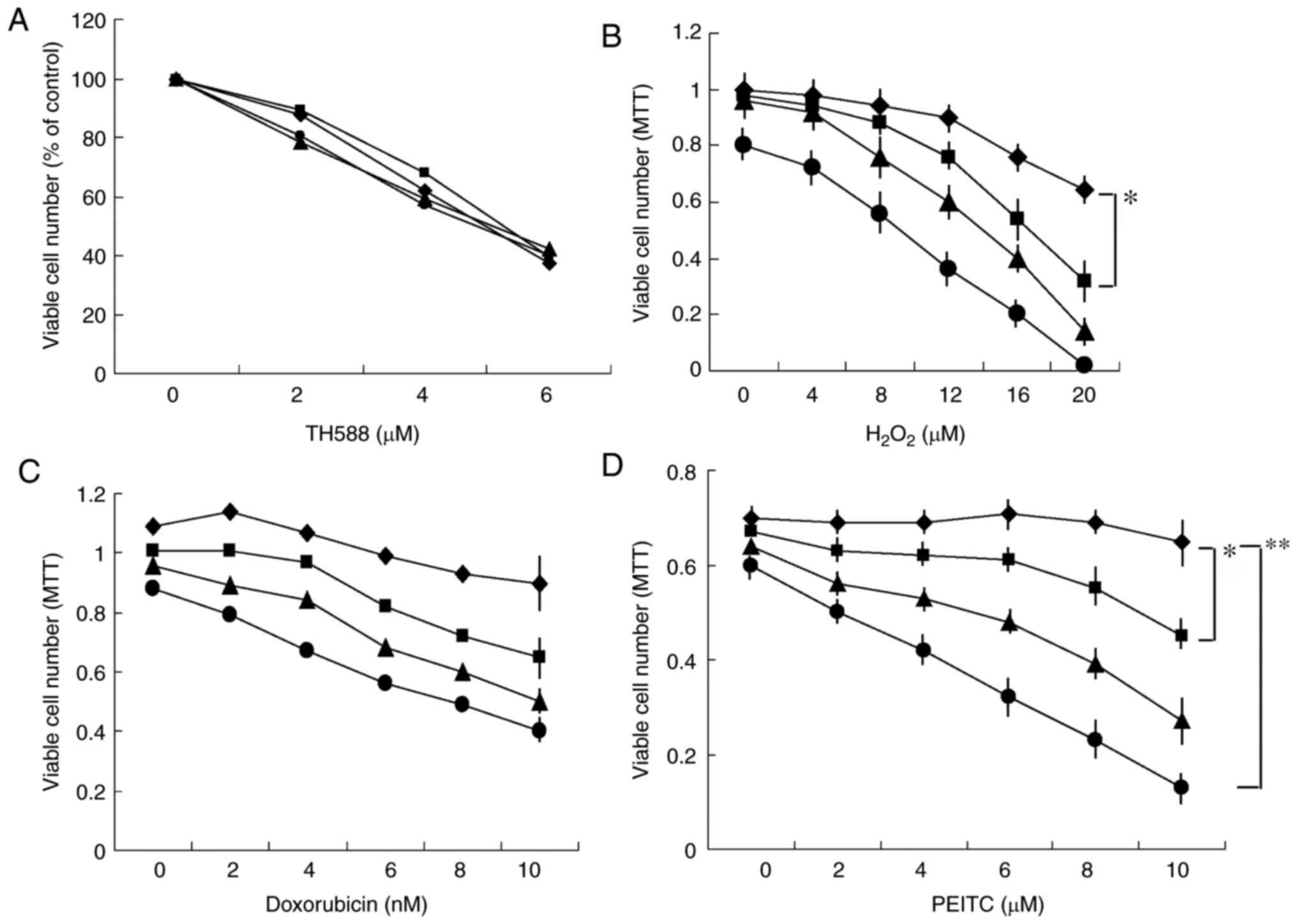
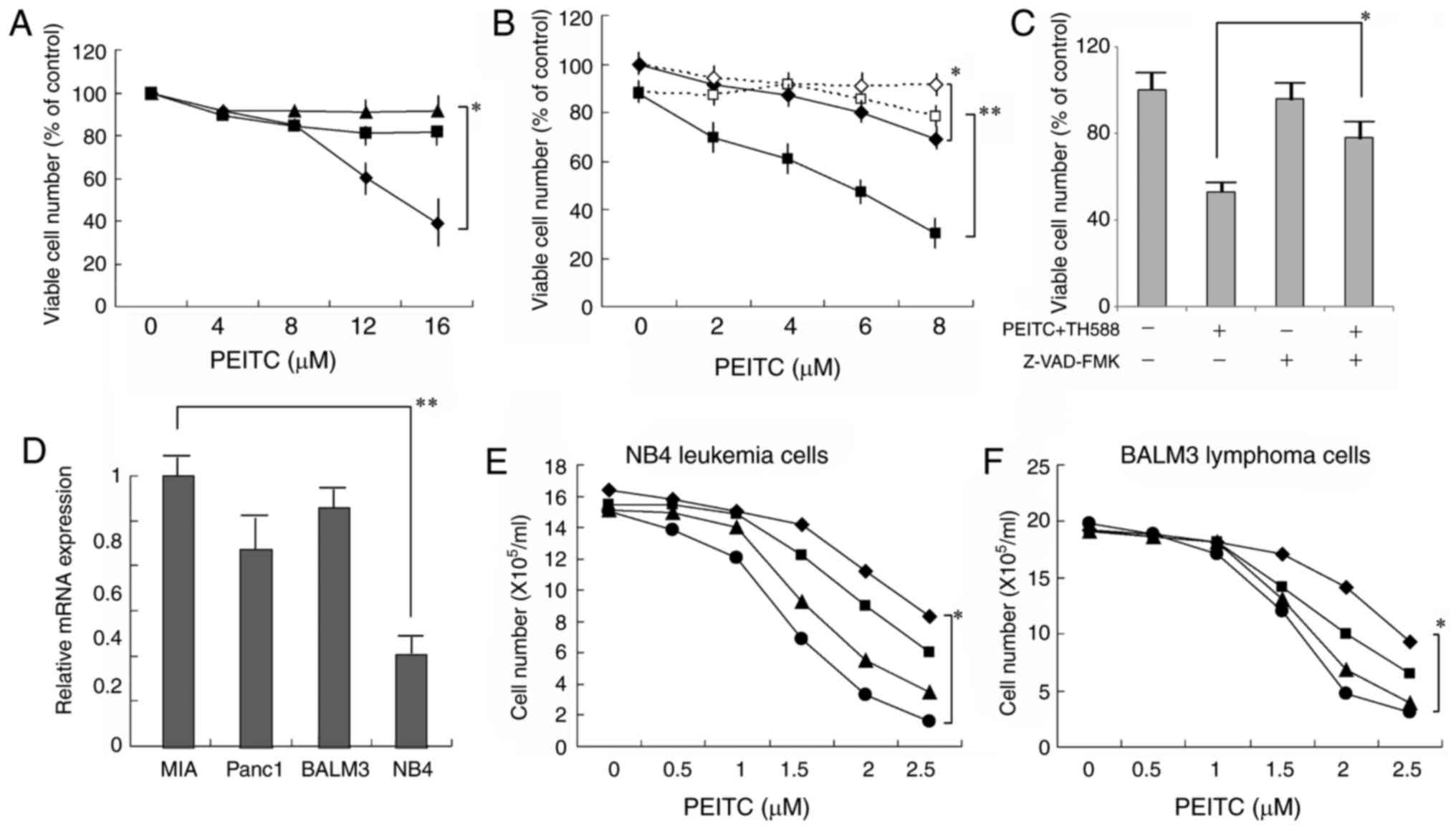
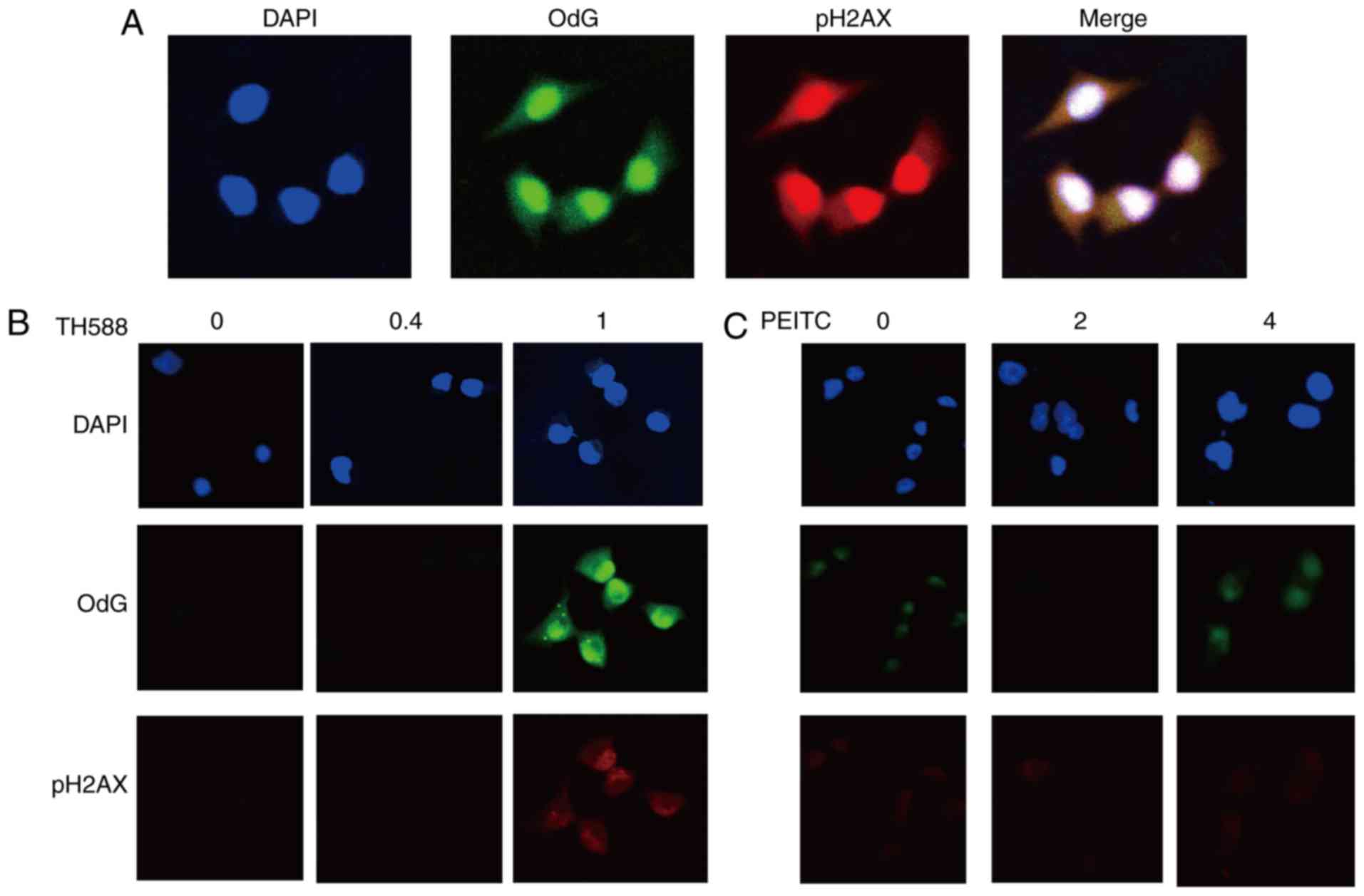
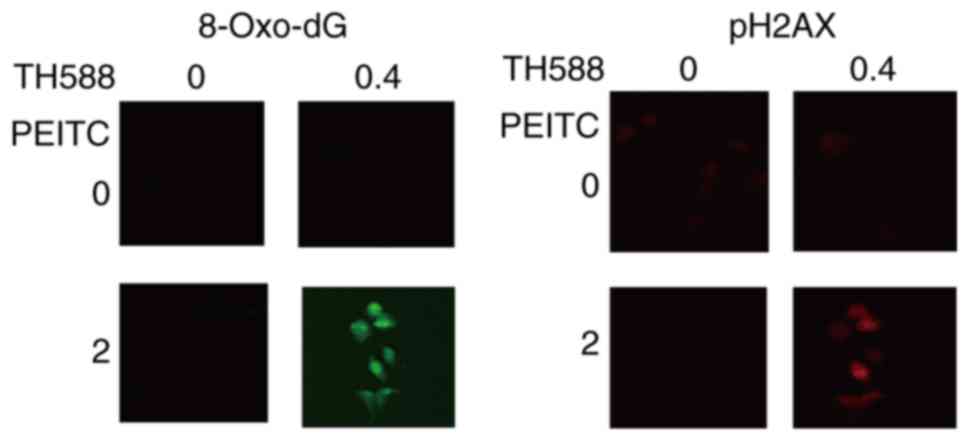
|
1
|
Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouché O,
Guimbaud R, Bécouarn Y, Adenis A, Raoul JL, Gourgou-Bourgade S, de
la Fouchardière C, et al: FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for
metastatic pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 364:1817–1825. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shaw AT, Winslow MM, Magendantz M, Ouyang
C, Dowdle J, Subramanian A, Lewis TA, Maglathin RL, Tolliday N and
Jacks T: Selective killing of K-ras mutant cancer cells by small
molecule inducers of oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:pp. 8773–8778. 2011; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Trachootham D, Zhou Y, Zhang H, Demizu Y,
Chen Z, Pelicano H, Chiao PJ, Achanta G, Arlinghaus RB, Liu J and
Huang P: Selective killing of oncogenically transformed cells
through a ROS-mediated mechanism by beta-phenylethyl
isothiocyanate. Cancer Cell. 10:241–252. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Henzel AF, Kimmelman AC, Stanger BZ,
Bardeesy N and Depinho RA: Genetics and biology of pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma. Genes Dev. 20:1218–1249. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu X, Zhou QH and Xu K: Are
isothiocyanates potential anti-cancer drugs? Acta Pharmacol Sin.
30:501–512. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu X, Kassie F and Mersch-Sundermann V:
Induction of apoptosis in tumor cells by naturally occurring
