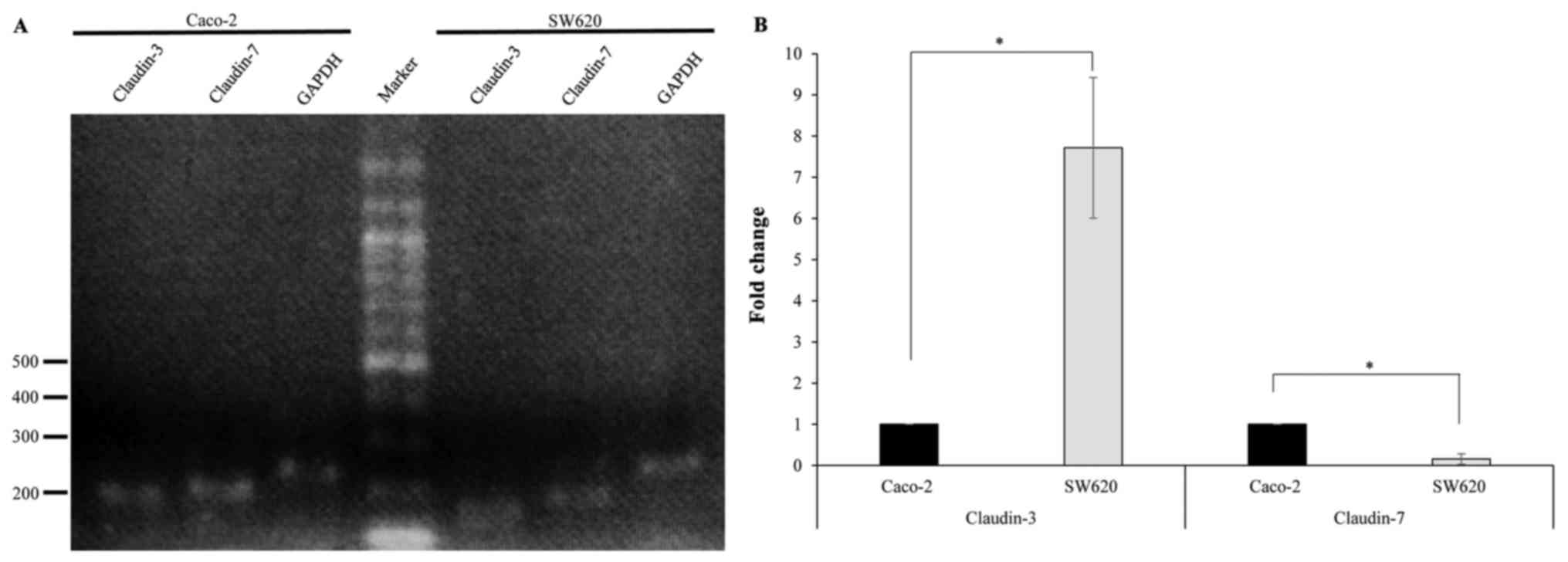
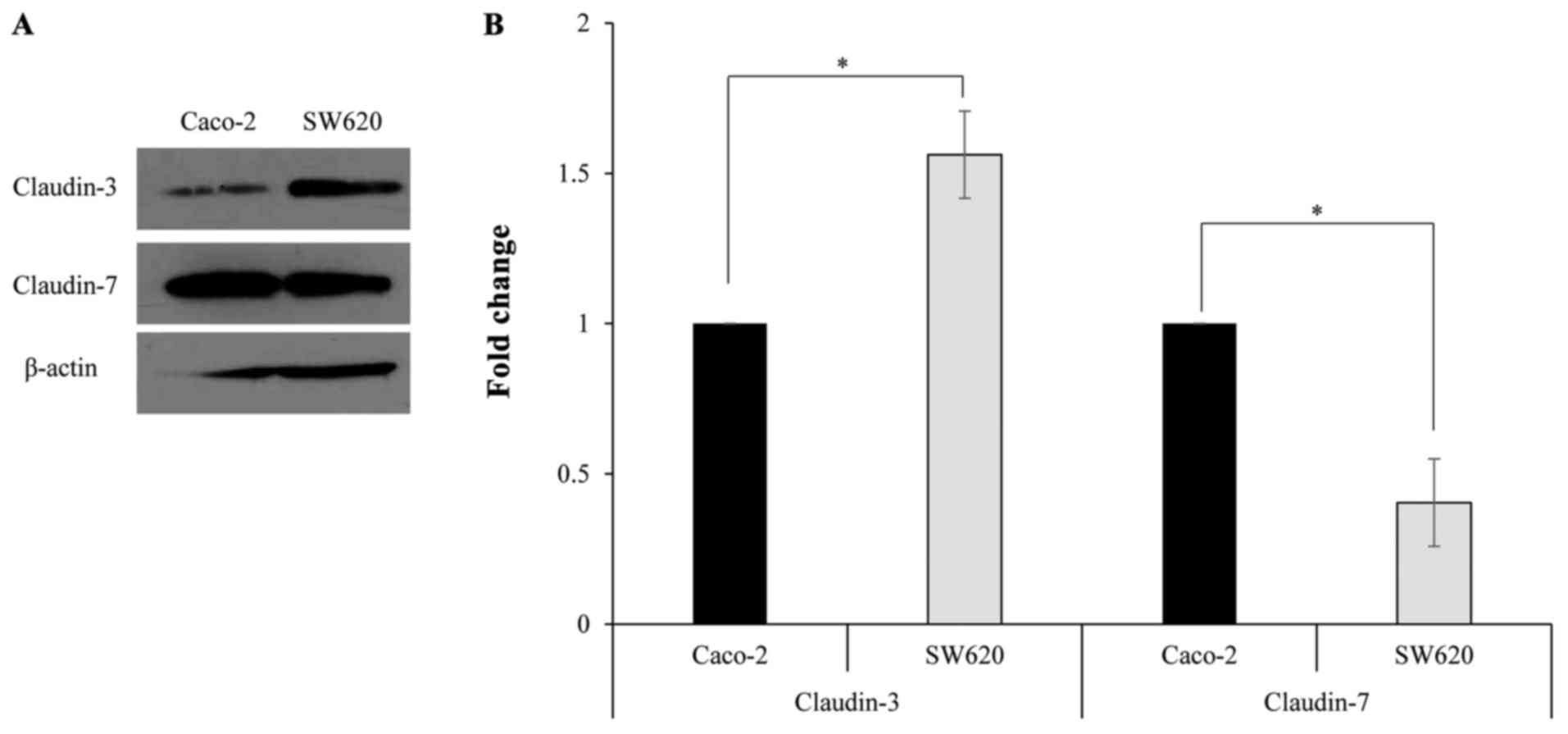
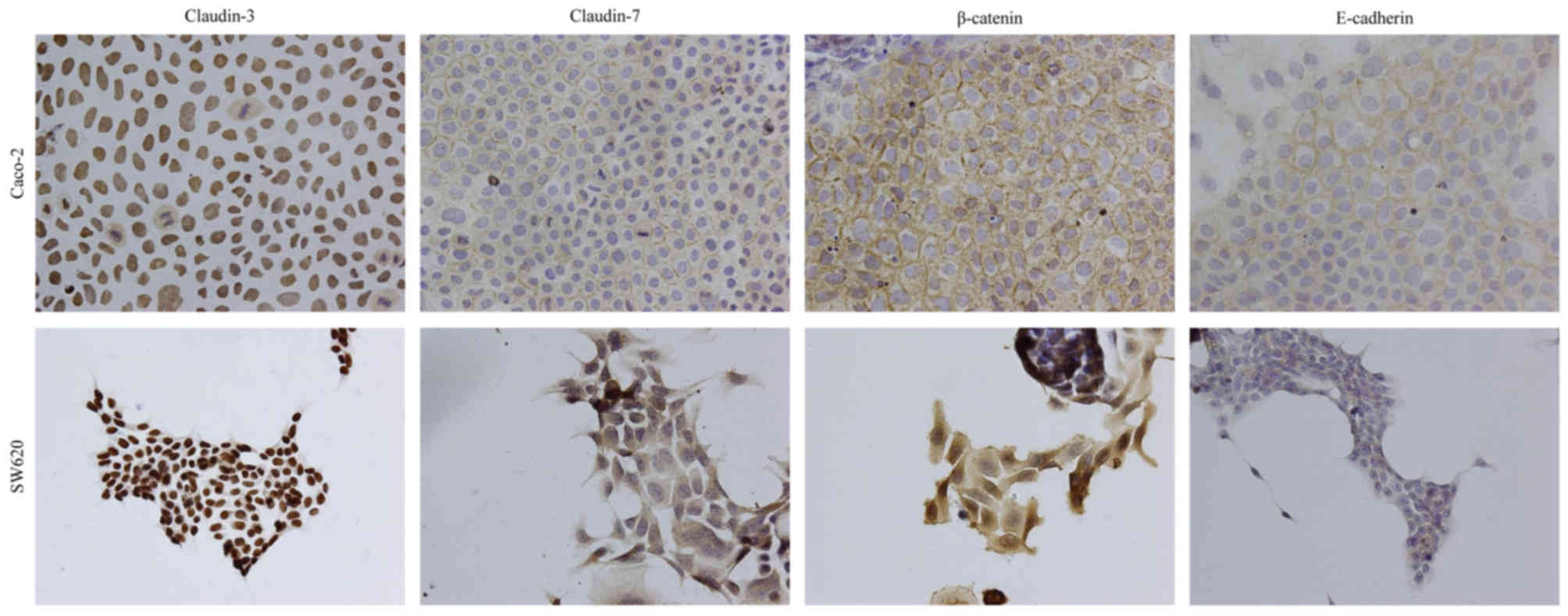
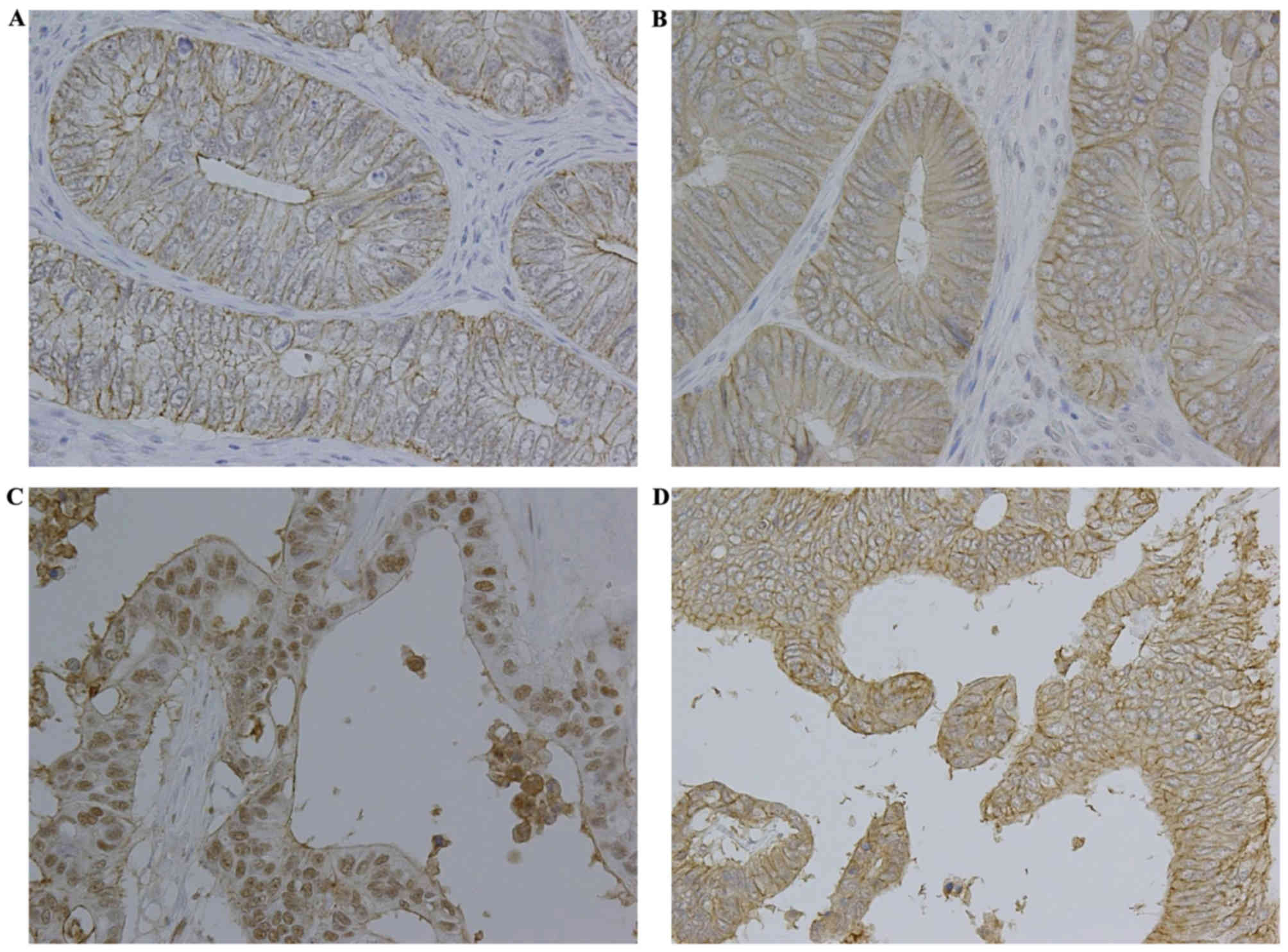
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Weitz J, Koch M, Debus J, Höhler T, Galle
PR and Büchler MW: Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 365:153–165. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fearon ER and Vogelstein B: A genetic
model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 61:759–767. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huber MA, Kraut N and Beug H: Molecular
requirements for epithelial-mesenchymal transition during tumor
progression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 17:548–558. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in development and pathologies. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
15:740–746. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Laskowski P, Klim B, Ostrowski K,
Szkudlarek M, Litwiejko-Pietryńczak E, Kitlas K, Nienartowicz S and
Dzięcioł J: Local inflammatory response in colorectal cancer. Pol J
