|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Weng D, Song B, Durfee J, Sugiyama V, Wu
Z, Koido S, Calderwood SK and Gong J: Induction of cytotoxic T
lymphocytes against ovarian cancer-initiating cells. Int J Cancer.
129:1990–2001. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Takahara A, Koido S, Ito M, Nagasaki E,
Sagawa Y, Iwamoto T, Komita H, Ochi T, Fujiwara H, Yasukawa M, et
al: Gemcitabine enhances Wilms' tumor gene WT1 expression and
sensitizes human pancreatic cancer cells with
WT1-specificT-cell-mediated antitumor immune response. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 60:1289–1297. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Weng D, Song B, Koido S, Calderwood SK and
Gong J: Immunotherapy of radioresistant mammary tumors with early
metastasis using molecular chaperone vaccines combined with
ionizing radiation. J Immunol. 191:755–763. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wagner P, Koch M, Nummer D, Palm S,
Galindo L, Autenrieth D, Rahbari N, Schmitz-Winnenthal FH,
Schirrmacher V, Büchler MW, et al: Detection and functional
analysis of tumor infiltrating T-lymphocytes (TIL) in liver
metastases from colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 15:2310–2317.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pagès F, Berger A, Camus M, Sanchez-Cabo
F, Costes A, Molidor R, Mlecnik B, Kirilovsky A, Nilsson M, Damotte
D, et al: Effector memory T cells, early metastasis, and survival
in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 353:2654–2666. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Masopust D, Vezys V, Marzo AL and
Lefrançois L: Preferential localization of effector memory cells in
nonlymphoid tissue. Science. 291:2413–2417. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vezys V, Yates A, Casey KA, Lanier G,
Ahmed R, Antia R and Masopust D: Memory CD8 T-cell compartment
grows in size with immunological experience. Nature. 457:196–199.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Abbas AK, Murphy KM and Sher A: Functional
diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 383:787–793. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Numasaki M, Watanabe M, Suzuki T,
Takahashi H, Nakamura A, McAllister F, Hishinuma T, Goto J, Lotze
MT, Kolls JK and Sasaki H: IL-17 enhances the net angiogenic
activity and in vivo growth of human non-small cell lung cancer in
SCID mice through promoting CXCR-2-dependent angiogenesis. J
Immunol. 175:6177–6189. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He D, Li H, Li H, Yusuf N, Elmets CA, Li
J, Mountz JD and Xu H: IL-17 promotes tumor development through the
induction of tumor promoting microenvironments at tumor sites and
myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Immunol. 184:2281–2288. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Beauchemin N and Arabzadeh A:
Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecules (CEACAMs)
in cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
32:643–671. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jantscheff P, Terracciano L, Lowy A,
Glatz-Krieger K, Grunert F, Micheel B, Brümmer J, Laffer U, Metzger
U, Herrmann R and Rochlitz C: Expression of CEACAM6 in resectable
colorectal cancer: A factor of independent prognostic significance.
J Clin Oncol. 21:3638–3646. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cheuk AT, Mufti GJ and Guinn BA: Role of
4-1BB:4-1BB ligand in cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Gene Ther.
11:215–226. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tan JT, Whitmire JK, Ahmed R, Pearson TC
and Larsen CP: 4-1BB ligand, a member of the TNF family, is
important for the generation of antiviral CD8 T cell responses. J
Immunol. 163:4859–4868. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rabu C, Quéméner A, Jacques Y,
Echasserieau K, Vusio P and Lang F: roduction of recombinant human
trimetric CD137L (4-1BBL). Cross-linking is essential to its T cell
co-stimulation activity. J Biol Chem. 280:41472–41481. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jin C, Liu Y, Zhu J, Xia T, Zhang B, Fei
Y, Ma B, Ye J and Chen W: Recombinant Salmonella-based CEACAM6 and
4-1BBL vaccine enhances T-cell immunity and inhibits the
development of colorectal cancer in rats: In vivo effects of
vaccine containing 4-1BBL and CEACAM6. Oncol Rep. 33:2837–2844.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kyriakos M: The President's cancer, the
Dukes classification, and confusion. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
109:1063–1066. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kawai H, Ishii A, Washiya K, Konno T, Kon
H, Yamaya C, Ono I, Minamiya Y and Ogawa J: Estrogen receptor alpha
and beta are prognostic factors in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 11:5084–5089. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Maskens AP: Histogenesis and growth
pattern of 1, 2-dimethylhydrazine-induced rat colon adenocarcinoma.
