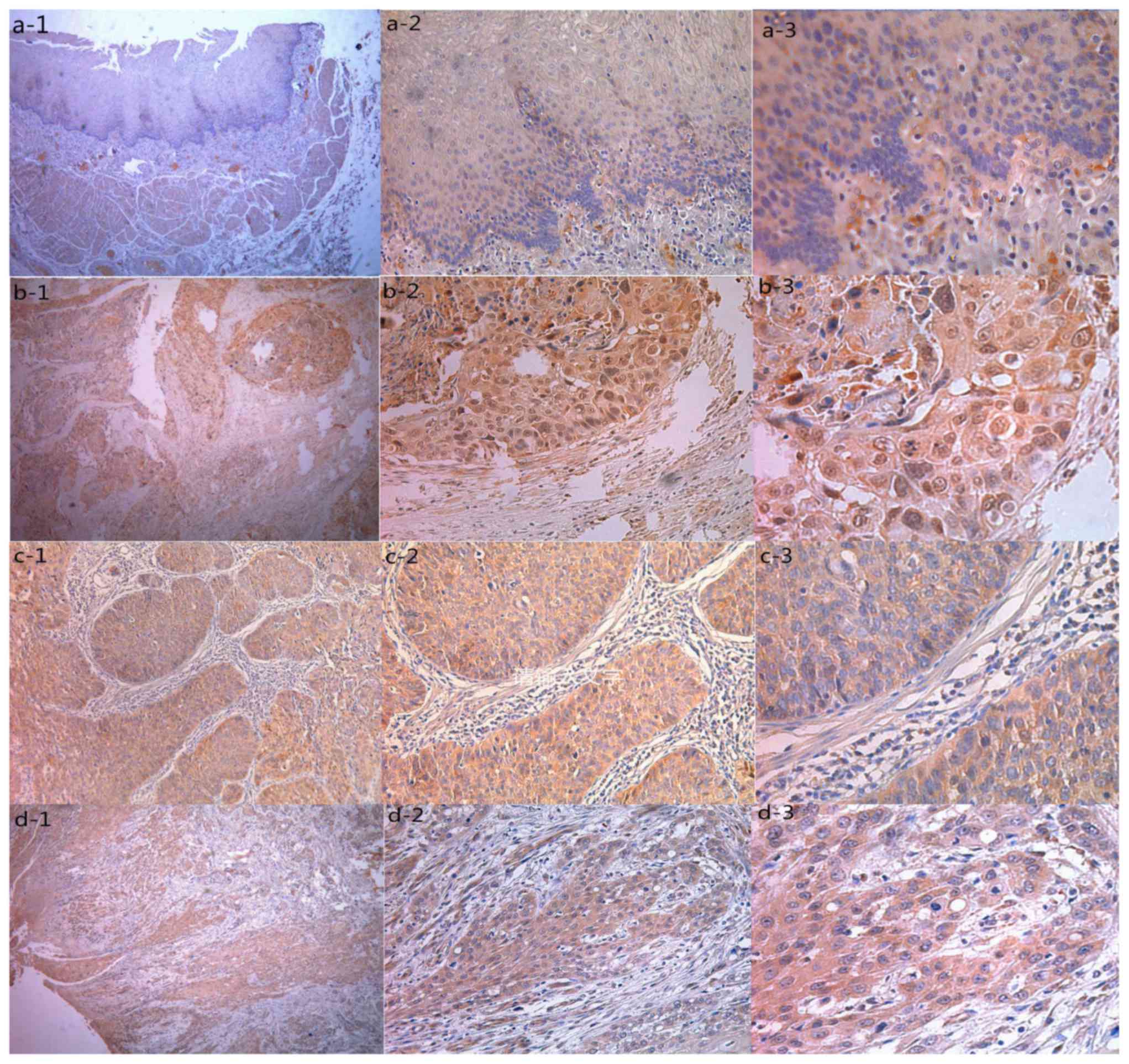
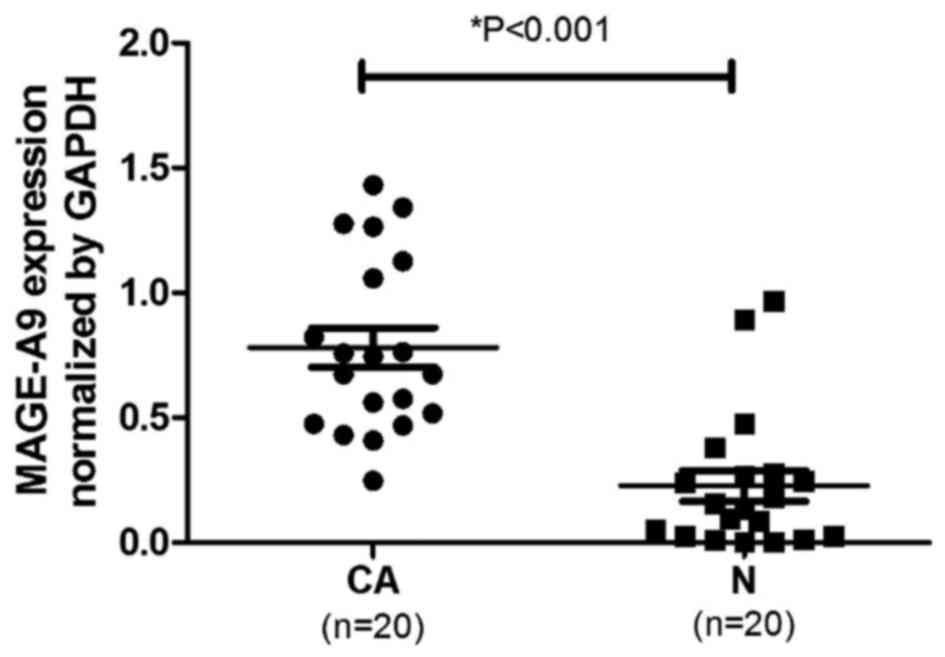
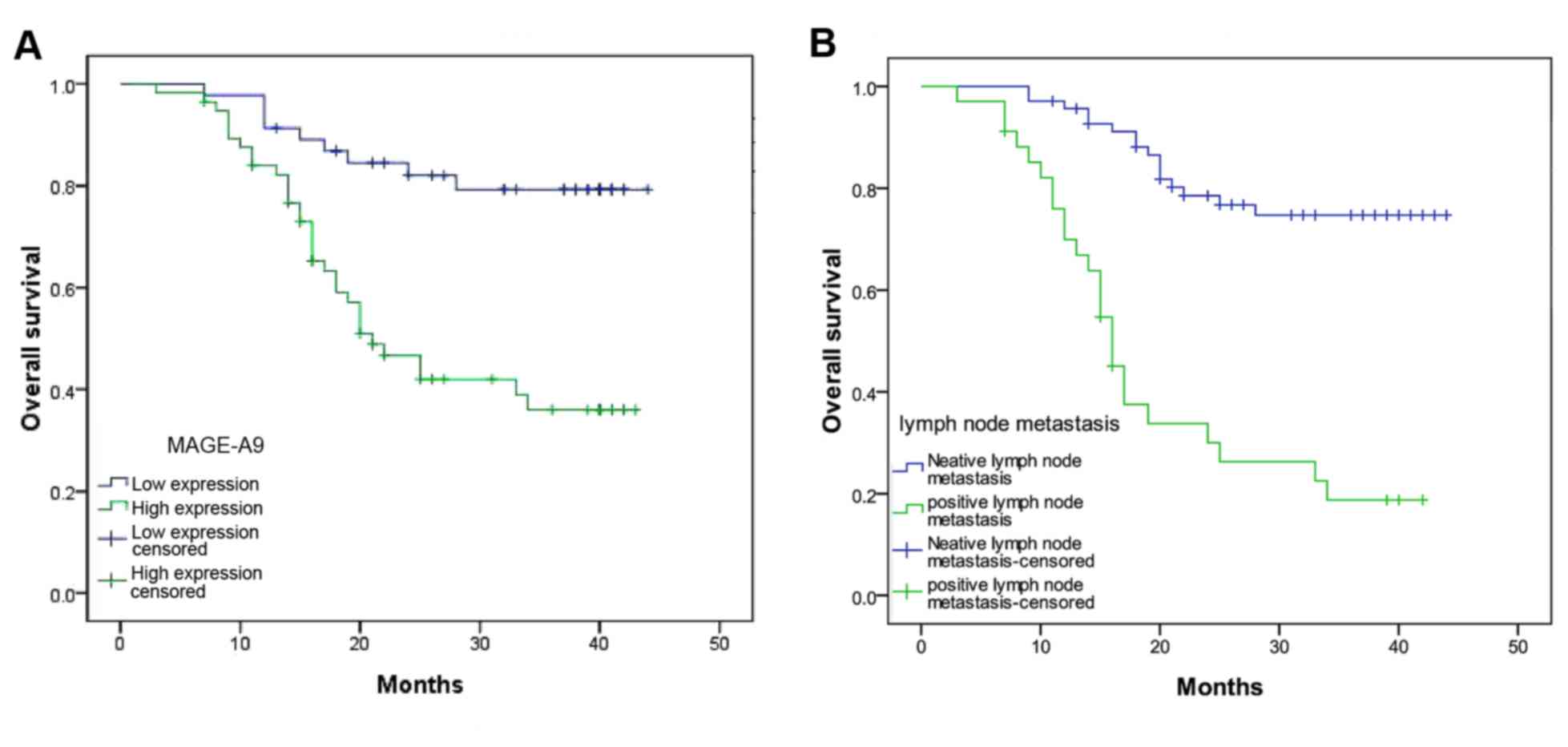
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
He J and Chen WQ: Chinese cancer registry
annual report. Military Medical Science Press; Beijing: 2012. pp.
