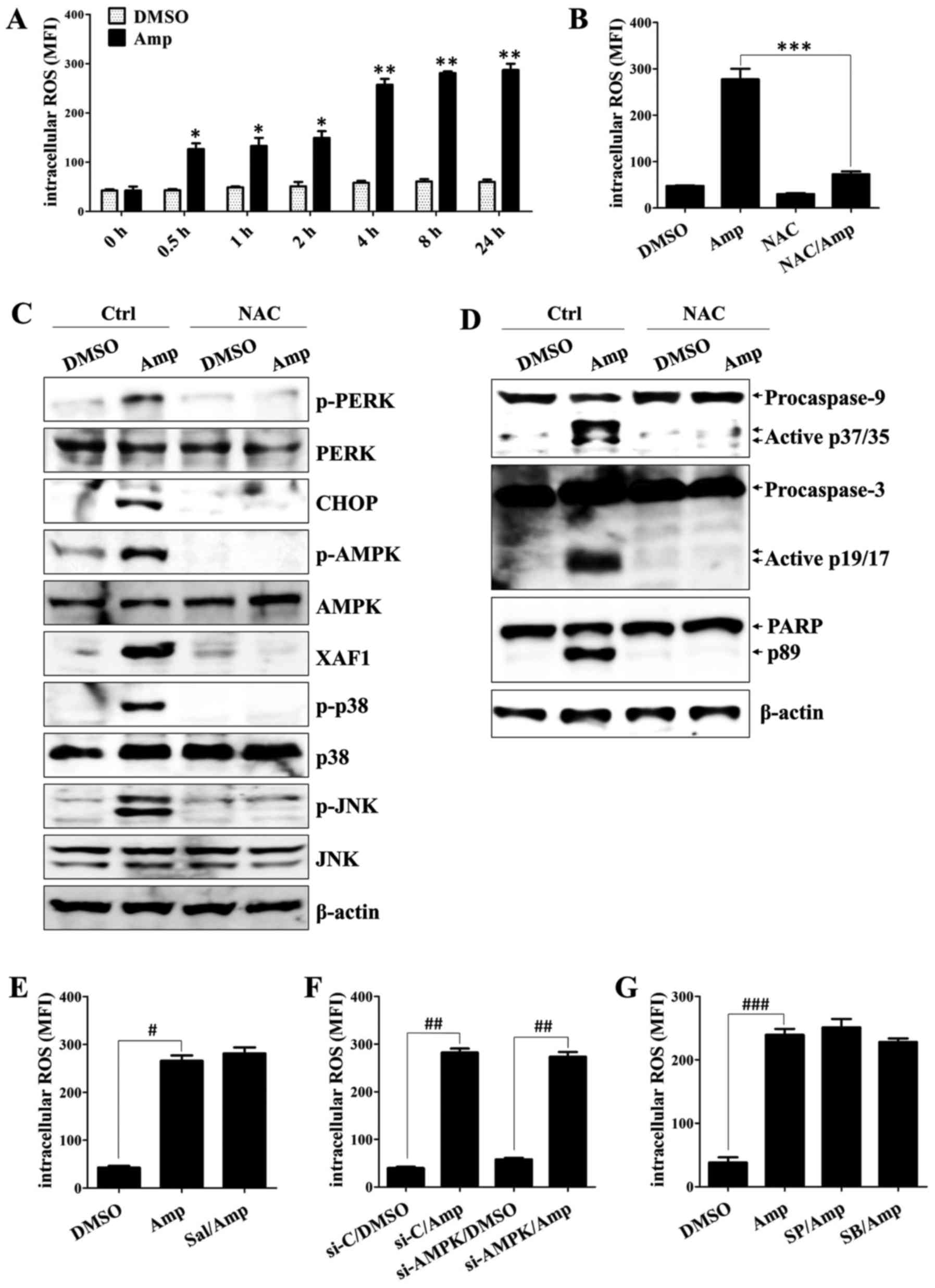
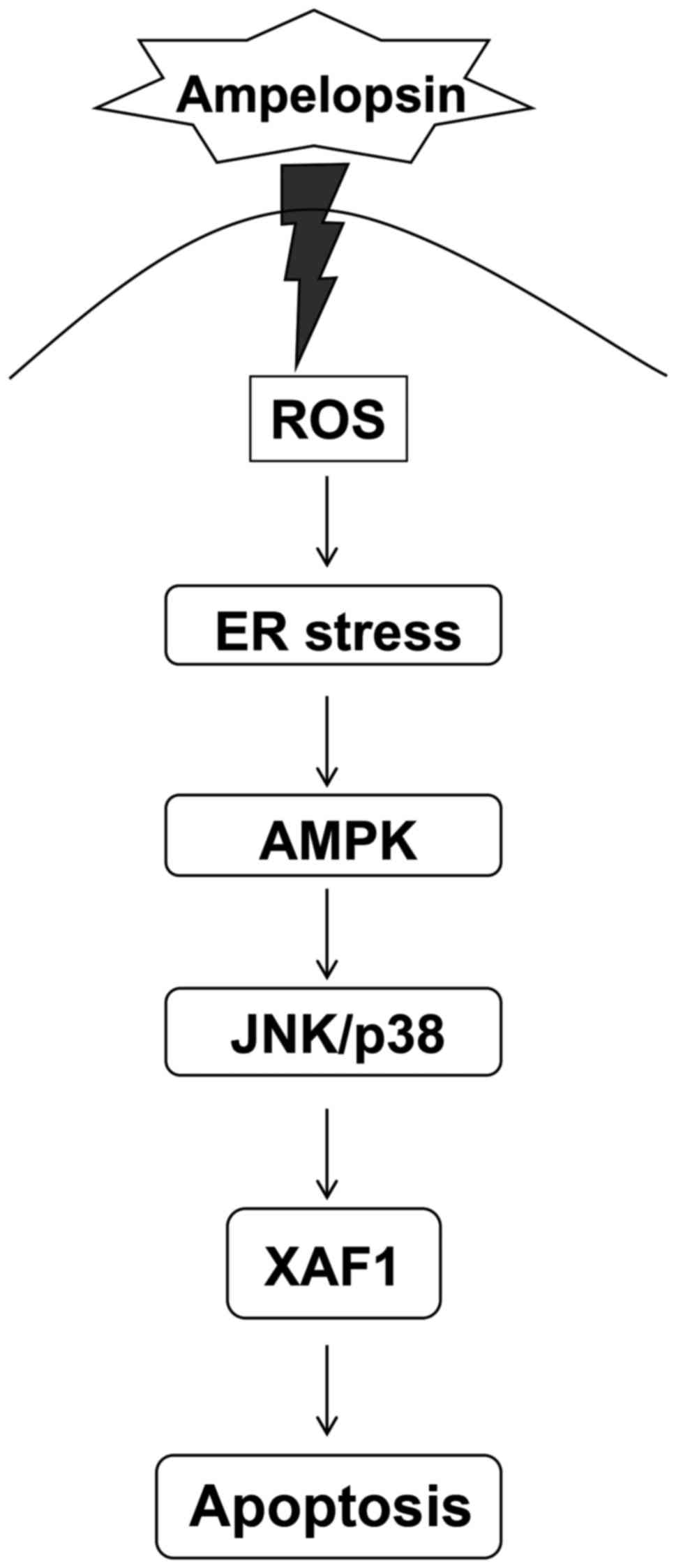
|
1
|
Hardie DG and Carling D: The AMP-activated
protein kinase-fuel gauge of the mammalian cell? Eur J Biochem.
246:259–273. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kemp BE, Mitchelhill KI, Stapleton D,
Michell BJ, Chen ZP and Witters LA: Dealing with energy demand: The
AMP-activated protein kinase. Trends Biochem Sci. 24:22–25. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Steinberg GR and Kemp BE: AMPK in health
and disease. Physiol Rev. 89:1025–1078. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hardie DG, Ross FA and Hawley SA: AMPK: A
nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:251–262. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yuan HX, Xiong Y and Guan KL: Nutrient
sensing, metabolism, and cell growth control. Mol Cell. 49:379–387.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shaw RJ, Bardeesy N, Manning BD, Lopez L,
Kosmatka M, DePinho RA and Cantley LC: The LKB1 tumor suppressor
negatively regulates mTOR signaling. Cancer Cell. 6:91–99. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Laderoute KR, Calaoagan JM, Chao WR, Dinh
D, Denko N, Duellman S, Kalra J, Liu X, Papandreou I, Sambucetti L
and Boros LG: 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) supports the
growth of aggressive experimental human breast cancer tumors. J
Biol Chem. 289:22850–22864. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kefas BA, Cai Y, Ling Z, Heimberg H, Hue
L, Pipeleers D and Van de Casteele M: AMP-activated protein kinase
can induce apoptosis of insulin-producing MIN6 cells through
stimulation of c-Jun-N-terminal kinase. J Mol Endocrinol.
