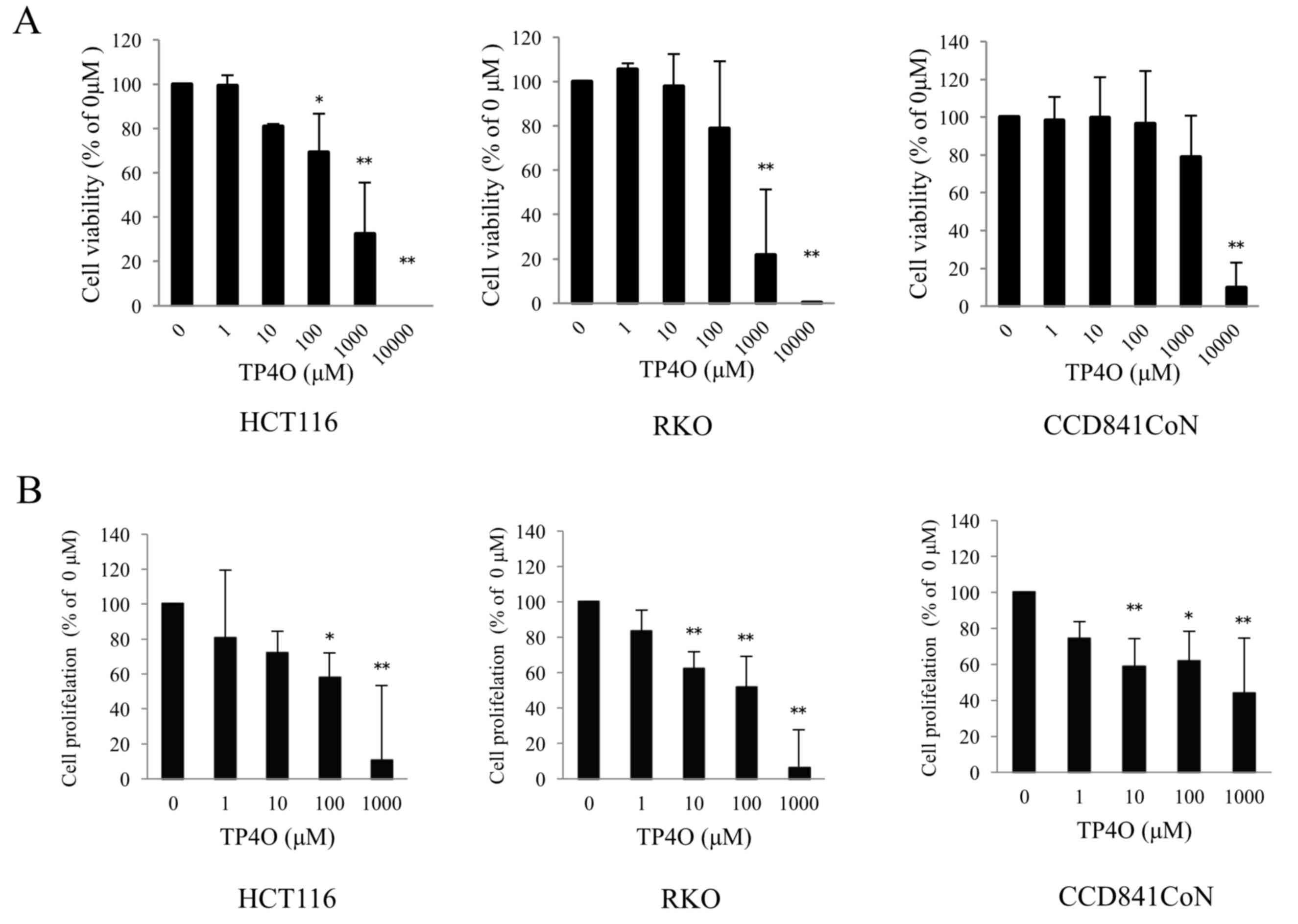
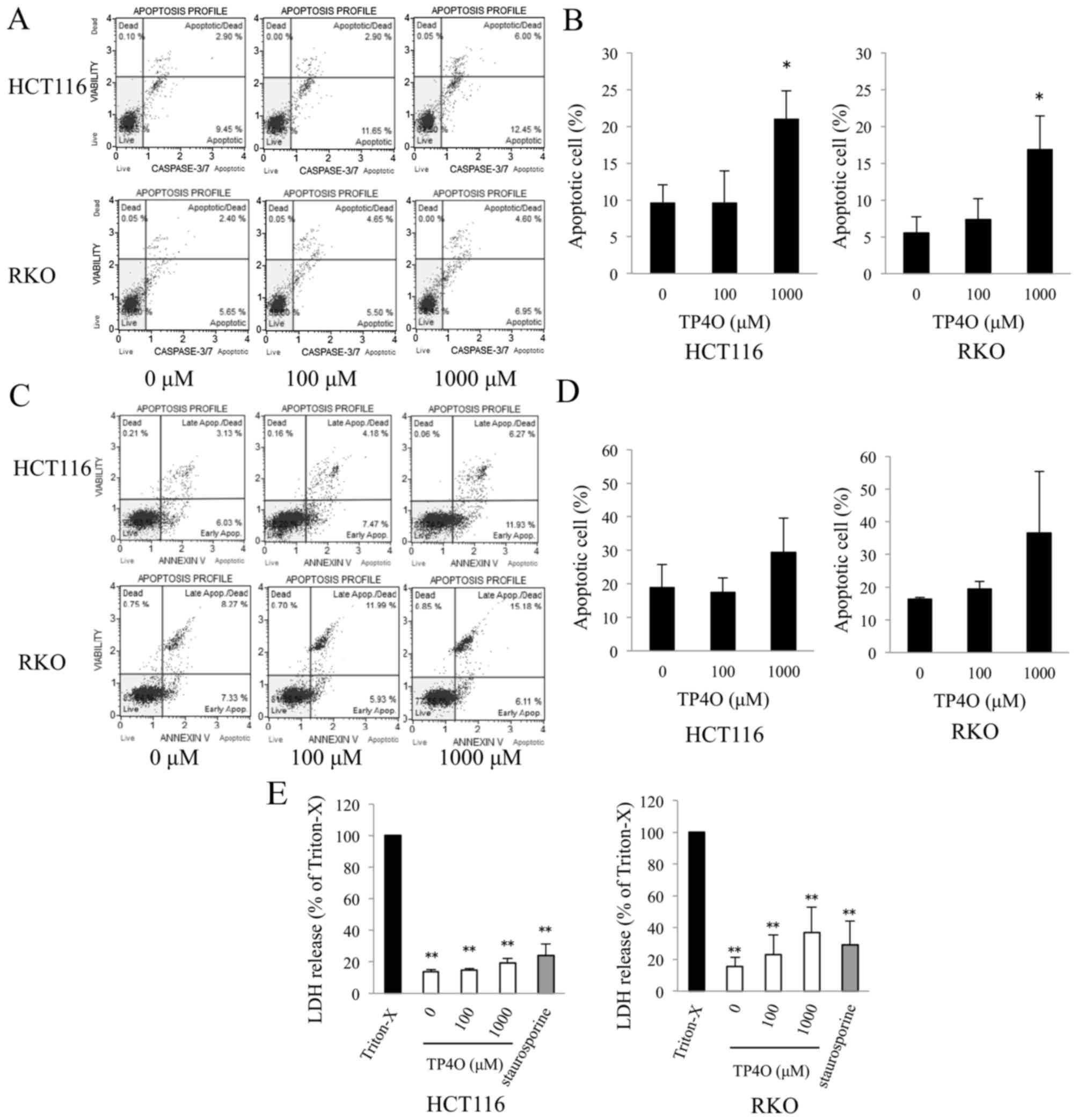
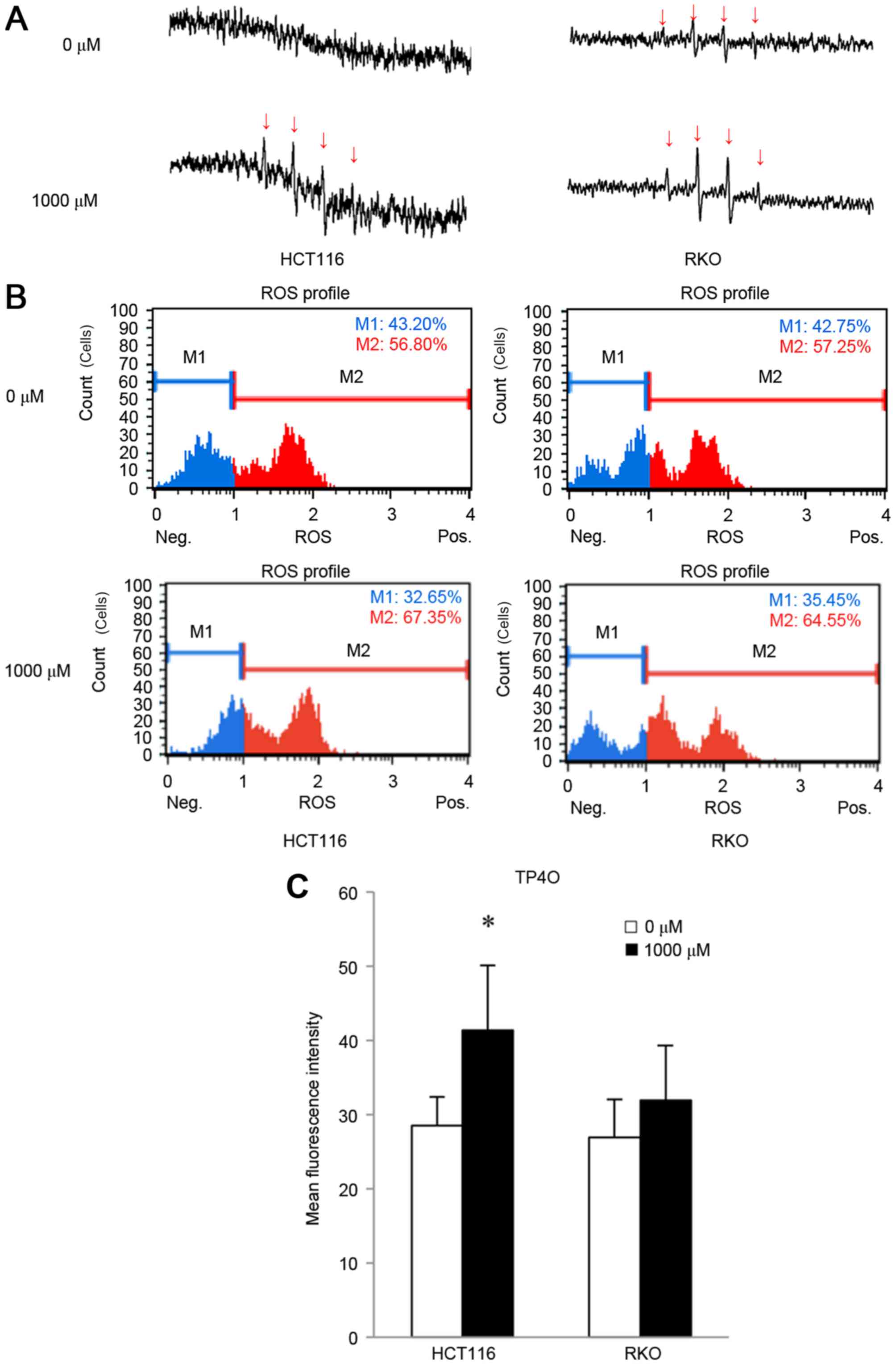
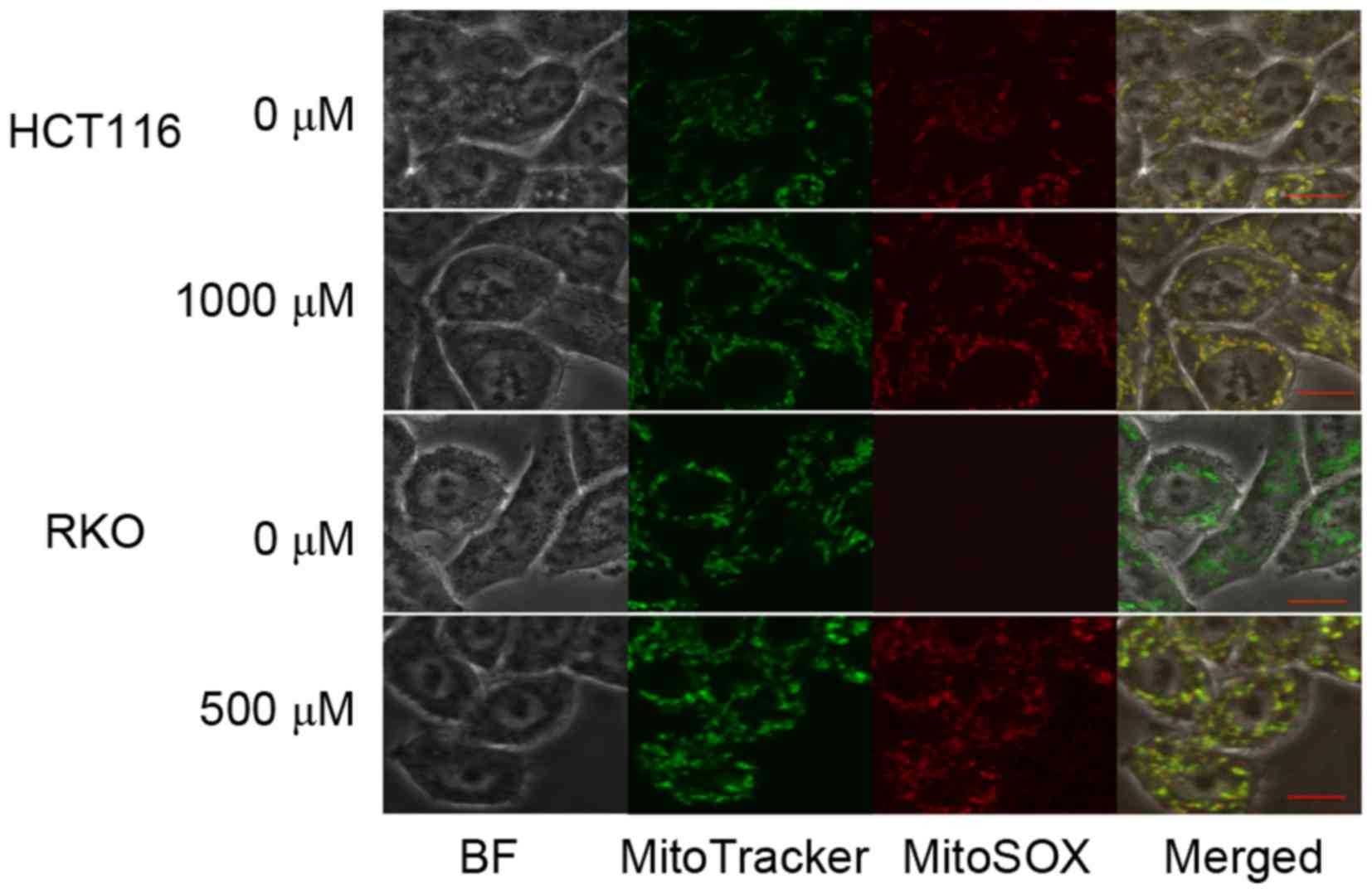
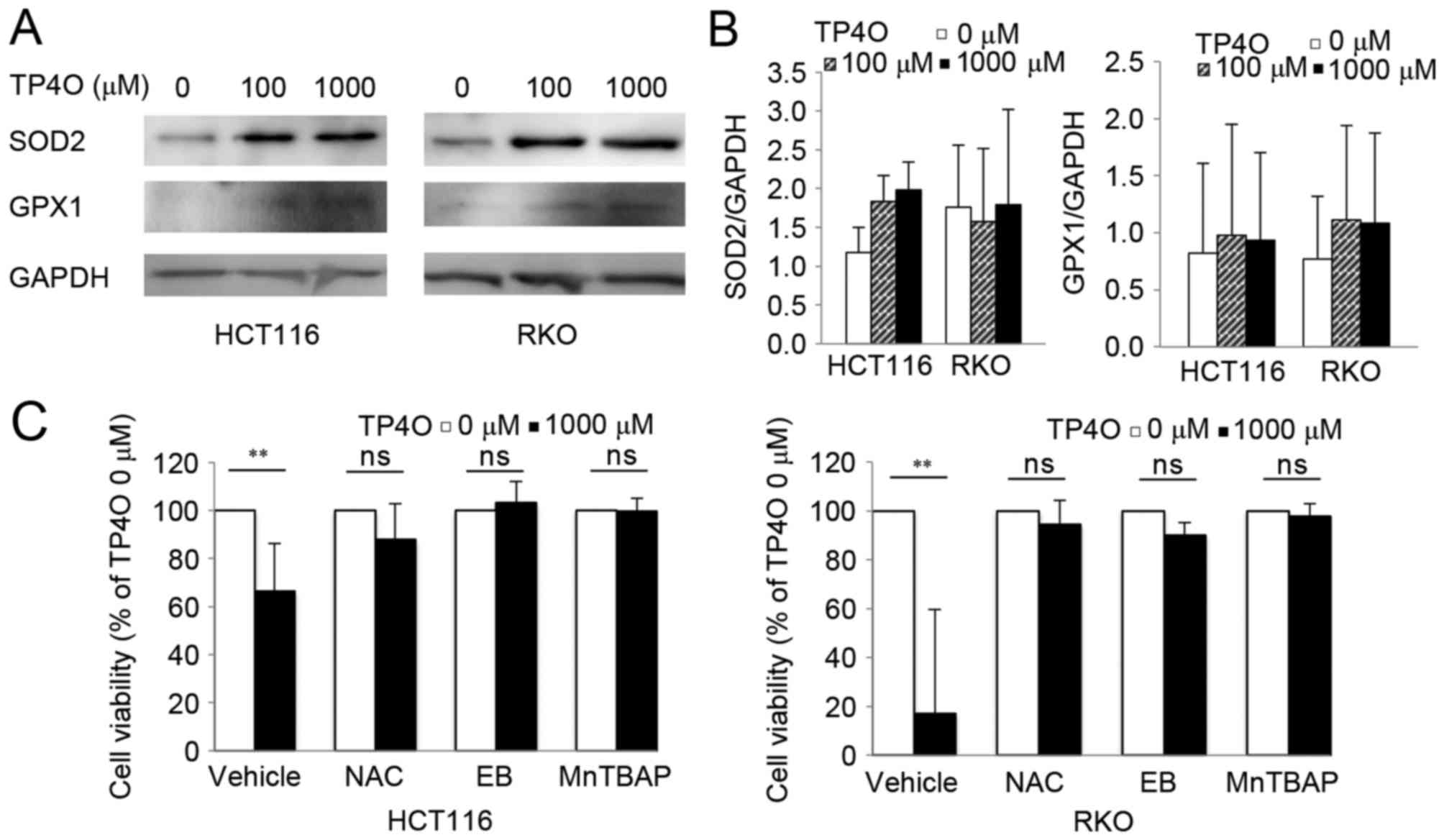
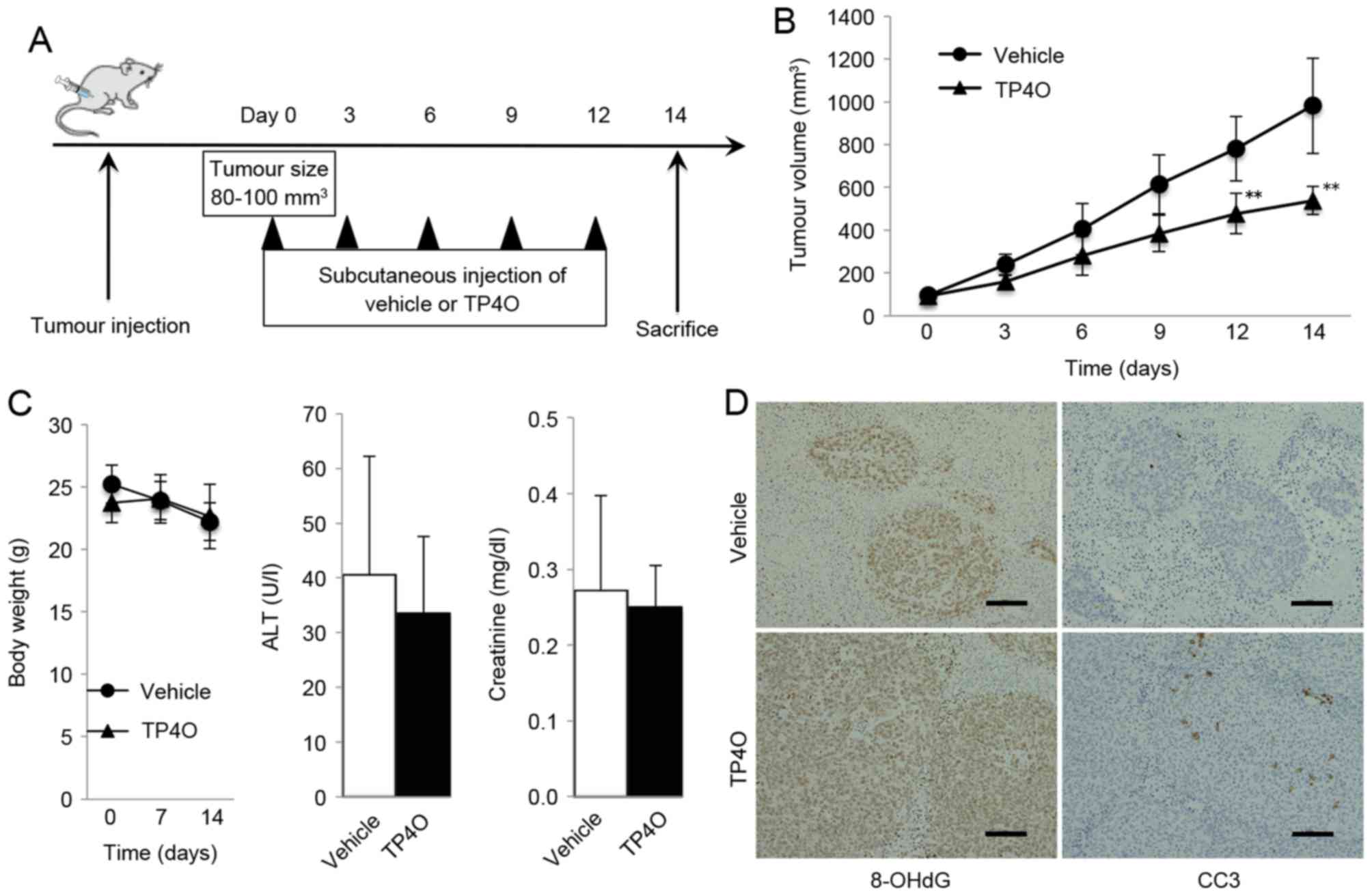
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Siegel
RL, Stein KD, Kramer JL, Alteri R, Robbins AS and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin.
