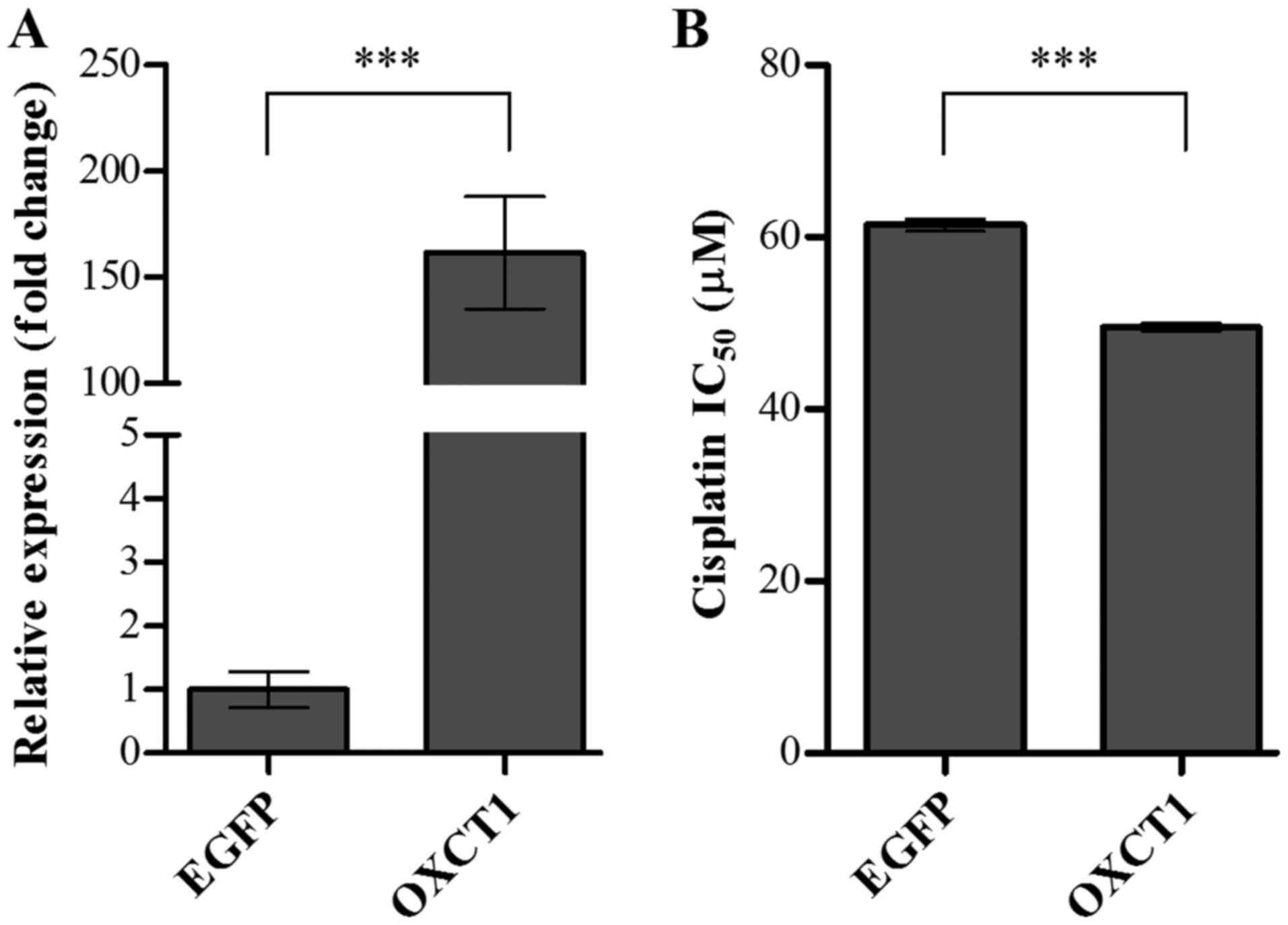
|
1
|
Lowe KA, Chia VM, Taylor A, O'Malley C,
Kelsh M, Mohamed M, Mowat FS and Goff B: An international
assessment of ovarian cancer incidence and mortality. Gynecol
Oncol. 130:107–114. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Notani PN: Global variation in cancer
incidence and mortality. Curr Sci-Bangalore. 81:465–474. 2001.
