation of
radiosensitivity in Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts by cisplatin.
Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 86:257–263. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang X, Yang H, Gu K, Chen J, Rui M and
Jiang GL: In vitro and in vivo study of a nanoliposomal cisplatin
as a radiosensitizer. Int J Nanomedicine. 6:437–444. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yoshimura M, Itasaka S, Harada H and
Hiraoka M: Microenvironment and radiation therapy. Biomed Res Int.
2013:6853082013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kizaka-Kondoh S, Tanaka S, Harada H and
Hiraoka M: The HIF-1-active microenvironment: An environmental
target for cancer therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 61:623–632. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Peng F, Xu Z, Wang J, Chen Y, Li Q, Zuo Y,
Chen J, Hu X, Zhou Q, Wang Y, et al: Recombinant human endostatin
normalizes tumor vasculature and enhances radiation response in
xenografted human nasopharyngeal carcinoma models. PLoS One.
7:e346462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fukumura D and Jain RK: Tumor
microvasculature and microenvironment: Targets for
anti-angiogenesis and normalization. Microvasc Res. 74:72–84. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kobayashi H and Lin PC: Antiangiogenic and
radiotherapy for cancer treatment. Histol Histopathol.
21:1125–1134. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Han JY, Fan JY, Horie Y, Miura S, Cui DH,
Ishii H, Hibi T, Tsuneki H and Kimura I: Ameliorating effects of
compounds derived from Salvia miltiorrhiza root extract on
microcirculatory disturbance and target organ injury by ischemia
and reperfusion. Pharmacol Ther. 117:280–295. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lei XL and Chiou GC: Cardiovascular
pharmacology of Panax notoginseng (Burk) F.H. Chen and Salvia
miltiorrhiza. Am J Chin Med. 14:145–152. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu L, Qiao H, Li Y and Li L: Protective
roles of puerarin and Danshensu on acute ischemic myocardial injury
in rats. Phytomedicine. 14:652–658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sugiyama A, Zhu BM, Takahara A, Satoh Y
and Hashimoto K: Cardiac effects of salvia miltiorrhiza/dalbergia
odorifera mixture, an intravenously applicable Chinese medicine
widely used for patients with ischemic heart disease in China. Circ
J. 66:182–184. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jin UH, Kang SK, Suh SJ, Hong SY, Park SD,
Kim DW, Chang HW, Son JK, Lee SH, Son KH and Kim CH: Inhibitory
effect of Salvia miltiorrhia BGE on matrix metalloproteinase-9
activity and migration of TNF-alpha-induced human aortic smooth
muscle cells. Vascul Pharmacol. 44:345–353. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tian XM, Wang R, Zhang BK, Wang CL, Guo H
and Zhang SJ: Impact of Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharide and
Danshensu on vascular endothelial growth factor in the process of
retinal neovascularization of rabbit. Int J Ophthalmol. 6:59–61.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cheng F, Wang X, Zhong D, Sun L, Wang Q
and Liu C: Significance of detection of serum carbonic anhydrase IX
in the diagnosis of lung cancer. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 18:29–33.
2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen FH, Chiang CS, Wang CC, Tsai CS, Jung
SM, Lee CC, McBride WH and Hong JH: Radiotherapy decreases vascular
density and causes hypoxia with macrophage aggregation in TRAMP-C1
prostate tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 15:1721–1729. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sundov Z, Tomic S, Alfirevic S, Sundov A,
Capkun V, Nincevic Z, Nincevic J, Kunac N, Kontic M, Poljak N and
Druzijanic N: Prognostic value of MVD, LVD and vascular invasion in
lymph node-negative colon cancer. Hepatogastroenterology.
60:432–438. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li J, Wang S, Yang X, Pang G, Zheng H,
Shen B, Li G, Shi D, Wang J, Feng L, et al: Effect of sulfated
polysaccharides from Laminaria japonica on vascular endothelial
cells in psychological stress rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 151:601–608.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang ZJ, Yu YH, Chen J and Zhao YT:
Correlation between oligohydramnios and abnormal expressions of
TXA2, PGI2 and TXA2R in the umbilical arterial blood and placenta.
Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 29:1917–1918. 2009.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang FH: Effects of acupuncture at 7-9 am
and 3-5 pm on plasma thromboxane and prostaglandin in patients with
ischemic cerebrovascular disease. J Tradit Chin Med. 30:9–12. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu HJ, Ma JW, Qiao ZY and Xu B: Study of
molecular mechanism of Prostaglandin E1 in inhibiting coronary
heart disease. Mol Biol Rep. 40:6701–6708. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|