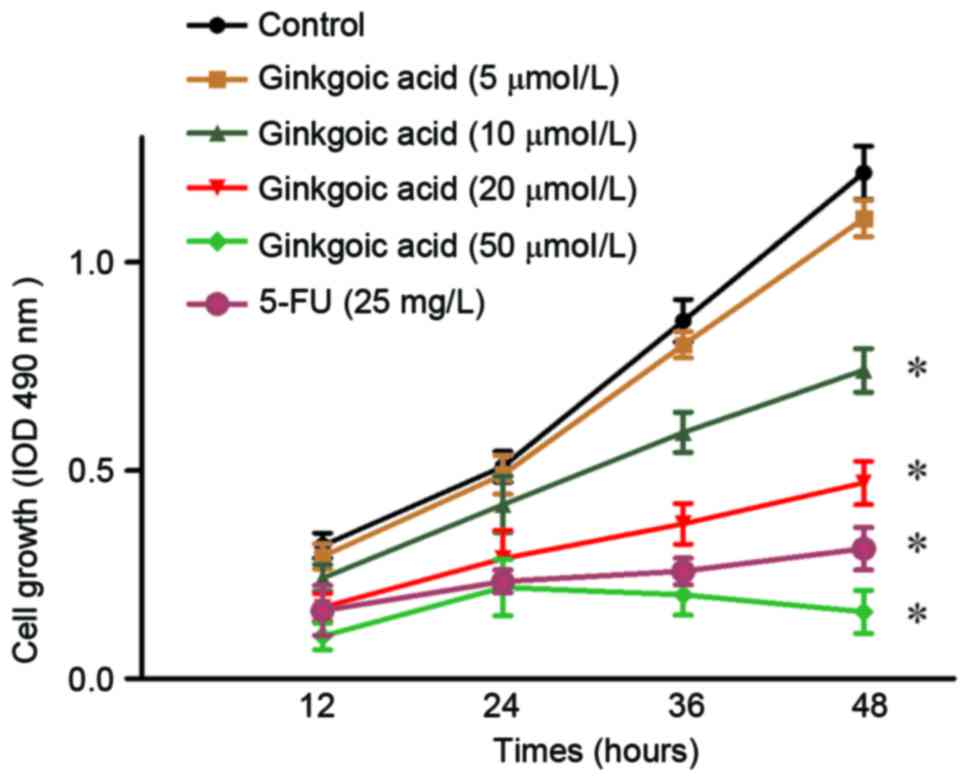
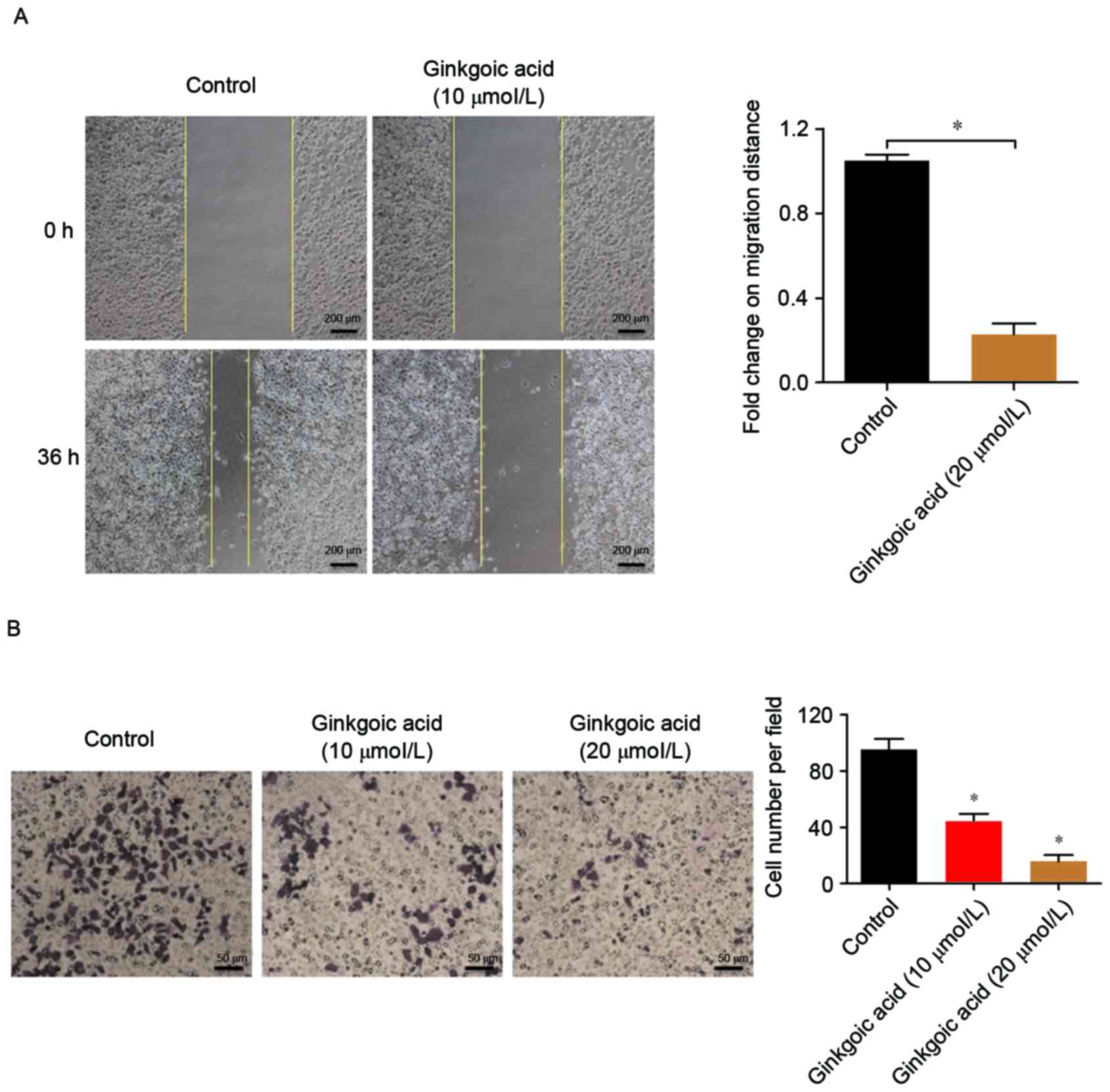
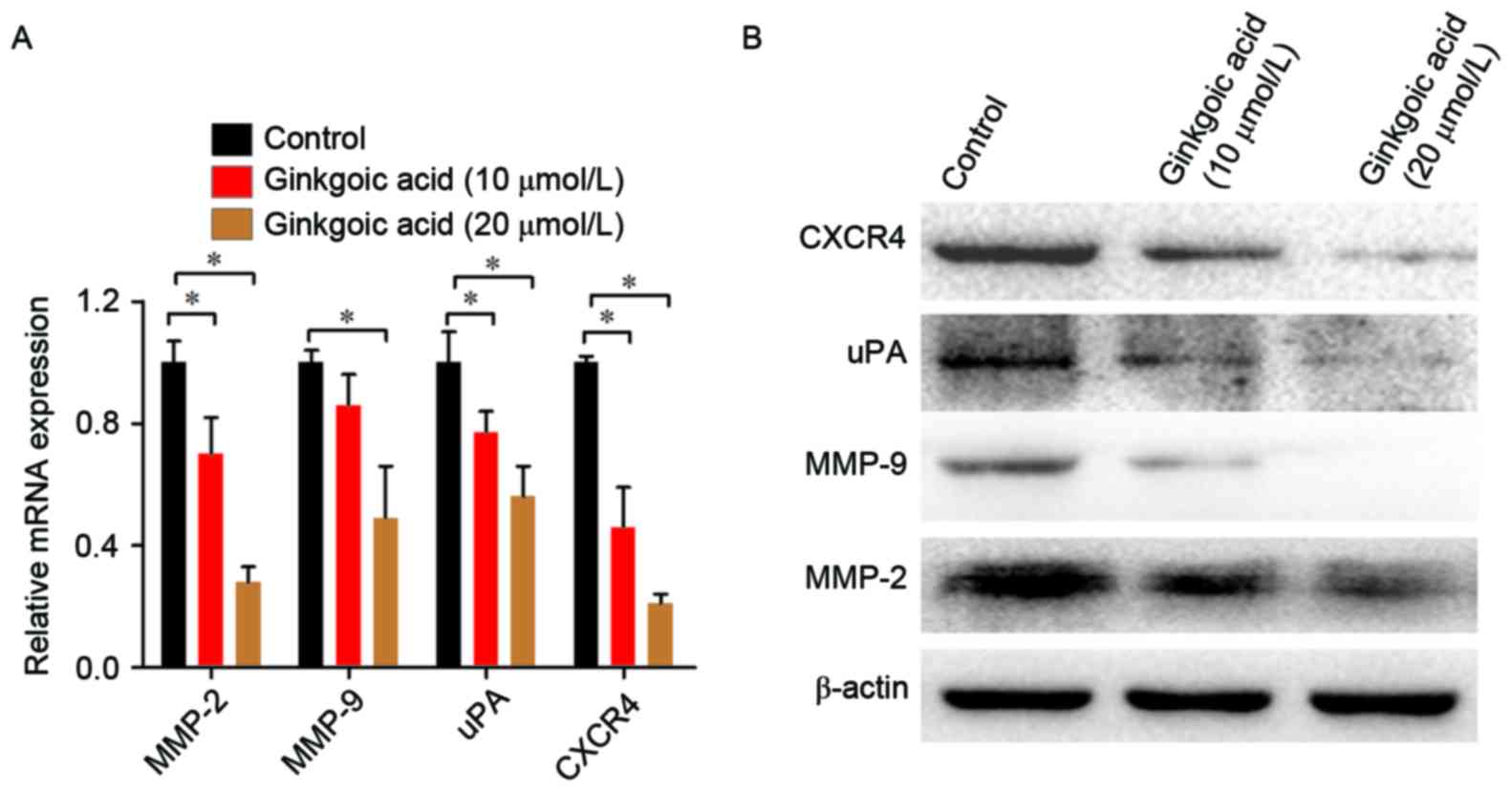
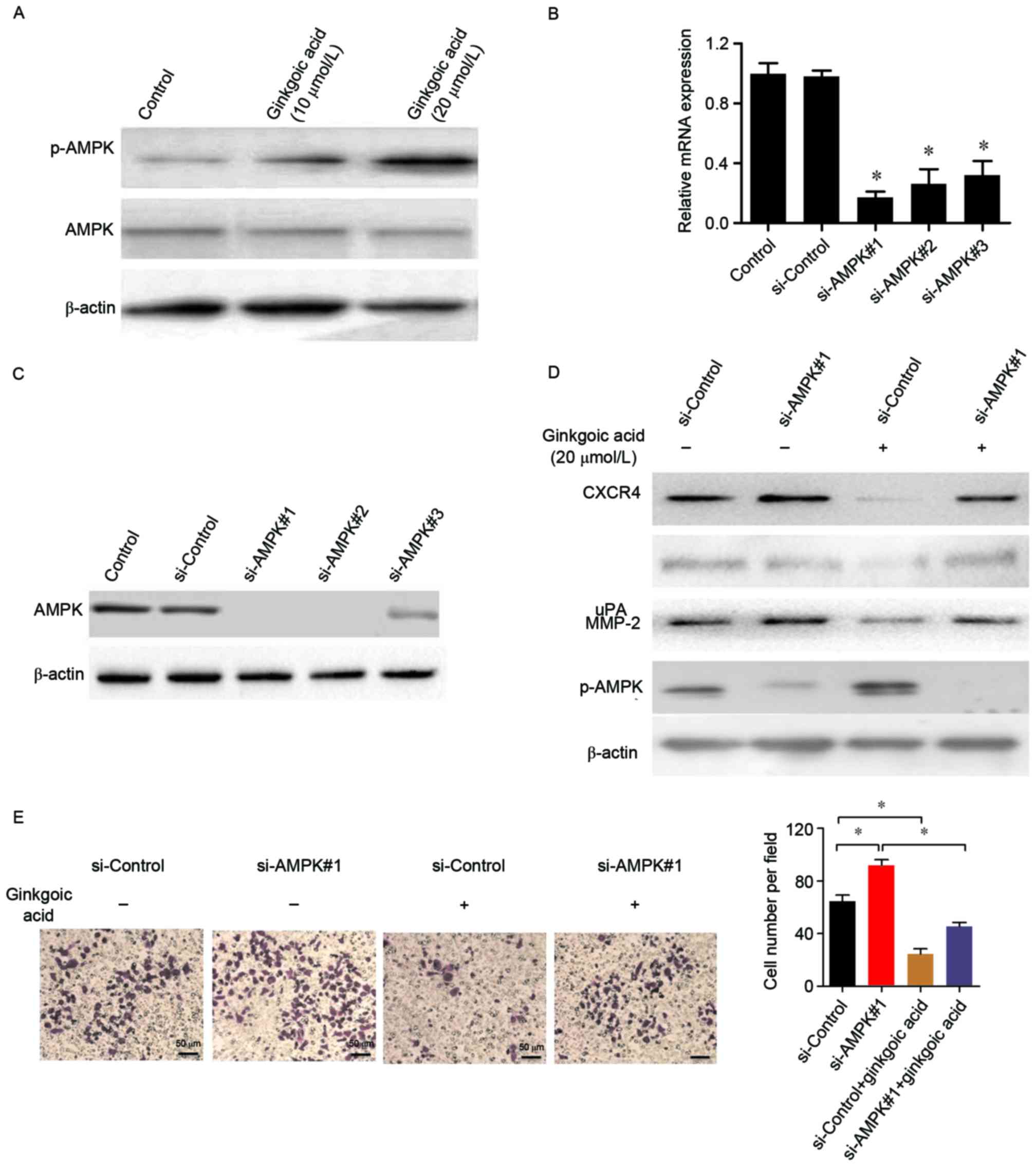
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sung JJ, Ng SC, Chan FK, Chiu HM, Kim HS,
Matsuda T, Ng SS, Lau JY, Zheng S, Adler S, et al: An updated Asia
Pacific Consensus Recommendations on colorectal cancer screening.
Gut. 64:121–132. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Abad A, Massuti B, Antón A, Vega ME, Yuste
AL, Marcuello E, Manzano JL, Alonso V, Carrato A,
Martinez-Villacampa M, et al: Colorectal cancer metastasis
resectability after treatment with the combination of oxaliplatin,
irinotecan and 5-fluorouracil. Final results of a phase II study.
Acta Oncol. 47:286–292. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Abdel-Misih SR, Schmidt CR and Bloomston
PM: Update and review of the multidisciplinary management of stage
IV colorectal cancer with liver metastases. World J Surg Oncol.
7:722009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brandi G, De Lorenzo S, Nannini M, Curti
S, Ottone M, Dall'Olio FG, Barbera MA, Pantaleo MA and Biasco G:
Adjuvant chemotherapy for resected colorectal cancer metastases:
Literature review and meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol.
