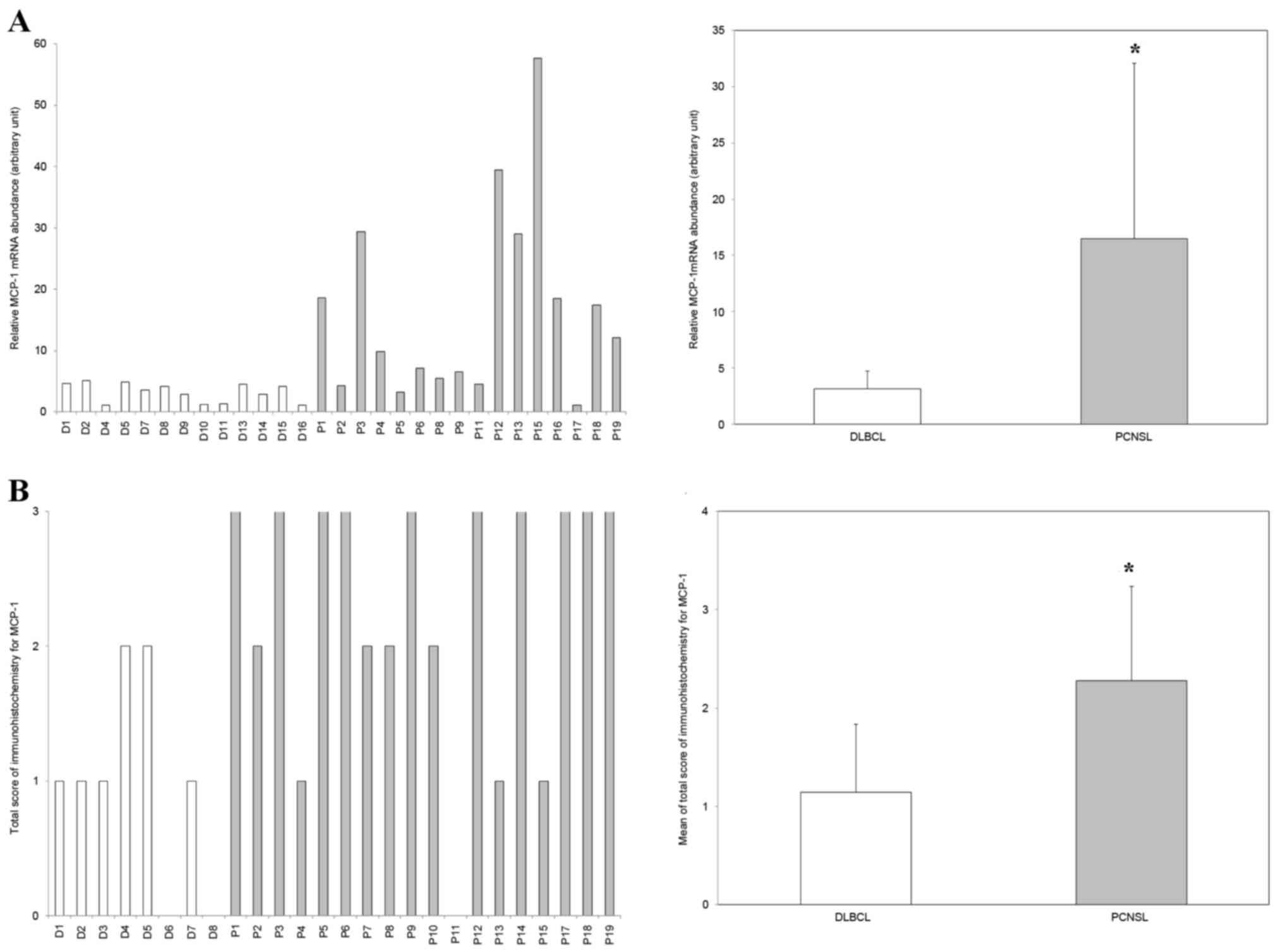
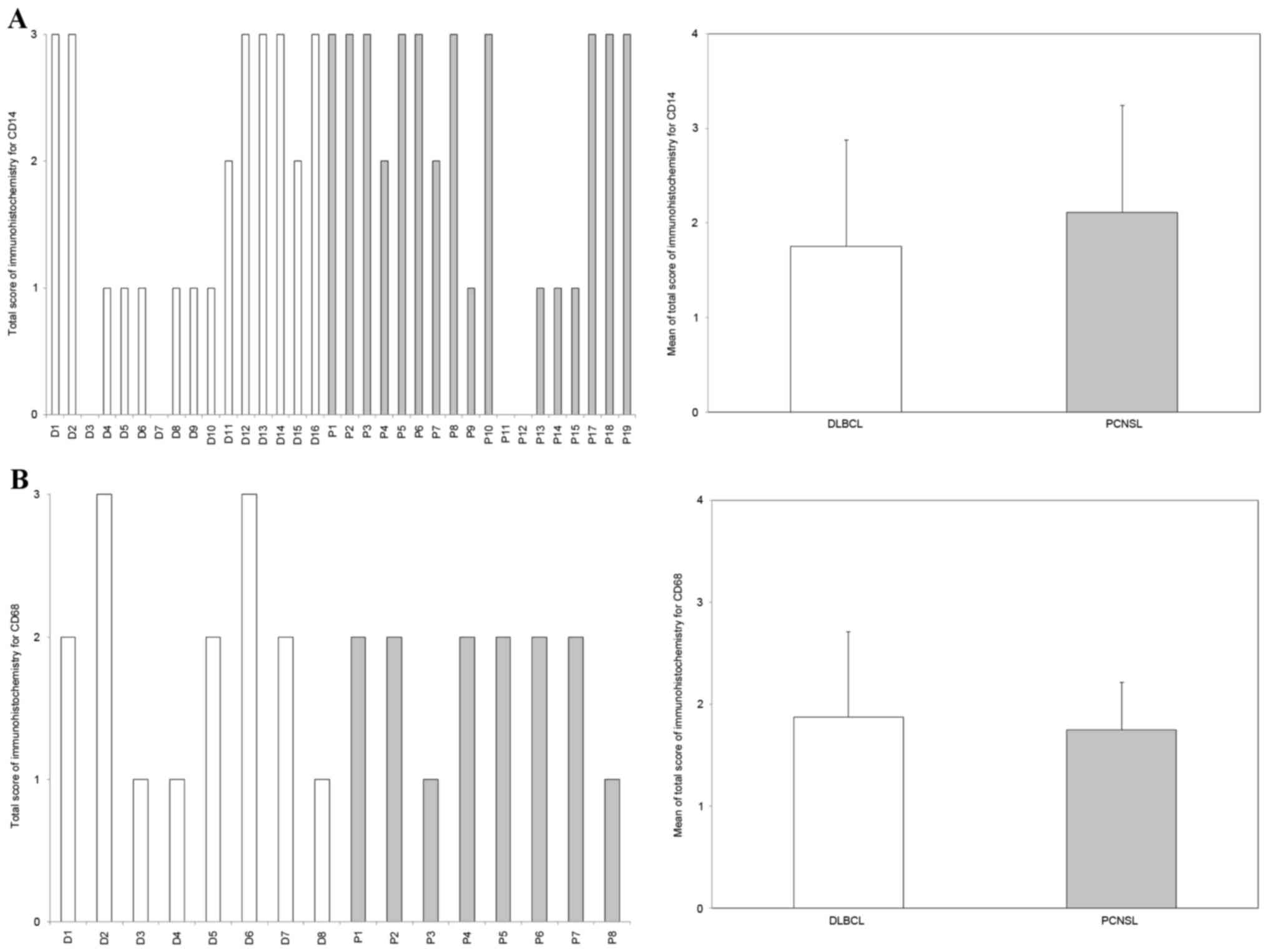
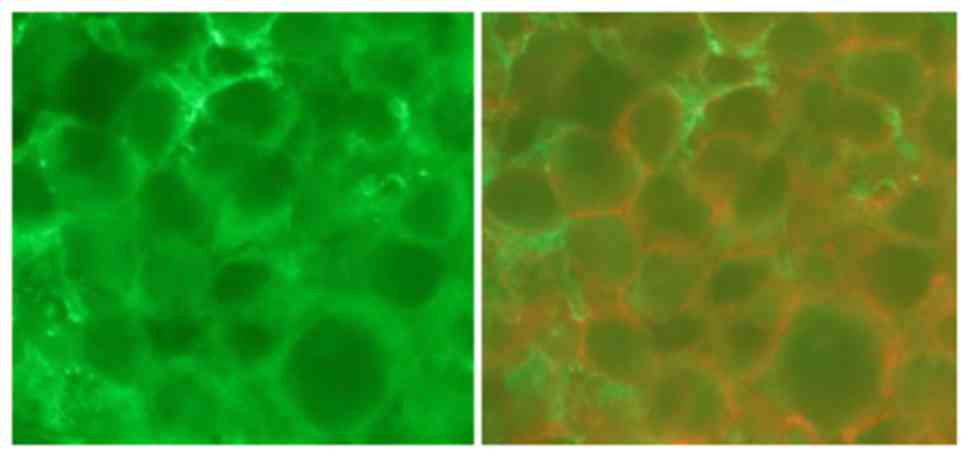
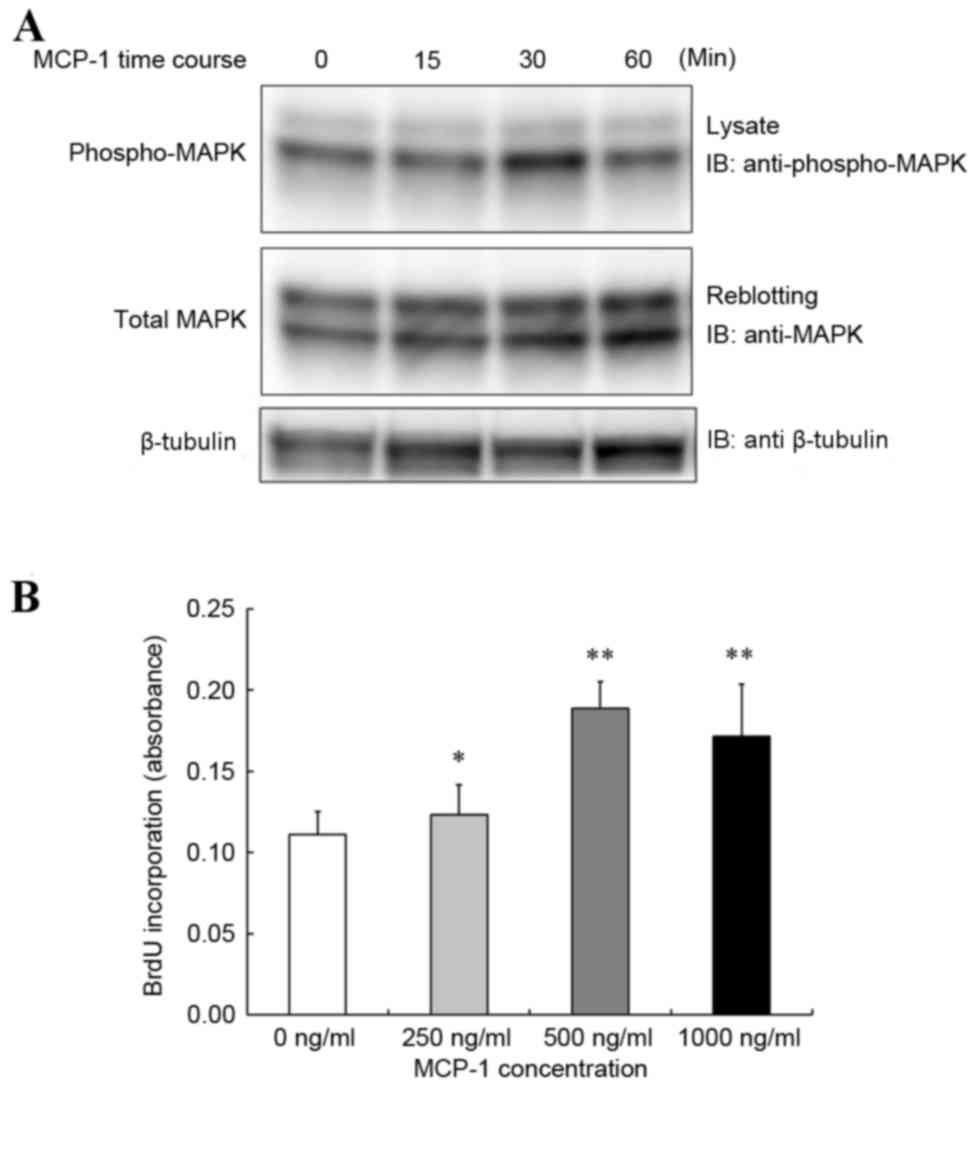
|
1
|
Olson JE, Janney CA, Rao RD, Cerhan JR,
Kurtin PJ, Schiff D, Kaplan RS and O'Neill BP: The continuing
increase in the incidence of primary central nervous system
non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A surveillance, epidemiology, and end results
analysis. Cancer. 95:1504–1510. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Prodduturi P and Bierman PJ: Current and
emerging pharmacotherapies for primary CNS lymphoma. Clin Med
Insights Oncol. 6:219–231. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bingle L, Brown NJ and Lewis C: The role