sulfur-containing compounds. Mutat Res. 589:81–102. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kasukabe T, Honma Y, Okabe-Kado J, Higuchi
Y, Kato N and Kumakura S: Combined treatment with cotylenin A and
phenethyl isothiocyanate induces strong antitumor activity mainly
through the induction of ferroptotic cell death in human pancreatic
cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 36:968–976. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xiao D, Powolny AA, Moura MB, Kelley EE,
Bommareddy A, Kim SH, Hahm ER, Normolle D, Van Houten B and Singh
SV: Phenethyl isothiocyanate inhibits oxidative phosphorylation to
trigger reactive oxygen species-mediated death of human prostate
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 285:26558–26569. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Topal MD and Baker MS: DNA precursor pool:
A significant target for N-methyl-N-nitrosourea in C3H/10T1/2 clone
8 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 79:pp. 2211–2215. 1982; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yoshimura D, Sakumi K, Ohno M, Sakai Y,
Furuichi M, Iwai S and Nakabeppu Y: An oxidized purine nucleoside
triphosphatase, MTH1, suppresses cell death caused by oxidative
stress. J Biol Chem. 278:37965–37973. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sakai Y, Furuichi M, Takahashi M, Mishima
M, Iwai S, Shirakawa M and Nakabeppu Y: A molecular basis for the
selective recognition of 2-hydroxy-dATP and 8-oxo-dGTP by human
MTH1. J Biol Chem. 277:8579–8587. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kennedy CH, Pass HI and Mitchell JB:
Expression of human MutT homologue (hMTH1) protein in primary
non-small-cell lung carcinomas and histologically normal
surrounding tissue. Free Radic Biol Med. 34:1447–1457. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Giribaldi MG, Munoz A, Halvorsen K, Patel
A and Rai P: MTH1 expression is required for effective
transformation by oncogenic HRAS. Oncotarget. 6:11519–11529. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Patel A, Burton DG, Halvorsen K, Balkan W,
Reiner T, Perez-Stable C, Cohen A, Munoz A, Giribaldi MG, Singh S,
et al: MutT homolog 1 (MTH1) maintains multiple KRAS-driven
pro-malignant pathways. Oncogene. 34:2586–2596. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gad H, Koolmeister T, Jemth AS, Eshtad S,
Jacques SA, Ström CE, Svensson LM, Schultz N, Lundbäck T,
Einarsdottir BO, et al: MTH1 inhibition eradicates cancer by
preventing sanitation of the dNTP pool. Nature. 508:215–221. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huber KV, Salah E, Radic B, Gridling M,
Elkins JM, Stukalov A, Jemth AS, Göktürk C, Sanjiv K, Strömberg K,
et al: Stereospecific targeting of MTH1 by (S)-crizotinib as an
anticancer strategy. Nature. 508:222–227. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kawamura T, Kawatani M, Muroi M, Kondoh Y,
Futamura Y, Aono H, Tanaka M, Honda K and Osada H: Proteomic
profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of
MTH1 for cancer cell survival. Sci Rep. 6:265212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kettle JG, Alwan H, Bista M, Breed J,
Davies NL, Eckersley K, Fillery S, Foote KM, Goodwin L, Jones DR,
et al: Potent and selective inhibitors of MTH1 probe its role in