64:252–271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Scott AM, Wolchok JD and Old LJ: Antibody
therapy of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:278–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gustavsson B, Carlsson G, Machover D,
Petrelli N, Roth A, Schmoll HJ, Tveit KM and Gibson F: A review of
the evolution of systemic chemotherapy in the management of
colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 14:1–10. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mann J: Natural products in cancer
chemotherapy: Past, present and future. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:143–148.
2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Newman DJ and Cragg GM: Natural products
as sources of new drugs over the 30 years from 1981 to 2010. J Nat
Prod. 75:311–335. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Edris AE: Pharmaceutical and therapeutic
potentials of essential oils and their individual volatile
constituents: A review. Phytother Res. 21:308–323. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Aggarwal BB, Prasad S, Reuter S, Kannappan
R, Yadev VR, Park B, Kim JH, Gupta SC, Phromnoi K, Sundaram VR, et
al: Identification of novel anti-inflammatory agents from Ayurvedic
medicine for prevention of chronic diseases: ‘Reverse pharmacology’
and ‘bedside to bench’ approach. Curr Drug Targets. 12:1595–1653.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gautam N, Mantha AK and Mittal S:
Essential oils and their constituents as anticancer agents: A
mechanistic view. Biomed Res Int. 2014:1541062014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sobral MV, Xavier AL, Lima TC and de Sousa
DP: Antitumor activity of monoterpenes found in essential oils.