30:151–161. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Okoshi R, Ozaki T, Yamamoto H, Ando K,
Koida N, Ono S, Koda T, Kamijo T, Nakagawara A and Kizaki H:
Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase induces p53-dependent
apoptotic cell death in response to energetic stress. J Biol Chem.
283:3979–3987. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim HS, Wannatung T, Lee S, Yang WK, Chung
SH, Lim JS, Choe W, Kang I, Kim SS and Ha J: Quercetin enhances
hypoxia-mediated apoptosis via direct inhibition of AMPK activity
in HCT116 colon cancer. Apoptosis. 17:938–949. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen MB, Zhang Y, Wei MX, Shen W, Wu XY,
Yao C and Lu PH: Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)
mediates plumbagin-induced apoptosis and growth inhibition in
cultured human colon cancer cells. Cell Signal. 25:1993–2002. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schröder M: Endoplasmic reticulum stress
responses. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:862–894. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Malhotra JD and Kaufman RJ: The
endoplasmic reticulum and the unfolded protein response. Semin Cell
Dev Biol. 18:716–731. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Høyer-Hansen M, Bastholm L, Szyniarowski
P, Campanella M, Szabadkai G, Farkas T, Bianchi K, Fehrenbacher N,
Elling F, Rizzuto R, et al: Control of macroautophagy by calcium,
calmodulin-dependent kinase kinase-beta, and Bcl-2. Mol Cell.
25:193–205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hsu YC and Ip MM: Conjugated linoleic
acid-induced apoptosis in mouse mammary tumor cells is mediated by
both G protein coupled receptor-dependent activation of the
AMP-activated protein kinase pathway and by oxidative stress. Cell
Signal. 23:2013–2020. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Leclerc GM, Leclerc GJ, Kuznetsov JN,
DeSalvo J and Barredo JC: Metformin induces apoptosis through
AMPK-dependent inhibition of UPR signaling in ALL lymphoblasts.
PLoS One. 8:e744202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin YC, Wu MH, Wei TT, Lin YC, Huang WC,
Huang LY, Lin YT and Chen CC: Metformin sensitizes anticancer
effect of dasatinib in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells
through AMPK-dependent ER stress. Oncotarget. 5:298–308.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K
and Thun MJ: Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a
prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med.
348:1625–1638. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ambrosini G, Adida C and Altieri DC: A
novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and
lymphoma. Nat Med. 3:917–921. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fong WG, Liston P, Rajcan-Separovic E, St
Jean M, Craig C and Korneluk RG: Expression and genetic analysis of
XIAP-associated factor 1 (XAF1) in cancer cell lines. Genomics.
70:113–122. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liston P, Fong WG, Kelly NL, Toji S,
Miyazaki T, Conte D, Tamai K, Craig CG, McBurney MW and Korneluk
RG: Identification of XAF1 as an antagonist of XIAP anti-Caspase
activity. Nat Cell Biol. 3:128–133. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang L, Cao Z, Yan H and Wood WC:
Coexistence of high levels of apoptotic signaling and inhibitor of
apoptosis proteins in human tumor cells: Implication for cancer
specific therapy. Cancer Res. 63:6815–6824. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang J, Peng Y, Sun YW, He H, Zhu S, An X,
Li M, Lin MC, Zou B, Xia HH, et al: All-trans retinoic acid induces
XAF1 expression through an interferon regulatory factor-1 element
in colon cancer. Gastroenterology. 130:747–758. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu LF, Wang J, Zou B, Lin MC, Wu YL, Xia
HH, Sun YW, Gu Q, He H, Lam SK, et al: XAF1 mediates apoptosis
through an extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway in colon
cancer. Cancer. 109:1996–2003. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qi S, Xin Y, Guo Y, Diao Y, Kou X, Luo L
and Yin Z: Ampelopsin reduces endotoxic inflammation via repressing
ROS-mediated activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathways. Int
Immunopharmacol. 12:278–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Murakami T, Miyakoshi M, Araho D, Mizutani
K, Kambara T, Ikeda T, Chou WH, Inukai M, Takenaka A and Igarashi
K: Hepatoprotective activity of tocha, the stems and leaves of
Ampelopsis grossedentata, and ampelopsin. Biofactors. 21:175–178.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ni F, Gong Y, Li L, Abdolmaleky HM and
Zhou JR: Flavonoid ampelopsin inhibits the growth and metastasis of
prostate cancer in vitro and in mice. PLoS One. 7:e388022012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang B, Dong S, Cen X, Wang X, Liu X,
Zhang H, Zhao X and Wu Y: Ampelopsin sodium exhibits antitumor
effects against bladder carcinoma in orthotopic xenograft models.
