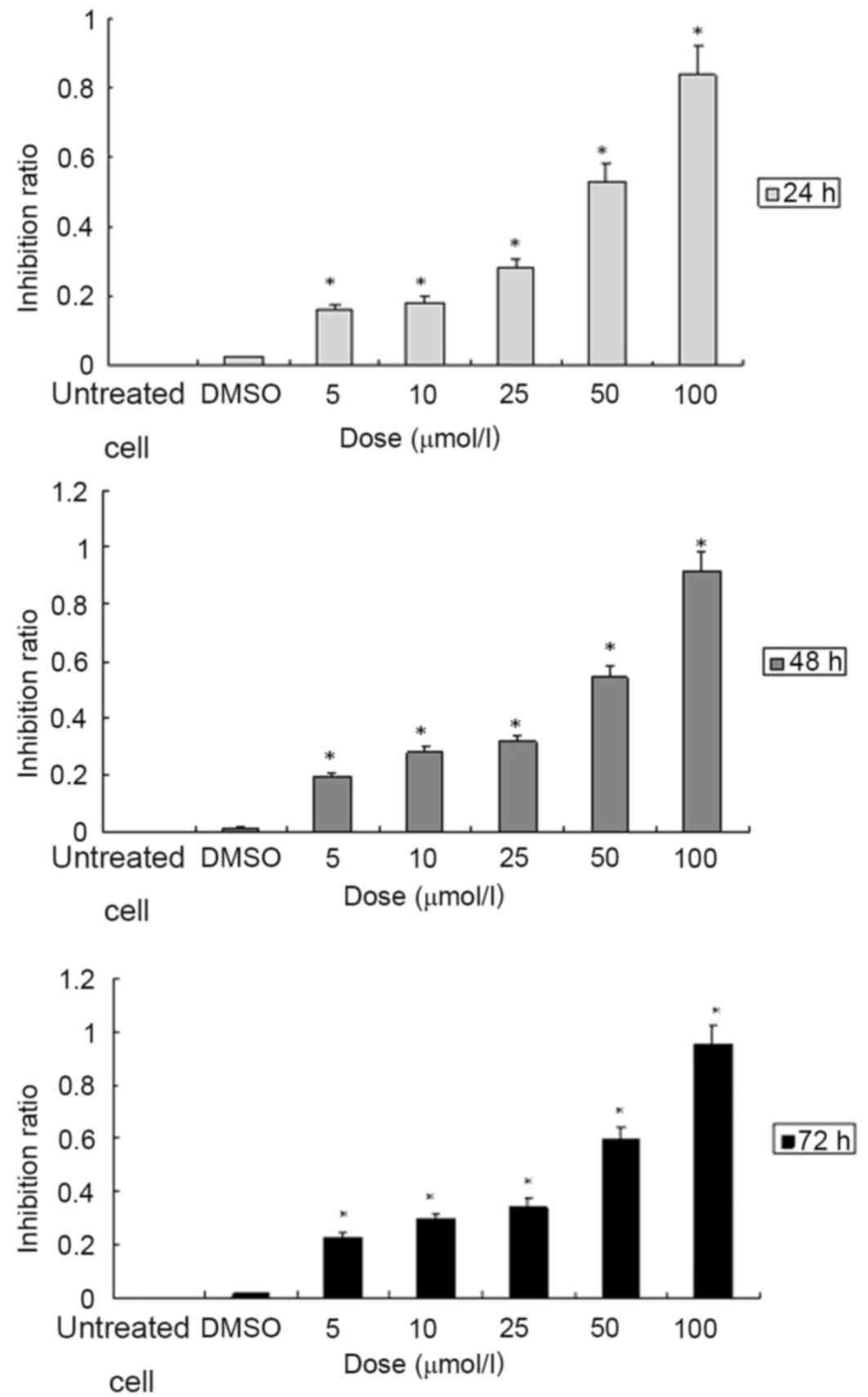
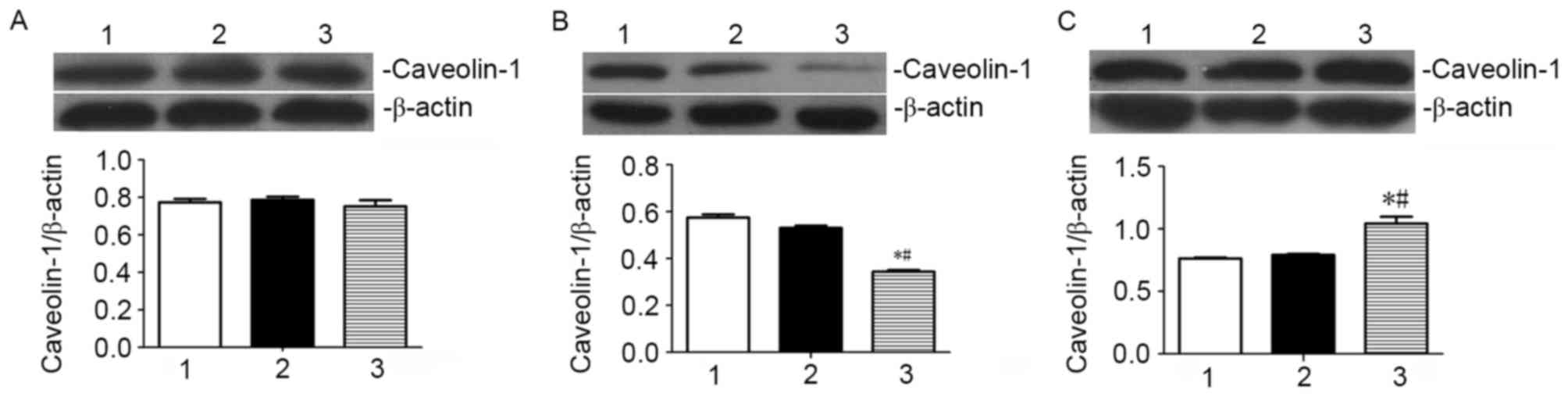
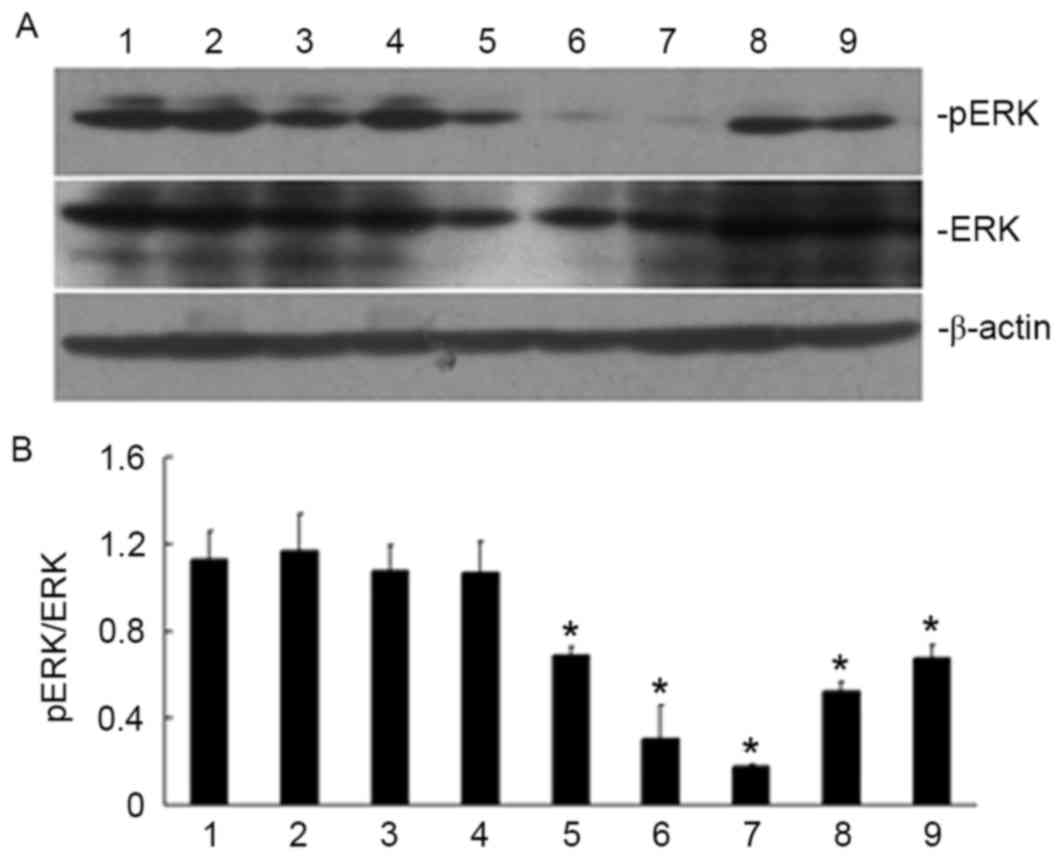
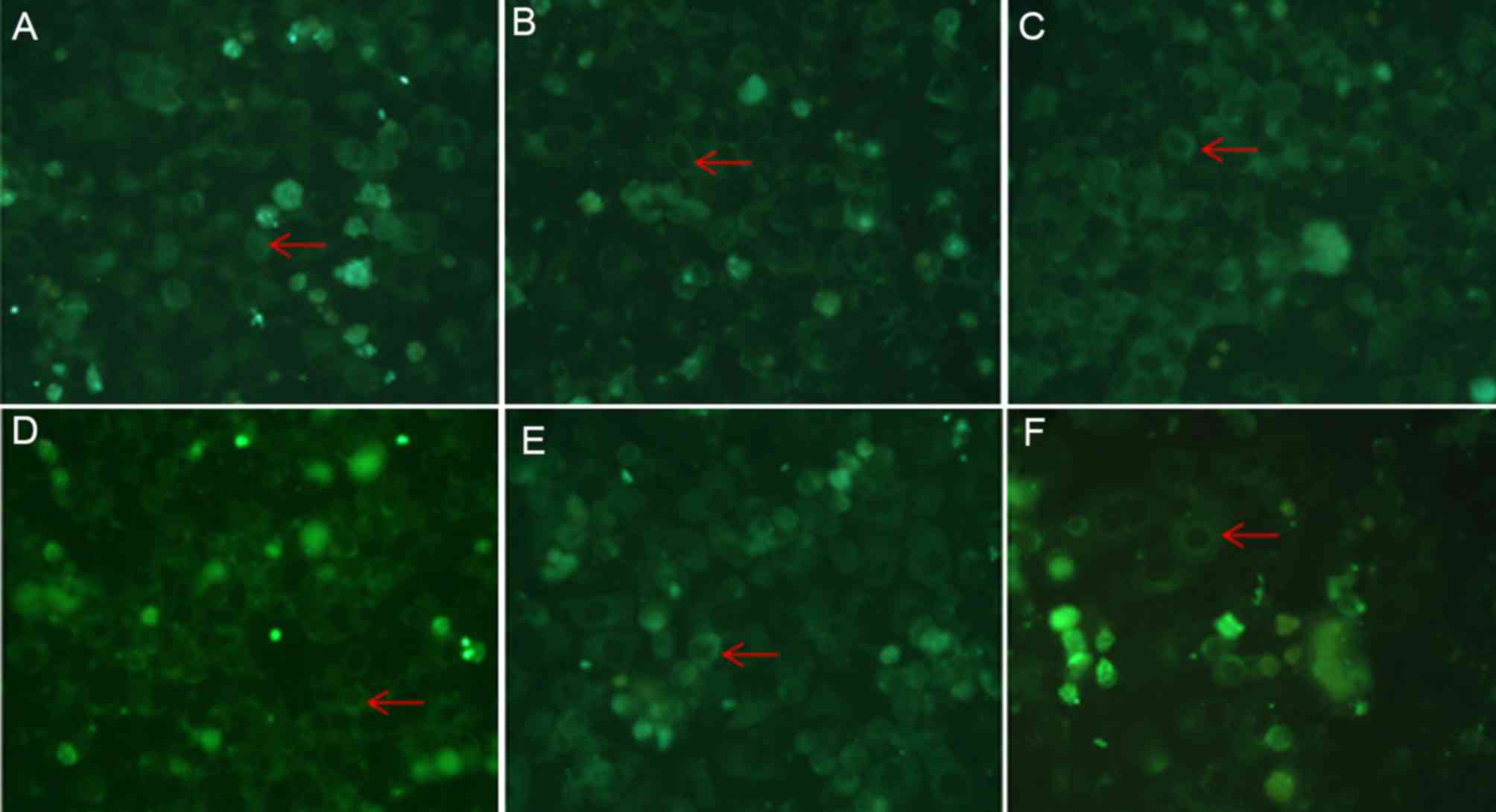
|
1
|
Kamińska K, Szczylik C, Bielecka ZF,
Bartnik E, Porta C, Lian F and Czarnecka AM: The role of the
cell-cell interactions in cancer progression. J Cell Mol Med.
19:283–296. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kovtun O, Tillu VA, Ariotti N, Parton RG
and Collins BM: Cavin family proteins and the assembly of caveolae.
