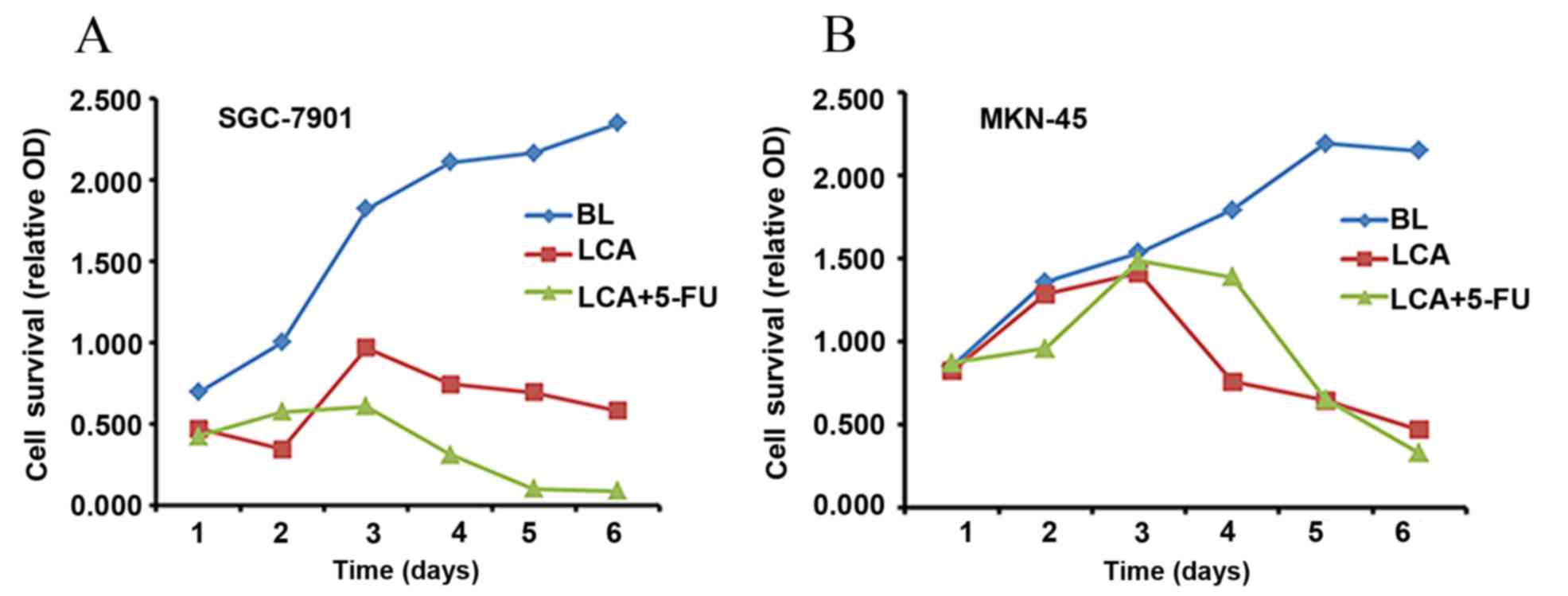
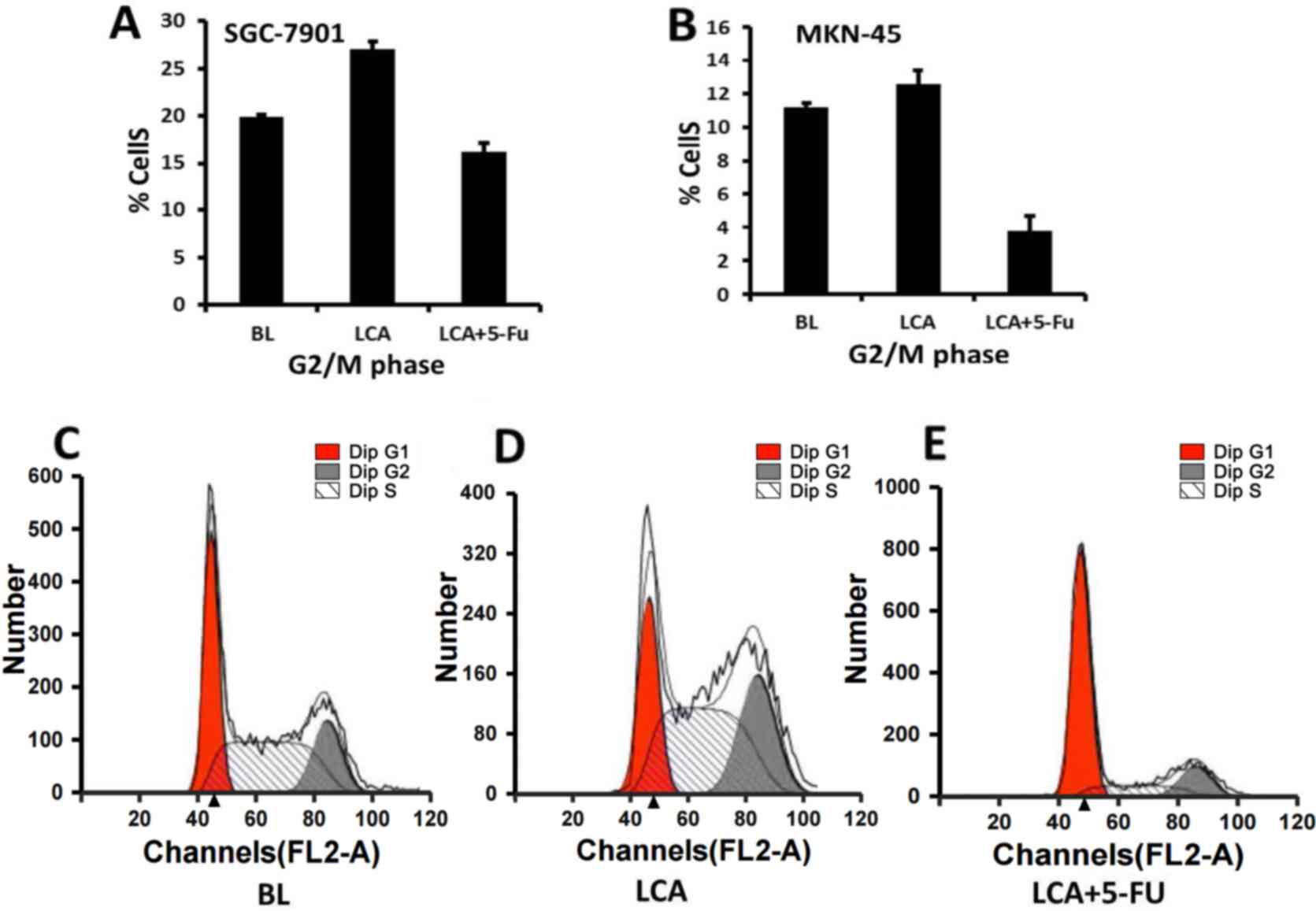
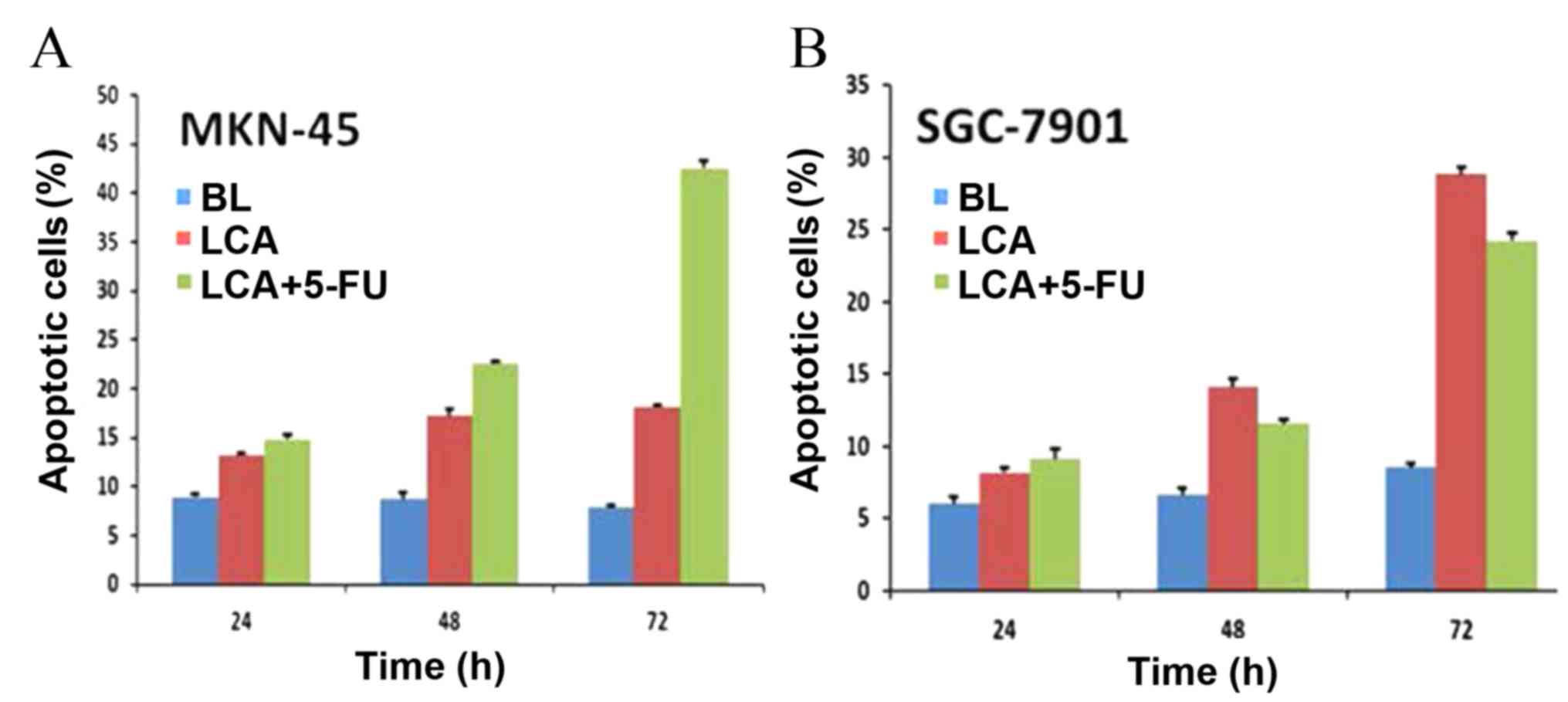
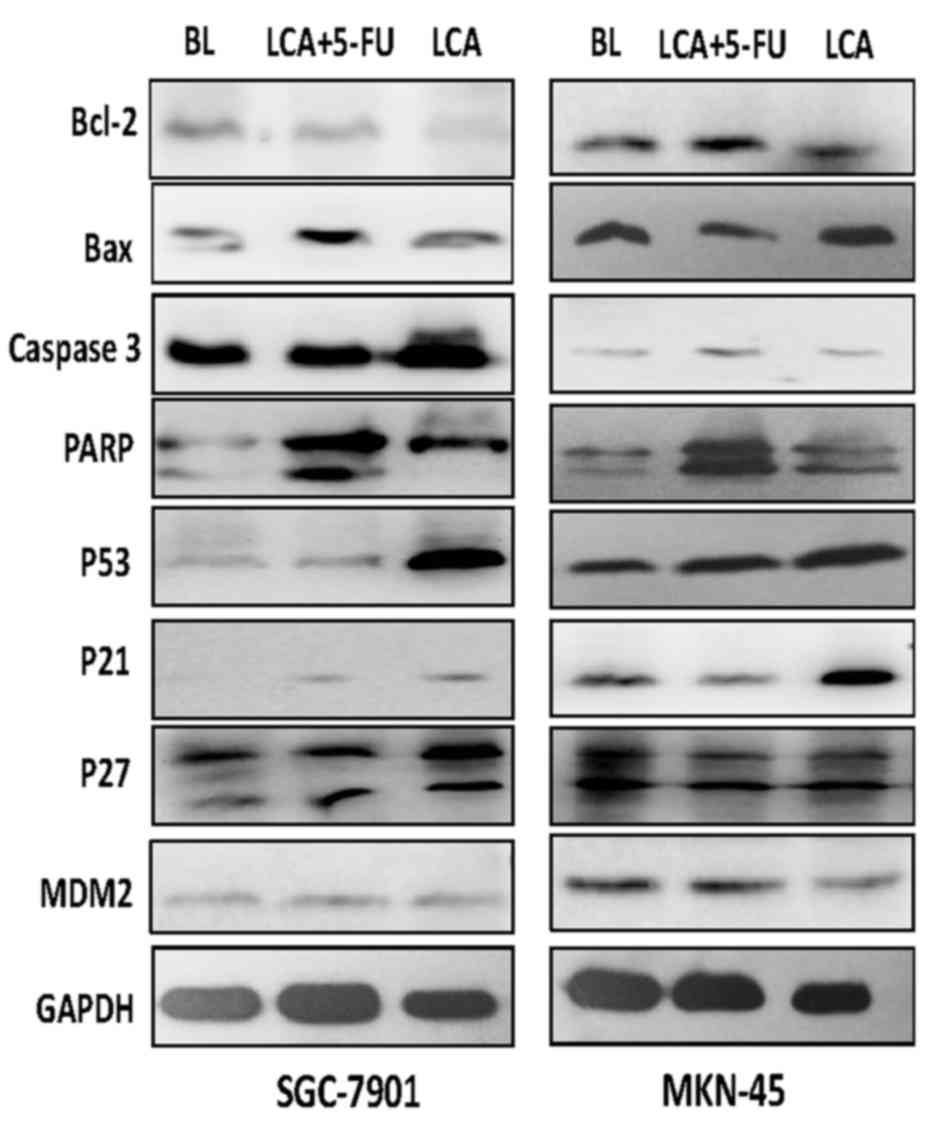
|
1
|
Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A,
Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, Lordick F, Ohtsu A, Omuro Y, Satoh T,
et al: Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus
chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric
or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): A phase 3,
open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 376:687–697. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kamangar F, Dores GM and Anderson WF:
Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five
continents: Defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in
different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol.