Anticancer Drugs. 23:590–596. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou Y, Shu F, Liang X, Chang H, Shi L,
Peng X, Zhu J and Mi M: Ampelopsin induces cell growth inhibition
and apoptosis in breast cancer cells through ROS generation and
endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. PLoS One. 9:e890212014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou Y, Liang X, Chang H, Shu F, Wu Y,
Zhang T, Fu Y, Zhang Q, Zhu JD and Mi M: Ampelopsin-induced
autophagy protects breast cancer cells from apoptosis through
Akt-mTOR pathway via endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cancer Sci.
105:1279–1287. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liang X, Zhang T, Shi L, Kang C, Wan J,
Zhou Y, Zhu J and Mi M: Ampelopsin protects endothelial cells from
hyperglycemia-induced oxidative damage by inducing autophagy via
the AMPK signaling pathway. Biofactors. 41:463–475. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rosenkranz AR, Schmaldienst S, Stuhlmeier
KM, Chen W, Knapp W and Zlabinger GJ: A microplate assay for the
detection of oxidative products using
2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin-diacetate. J Immunol Methods. 156:39–45.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nishitoh H, Saitoh M, Mochida Y, Takeda K,
Nakano H, Rothe M, Miyazono K and Ichijo H: ASK1 is essential for
JNK/SAPK activation by TRAF2. Mol Cell. 2:389–395. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Urano F, Wang X, Bertolotti A, Zhang Y,
Chung P, Harding HP and Ron D: Coupling of stress in the ER to
activation of JNK protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase
IRE1. Science. 287:664–666. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hwang JT, Ha J, Park IJ, Lee SK, Baik HW,
Kim YM and Park OJ: Apoptotic effect of EGCG in HT-29 colon cancer
cells via AMPK signal pathway. Cancer Lett. 247:115–121. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zheng HQ and Liu DY: Anti-invasive and
anti-metastatic effect of ampelopsin on melanoma. Ai Zheng.
22:363–367. 2003.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Oyadomari S and Mori M: Roles of
CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ.
11:381–389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kaufman RJ: Stress signaling from the
lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum: Coordination of gene
transcriptional and translational controls. Genes Dev.
13:1211–1233. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM and Samali
A: Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis.
EMBO Rep. 7:880–885. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhao L and Ackerman SL: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress in health and disease. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
18:444–452. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim A, Im M and Ma JY: Ethanol extract of
Remotiflori radix induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated
cell death through AMPK/mTOR signaling in human prostate cancer
cells. Sci Rep. 5:83942015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang J, He H, Yu L, Xia HH, Lin MC, Gu Q,
Li M, Zou B, An X, Jiang B, et al: HSF1 down-regulates XAF1 through
transcriptional regulation. J Biol Chem. 281:2451–2459. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tu SP, Sun YW, Cui JT, Zou B, Lin MC, Gu
Q, Jiang SH, Kung HF, Korneluk RG and Wong BC: Tumor suppressor
XIAP-Associated factor 1 (XAF1) cooperates with tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand to suppress colon cancer
growth and trigger tumor regression. Cancer. 116:1252–1263. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Straszewski-Chavez SL, Visintin IP,
Karassina N, Los G, Liston P, Halaban R, Fadiel A and Mor G: XAF1
mediates tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis and X-linked
inhibitor of apoptosis cleavage by acting through the mitochondrial
pathway. J Biol Chem. 282:13059–13072. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Park GB, Kim YS, Kim D, Kim S, Lee HK, Cho
DH, Lee WJ and Hur DY: Melphalan-induced apoptosis of
EBV-transformed B cells through upregulation of TAp73 and XAF1 and
nuclear import of XPA. J Immunol. 191:6281–6291. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Rigoulet M, Yoboue ED and Devin A:
Mitochondrial ROS generation and its regulation: Mechanisms
involved in H(2)O(2) signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal. 14:459–468.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Huang J, Lam GY and Brumell JH: Autophagy
signaling through reactive oxygen species. Antioxid Redox Signal.
14:2215–2231. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu B, Tan X, Liang J, Wu S, Liu J, Zhang
Q and Zhu R: A reduction in reactive oxygen species contributes to
dihydromyricetin-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Sci Rep. 4:70412014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|