Pathol. 67:163–171. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Matter K and Balda MS: Signalling to and
from tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 4:225–236. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tsukita S, Furuse M and Itoh M:
Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
2:285–293. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mitic LL, Van Itallie CM and Anderson JM:
Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of tight junctions I.
Tight junction structure and function: Lessons from mutant animals
and proteins. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
279:G250–G254. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mitic LL and Anderson JM: Molecular
architecture of tight junctions. Annu Rev Physiol. 60:121–142.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Langbein L, Pape UF, Grund C, Kuhn C,
Praetzel S, Moll I, Moll R and Franke WW: Tight junction-related
structures in the absence of a lumen: Occludin, claudins and tight
junction plaque proteins in densely packed cell formations of
stratified epithelia and squamous cell carcinomas. Eur J Cell Biol.
82:385–400. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Itoh M and Bissell MJ: The organization of
tight junctions in epithelia: Implications for mammary gland
biology and breast tumorigenesis. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia.
8:449–462. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Martin TA and Jiang WG: Tight junctions
and their role in cancer metastasis. Histol Histopathol.
16:1183–1195. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Martin TA and Jiang WG: Loss of tight
junction barrier function and its role in cancer metastasis.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1788:872–891. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Morita K, Furuse M, Fujimoto K and Tsukita
S: Claudin multigene family encoding four-transmembrane domain
protein components of tight junction strands. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 96:pp. 511–516. 1999; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
McCarthy KM, Skare IB, Stankewich MC,
Furuse M, Tsukita S, Rogers RA, Lynch RD and Schneeberger EE:
Occludin is a functional component of the tight junction. J Cell
Sci. 109:2287–2298. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Matter K, Aijaz S, Tsapara A and Balda MS:
Mammalian tight junctions in the regulation of epithelial
differentiation and proliferation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 17:453–458.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tsukita S, Yamazaki Y, Katsuno T, Tamura A
and Tsukita S: Tight junction-based epithelial microenvironment and
cell proliferation. Oncogene. 27:6930–6938. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dhawan P, Singh AB, Deane NG, No Y, Shiou
SR, Schmidt C, Neff J, Washington MK and Beauchamp RD: Claudin-1
regulates cellular transformation and metastatic behavior in colon
cancer. J Clin Invest. 115:1765–1776. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Itoh M, Furuse M, Morita K, Kubota K,
Saitou M and Tsukita S: Direct binding of three tight
junction-associated MAGUKs, ZO-1, ZO-2 and ZO-3, with the COOH
termini of claudins. J Cell Biol. 147:1351–1363. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mineta K, Yamamoto Y, Yamazaki Y, Tanaka
H, Tada Y, Saito K, Tamura A, Igarashi M, Endo T, Takeuchi K and
Tsukita S: Predicted expansion of the claudin multigene family.
