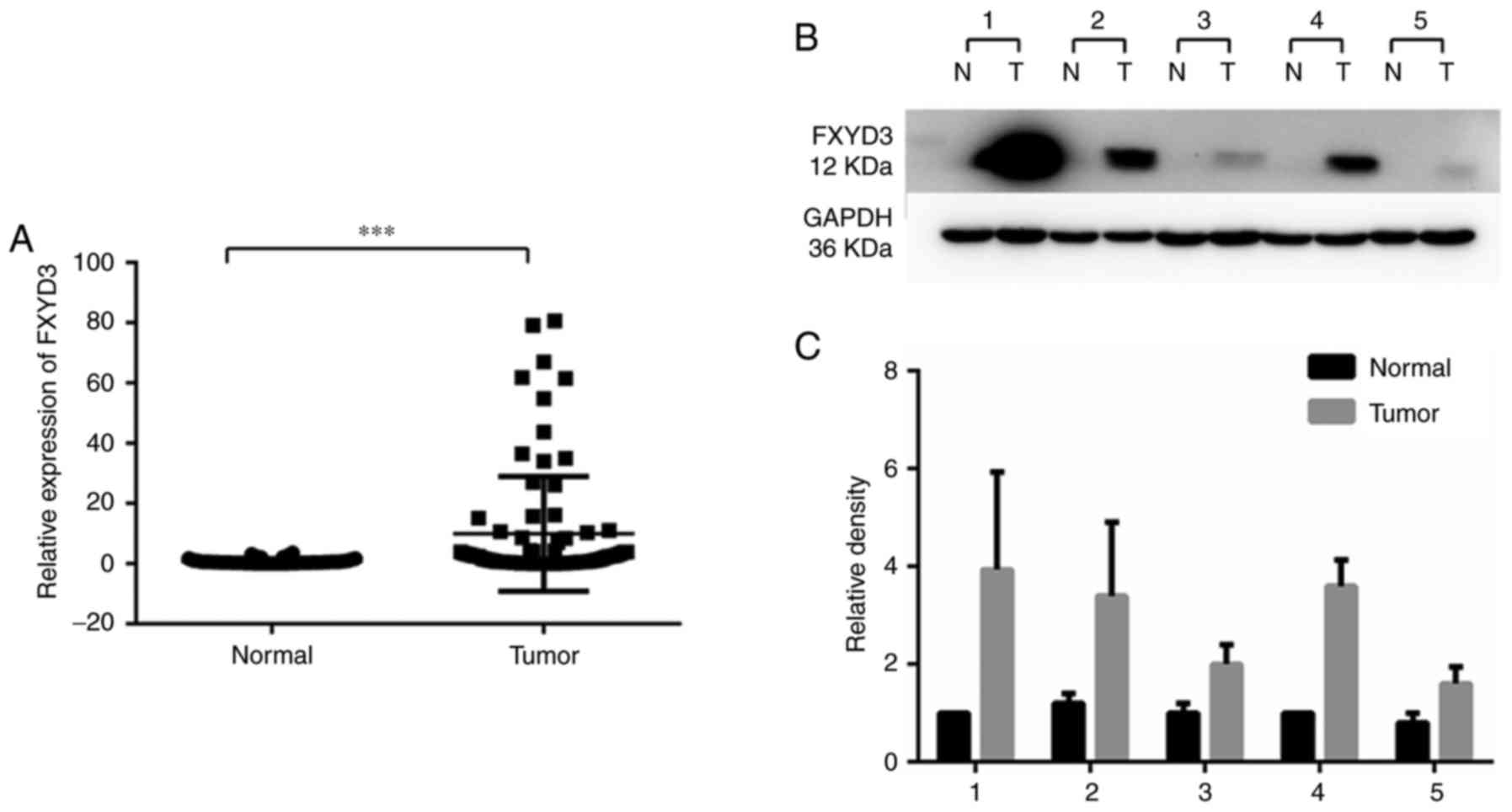
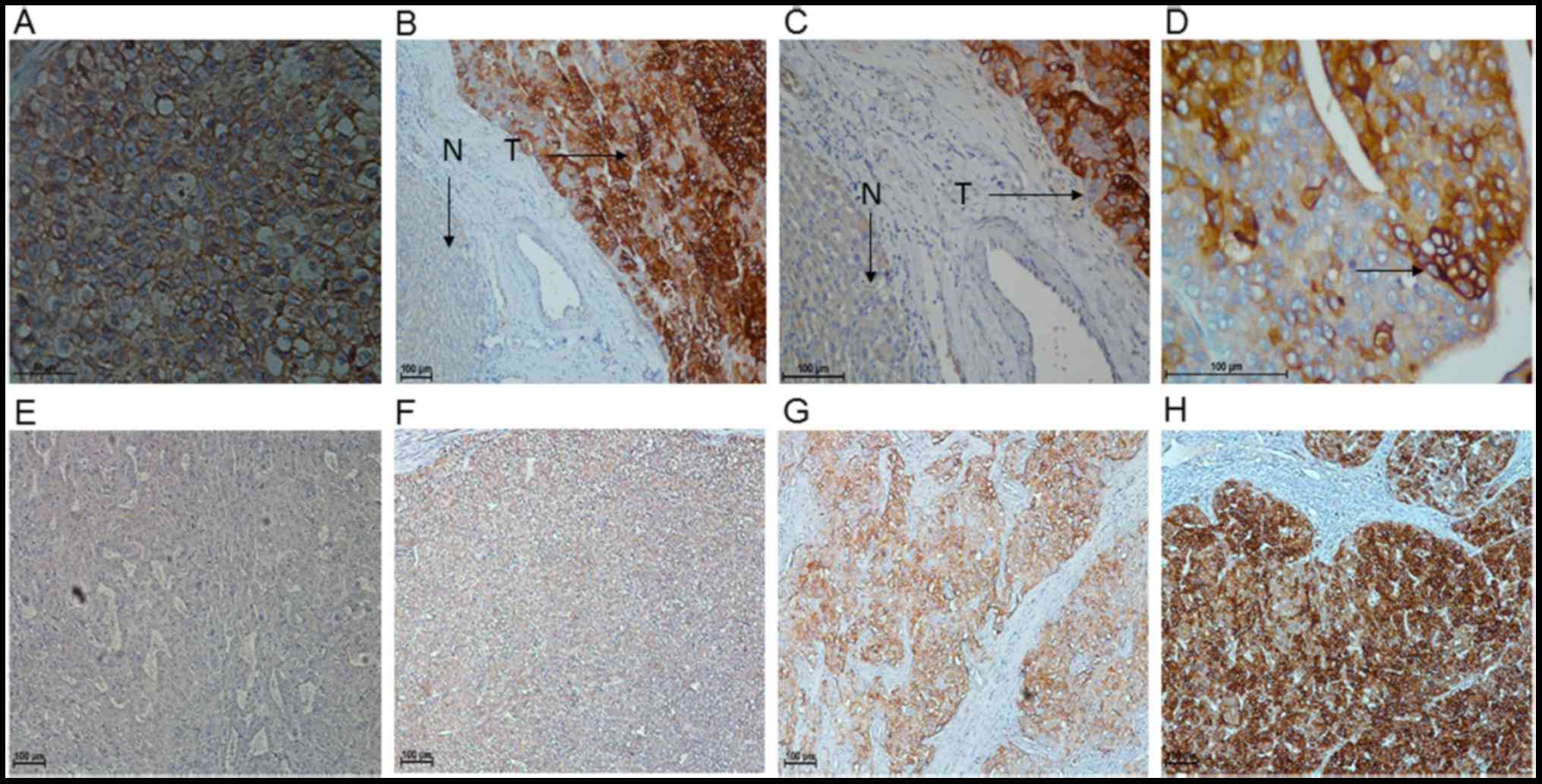
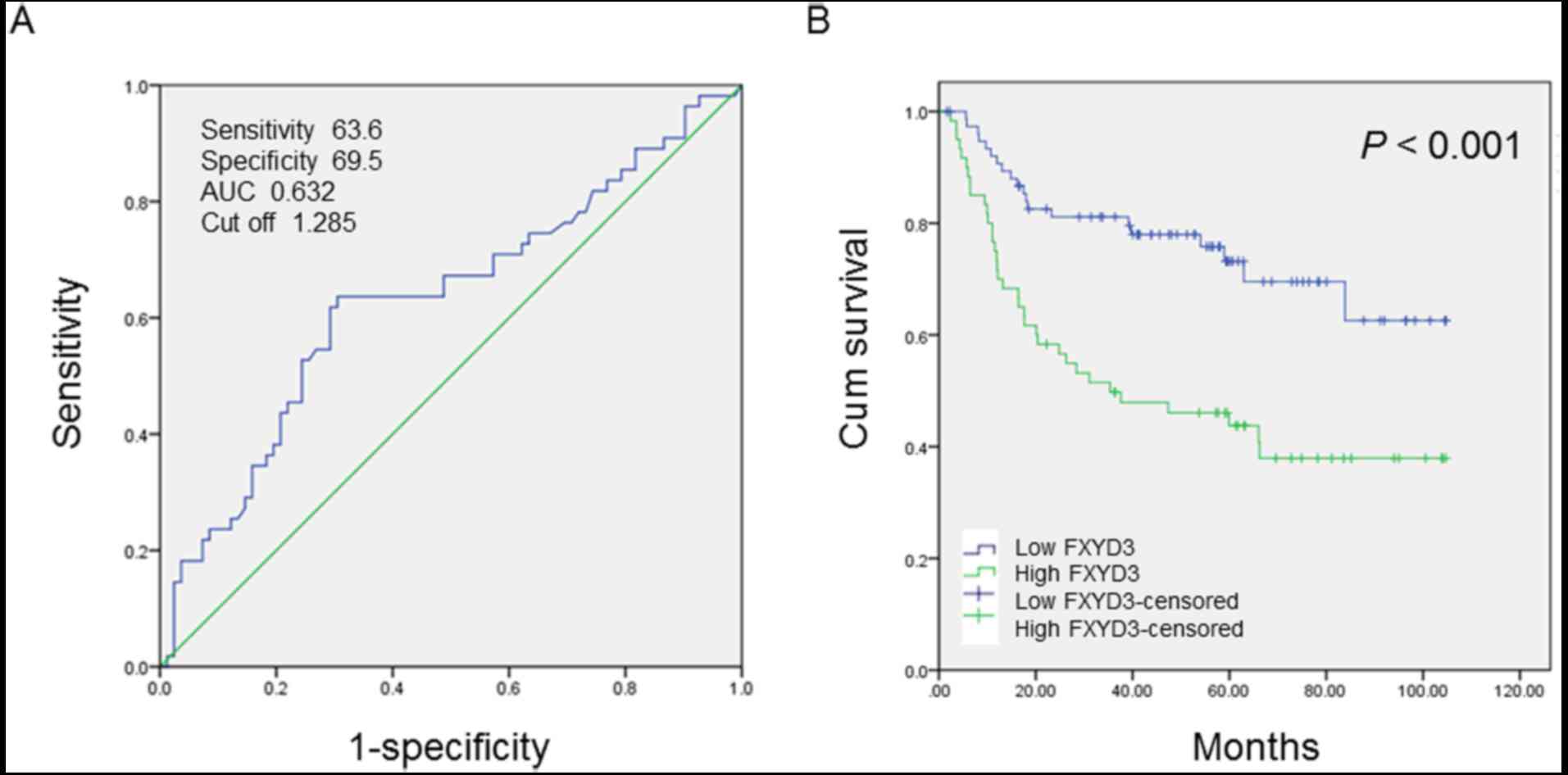
|
1
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
He G, Dhar D, Nakagawa H, Font-Burgada J,
Ogata H, Jiang Y, Shalapour S, Seki E, Yost SE, Jepsen K, et al:
Identification of liver cancer progenitors whose malignant
progression depends on autocrine IL-6 signaling. Cell. 155:384–396.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li Z, Tuteja G, Schug J and Kaestner KH:
Foxa1 and Foxa2 are essential for sexual dimorphism in liver
cancer. Cell. 148:72–83. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maluccio M and Covey A: Recent progress in
understanding, diagnosing, and treating hepatocellular carcinoma.
