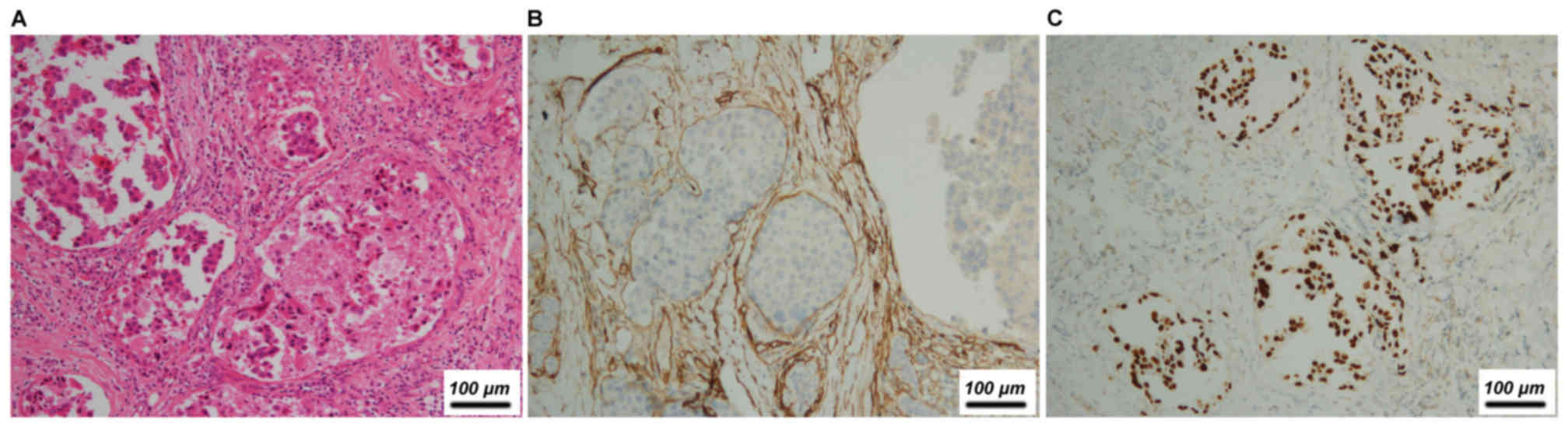
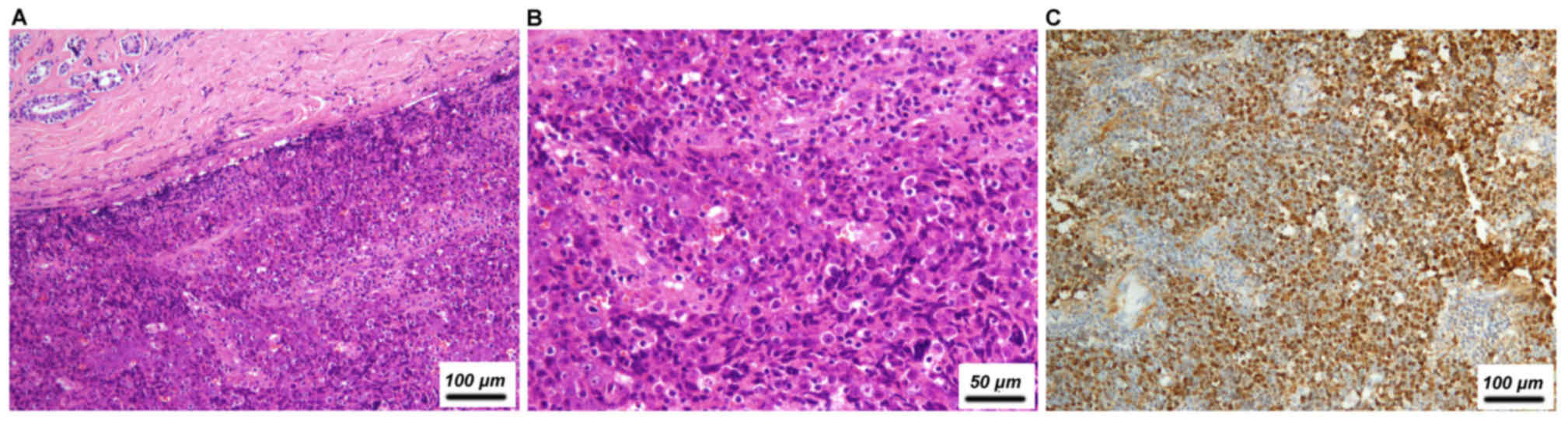