24:2137–2150. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zare A, Mahmoodi M, Mohammad K, Zeraati H,
Hosseini M and Naieni K Holakouie: Factors affecting the survival
of patients with gastric cancer undergone surgery at iran cancer
institute: Univariate and multivariate analyses. Iran J Public
Health. 43:800–808. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schwartz GK, Winter K, Minsky BD, Crane C,
Thomson PJ, Anne P, Gross H, Willett C and Kelsen D: Randomized
phase II trial evaluating two paclitaxel and cisplatin-containing
chemoradiation regimens as adjuvant therapy in resected gastric
cancer (RTOG-0114). J Clin Oncol. 27:1956–1962. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zan X, Cui F, Li Y, Yang Y, Wu D, Sun W
and Ping L: Hericium erinaceus polysaccharide-protein HEG-5
inhibits SGC-7901 cell growth via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
Int J Biol Macromol. 76:242–253. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rasul A, Yu B, Khan M, Zhang K, Iqbal F,
Ma T and Yang H: Magnolol, a natural compound, induces apoptosis of
SGC-7901 human gastric adenocarcinoma cells via the mitochondrial
and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Int J Oncol. 40:1153–1161.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee Y: Induction of apoptosis by
S-allylmercapto-L-cysteine, a biotransformed garlic derivative, on
a human gastric cancer cell line. Int J Mol Med. 21:765–770.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ma K, Liu Y, Zhu Q, Liu CH, Duan JL, Tan
BK and Zhu YZ: H2S donor, S-propargyl-cysteine, increases CSE in
SGC-7901 and cancer-induced mice: Evidence for a novel anti-cancer
effect of endogenous H2S? PLoS One. 6:e205252011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma J, Liu C, Chen Y, Jiang J and Qin Z:
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of the Ganoderma applanatum
extracts induces apoptosis on SGC-7901 gastric cancer cells. Cell
Biochem Funct. 29:175–182. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cuendet M, Guo J, Luo Y, Chen S, Oteham
CP, Moon RC, van Breemen RB, Marler LE and Pezzuto JM: Cancer
chemopreventive activity and metabolism of isoliquiritigenin, a
compound found in licorice. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 3:221–232.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tamir S, Eizenberg M, Somjen D, Stern N,
Shelach R, Kaye A and Vaya J: Estrogenic and antiproliferative
properties of glabridin from licorice in human breast cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 60:5704–5709. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim YH, Shin EK, Kim DH, Lee HH, Park JH
and Kim JK: Antiangiogenic effect of licochalcone A. Biochem
Pharmacol. 80:1152–1159. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee CK, Son SH, Park KK, Park JH, Lim SS,
Kim SH and Chung WY: Licochalcone A inhibits the growth of colon
carcinoma and attenuates cisplatin-induced toxicity without a loss
of chemotherapeutic efficacy in mice. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol.
103:48–54. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yo YT, Shieh GS, Hsu KF, Wu CL and Shiau
AL: Licorice and licochalcone-A induce autophagy in LNCaP prostate
cancer cells by suppression of Bcl-2 expression and the mTOR
pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 57:8266–8273. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xiao XY, Hao M, Yang XY, Ba Q, Li M, Ni
SJ, Wang LS and Du X: Licochalcone A inhibits growth of gastric
cancer cells by arresting cell cycle progression and inducing
apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 302:69–75. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Takeyoshi I, Makita F, Tanahashi Y,
Iwazaki S, Ogawa T, Tomizawa N, Nakamura S, Ishikawa H, Ohya T,
Kakinuma S, et al: A Phase II Study of Weekly Paclitaxel and
doxifluridine combination chemotherapy for advanced/recurrent
gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 31:287–291. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cai XZ, Huang WY, Qiao Y, Du SY, Chen Y,
Chen D, Yu S, Che RC, Liu N and Jiang Y: Inhibitory effects of
curcumin on gastric cancer cells: A proteomic study of molecular
targets. Phytomedicine. 20:495–505. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ye YW, Hu S, Shi YQ, Zhang XF, Zhou Y,
Zhao CL, Wang GJ, Wen JG and Zong H: Combination of the FGFR4
inhibitor PD173074 and 5-fluorouracil reduces proliferation and
promotes apoptosis in gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 30:2777–2784.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liang X, Tang J, Liang Y, Jin R and Cai X:
Suppression of autophagy by chloroquine sensitizes
5-fluorouracil-mediated cell death in gallbladder carcinoma cells.