ScientificWorldJournal. 2014:9534512014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pazyar N, Yaghoobi R, Bagherani N and
Kazerouni A: A review of applications of tea tree oil in
dermatology. Int J Dermatol. 52:784–790. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Carson CF and Riley TV: Antimicrobial
activity of the major components of the essential oil of Melaleuca
alternifolia. J Appl Bacteriol. 78:264–269. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hart PH, Brand C, Carson CF, Riley TV,
Prager RH and Finlay-Jones JJ: Terpinen-4-ol, the main component of
the essential oil of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree oil),
suppresses inflammatory mediator production by activated human
monocytes. Inflamm Res. 49:619–626. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Calcabrini A, Stringaro A, Toccacieli L,
Meschini S, Marra M, Colone M, Salvatore G, Mondello F, Arancia G
and Molinari A: Terpinen-4-ol, the main component of Melaleuca
alternifolia (tea tree) oil inhibits the in vitro growth of human
melanoma cells. J Invest Dermatol. 122:349–360. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu CS, Chen YJ, Chen JJ, Shieh JJ, Huang
CH, Lin PS, Chang GC, Chang JT and Lin CC: Terpinen-4-ol induces
apoptosis in human nonsmall cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012:8182612012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Banjerdpongchai R and Khaw-On P:
Terpinen-4-ol induces autophagic and apoptotic cell death in human
leukemic HL-60 cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:7537–7542. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shapira S, Pleban S, Kazanov D, Tirosh P
and Arber N: Terpinen-4-ol: A novel and promising therapeutic agent
for human gastrointestinal cancers. PLoS One. 11:e01565402016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Legrand C, Bour JM, Jacob C, Capiaumont J,
Martial A, Marc A, Wudtke M, Kretzmer G, Demangel C, Duval D, et
al: Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity of the cultured eukaryotic
cells as marker of the number of dead cells in the medium
[corrected]. J Biotechnol. 25:231–243. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tamura M, Matsui H, Kaneko T and Hyodo I:
Alcohol is an oxidative stressor for gastric epithelial cells:
Detection of superoxide in living cells. J Clin Biochem Nutr.
53:75–80. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bindokas VP, Jordán J, Lee CC and Miller
RJ: Superoxide production in rat hippocampal neurons: Selective
imaging with hydroethidine. J Neurosci. 16:1324–36. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Toyokuni S, Tanaka T, Hattori Y, Nishiyama
Y, Yoshida A, Uchida K, Hiai A, Ochi A and Osawa T: Quantitative
immunohistochemical determination of 8-hydroxy-2′deoxyguanosine by
a monoclonal antibody N45.1: Its application to ferric
nitrilotriacetate-induced renal carcinogenesis model. Lab Invest.
76:365–374. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vermes I, Haanen C, Steffens-Nakken H and
Reutelingsperger C: A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric
detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells
using fluorescein labelled Annexin V. J Immunol Methods. 17:39–51.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Britigan BE, Cohen MS and Rosen GM:
Detection of the production of oxygen-centered free radicals by
human neutrophils using spin trapping techniques: A critical
perspective. J Leukoc Biol. 41:349–362. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mahmoud SS and Croteau RB: Strategies for
transgenic manipulation of monoterpene biosynthesis in plants.
Trends Plant Sci. 7:366–373. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gupta SC, Prasad S, Sethumadhavan DR, Nair
MS, Mo YY and Aggarwal BB: Nimbolide, a limonoid triterpene,
inhibits growth of human colorectal cancer xenografts by
suppressing the proinflammatory microenvironment. Clin Cancer Res.