CA Cancer J Clin. 62:394–399. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Morrison BW and Leder P: Neu and ras
initiate murine mammary tumors that share genetic markers generally
absent in c-myc and int-2-initiated tumors. Oncogene. 9:3417–3426.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Morrison BW, Moorman JR, Kowdley GC,
Kobayashi YM, Jones LR and Leder P: Mat-8, a novel
phospholemman-like protein expressed in human breast tumors,
induces a chloride conductance in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem.
270:2176–2182. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhuang L, Xu L, Wang P, Jiang Y, Yong P,
Zhang C, Zhang H, Meng Z and Yang P:
Na+/K+-ATPase α1 subunit, a novel therapeutic
target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:28183–28193.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Capendeguy O and Horisberger JD:
Functional effects of Na+, K+-ATPase gene
mutations linked to familial hemiplegic migraine. Neuromolecular
Med. 6:105–116. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Capurro C, Coutry N, Bonvalet JP, Escoubet
B, Garty H and Farman N: Cellular localization and regulation of
CHIF in kidney and colon. Am J Physiol. 271:C753–C762. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vaarala MH, Porvari K, Kyllönen A and
Vihko P: Differentially expressed genes in two LNCaP prostate
cancer cell lines reflecting changes during prostate cancer
progression. Lab Invest. 80:1259–1268. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Grzmil M, Voigt S, Thelen P, Hemmerlein B,
Helmke K and Burfeind P: Up-regulated expression of the MAT-8 gene
in prostate cancer and its siRNA-mediated inhibition of expression
induces a decrease in proliferation of human prostate carcinoma
cells. Int J Oncol. 24:97–105. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Widegren E, Onnesjö S, Arbman G, Kayed H,
Zentgraf H, Kleeff J, Zhang H and Sun XF: Expression of FXYD3
protein in relation to biological and clinicopathological variables
in colorectal cancers. Chemotherapy. 55:407–413. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Maitra A, Olsen M,
Lowe AW, van Heek NT, Rosty C, Walter K, Sato N, Parker A, Ashfaq
R, et al: Exploration of global gene expression patterns in
pancreatic adenocarcinoma using cDNA microarrays. Am J Pathol.
162:1151–1162. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Friess H, Ding J, Kleeff J, Fenkell L,
Rosinski JA, Guweidhi A, Reidhaar-Olson JF, Korc M, Hammer J and
Büchler MW: Microarray-based identification of differentially
expressed growth- and metastasis-associated genes in pancreatic
cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. 60:1180–1199. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Logsdon CD, Simeone DM, Binkley C,
Arumugam T, Greenson JK, Giordano TJ, Misek DE, Kuick R and Hanash
S: Molecular profiling of pancreatic adenocarcinoma and chronic
pancreatitis identifies multiple genes differentially regulated in
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 63:2649–2657. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhu ZL, Yan BY, Zhang Y, Yang YH, Wang MW,
Zentgraf H, Zhang XH and Sun XF: Overexpression of FXYD-3 is
involved in the tumorigenesis and development of esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Markers. 35:195–202. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gordon GJ, Richards WG, Sugarbaker DJ,
Jaklitsch MT and Bueno R: A prognostic test for adenocarcinoma of
the lung from gene expression profiling data. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 12:905–910. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Okudela K, Yazawa T, Ishii J, Woo T,
Mitsui H, Bunai T, Sakaeda M, Shimoyamada H, Sato H, Tajiri M, et
al: Down-regulation of FXYD3 expression in human lung cancers: Its
mechanism and potential role in carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol.