22:519–533. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu QQ, Qiu H, Zhang MS, Hu GY, Liu B,
Huang L, Liao X, Li QX, Li ZH and Yuan XL: Predictive effects of
bilirubin on response of colorectal cancer to irinotecan-based
chemotherapy. World J Gastroenterol. 22:4250–4258. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Major RT: The ginkgo, the most ancient
living tree. The resistance of Ginkgo biloba L. To pests
accounts in part for the longevity of this species. Science.
157:1270–1273. 1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
van Beek TA and Wintermans MS: Preparative
isolation and dual column high-performance liquid chromatography of
ginkgolic acids from Ginkgo biloba. J Chromatogr A.
930:109–117. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang XM, Wang YF, Li YY and Ma HL: Thermal
stability of ginkgolic acids from Ginkgo biloba and the
effects of ginkgol C17:1 on the apoptosis and migration of SMMC7721
cells. Fitoterapia. 98:66–76. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ma J, Duan W, Han S, Lei J, Xu Q, Chen X,
Jiang Z, Nan L, Li J, Chen K, et al: Ginkgolic acid suppresses the
development of pancreatic cancer by inhibiting pathways driving
lipogenesis. Oncotarget. 6:20993–21003. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou C, Li X, Du W, Feng Y, Kong X, Li Y,
Xiao L and Zhang P: Antitumor effects of ginkgolic acid in human
cancer cell occur via cell cycle arrest and decrease the Bcl-2/Bax
ratio to induce apoptosis. Chemotherapy. 56:393–402. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shilpa P, Kaveri K and Salimath BP:
Anti-metastatic action of anacardic acid targets VEGF-induced
signalling pathways in epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Drug
Discov Ther. 9:53–65. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zaha VG and Young LH: AMP-activated
protein kinase regulation and biological actions in the heart. Circ
Res. 111:800–814. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Evans JM, Donnelly LA, Emslie-Smith AM,
Alessi DR and Morris AD: Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in
diabetic patients. BMJ. 330:1304–1305. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Decensi A, Puntoni M, Goodwin P, Cazzaniga
M, Gennari A, Bonanni B and Gandini S: Metformin and cancer risk in
diabetic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer
Prev Res (Phila). 3:1451–1461. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ioannou GN and Boyko EJ: Metformin and
colorectal cancer risk in diabetic patients. Diabetes Care.
34:2336–2337. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Montales MT, Simmen RC, Ferreira ES, Neves
VA and Simmen FA: Metformin and soybean-derived bioactive molecules
attenuate the expansion of stem cell-like epithelial subpopulation
and confer apoptotic sensitivity in human colon cancer cells. Genes
Nutr. 10:492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li X, Ma Q, Xu Q, Liu H, Lei J, Duan W,
Bhat K, Wang F, Wu E and Wang Z: SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling induces
pancreatic cancer cell invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in vitro through non-canonical activation of Hedgehog
pathway. Cancer Lett. 322:169–176. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Smith JJ, Deane NG, Wu F, Merchant NB,
Zhang B, Jiang A, Lu P, Johnson JC, Schmidt C, Bailey CE, et al:
Experimentally derived metastasis gene expression profile predicts
recurrence and death in patients with colon cancer.
Gastroenterology. 138:958–968. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lü JM, Yan S, Jamaluddin S, Weakley SM,
Liang Z, Siwak EB, Yao Q and Chen C: Ginkgolic acid inhibits HIV
protease activity and HIV infection in vitro. Med Sci Monit.
18:BR293–BR298. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee JH, Kim YG, Ryu SY, Cho MH and Lee J:
Ginkgolic acids and Ginkgo biloba extract inhibit
Escherichia coli O157: H7 and Staphylococcus aureus
biofilm formation. Int J Food Microbiol. 174:47–55. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fukuda I, Ito A, Hirai G, Nishimura S,
Kawasaki H, Saitoh H, Kimura K, Sodeoka M and Yoshida M: Ginkgolic
acid inhibits protein SUMOylation by blocking formation of the
E1-SUMO intermediate. Chem Biol. 16:133–140. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Oh J, Hwang IH, Hong CE, Lyu SY and Na M:
Inhibition of fatty acid synthase by ginkgolic acids from the
leaves of Ginkgo biloba and their cytotoxic activity. J
Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 28:565–568. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Guo F, Wang Y, Liu J, Mok SC, Xue F and
Zhang W: CXCL12/CXCR4: A symbiotic bridge linking cancer cells and
their stromal neighbors in oncogenic communication networks.
