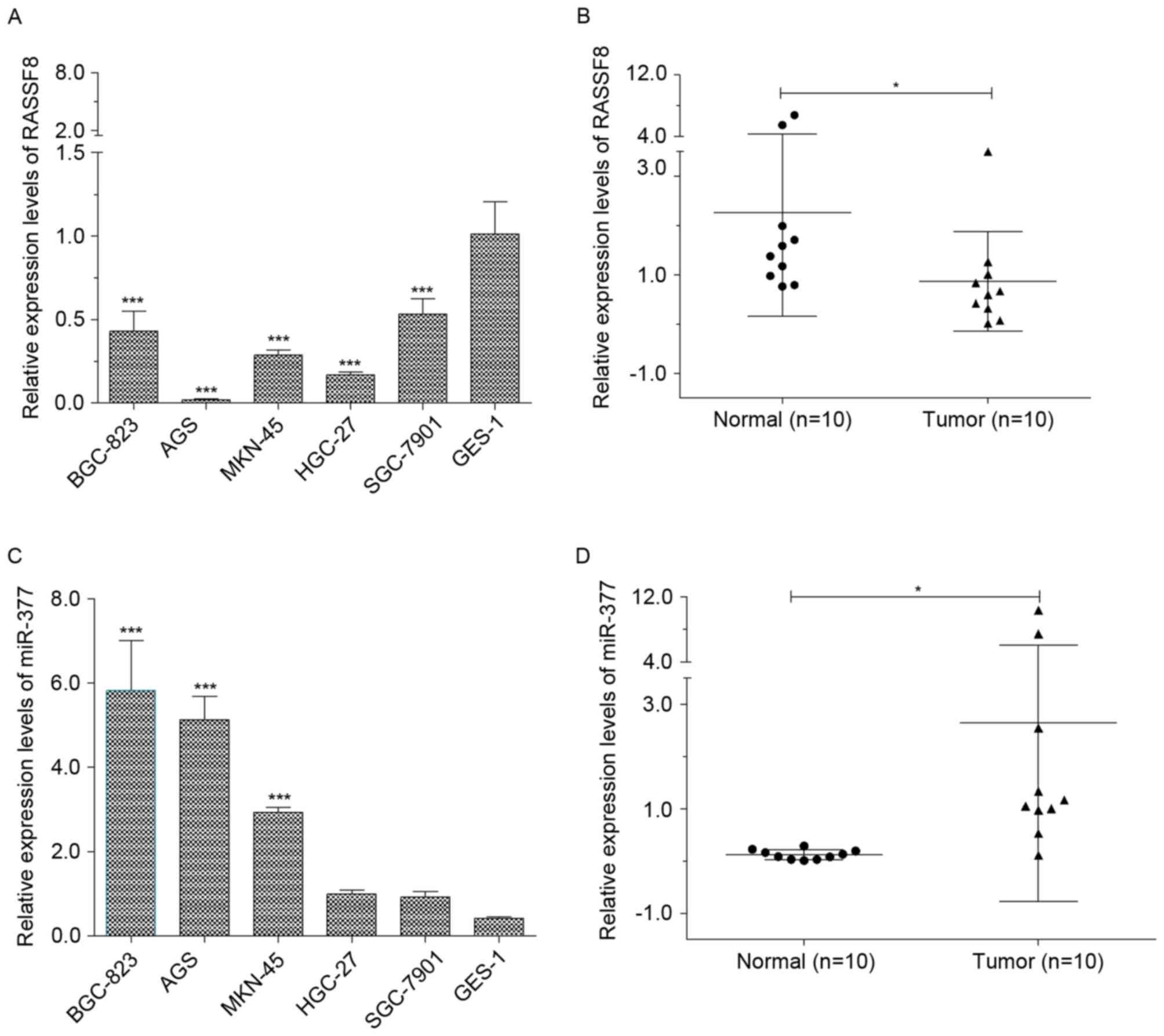
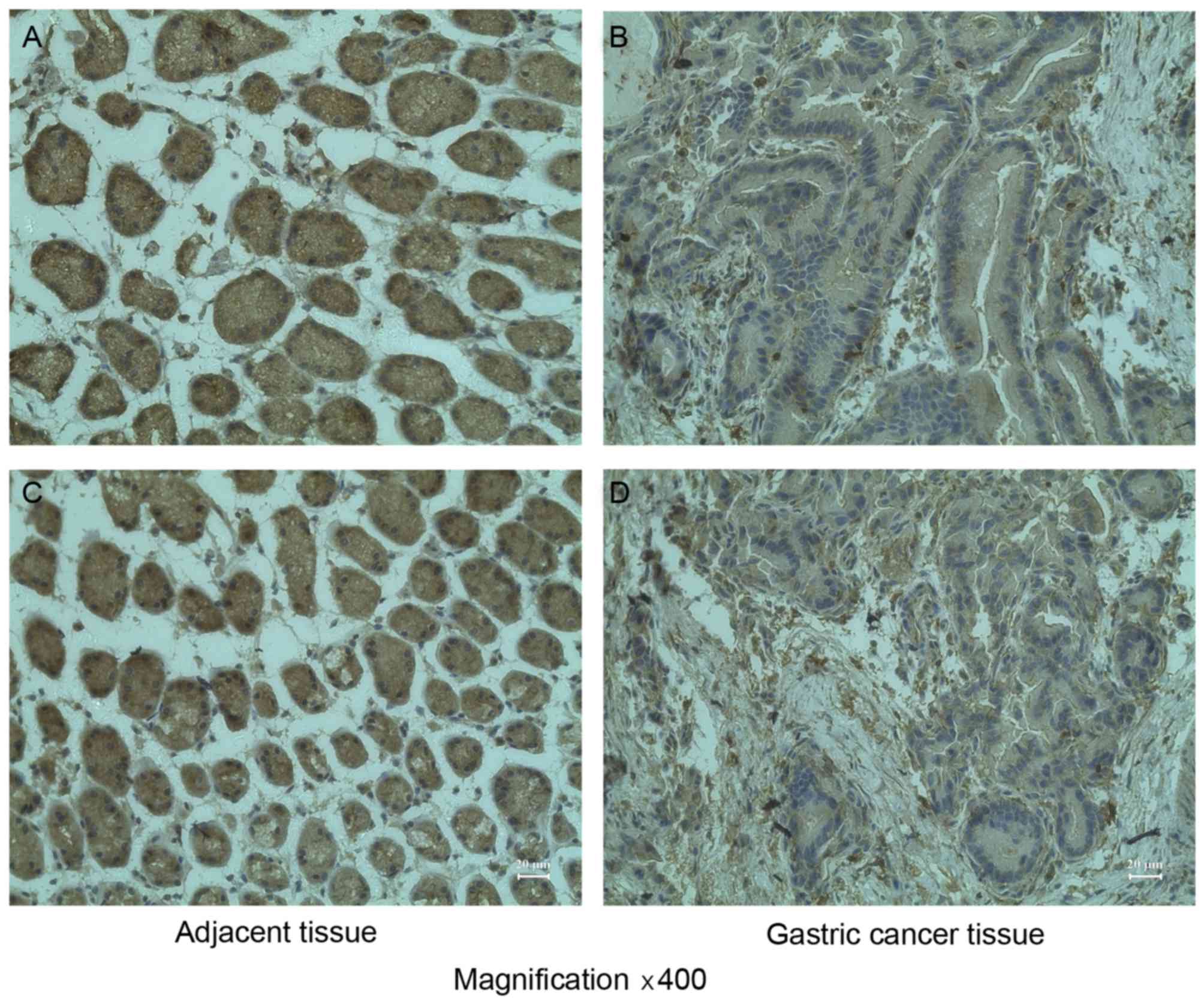
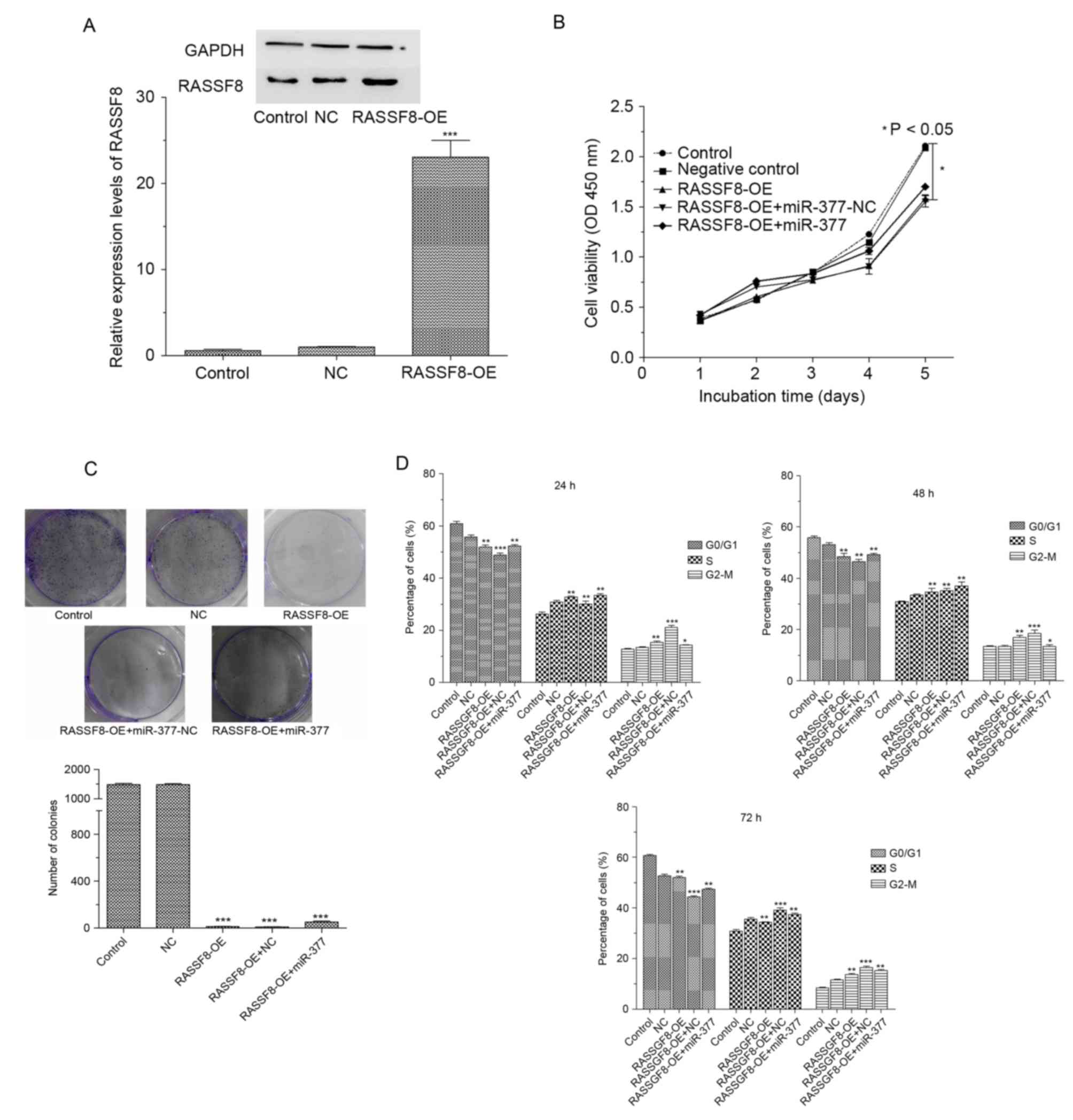
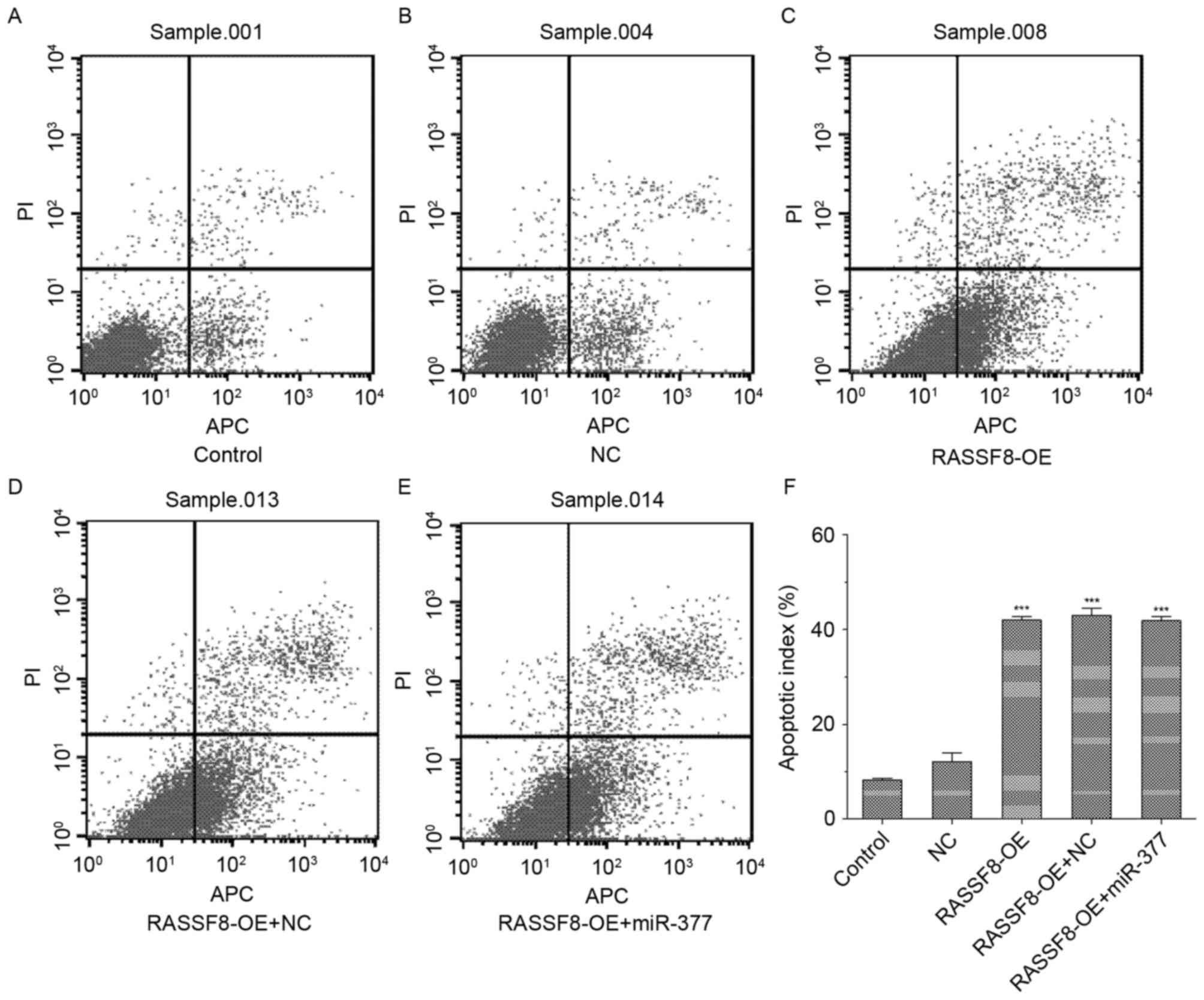
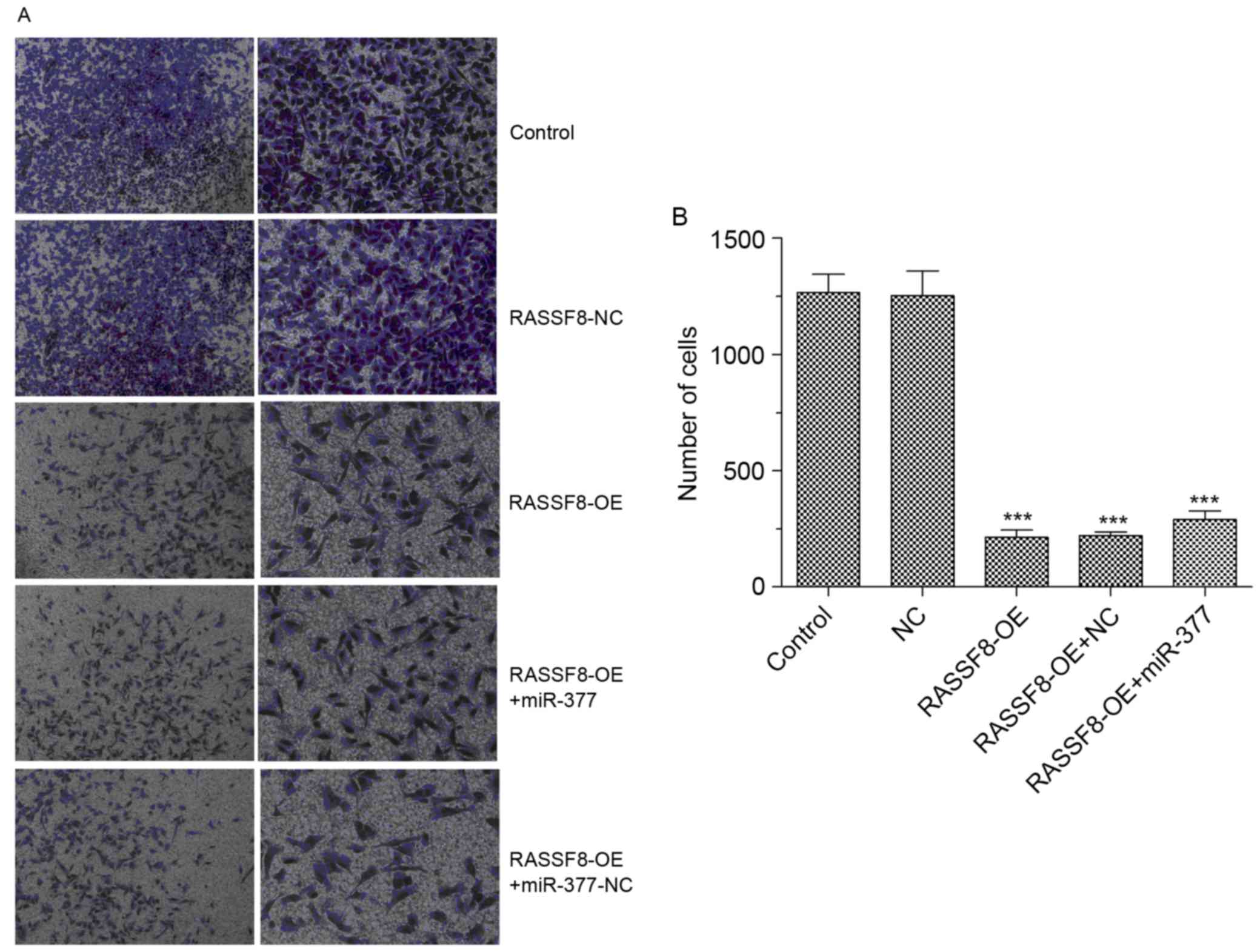
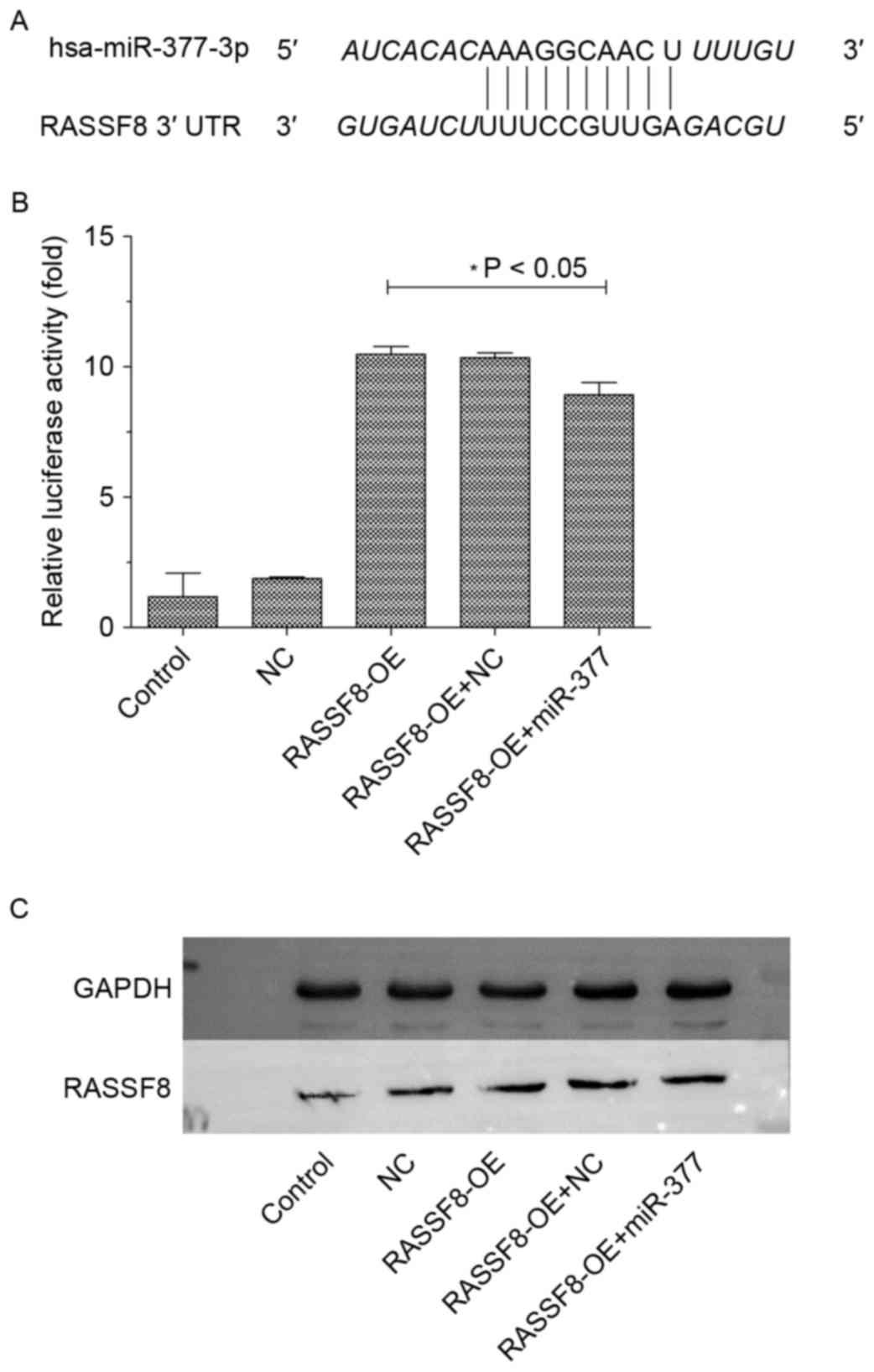
|
1
|
Gibson CJ, Britton KA, Miller AL and
Loscalzo J: Clinical problem-solving. Out of the blue. N Engl J
Med. 370:1742–1748. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wu WK, Lee CW, Cho CH, Fan D, Wu K, Yu J
and Sung JJ: MicroRNA dysregulation in gastric cancer: A new player
enters the game. Oncogene. 29:5761–5771. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Catalano V, Labianca R, Beretta GD, Gatta
G, de Braud F and Van Cutsem E: Gastric cancer. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 71:127–164. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gomceli I, Demiriz B and Tez M: Gastric
carcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 18:5164–5170.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Beckman JD, Chen C, Nguyen J, Thayanithy
V, Subramanian S, Steer CJ and Vercellotti GM: Regulation of heme
oxygenase-1 protein expression by miR-377 in combination with
miR-217. J Biol Chem. 286:3194–3202. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mascaux C, Iannino N, Martin B, Paesmans
M, Berghmans T, Dusart M, Haller A, Lothaire P, Meert AP, Noel S,
et al: The role of RAS oncogene in survival of patients with lung
cancer: A systematic review of the literature with meta-analysis.
