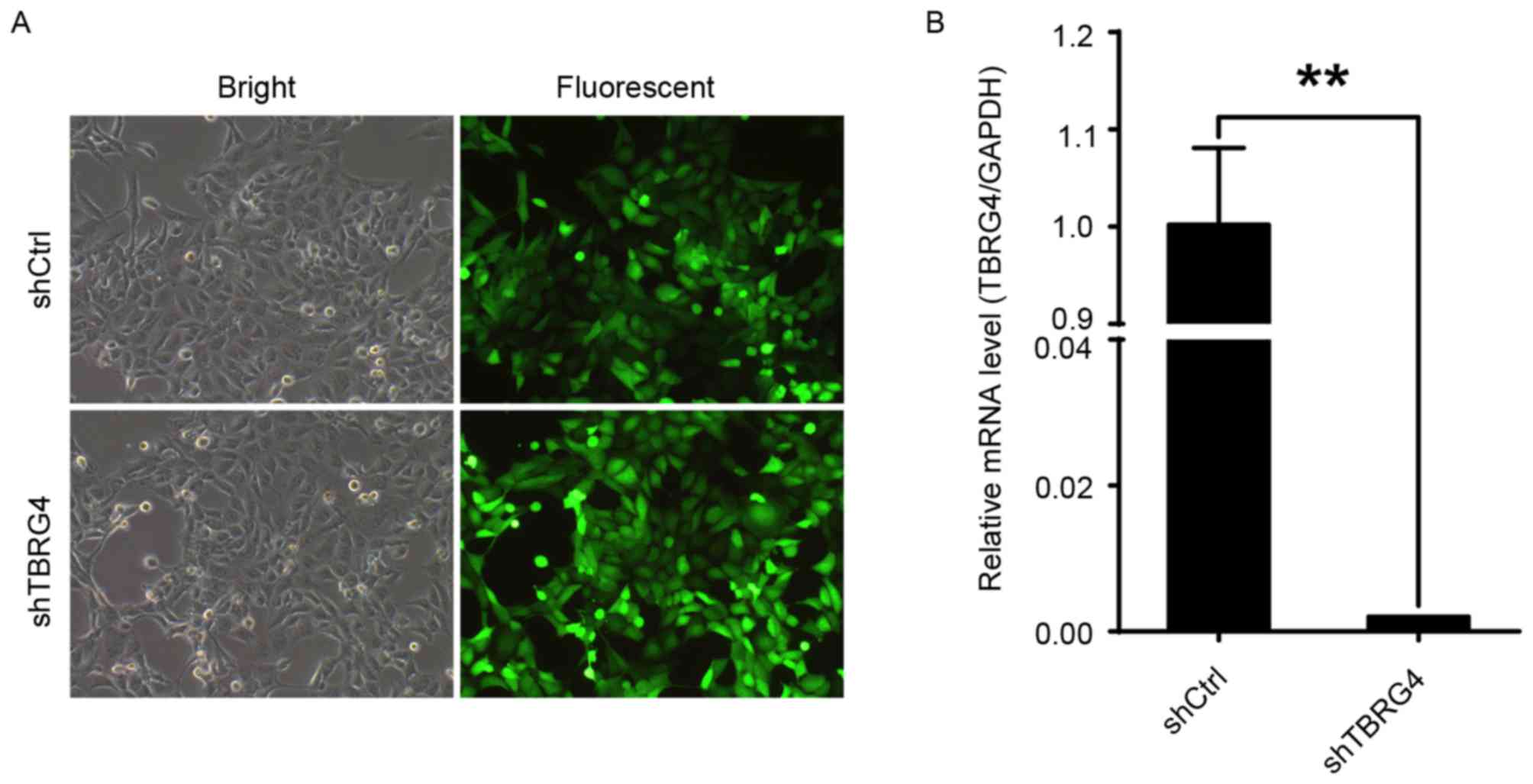
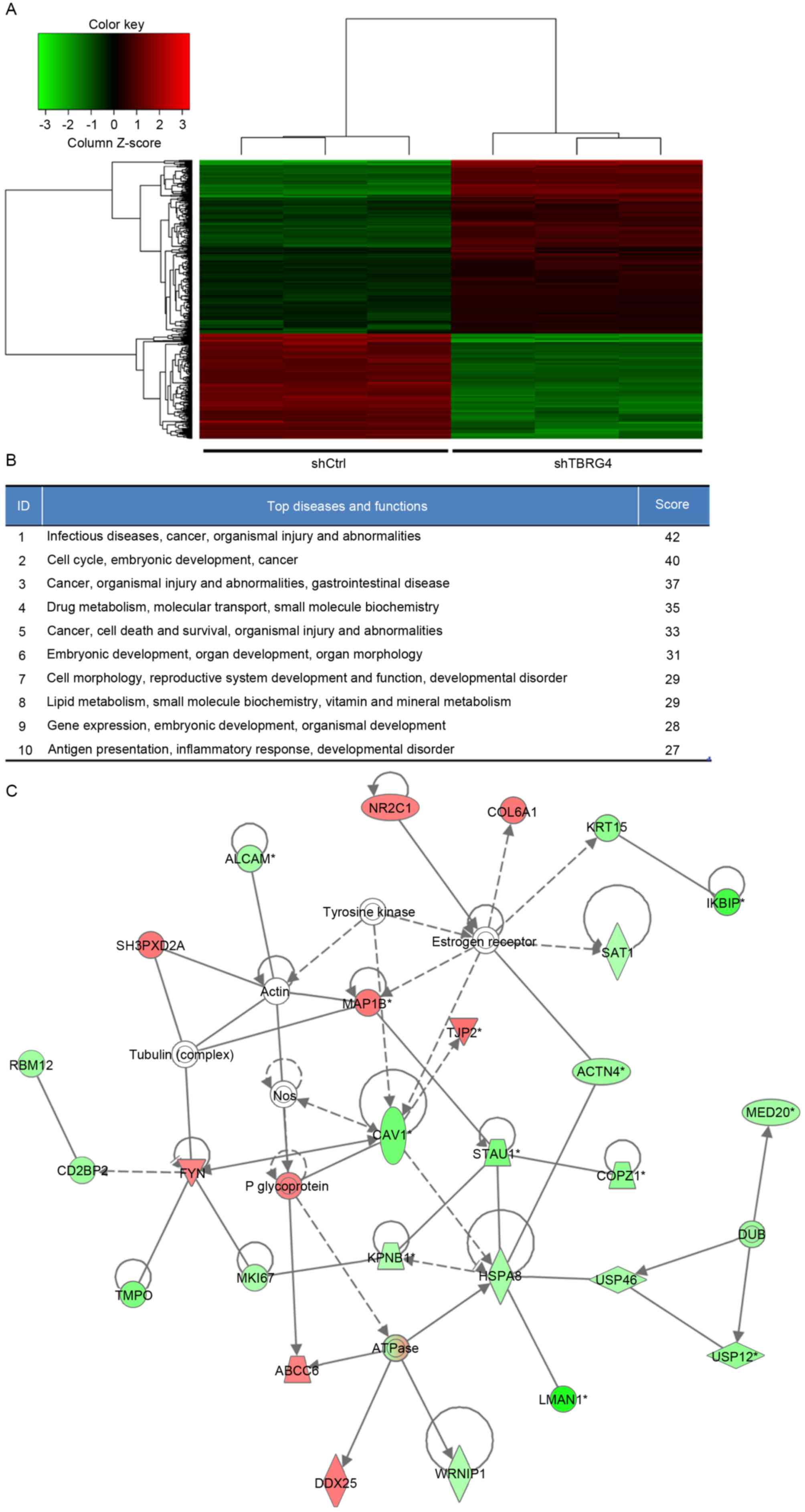
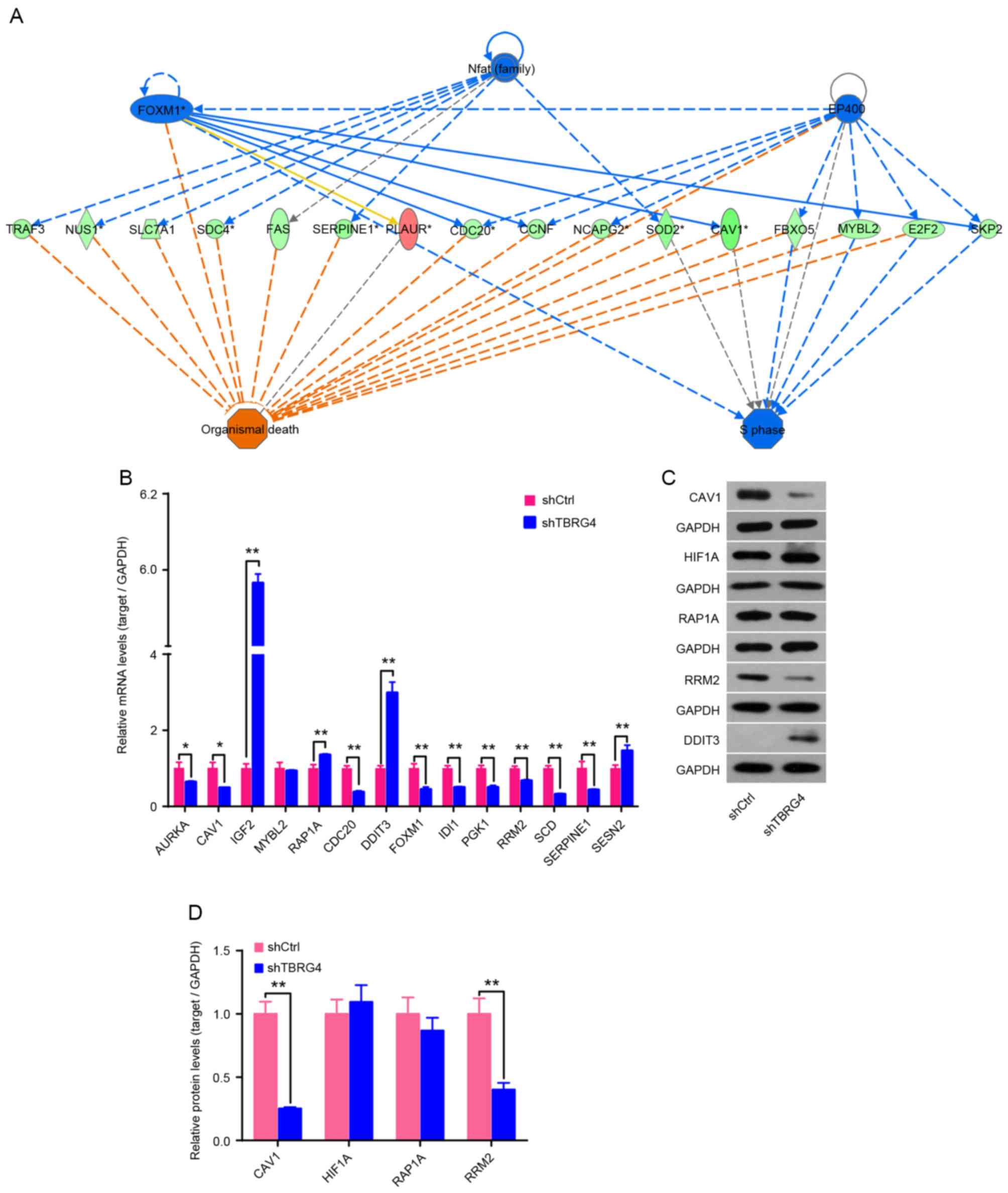
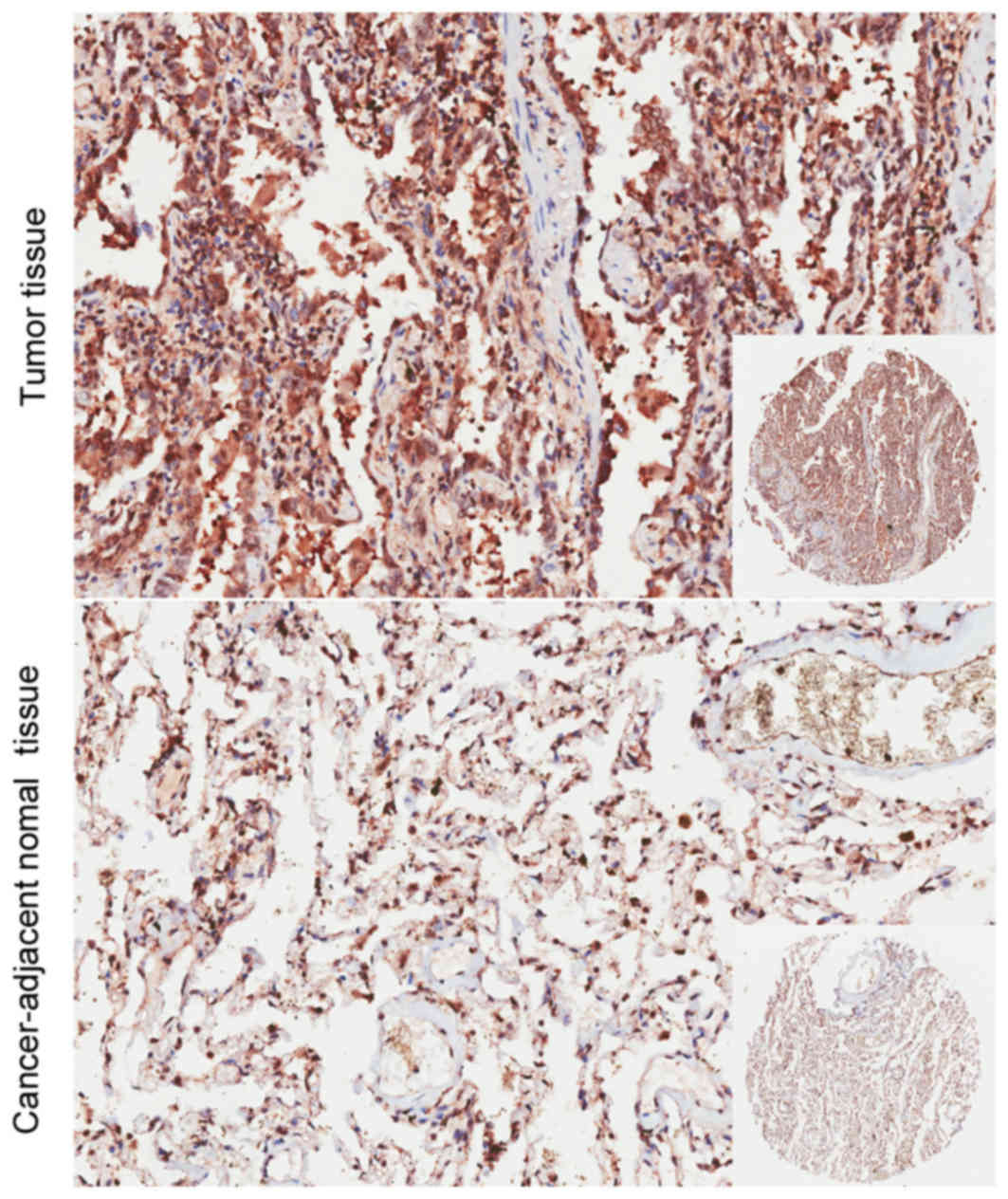
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Reungwetwattana T and Dy GK: Targeted
therapies in development for non-small cell lung cancer. J
Carcinog. 12:222013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kumarakulasinghe NB, van Zanwijk N and Soo
RA: Molecular targeted therapy in the treatment of advanced stage
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Respirology. 20:370–378. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chang JW, Wei NC, Su HJ, Huang JL, Chen
TC, Wu YC, Yu CT, Hou MM, Hsieh CH, Hsieh JJ, et al: Comparison of
genomic signatures of non-small cell lung cancer recurrence between
two microarray platforms. Anticancer Res. 32:1259–1265.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gridelli C and Felip E: Targeted therapies
development in the treatment of advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer.