Oncogene. 35:816–826. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim J, Takeuchi H, Lam ST, Turner RR, Wang
HJ, Kuo C, Foshag L, Bilchik AJ and Hoon DS: Chemokine receptor
CXCR4 expression in colorectal cancer patients increases the risk
for recurrence and for poor survival. J Clin Oncol. 23:2744–2753.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim J, Mori T, Chen SL, Amersi FF,
Martinez SR, Kuo C, Turner RR, Ye X, Bilchik AJ, Morton DL and Hoon
DS: Chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression in patients with melanoma
and colorectal cancer liver metastases and the association with
disease outcome. Ann Surg. 244:113–120. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Murakami T, Kawada K, Iwamoto M, Akagami
M, Hida K, Nakanishi Y, Kanda K, Kawada M, Seno H, Taketo MM and
Sakai Y: The role of CXCR3 and CXCR4 in colorectal cancer
metastasis. Int J Cancer. 132:276–287. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schimanski CC, Schwald S, Simiantonaki N,
Jayasinghe C, Gönner U, Wilsberg V, Junginger T, Berger MR, Galle
PR and Moehler M: Effect of chemokine receptors CXCR4 and CCR7 on
the metastatic behavior of human colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 11:1743–1750. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brand S, Dambacher J, Beigel F, Olszak T,
Diebold J, Otte JM, Göke B and Eichhorst ST: CXCR4 and CXCL12 are
inversely expressed in colorectal cancer cells and modulate cancer
cell migration, invasion and MMP-9 activation. Exp Cell Res.
310:117–130. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sakai N, Yoshidome H, Shida T, Kimura F,
Shimizu H, Ohtsuka M, Takeuchi D, Sakakibara M and Miyazaki M:
CXCR4/CXCL12 expression profile is associated with tumor
microenvironment and clinical outcome of liver metastases of
colorectal cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis. 29:101–110. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lv S, Yang Y, Kwon S, Han M, Zhao F, Kang
H, Dai C and Wang R: The association of CXCR4 expression with
prognosis and clinicopathological indicators in colorectal
carcinoma patients: A meta-analysis. Histopathology. 64:701–712.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Abedini F, Ismail M, Hosseinkhani H,
Ibrahim TA, Omar AR, Chong PP, Bejo MH and Domb AJ: Effects of
CXCR4 siRNA/dextran-spermine nanoparticles on CXCR4 expression and
serum LDH levels in a mouse model of colorectal cancer metastasis
to the liver. Cancer Manag Res. 3:301–309. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li JK, Yu L, Shen Y, Zhou LS, Wang YC and
Zhang JH: Inhibition of CXCR4 activity with AMD3100 decreases
invasion of human colorectal cancer cells in vitro. World J
Gastroenterol. 14:2308–2313. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kuhajda FP: AMP-activated protein kinase
and human cancer: Cancer metabolism revisited. Int J Obes (Lond).
32 Suppl 4:S36–S41. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Baur DM, Klotsche J, Hamnvik OP, Sievers
C, Pieper L, Wittchen HU, Stalla GK, Schmid RM, Kales SN and
Mantzoros CS: Type 2 diabetes mellitus and medications for type 2
diabetes mellitus are associated with risk for and mortality from
cancer in a German primary care cohort. Metabolism. 60:1363–1371.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Aljada A and Mousa SA: Metformin and
neoplasia: Implications and indications. Pharmacol Ther.
133:108–115. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|