Br J Cancer. 92:131–139. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ellis CA and Clark G: The importance of
being K-Ras. Cell Signal. 12:425–434. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Falvella FS, Manenti G, Spinola M,
Pignatiello C, Conti B, Pastorino U and Dragani TA: Identification
of RASSF8 as a candidate lung tumor suppressor gene. Oncogene.
25:3934–3938. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: RAS oncogenes:
The first 30 years. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:459–465. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Downward J: Targeting RAS signalling
pathways in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:11–22. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wohlgemuth S, Kiel C, Krämer A, Serrano L,
Wittinghofer F and Herrmann C: Recognizing and defining true Ras
binding domains I: Biochemical analysis. J Mol Biol. 348:741–758.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sherwood V, Manbodh R, Sheppard C and
Chalmers AD: RASSF7 is a member of a new family of RAS association
domain-containing proteins and is required for completing mitosis.
Mol Biol Cell. 19:1772–1782. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zehavi L, Schayek H, Jacob-Hirsch J, Sidi
Y, Leibowitz-Amit R and Avni D: MiR-377 targets E2F3 and alters the
NF-kB signaling pathway through MAP3K7 in malignant melanoma. Mol
Cancer. 14:682015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ueda T, Volinia S, Okumura H, Shimizu M,
Taccioli C, Rossi S, Alder H, Liu CG, Oue N, Yasui W, et al:
Relation between microRNA expression and progression and prognosis
of gastric cancer: A microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol.
11:136–146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rachagani S, Kumar S and Batra SK:
MicroRNA in pancreatic cancer: Pathological, diagnostic and
therapeutic implications. Cancer Lett. 292:8–16. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang QZ, Xu W, Habib N and Xu R: Potential
uses of microRNA in lung cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy.
Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 9:572–594. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Balch C, Fang F, Matei DE, Huang TH and
Nephew KP: Minireview: Epigenetic changes in ovarian cancer.
Endocrinology. 150:4003–4011. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Faber C, Kirchner T and Hlubek F: The
impact of microRNAs on colorectal cancer. Virchows Arch.
454:359–367. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mott JL: MicroRNAs involved in tumor
suppressor and oncogene pathways: Implications for hepatobiliary
neoplasia. Hepatology. 50:630–637. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Inui M, Martello G and Piccolo S: MicroRNA
control of signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 11:252–263.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu C, Guo X, Wang W, Wang Y, Shan Y, Zhang
B, Song W, Ma S, Ge J, Deng H and Zhu M:
N-Acetylgalactosaminyltransferase-14 as a potential biomarker for
breast cancer by immunohistochemistry. BMC Cancer. 10:1232010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lang Y, Xu S, Ma J, Wu J, Jin S, Cao S and
Yu Y: MicroRNA-429 induces tumorigenesis of human non-small cell
lung cancer cells and targets multiple tumor suppressor genes.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 450:154–159. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wen X, Wu JQ, Peng W, Feng JF and Tang JH:
MicroRNA-377 predicts poor clinical outcome of gastric cancer and
induces tumorigenesis by targeting multiple tumor-suppressor genes.
Oncol Rep. 34:203–210. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lock FE, Underhill-Day N, Dunwell T,
Matallanas D, Cooper W, Hesson L, Recino A, Ward A, Pavlova T,
Zabarovsky E, et al: The RASSF8 candidate tumor suppressor inhibits
cell growth and regulates the Wnt and NF-kappaB signaling pathways.
Oncogene. 29:4307–4316. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|