of tumour-associated macrophages in tumour progression:
Implications for new anticancer therapies. J Pathol. 196:254–265.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, Allavena
P and Sica A: Macrophage polarization: Tumor-associated macrophages
as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends
Immunol. 23:549–555. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pollard JW: Tumour-educated macrophages
promote tumour progression and metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:71–78.
2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Komohara Y, Jinushi M and Takeya M:
Clinical significance of macrophage heterogeneity in human
malignant tumors. Cancer Sci. 105:1–8. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ding P, Wang W, Wang J, Yang Z and Xue L:
Expression of tumor-associated macrophage in progression of human
glioma. Cell Biochem Biophys. 70:1625–1631. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Komohara Y, Horlad H, Ohnishi K, Fujiwara
Y, Bai B, Nakagawa T, Suzu S, Nakamura H, Kuratsu J and Takeya M:
Importance of direct macrophage-tumor cell interaction on
progression of human glioma. Cancer Sci. 103:2165–2172. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Komohara Y, Hasita H, Ohnishi K, Fujiwara
Y, Suzu S, Eto M and Takeya M: Macrophage infiltration and its
prognostic relevance in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer
Sci. 102:1424–1431. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Komohara Y, Niino D, Saito Y, Ohnishi K,
Horlad H, Ohshima K and Takeya M: Clinical significance of
CD163+ tumor-associated macrophages in patients with
adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Cancer Sci. 104:945–951. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hasselblom S, Hansson U, Sigurdardottir M,
Nilsson-Ehle H, Ridell B and Andersson PO: Expression of CD68+
tumor-associated macrophages in patients with diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma and its relation to prognosis. Pathol Int. 58:529–532.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cai QC, Liao H, Lin SX, Xia Y, Wang XX,
Gao Y, Lin ZX, Lu JB and Huang HQ: High expression of
tumor-infiltrating macrophages correlates with poor prognosis in
patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Med Oncol.