J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011:4156412011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bergethon K, Shaw AT, Ou SH, Katayama R,
Lovly CM, McDonald NT, Massion PP, Siwak-Tapp C, Gonzalez A, Fang
R, et al: ROS1 rearrangements define a unique molecular class of
lung cancers. J Clin Oncol. 30:863–870. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hammerman PS, Sos ML, Ramos AH, Xu C, Dutt
A, Zhou W, Brace LE, Woods BA, Lin W, Zhang J, et al: Mutations in
the DDR2 kinase gene identify a novel therapeutic target in
squamous cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 1:78–89. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ding L, Getz G, Wheeler DA, Mardis ER,
McLellan MD, Cibulskis K, Sougnez C, Greulich H, Muzny DM, Morgan
MB, et al: Somatic mutations affect key pathways in lung
adenocarcinoma. Nature. 455:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Peifer M, Fernandez-Cuesta L, Sos ML,
George J, Seidel D, Kasper LH, Plenker D, Leenders F, Sun R, Zander
T, et al: Integrative genome analyses identify key somatic driver
mutations of small-cell lung cancer. Nat Genet. 44:1104–1110. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wangari-Talbot J and Hopper-Borge E: Drug
resistance mechanisms in non-small cell lung carcinoma. J Can Res
Updates. 2:265–282. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH,
Derge JG, Klausner RD, Collins FS, Wagner L, Shenmen CM, Schuler
GD, Altschul SF, et al: Generation and initial analysis of more
than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 99:pp. 16899–16903. 2002; PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Edwards MC, Liegeois N, Horecka J, DePinho
RA, Sprague GF Jr, Tyers M and Elledge SJ: Human CPR (cell cycle
progression restoration) genes impart a Far-phenotype on yeast
cells. Genetics. 147:1063–1076. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Simarro M, Gimenez-Cassina A, Kedersha N,
Lazaro JB, Adelmant GO, Marto JA, Rhee K, Tisdale S, Danial N,
Benarafa C, et al: Fast kinase domain-containing protein 3 is a
mitochondrial protein essential for cellular respiration. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 401:440–446. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sevcikova S, Paszekova H, Besse L,
Sedlarikova L, Kubaczkova V, Almasi M, Pour L and Hajek R:
Extramedullary relapse of multiple myeloma defined as the highest
risk group based on deregulated gene expression data. Biomed Pap
Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 159:288–293.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Prasad A, Rabionet R, Espinet B, Zapata L,
Puiggros A, Melero C, Puig A, Sarria-Trujillo Y, Ossowski S,
Garcia-Muret MP, et al: Identification of gene mutations and fusion
genes in patients with sezary syndrome. J Invest Dermatol.
136:1490–1499. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jager S, Cimermancic P, Gulbahce N,
Johnson JR, McGovern KE, Clarke SC, Shales M, Mercenne G, Pache L,
Li K, et al: Global landscape of HIV-human protein complexes.
Nature. 481:365–370. 2012.
|
|
17
|
Rolland T, Tasan M, Charloteaux B, Pevzner
SJ, Zhong Q, Sahni N, Yi S, Lemmens I, Fontanillo C, Mosca R, et
al: A proteome-scale map of the human interactome network. Cell.
159:1212–1226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wolf AR and Mootha VK: Functional genomic
analysis of human mitochondrial RNA processing. Cell Rep.
7:918–931. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu H, Liang S, Yang X, Ji Z, Zhao W, Ye X
and Rui J: RNAi-mediated RPL34 knockdown suppresses the growth of
human gastric cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 34:2267–2272. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li LH, He J, Hua D, Guo ZJ and Gao Q:
Lentivirus-mediated inhibition of Med19 suppresses growth of breast
cancer cells in vitro. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 68:207–215.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lois C, Hong EJ, Pease S, Brown EJ and
Baltimore D: Germline transmission and tissue-specific expression
of transgenes delivered by lentiviral vectors. Science.
295:868–872. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW and Dempfle L:
Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison
and statistical analysis of relative expression results in
real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:e362002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pfaffl MW: A new mathematical model for
relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res.