19:4465–4476. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Greay SJ, Ireland DJ, Kissick HT, Levy A,
Beilharz MW, Riley TV and Carson CF: Induction of necrosis and cell
cycle arrest in murine cancer cell lines by Melaleuca alternifolia
(tea tree) oil and terpinen-4-ol. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
65:877–888. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Brand C, Ferrante A, Prager RH, Riley TV,
Carson CF, Finlay-Jones JJ and Hart PH: The water-soluble
components of the essential oil of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree
oil) suppress the production of superoxide by human monocytes, but
not neutrophils, activated in vitro. Inflamm Res. 50:213–219. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim HJ, Chen F, Wu C, Wang X, Chung HY and
Jin Z: Evaluation of antioxidant activity of Australian tea tree
(Melaleuca alternifolia) oil and its components. J Agric Food Chem.
52:2849–2854. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schumacker PT: Reactive oxygen species in
cancer cells: live by the sword, die by the sword. Cancer Cell.
10:175–176. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nogueira V and Hay N: Molecular pathways:
Reactive oxygen species homeostasis in cancer cells and
implications for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 19:4309–4314.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Glasauer A, Sena LA, Diebold LP, Mazar AP
and Chandel NS: Targeting SOD1 reduces experimental non-small-cell
lung cancer. J Clin Invest. 124:117–128. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Provinciali M, Donnini A, Argentati K, Di
Stasio G, Bartozzi B and Bernardini G: Reactive oxygen species
modulate Zn(2+)-induced apoptosis in cancer cells. Free Radic Biol
Med. 32:431–445. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kuo PL, Chen CY and Hsu YL:
Isoobtusilactone A induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through
reactive oxygen species/apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1
signaling pathway in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
67:7406–7420. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Whibley CE, McPhail KL, Keyzers RA, Maritz
MF, Leaner VD, Birrer MJ, Davies-Coleman MT and Hendricks DT:
Reactive oxygen species mediated apoptosis of esophageal cancer
cells induced by marine triprenyl toluquinones and
toluhydroquinones. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:2535–2543. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Trachootham D, Zhou Y, Zhang H, Demizu Y,
Chen Z, Pelicano H, Chiao PJ, Achanta G, Arlinghaus RB, Liu J and
Huang P: Selective killing of oncogenically transformed cells
through a ROS-mediated mechanism by beta-phenylethyl
isothiocyanate. Cancer Cell. 10:241–252. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ka H, Park HJ, Jung HJ, Choi JW, Cho KS,
Ha J and Lee KT: Cinnamaldehyde induces apoptosis by ROS-mediated
mitochondrial permeability transition in human promyelocytic
leukemia HL-60 cells. Cancer Lett. 196:143–152. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Noh J, Kwon B, Han E, Park M, Yang W, Cho
W, Yoo W, Khang G and Lee D: Amplification of oxidative stress by a
dual stimuli-responsive hybrid drug enhances cancer cell death. Nat
Commun. 6:69072015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Avisetti DR, Babu KS and Kalivendi SV:
Activation of p38/JNK pathway is responsible for embelin induced
apoptosis in lung cancer cells: Transitional role of reactive
oxygen species. PLoS One. 9:e870502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ichijo H, Nishida E, Irie K, ten Dijke P,
Saitoh M, Moriguchi T, Takagi M, Matsumoto K, Miyazono K and Gotoh
Y: Induction of apoptosis by ASK1, a mammalian MAPKKK that
activates SAPK/JNK and p38 signaling pathways. Science. 275:90–94.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Toyokuni T and Akatsuka S: What has been
Learned from the Studies of Oxidative Stress-induced
Carcinogenesis: Proposal of the Concept of Oxygenomics. J Clin
Biochem Nutr. 39:3–10. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Perry G, Castellani RJ, Hirai K and Smith
MA: Reactive oxygen species mediate cellular damage in alzheimer
disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 1:45–55. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim YW and Byzova TV: Oxidative stress in
angiogenesis and vascular disease. Blood. 123:625–631. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rolo AP, Teodoro JS and Palmeira CM: Role
of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis. Free Radic Biol Med. 52:59–69. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Forbes JM, Coughlan MT and Cooper ME:
Oxidative stress as a major culprit in kidney disease in diabetes.
Diabetes. 57:1446–1454. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Berndtsson M, Hägg M, Panaretakis T,
Havelka AM, Shoshan MC and Linder S: Acute apoptosis by cisplatin
requires induction of reactive oxygen species but is not associated
with damage to nuclear DNA. Int J Cancer. 120:175–180. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|