P56–58. 2012, (In Chinese).
|
|
3
|
Bosset JF, Gignoux M, Triboulet JP, Tiret
E, Mantion G, Elias D, Lozach P, Ollier JC, Pavy JJ, Mercier M and
Sahmoud T: Chemoradiotherapy followed by surgery compared with
surgery alone in squamous-cell cancer of the esophagus. N Engl J
Med. 337:161–167. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang Y: Epidemiology of esophageal
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 19:5598–6006. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Roch N, Kutup A, Vashist Y, Yekebas E,
Kalinin V and Izbicki JR: Coexpression of MAGE-A peptides and HLA
class I molecules in hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res.
30:1617–1623. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lian Y, Sang M, Ding C, Zhou X, Fan X, Xu
Y, Lü W and Shan B: Expressions of MAGE-A10 and MAGE-A11 in breast
cancers and their prognostic significance: A retrospective clinical
study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:519–527. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hatiboglu G, Pritsch M, Macher-Goeppinger
S, Zöller M, Huber J, Haferkamp A, Pahernik S, Wagener N and
Hohenfellner M: Prognostic value of melanoma-associated antigen A9
in renal cell carcinoma. Scand J Urol. 47:311–322. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Melloni G, Ferreri AJ, Russo V, Gattinoni
L, Arrigoni G, Ceresoli GL, Zannini P and Traversari C: Prognostic
significance of cancer-testis gene expression in resected non-small
cell lung cancer patients. Oncol Rep. 12:145–151. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen YT, Chiu R, Lee P, Beneck D, Jin B
and Old LJ: Chromosome X-encoded cancer/testis antigens show
distinctive expression patterns in developing gonads and in
testicular seminoma. Hum Reprod. 26:3232–3243. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meek DW and Marcar L: MAGE-A antigens as
targets in tumour therapy. Cancer Lett. 324:126–132. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gu X, Fu M, Ge Z, Zhan F, Ding Y, Ni H,
Zhang W, Zhu Y, Tang X, Xiong L, et al: High expression of MAGE-A9
correlates with unfavorable survival in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Sci Rep. 4:66252014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu X, Tang X, Lu M, Tang Q, Zhang H, Zhu
H, Xu N, Zhang D, Xiong L, Mao Y and Zhu J: Overexpression of
MAGE-A9 predicts unfavorable outcome in breast cancer. Exp Mol
Pathol. 97:579–584. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang S, Zhai X, Wang G, Feng J, Zhu H, Xu
L, Mao G and Huang J: High expression of MAGE-A9 in tumor and
stromal cells of non-small cell lung cancer was correlated with
patient poor survival. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:541–550.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Han L, Jiang B, Wu H, Zhang S and Lu X:
Expression and prognostic value of MAGE-A9 in laryngeal squamous
cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:6734–6742. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bergeron A, Picard V, LaRue H, Harel F,
Hovington H, Lacombe L and Fradet Y: High frequency of MAGE-A4 and
MAGE-A9 expression in high-risk bladder cancer. Int J Cancer.
125:1365–1371. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sobin L, Gospodarowicz M and Wittekind C:
TNM classification of malignant tumors. 7th. New Jersey;
Wiley-Blackwell; 2009
|
|
17
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jungbluth AA, Busam KJ, Kolb D, Iversen K,
Coplan K, Chen YT, Spagnoli GC and Old LJ: Expression of
MAGE-antigens in normal tissues and cancer. Int J Cancer.
85:460–465. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Svobodová S, Browning J, MacGregor D,
Pollara G, Scolyer RA, Murali R, Thompson JF, Deb S, Azad A, Davis
ID and Cebon JS: Cancer-testis antigen expression in primary
cutaneous melanoma has independent prognostic value comparable to
that of Breslow thickness, ulceration and mitotic rate. Eur J
Cancer. 47:460–469. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ogata K, Aihara R, Mochiki E, Ogawa A,
Yanai M, Toyomasu Y, Ando H, Ohno T, Asao T and Kuwano H: Clinical
significance of melanoma antigen-encoding gene-1 (MAGE-1)
expression and its correlation with poor prognosis in
differentiated advanced gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol.
18:1195–1203. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jeon CH, Shin IH, Park JB and Chae HD:
Prognostic significance of MAGE in peritoneal washes in gastric
carcinoma patients without peritoneal metastasis: Results of a
5-year follow-up study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 44:682–686. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pastorcic-Grgic M, Sarcevic B, Dosen D,
Juretic A, Spagnoli GC and Grgic M: Prognostic value of MAGE-A and
NY-ESO-1 expression in pharyngeal cancer. Head Neck. 32:1178–1184.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sang M, Wang L, Ding C, Zhou X, Wang B,
Wang L, Lian Y and Shan B: Melanoma-associated antigen genes-an
update. Cancer Lett. 302:85–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Morishima N, Nakanishi K, Takenouchi H,
Shibata T and Yasuhiko Y: An endoplasmic reticulum stress-specific
caspase cascade in apoptosis cytochrome c-independent activation of
caspase-9 by caspase-12. J Biol Chem. 277:34287–34294. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Marcar L, MacLaine NJ, Hupp TR and Meek
DW: Mage-A cancer/testis antigens inhibit p53 function by blocking
its interaction with chromatin. Cancer Res. 70:10362–10370. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|