FEBS Lett. 585:606–612. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Turksen K and Troy TC: Barriers built on
claudins. J Cell Sci. 117:2435–2447. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Swisshelm K, Macek R and Kubbies M: Role
of claudins in tumorigenesis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 57:919–928. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Morin PJ: Claudin proteins in human
cancer: Promising new targets for diagnosis and therapy. Cancer
Res. 65:9603–9606. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Soini Y, Tommola S, Helin H and
Martikainen P: Claudins 1, 3, 4 and 5 in gastric carcinoma, loss of
claudin expression associates with the diffuse subtype. Virchows
Arch. 448:52–58. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Miwa N, Furuse M, Tsukita S, Niikawa N,
Nakamura Y and Furukawa Y: Involvement of claudin-1 in the
beta-catenin/Tcf signaling pathway and its frequent upregulation in
human colorectal cancers. Oncol Res. 12:469–476. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Leotlela PD, Wade MS, Duray PH, Rhode MJ,
Brown HF, Rosenthal DT, Dissanayake SK, Earley R, Indig FE,
Nickoloff BJ, et al: Claudin-1 overexpression in melanoma is
regulated by PKC and contributes to melanoma cell motility.
Oncogene. 26:3846–3856. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lee JW, Hsiao WT, Chen HY, Hsu LP, Chen
PR, Lin MD, Chiu SJ, Shih WL and Hsu YC: Upregulated claudin-1
expression confers resistance to cell death of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 126:1353–1366. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ikari A, Sato T, Watanabe R, Yamazaki Y
and Sugatani J: Increase in claudin-2 expression by an
EGFR/MEK/ERK/c-Fos pathway in lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1823:1110–1118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kominsky SL, Argani P, Korz D, Evron E,
Raman V, Garrett E, Rein A, Sauter G, Kallioniemi OP and Sukumar S:
Loss of the tight junction protein claudin-7 correlates with
histological grade in both ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive
ductal carcinoma of the breast. Oncogene. 22:2021–2033. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
de Oliveira SS, de Oliveira IM, De Souza W
and Morgado-Diaz JA: Claudins upregulation in human colorectal
cancer. FEBS Lett. 579:6179–6185. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kinugasa T, Huo Q, Higashi D, Shibaguchi
H, Kuroki M, Tanaka T, Futami K, Yamashita Y, Hachimine K, Maekawa
S, et al: Selective up-regulation of claudin-1 and claudin-2 in
colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 27:3729–3734. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gröne J, Weber B, Staub E, Heinze M,
Klaman I, Pilarsky C, Hermann K, Castanos-Velez E, Röpcke S, Mann
B, et al: Differential expression of genes encoding tight junction
proteins in colorectal cancer: Frequent dysregulation of claudin-1,
−8 and −12. Int J Colorectal Dis. 22:651–659. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ikari A, Watanabe R, Sato T, Taga S,
Shimobaba S, Yamaguchi M, Yamazaki Y, Endo S, Matsunaga T and
Sugatani J: Nuclear distribution of claudin-2 increases cell
proliferation in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1843:2079–2088. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schneider CA, Rasband WS and Eliceiri KW:
NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods.
9:671–675. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Japanese Society for Cancer of the Colon
and Rectum: Japanese Classification of Colorectal Carcinoma. 8th.
Kanehara, Tokyo: 2013
|
|
38
|
Jung H, Jun KH, Jung JH, Chin HM and Park
WB: The expression of claudin-1, claudin-2, claudin-3, and
claudin-4 in gastric cancer tissue. J Surg Res. 167:e185–e191.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zwanziger D, Badziong J, Ting S, Moeller
LC, Schmid KW, Siebolts U, Wickenhauser C, Dralle H and Fuehrer D:
The impact of CLAUDIN-1 on follicular thyroid carcinoma
aggressiveness. Endocr Relat Cancer. 22:819–830. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
French AD, Fiori JL, Camilli TC, Leotlela
PD, O'Connell MP, Frank BP, Subaran S, Indig FE, Taub DD and
Weeraratna AT: PKC and PKA phosphorylation affect the subcellular
localization of claudin-1 in melanoma cells. Int J Med Sci.
6:93–101. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rabinsky EF, Joshi BP, Pant A, Zhou J,
Duan X, Smith A, Kuick R, Fan S, Nusrat A, Owens SR, et al:
Overexpressed claudin-1 can be visualized endoscopically in colonic
adenomas in vivo. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2:222–237. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Islas S, Vega J, Ponce L and
Gonzalez-Mariscal L: Nuclear localization of the tight junction
protein ZO-2 in epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 274:138–148. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gottardi CJ, Arpin M, Fanning AS and
Louvard D: The junction-associated protein, zonula occludens-1,
localizes to the nucleus before the maturation and during the
remodeling of cell-cell contacts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:pp.