175:2646–2656. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang MW, Gu P, Zhang ZY, Zhu ZL, Geng Y,
Kayed H, Zentgraf H and Sun XF: FXYD3 expression in gliomas and its
clinicopathological significance. Oncol Res. 18:133–139. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Instructions of the Anti-FXYD3 antibody:
Anti-FXYD3 antibody [EPR17160] ab205534. http://www.abcam.com/fxyd3-antibody-epr17160-ab205534.html
|
|
23
|
Llovet JM, Brú C and Bruix J: Prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma: The BCLC staging classification. Semin
Liver Dis. 19:329–338. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
OuYang HY, Xu J, Luo J, Zou RH, Chen K, Le
Y, Zhang YF, Wei W, Guo RP and Shi M: MEP1A contributes to tumor
progression and predicts poor clinical outcome in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 63:1227–1239. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kaseb AO, Hassan MM, Lin E, Xiao L, Kumar
V, Pathak P, Lozano R, Rashid A, Abbruzzese JL and Morris JS:
V-CLIP: Integrating plasma vascular endothelial growth factor into
a new scoring system to stratify patients with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma for clinical trials. Cancer.
117:2478–2488. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kaseb AO, Abbruzzese JL, Vauthey JN, Aloia
TA, Abdalla EK, Hassan MM, Lin E, Xiao L, El-Deeb AS, Rashid A and
Morris JS: I-CLIP: Improved stratification of advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma patients by integrating plasma IGF-1 into
CLIP score. Oncology. 80:373–381. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yamamoto H, Mukaisho K, Sugihara H,
Hattori T and Asano S: Down-regulation of FXYD3 is induced by
transforming growth factor-β signaling via ZEB1/δEF1 in human
mammary epithelial cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 34:324–329. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Herrmann P and Aronica SM: Estrogen and
tamoxifen up-regulate FXYD3 on breast cancer cells: Assessing the
differential roles of ER α and ZEB1. SpringerPlus. 4:2452015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bibert S, Aebischer D, Desgranges F, Roy
S, Schaer D, Kharoubi-Hess S, Horisberger JD and Geering K: A link
between FXYD3 (Mat-8)-mediated Na,K-ATPase regulation and
differentiation of Caco-2 intestinal epithelial cells. Mol Biol
Cell. 20:1132–1140. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Maxwell PJ, Longley DB, Latif T, Boyer J,
Allen W, Lynch M, McDermott U, Harkin DP, Allegra CJ and Johnston
PG: Identification of 5-fluorouracil-inducible target genes using
cDNA microarray profiling. Cancer Res. 63:4602–4606.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kanai R, Ogawa H, Vilsen B, Cornelius F
and Toyoshima C: Crystal structure of a Na+-bound
Na+,K+-ATPase preceding the E1P state.
Nature. 502:201–206. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Durlacher CT, Chow K, Chen XW, He ZX,
Zhang X, Yang T and Zhou SF: Targeting
Na+/K+-translocating adenosine triphosphatase
in cancer treatment. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 42:427–443. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Crambert G, Li C, Claeys D and Geering K:
FXYD3 (Mat-8), a new regulator of Na, K-ATPase. Mol Biol Cell.
16:2363–2371. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yue Q, Zhen H, Huang M, Zheng X, Feng L,
Jiang B, Yang M, Wu W, Liu X and Guo D: Proteasome inhibition
contributed to the cytotoxicity of arenobufagin after its binding
with Na, K-ATPase in human cervical carcinoma HeLa cells. PLoS One.
11:e01590342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen Z, Chen HY, Lang QB, Li B, Zhai XF,
Guo YY, Yue XQ and Ling CQ: Preventive effects of jiedu granules
combined with cinobufacini injection versus transcatheter arterial
chemoembolization in post-surgical patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma: A case-control trial. Chin J Integr Med. 18:339–344.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hart GW and Copeland RJ: Glycomics hits
the big time. Cell. 143:672–676. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dalziel M, Crispin M, Scanlan CN, Zitzmann
N and Dwek RA: Emerging principles for the therapeutic exploitation
of glycosylation. Science. 343:12356812014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|