|
|
3
|
Salani R, Backes FJ, Fung MF, Holschneider
CH, Parker LP, Bristow RE and Goff BA: Posttreatment surveillance
and diagnosis of recurrence in women with gynecologic malignancies:
Society of gynecologic oncologists recommendations. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 204:466–478. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ruan Z, Liu J and Kuang Y: Isolation and
characterization of side population cells from the human ovarian
cancer cell line SK-OV-3. Exp Ther Med. 10:2071–2078. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Borley J, Wilhelm-Benartzi C, Brown R and
Ghaem-Maghami S: Does tumour biology determine surgical success in
the treatment of epithelial ovarian cancer? A systematic literature
review. Br J Cancer. 107:1069–1074. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mantia-Smaldone GM, Edwards RP and Vlad
AM: Targeted treatment of recurrent platinum-resistant ovarian
cancer: Current and emerging therapies. Cancer Manag Res. 3:25–38.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lopez J, Percharde M, Coley HM, Webb A and
Crook T: The context and potential of epigenetics in oncology. Br J
Cancer. 100:571–577. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bird A: Does DNA methylation control
transposition of selfish elements in the germline? Trends Genet.
13:469–472. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thiel G, Lietz M and Hohl M: How mammalian
transcriptional repressors work. Eur J Biochem. 271:2855–2862.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Suzuki MM and Bird A: DNA methylation
landscapes: Provocative insights from epigenomics. Nat Rev Genet.
9:465–476. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chang X, Monitto CL, Demokan S, Kim MS,
Chang SS, Zhong X, Califano JA and Sidransky D: Identification of
hypermethylated genes associated with cisplatin resistance in human
cancers. Cancer Res. 70:2870–2879. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen CC, Lee KD, Pai MY, Chu PY, Hsu CC,
Chiu CC, Chen LT, Chang JY, Hsiao SH and Leu YW: Changes in DNA
methylation are associated with the development of drug resistance
in cervical cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 15:982015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Su HY, Lai HC, Lin YW, Liu CY, Chen CK,
Chou YC, Lin SP, Lin WC, Lee HY and Yu MH: Epigenetic silencing of
SFRP5 is related to malignant phenotype and chemoresistance of
ovarian cancer through Wnt signaling pathway. Int J Cancer.
127:555–567. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li M, Balch C, Montgomery JS, Jeong M,
Chung JH, Yan P, Huang TH, Kim S and Nephew KP: Integrated analysis
of DNA methylation and gene expression reveals specific signaling
pathways associated with platinum resistance in ovarian cancer. BMC
Med Genomics. 2:342009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nam GH, Ahn K, Bae JH, Cho BW, Park KD,
Lee HK, Yang YM, Kim TH, Seong HH, Han K and Kim HS: Identification
of ORF sequences and exercise-induced expression change in
thoroughbred horse OXCT1 gene. Gene. 496:45–48. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Smyth GK: Linear models and empirical
bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray
experiments. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol. 3:Article32004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J R Statist Soc B. 57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang YW, Zheng Y, Wang JZ, Lu XX, Wang Z,
Chen LB, Guan XX and Tong JD: Integrated analysis of DNA
methylation and mRNA expression profiling reveals candidate genes
associated with cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer.
Epigenetics. 9:896–909. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang G, Reed E and Li QQ: Molecular basis
of cellular response to cisplatin chemotherapy in non-small cell
lung cancer (Review). Oncol Rep. 12:955–965. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shen DW, Pouliot LM, Hall MD and Gottesman
MM: Cisplatin resistance: A cellular self-defense mechanism
resulting from multiple epigenetic and genetic changes. Pharmacol
Rev. 64:706–721. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sanchez-Alvarez R, Martinez-Outschoorn UE,
Lin Z, Lamb R, Hulit J, Howell A, Sotgia F, Rubin E and Lisanti MP:
Ethanol exposure induces the cancer-associated fibroblast phenotype
and lethal tumor metabolism: Implications for breast cancer
prevention. Cell Cycle. 12:289–301. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shi S, Wang Q, Xu J, Jang JH, Padilla MT,
Nyunoya T, Xing C, Zhang L and Lin Y: Synergistic anticancer effect
of cisplatin and Chal-24 combination through IAP and c-FLIPL
degradation, Ripoptosome formation and autophagy-mediated
apoptosis. Oncotarget. 6:1640–1651. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kimmelman AC: The dynamic nature of
autophagy in cancer. Genes Dev. 25:1999–2010. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu WK, Coffelt SB, Cho CH, Wang XJ, Lee
CW, Chan FK, Yu J and Sung JJ: The autophagic paradox in cancer
therapy. Oncogene. 31:939–953. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|