10779–10784. 1996; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kosugi S, Hasebe M, Tomita M and Yanagawa
H: Systematic identification of cell cycle-dependent yeast
nucleocytoplasmic shuttling proteins by prediction of composite
motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:pp. 10171–10176. 2009;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Du G, Gu Y, Hao C, Yuan Z, He J, Jiang WG
and Cheng S: The cellular distribution of Na+/H+ exchanger
regulatory factor 1 is determined by the PDZ-I domain and regulates
the malignant progression of breast cancer. Oncotarget.
7:29440–29453. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kausalya PJ, Phua DC and Hunziker W:
Association of ARVCF with zonula occludens (ZO)-1 and ZO-2: binding
to PDZ-domain proteins and cell-cell adhesion regulate plasma
membrane and nuclear localization of ARVCF. Mol Biol Cell.
15:5503–5515. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fabbro M and Henderson BR: Regulation of
tumor suppressors by nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling. Exp Cell Res.
282:59–69. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fagotto F, Glück U and Gumbiner BM:
Nuclear localization signal-independent and
importin/karyopherin-independent nuclear import of beta-catenin.
Curr Biol. 8:181–190. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kemler R: From cadherins to catenins:
Cytoplasmic protein interactions and regulation of cell adhesion.
Trends Genet. 9:317–321. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Munemitsu S, Albert I, Souza B, Rubinfeld
B and Polakis P: Regulation of intracellular beta-catenin levels by
the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) tumor-suppressor protein. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:pp. 3046–3050. 1995; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Liebner S, Corada M, Bangsow T, Babbage J,
Taddei A, Czupalla CJ, Reis M, Felici A, Wolburg H, Fruttiger M, et
al: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling controls development of the
blood-brain barrier. J Cell Biol. 183:409–417. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Fogh J, Wright WC and Loveless JD: Absence
of HeLa cell contamination in 169 cell lines derived from human
tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 58:209–214. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Leibovitz A, Stinson JC, McCombs WB III,
McCoy CE, Mazur KC and Mabry ND: Classification of human colorectal
adenocarcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 36:4562–4569.
1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hewitt RE, McMarlin A, Kleiner D, Wersto
R, Martin P, Tsokos M, Stamp GW and Stetler-Stevenson WG:
Validation of a model of colon cancer progression. J Pathol.
192:446–454. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Agarwal R, D'Souza T and Morin PJ:
Claudin-3 and claudin-4 expression in ovarian epithelial cells
enhances invasion and is associated with increased matrix
metalloproteinase-2 activity. Cancer Res. 65:7378–7385. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kwon MJ, Kim SS, Choi YL, Jung HS, Balch
C, Kim SH, Song YS, Marquez VE, Nephew KP and Shin YK: Derepression
of CLDN3 and CLDN4 during ovarian tumorigenesis is associated with
loss of repressive histone modifications. Carcinogenesis.
31:974–983. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Symonds DA and Vickery AL: Mucinous
carcinoma of the colon and rectum. Cancer. 37:1891–1900. 1976.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Umpleby HC, Ranson DL and Williamson RC:
Peculiarities of mucinous colorectal carcinoma. Br J Surg.
72:715–718. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Minsky BD, Mies C, Rich TA, Recht A and
Chaffey JT: Colloid carcinoma of the colon and rectum. Cancer.
60:3103–3112. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hugen N, van de Velde CJ, de Wilt JH and
Nagtegaal ID: Metastatic pattern in colorectal cancer is strongly
influenced by histological subtype. Ann Oncol. 25:651–657. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Catalano V, Loupakis F, Graziano F,
Torresi U, Bisonni R, Mari D, Fornaro L, Baldelli AM, Giordani P,
Rossi D, et al: Mucinous histology predicts for poor response rate
and overall survival of patients with colorectal cancer and treated
with first-line oxaliplatin- and/or irinotecan-based chemotherapy.
Br J Cancer. 100:881–887. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chen JS, Hsieh PS, Hung SY, Tang R, Tsai
WS, Changchien CR, Lin PY, Wang JY and Yeh CY: Clinical
significance of signet ring cell rectal carcinoma. Int J Colorectal
Dis. 19:102–107. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Mekenkamp LJ, Heesterbeek KJ, Koopman M,
Tol J, Teerenstra S, Venderbosch S, Punt CJ and Nagtegaal ID:
Mucinous adenocarcinomas: Poor prognosis in metastatic colorectal
cancer. Eur J Cancer. 48:501–509. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|