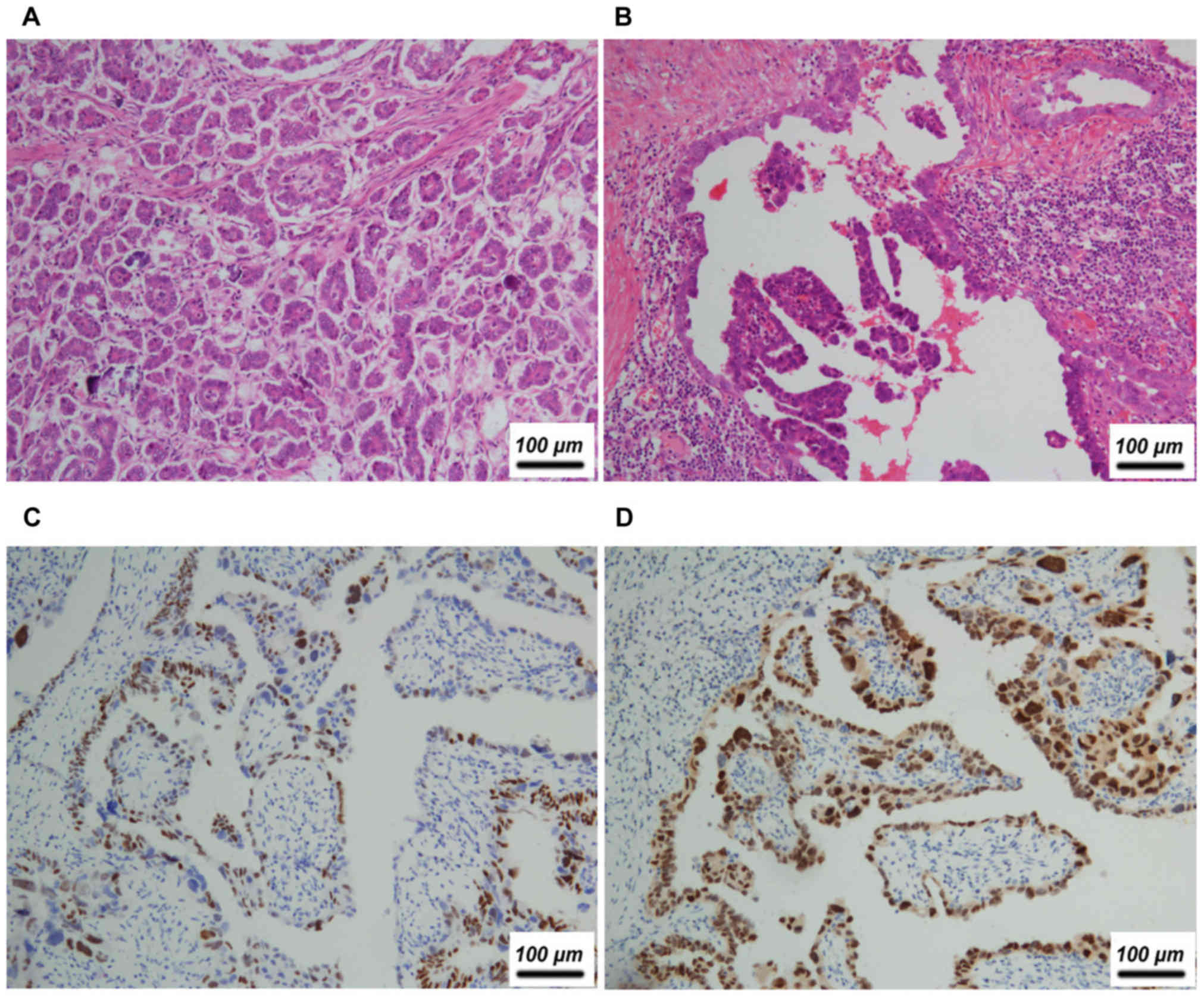
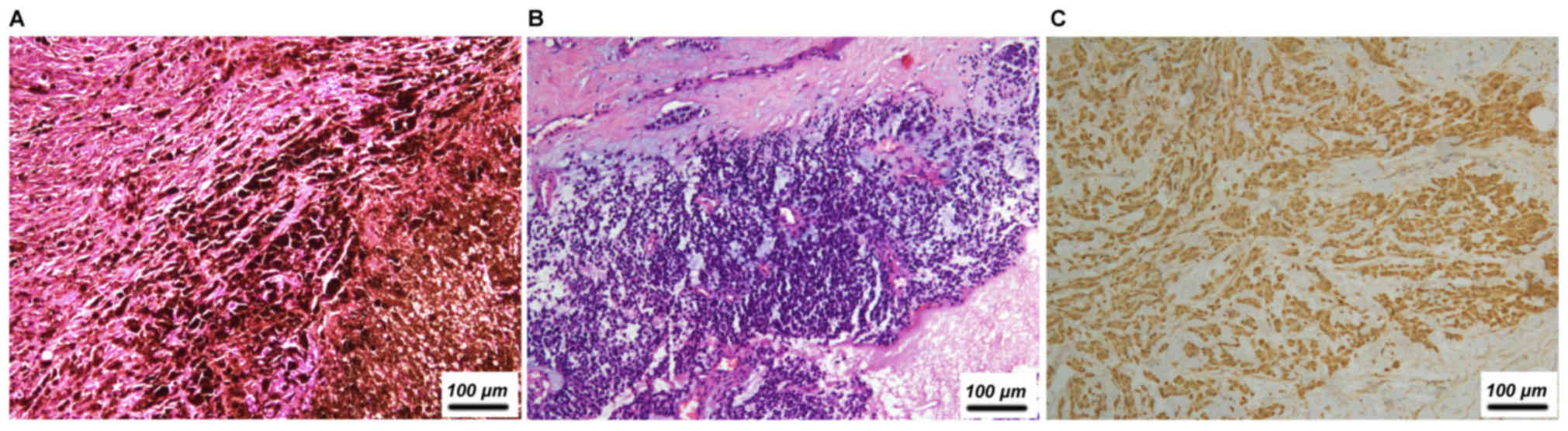