Cancer Res. 36:1585–1592. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Janeway CA Jr: The T cell receptor as a
multicomponent signaling machine: CD4/CD8 co-receptors and CD45 in
T cell activation. Ann Rev Immunol. 10:645–674. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Woodland DL and Kohlmeier JE: Migration,
maintenance and recall of memory T cells in peripheral tissues. Nat
Rev Immunol. 9:153–161. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wakatsuki K, Sho M, Yamato I, Takayama T,
Matsumoto S, Tanaka T, Migita K, Ito M, Hotta K and Nakajima Y:
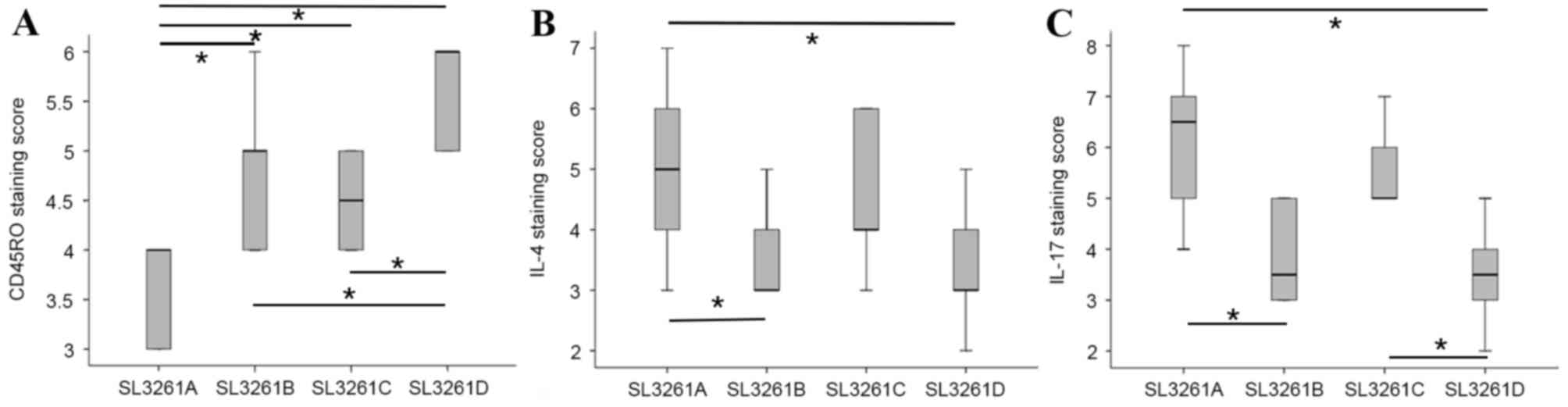
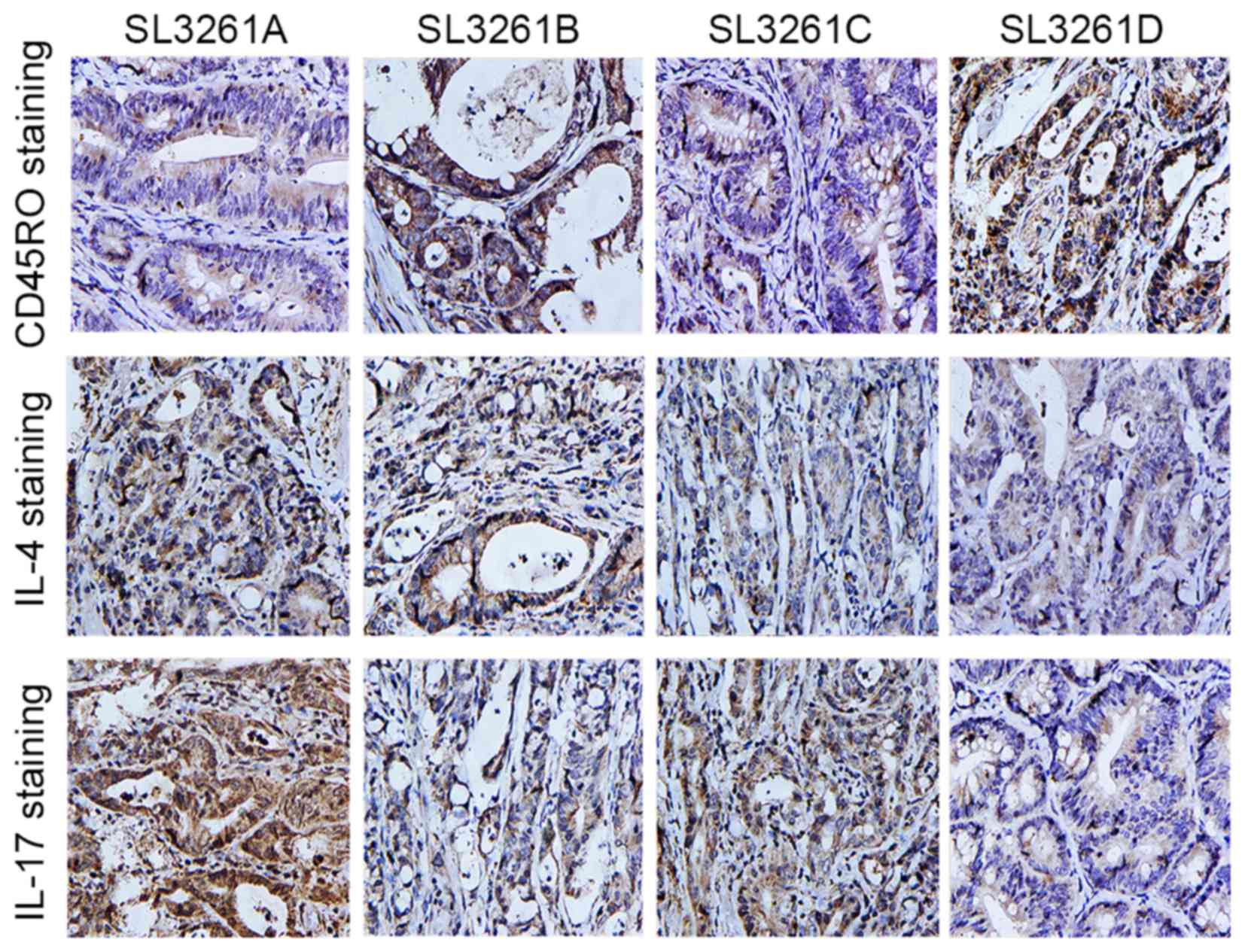
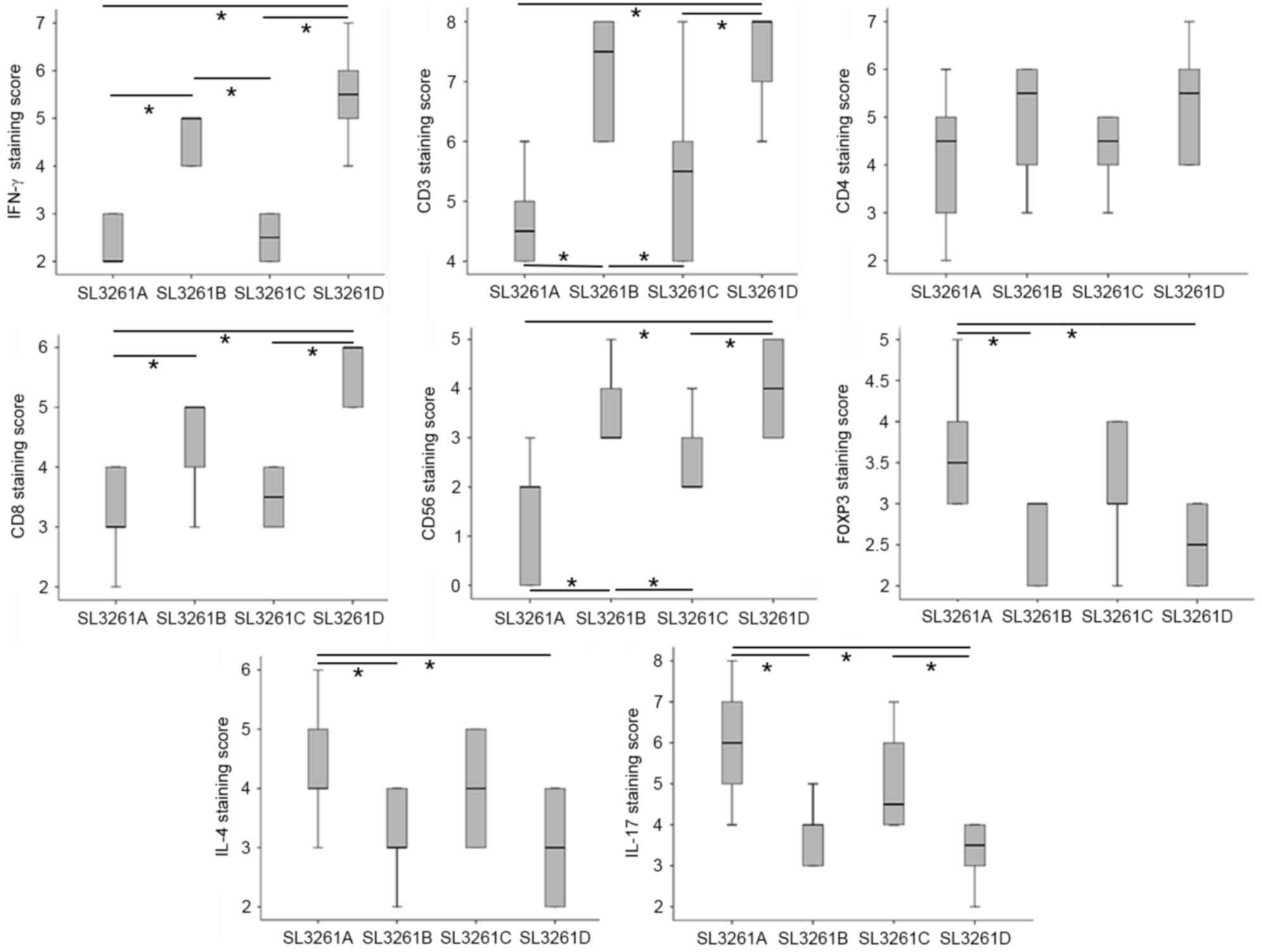
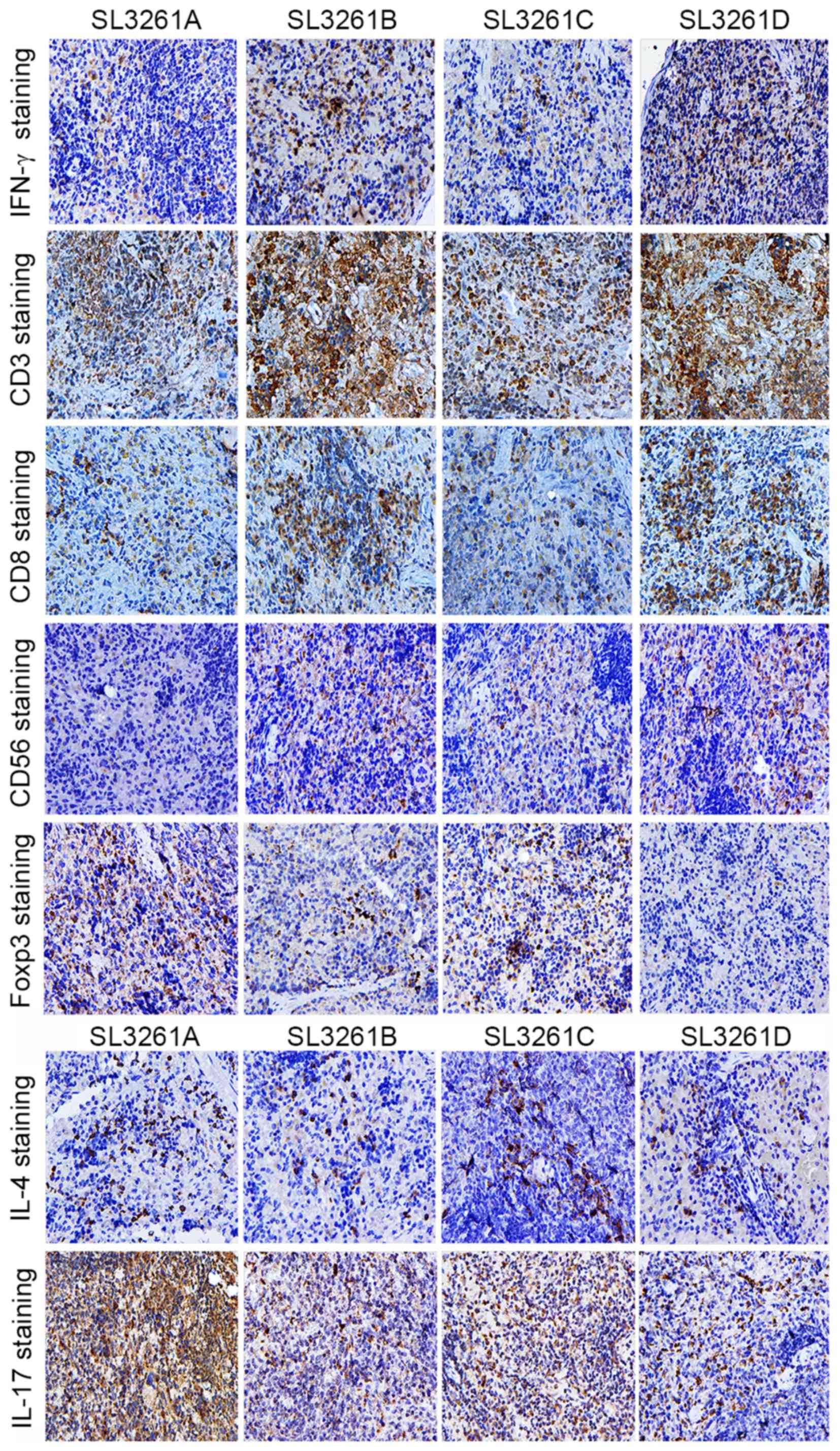
Clinical impact of tumor-infiltrating CD45RO+ memory T
cells on human gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 29:1756–1762.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hori S, Nomura T and Sakaguchi S: Control
of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3.
Science. 299:1057–1061. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hiraoka N, Onozato K, Kosuge T and
Hirohashi S: Prevalence of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells increases
during the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its
premalignant lesions. Clin Cancer Res. 12:5423–5434. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kobayashi N, Hiraoka N, Yamagami W, Ojima
H, Kanai Y, Kosuge T, Nakajima A and Hirohashi S: FOXP3+ regulatory
T cells affect the development and progression of
hepatocarcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 13:902–911. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|