29:e452001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dubey R, Chhabra R and Saini N: Small
interfering RNA against transcription factor STAT6 leads to
increased cholesterol synthesis in lung cancer cell lines. PLoS
One. 6:e285092011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American Joint
Committee on Cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cho KR and Shih IeM: Ovarian cancer. Annu
Rev Pathol. 4:287–313. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Harvey JM, Clark GM, Osborne CK and Allred
DC: Estrogen receptor status by immunohistochemistry is superior to
the ligand-binding assay for predicting response to adjuvant
endocrine therapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 17:1474–1481.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dyer MJ, Nacheva E, Fischer P, Heward JM,
Labastide W and Karpas A: A new human T-cell lymphoma cell line
(Karpas 384) of the T-cell receptor gamma/delta lineage with
translocation t(7:14) (p13;q11.2). Leukemia. 7:1047–1053.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu H, Krizek J and Bretscher A:
Construction of a GAL1-regulated yeast cDNA expression library and
its application to the identification of genes whose overexpression
causes lethality in yeast. Genetics. 132:665–673. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Carey TE, Van Dyke DL and Worsham MJ:
Nonrandom chromosome aberrations and clonal populations in head and
neck cancer. Anticancer Res. 13:2561–2567. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Han J, Murthy R, Wood B, Song B, Wang S,
Sun B, Malhi H and Kaufman RJ: ER stress signalling through eIF2α
and CHOP, but not IRE1α, attenuates adipogenesis in mice.
Diabetologia. 56:911–924. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Flocke LS, Trondl R, Jakupec MA and
Keppler BK: Molecular mode of action of NKP-1339-a clinically
investigated ruthenium-based drug-involves ER- and ROS-related
effects in colon carcinoma cell lines. Invest New Drugs.
34:261–268. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Engelman JA, Chu C, Lin A, Jo H, Ikezu T,
Okamoto T, Kohtz DS and Lisanti MP: Caveolin-mediated regulation of
signaling along the p42/44 MAP kinase cascade in vivo. A role for
the caveolin-scaffolding domain. FEBS Lett. 428:205–211. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Podar K, Tai YT, Cole CE, Hideshima T,
Sattler M, Hamblin A, Mitsiades N, Schlossman RL, Davies FE, Morgan
GJ, et al: Essential role of caveolae in interleukin-6- and
insulin-like growth factor I-triggered Akt-1-mediated survival of
multiple myeloma cells. J Biol Chem. 278:5794–5801. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Quest AF, Gutierrez-Pajares JL and Torres
VA: Caveolin-1: An ambiguous partner in cell signalling and cancer.
J Cell Mol Med. 12:1130–1150. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li M, Chen H, Diao L, Zhang Y, Xia C and
Yang F: Caveolin-1 and VEGF-C promote lymph node metastasis in the
absence of intratumoral lymphangiogenesis in non-small cell lung
cancer. Tumori. 96:734–743. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fan H, Villegas C and Wright JA:
Ribonucleotide reductase R2 component is a novel malignancy
determinant that cooperates with activated oncogenes to determine
transformation and malignant potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
93:pp. 14036–14040. 1996; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rahman MA, Amin AR, Wang D, Koenig L,
Nannapaneni S, Chen Z, Wang Z, Sica G, Deng X, Chen ZG and Shin DM:
RRM2 regulates Bcl-2 in head and neck and lung cancers: A potential
target for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 19:3416–3428. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mah V, Alavi M, Márquez-Garbán DC, Maresh
EL, Kim SR, Horvath S, Bagryanova L, Huerta-Yepez S, Chia D,
Pietras R and Goodglick L: Ribonucleotide reductase subunit M2
predicts survival in subgroups of patients with non-small cell lung
carcinoma: Effects of gender and smoking status. PLoS One.
10:e01276002015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang H, Liu X, Warden CD, Huang Y, Loera
S, Xue L, Zhang S, Chu P, Zheng S and Yen Y: Prognostic and
therapeutic significance of ribonucleotide reductase small subunit
M2 in estrogen-negative breast cancers. BMC Cancer. 14:6642014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu X, Zhang H, Lai L, Wang X, Loera S,
Xue L, He H, Zhang K, Hu S, Huang Y, et al: Ribonucleotide
reductase small subunit M2 serves as a prognostic biomarker and
predicts poor survival of colorectal cancers. Clin Sci (Lond).
124:567–578. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|