29:2317–2322. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wada N, Zaki MA, Hori Y, Hashimoto K,
Tsukaguchi M, Tatsumi Y, Ishikawa J, Tominaga N, Sakoda H, Take H,
et al: Tumour-associated macrophages in diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma: A study of the osaka lymphoma study group.
Histopathology. 60:313–319. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Komohara Y, Horlad H, Ohnishi K, Ohta K,
Makino K, Hondo H, Yamanaka R, Kajiwara K, Saito T, Kuratsu J and
Takeya M: M2 macrophage/microglil cells induce activation of Stat3
in primary central nervous system lymphoma. J Clin Exp Hematop.
51:93–99. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sasayama T, Tanaka K, Mizowaki T,
Nagashima H, Nakamizo S, Tanaka H, Nishihara M, Mizukawa K, Hirose
T, Itoh T and Kohmura E: Tumor-associated macrophages associate
with cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-10 and survival in primary
central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL). Brain Pathol. 26:479–487.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiménez-Sainz MC, Fast B, Mayor F Jr and
Aragay AM: Signaling pathways for monocyte chemoattractant protein
1-mediated extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Mol
Pharmacol. 64:773–782. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Johnson Z, Power CA, Weiss C, Rintelen F,
Ji H, Ruckle T, Camps M, Wells TN, Schwarz MK, Proudfoot AE and
Rommel C: Chemokine inhibition - why, when, where, which and how?
Biochem Soc Trans. 32:366–377. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mellado M, Rodríguez-Frade JM, Aragay A,
Del Real G, Martín AM, Vila-Coro AJ, Serrano A, Mayor F Jr and
Martínez-A C: The chemokine monocyte chemotactic protein 1 triggers
Janus kinase 2 activation and tyrosine phosphorylation of the CCR2B
receptor. J Immunol. 161:805–813. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Balkwill F and Mantovani A: Inflammation
and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet. 357:539–545. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Conti I and Rollins BJ: CCL2 (monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1) and cancer. Semin Cancer Biol.
14:149–154. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fujiwara T, Fukushi J, Yamamoto S,
Matsumoto Y, Setsu N, Oda Y, Yamada H, Okada S, Watari K, Ono M, et
al: Macrophage infiltration predicts a poor prognosis for human
ewing sarcoma. Am J Pathol. 179:1157–1170. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Loberg RD, Day LL, Harwood J, Ying C, St
John LN, Giles R, Neeley CK and Pienta KJ: CCL2 is a potent
regulator of prostate cancer cell migration and proliferation.
Neoplasia. 8:578–586. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kitai R, Ishisaka K, Sato K, Sakuma T,
Yamauchi T, Imamura Y, Matsumoto H and Kubota T: Primary central
nervous system lymphoma secretes monocyte chemoattractant protein
1. Med Mol Morphol. 40:18–22. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Steidl C, Lee T, Shah SP, Farinha P, Han
G, Nayar T, Delaney A, Jones SJ, Iqbal J, Weisenburger DD, et al:
Tumor-associated macrophages and survival in classic Hodgkin's
lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 362:875–885. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Takayama H, Nishimura K, Tsujimura A,
Nakai Y, Nakayama M, Aozasa K, Okuyama A and Nonomura N: Increased
infiltration of tumor associated macrophages is associated with
poor prognosis of bladder carcinoma in situ after intravesical
bacillus Calmette-Guerin instillation. J Urol. 181:1894–1900. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tan KL, Scott DW, Hong F, Kahl BS, Fisher
RI, Bartlett NL, Advani RH, Buckstein R, Rimsza LM, Connors JM, et
al: Tumor-associated macrophages predict inferior outcomes in
classic Hodgkin lymphoma: A correlative study from the E2496
Intergroup trial. Blood. 120:3280–3287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yao H, Peng F, Dhillon N, Callen S,
Bokhari S, Stehno-Bittel L, Ahmad OS, Wang JQ and Buch S:
Involvement of TRPC channels in CCL2-mediated neuroprotection
against tat toxicity. J Neurosci. 29:1657–1669. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|