Cell Biosci. 4:102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jiang CP, Wu BH, Wang BQ, Fu MY, Yang M,
Zhou Y and Liu F: Overexpression of ECRG4 enhances chemosensitivity
to 5-fluorouracil in the human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cell line.
Tumour Biol. 34:2269–2273. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 protein
family: Arbiters of cell survival. Science. 281:1322–1326. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fan Y, Liu C, Huang Y, Zhang J, Cai L,
Wang S, Zhang Y, Duan X and Yin Z: Dipyrithione induces cell-cycle
arrest and apoptosis in four cancer cell lines in vitro and
inhibits tumor growth in a mouse model. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol.
14:542013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fu Z, Ren L, Wei H, Lv J, Che X, Zhu Z,
Jia J, Wang L, Lin G, Lu R and Yao Z: Effects of Tyroserleutide on
phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/AKT pathway in human hepatocellular
carcinoma cell. J Drug Target. 22:146–155. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
As MN and Hosseinzadeh H: Review of
pharmacological effects of Glycyrrhiza sp. and its bioactive
compounds. Phytother Res. 22:709–724. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cho JJ, Chae JI, Yoon G, Kim KH, Cho JH,
Cho SS, Cho YS and Shim JH: Licochalcone A, a natural chalconoid
isolated from Glycyrrhiza inflata root, induces apoptosis via Sp1
and Sp1 regulatory proteins in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J
Oncol. 45:667–674. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schuhmacher C, Gretschel S, Lordick F,
Reichardt P, Hohenberger W, Eisenberger CF, Haag C, Mauer ME, Hasan
B, Welch J, et al: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy compared with surgery
alone for locally advanced cancer of the stomach and cardia:
European organisation for research and treatment of cancer
randomized trial 40954. J Clin Oncol. 28:5210–5218. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wagner AD, Grothe W, Haerting J, Kleber G,
Grothey A and Fleig WE: Chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis based on aggregate data. J Clin
Oncol. 24:2903–2909. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hallett RM, Huang C, Motazedian A, Auf der
Mauer S, Pond GR, Hassell JA, Nordon RE and Draper JS:
Treatment-induced cell cycle kinetics dictate tumor response to
chemotherapy. Oncotarget. 6:7040–7052. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Malumbres M: Cyclin-dependent kinases.
Genome Biol. 15:1222014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yadav V, Sultana S, Yadav J and Saini N:
Gatifloxacin induces S and G2-phase cell cycle arrest in pancreatic
cancer cells via p21/p27/p53. PLoS One. 7:e477962012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lin HP, Lin CY, Huo C, Hsiao PH, Su LC,
Jiang SS, Chan TM, Chang CH, Chen LT, Kung HJ, et al: Caffeic acid
phenethyl ester induced cell cycle arrest and growth inhibition in
androgen-independent prostate cancer cells via regulation of Skp2,
p53, p21Cip1 and p27Kip1. Oncotarget. 6:6684–6707. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Datto MB, Li Y, Panus JF, Howe DJ, Xiong Y
and Wang XF: Transforming growth factor beta induces the
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 through a p53-independent
mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:5545–5549. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Asghar U, Witkiewicz AK, Turner NC and
Knudsen ES: The history and future of targeting cyclin-dependent
kinases in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 14:130–146. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Park MT and Lee SJ: Cell Cycle and Cancer.
J Biochem Mol Biol. 36:60–65. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nag S, Zhang X, Srivenugopal KS, Wang MH,
Wang W and Zhang R: Targeting MDM2-p53 interaction for cancer
therapy: Are we there Yet? Curr Med Chem. 21:553–574. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 apoptotic
switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene. 26:1324–1337.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zimmermann KC, Bonzon C and Green DR: The
machinery of programmed cell death. Pharmacol Ther. 92:57–70. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jo EH, Kim SH, Ra JC, Kim SR, Cho SD, Jung
JW, Yang SR, Park JS, Hwang JW, Aruoma OI, et al: Chemopreventive
properties of the ethanol extract of chinese licorice
(Glycyrrhizauralensis) root: Induction of apoptosis and G1 cell
cycle arrest in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
230:239–247. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|