cancer cell survival. J Med Chem. 59:2346–2361. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kawakami K, Hattori M, Inoue T, Maruyama
Y, Ohkanda J, Kato N, Tongu M, Yamada T, Akimoto M, Takenaga K, et
al: A novel fusicoccin derivative preferentially targets hypoxic
tumor cells and inhibits tumor growth in xenografts. Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 12:791–800. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang X, Song W, Zhou Y, Mao F, Lin Y,
Guan J and Sun Q: Expression and function of MutT homolog 1 in
distinct subtypes of breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 13:2161–2168. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Struthers L, Patel R, Clark J and Thomas
S: Direct detection of 8-oxodeoxyguanosine and 8-oxoguanine by
avidin and its analogues. Anal Biochem. 255:20–31. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Conners R, Hooley E, Clarke AR, Thomas S
and Brady R: Recognition of oxidatively modified bases within the
biotin-binding site by avidin. J Mol Biol. 357:263–274. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Goodman J and Hochstein P: Generation of
free radicals and lipid peroxidation by redox cycling of adriamycin
and daunomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 77:797–803. 1977.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hattori M, Kawakami K, Akimoto M, Takenaga
K, Suzumiya J and Honma Y: Antitumor effect of Japanese apricot
extract (MK615) on human cancer cells in vitro and in vivo through
a reactive oxygen species-dependent mechanism. Tumori. 99:239–248.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ishii Y, Hori Y, Sakai S and Honma Y:
Control of differentiation and apoptosis of human myeloid leukemia
cells by cytokinins and cytokinin nucleosides, plant
redifferentiation-inducing hormones. Cell Growth Differ. 13:19–26.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang JY, Jin L, Yan XG, Sherwin S,
Farrelly M, Zhang YY, Liu F, Wang CY, Guo ST, Yari H, et al:
Reactive oxygen species dictate the apoptotic response of melanoma
cells to TH588. J Invest Dermatol. 136:2277–2286. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tu Y, Wang Z, Wang X, Yang H, Zhang P,
Johnson M, Liu N, Liu H, Jin W, Zhang Y and Cui D4: Birth of MTH1
as a therapeutic target for glioblastoma: MTH1 is indispensable for
gliomatumorigenesis. Am J Transl Res. 8:2803–2811. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Akiyama S, Saeki H, Nakashima Y, Iimori M,
Kitao H, Oki E, Oda Y, Nakabeppu Y, Kakeji Y and Maehara Y:
Prognostic impact of MutT homolog-1 expression on esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. 6:258–266. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhu C, Hu W, Wu H and Hu X: No evident
dose-response relationship between cellular ROS level and its
cytotoxicity-a paradoxical issue in ROS-based cancer therapy. Sci
Rep. 4:50292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kumari V, Dyba MA, Holland RJ, Liang YH,
Singh SV and Ji X: Irreversible inhibition of glutathione
S-transferase by phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC), a dietary cancer
chemopreventive phytochemical. PLoS One. 11:e01638212016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|