J Cell Sci. 128:1269–1278. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cheng JP and Nichols BJ: Caveolae: One
function or many? Trends Cell Biol. 26:177–189. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fridolfsson HN, Roth DM, Insel PA and
Patel HH: Regulation of intracellular signaling and function by
caveolin. FASEB J. 28:3823–3831. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun GY, Wu JX, Wu JS, Pan YT and Jin R:
Caveolin-1, E-cadherin and β-catenin in gastric carcinoma,
precancerous tissues and chronic non-atrophic gastritis. Chin J
Cancer Res. 24:23–28. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu L, Qu X, Li H, Li C, Liu J, Zheng H and
Liu Y: Src/caveolin-1-regulated EGFR activation antagonizes
TRAIL-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
32:318–324. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhao X, He Y, Gao J, Fan L, Li Z, Yang G
and Chen H: Caveolin-1 expression level in cancer associated
fibroblasts predicts outcome in gastric cancer. PLoS One.
8:e591022013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schenk T, Stengel S and Zelent A:
Unlocking the potential of retinoic acid in anticancer therapy. Br
J Cancer. 111:2039–2045. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma HS, Greenblatt SM, Shirley CM, Duffield
AS, Bruner JK, Li L, Nguyen B, Jung E, Aplan PD, Ghiaur G, et al:
All-trans retinoic acid synergizes with FLT3 inhibition to
eliminate FLT3/ITD+ leukemia stem cells in vitro and in vivo.
Blood. 127:2867–2878. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dutta A, Sen T and Chatterjee A: All-trans
retinoic acid (ATRA) downregulates MMP-9 by modulating its
regulatory molecules. Cell Adh Migr. 4:409–418. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ju J, Wang N, Wang X and Chen F: A novel
all-trans retinoic acid derivative inhibits proliferation and
induces differentiation of human gastric carcinoma xenografts via
up-regulating retinoic acid receptor β. Am J Transl Res. 7:856–865.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Scudiero DA, Shoemaker RH, Paull KD, Monks
A, Tierney S, Nofziger TH, Currens MJ, Seniff D and Boyd MR:
Evaluation of a soluble tetrazolium/formazan assay for cell growth
and drug sensitivity in culture using human and other tumor cell
lines. Cancer Res. 48:4827–4833. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jin K, Li T, van Dam H, Zhou F and Zhang
L: Molecular insights into tumour metastasis: Tracing the dominant
events. J Pathol. 241:567–577. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Fine SW, Lisanti MP, Galbiati F and Li M:
Elevated expression of Caveolin-1 in adenocarcinoma of the colon.
Am J Clin Pathol. 115:719–724. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang Y, Hu XJ, Zhang LL, Sun LP, Yuan Y,
Qu XJ and Liu YP: Interaction among Caveolin-1 genotypes
(rs3807987/rs7804372), H. pylori infection, and risk of gastric
cancer in a Chinese population. Tumour Biol. 35:1511–1516. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Burgermeister E, Xing X, Röcken C, Juhasz
M, Chen J, Hiber M, Mair K, Shatz M, Liscovitch M, Schmid RM and
Ebert MP: Differential expression and function of caveolin-1 in
human gastric cancer progression. Cancer Res. 67:8519–8526. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Galbiati F, Volonté D, Liu J, Capozza F,
Frank PG, Zhu L, Pestell RG and Lisanti MP: Caveolin-1 expression
negatively regulates cell cycle progression by inducingG(0)/G(1)
arrest via a p53/p21(WAF1/Cip1)-dependent mechanism. Mol Biol Cell.
12:2229–2244. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Williams TM and Lisanti MP: The Caveolin
genes: From cell biology to medicine. Ann Med. 36:584–595. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hitkova I, Yuan G, Anderl F, Gerhard M,
Kirchner T, Reu S, Röcken C, Schäfer C, Schmid RM, Vogelmann R, et
al: Caveolin-1 protects B6129 mice against Helicobacter pylori
gastritis. PloS Pathog. 9:e10032512013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kannan A, Krishnan A, Ali M, Subramaniam
S, Halagowder D and Sivasithamparam ND: Caveolin-1 promotes gastric
cancer progression by up-regulating epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by crosstalk of signalling mechanisms under hypoxic
condition. Eur J Cancer. 50:204–215. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chu JH, Gao ZH and Qu XJ: Down-regulation
of sphingosine kinase 2 (SphK2) increases the effects of
all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) on colon cancer cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 68:1089–1097. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun R, Liu Y, Li SY, Shen S, Du XJ, Xu CF,
Cao ZT, Bao Y, Zhu YH, Li YP, et al: Co-delivery of
all-trans-retinoic acid and doxorubicin for cancer therapy with
synergistic inhibition of cancerstem cells. Biomaterials.
37:405–414. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin E, Chen MC, Huang CY, Hsu SL, Huang
WJ, Lin MS, Wu JC and Lin H: All-trans retinoic acid induces DU145
cell cycle arrest through Cdk5 activation. Cell Physiol Biochem.
33:1620–1630. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|