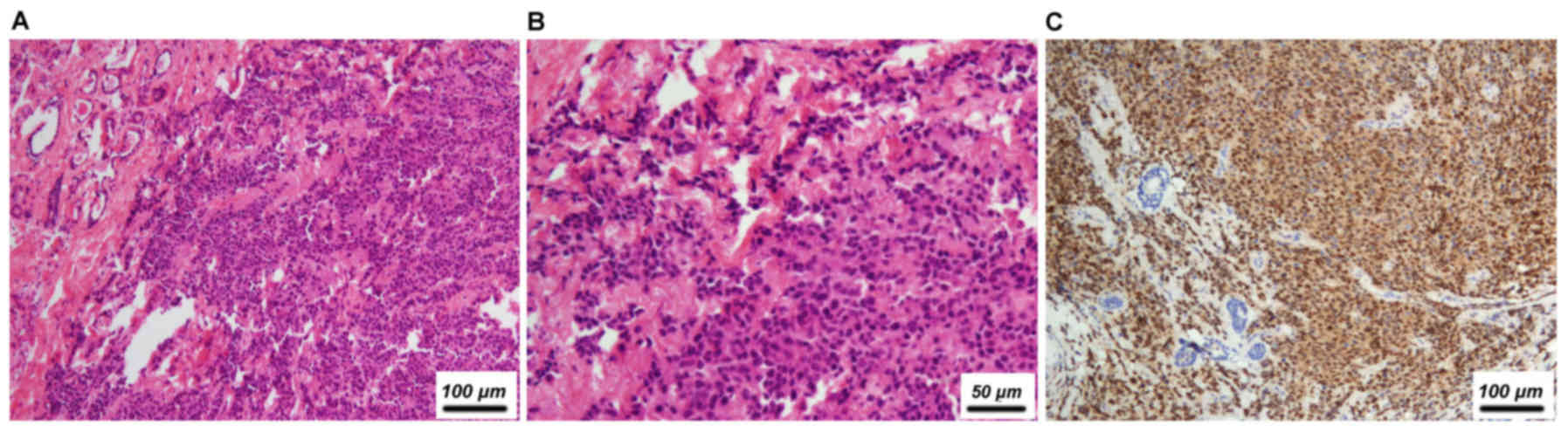
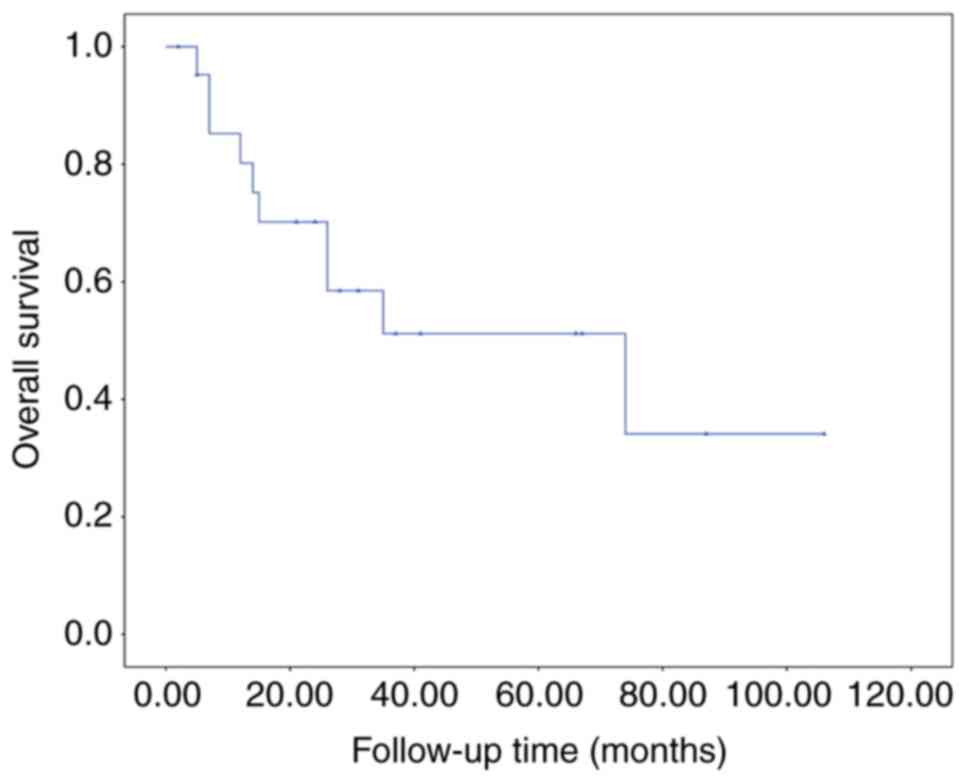
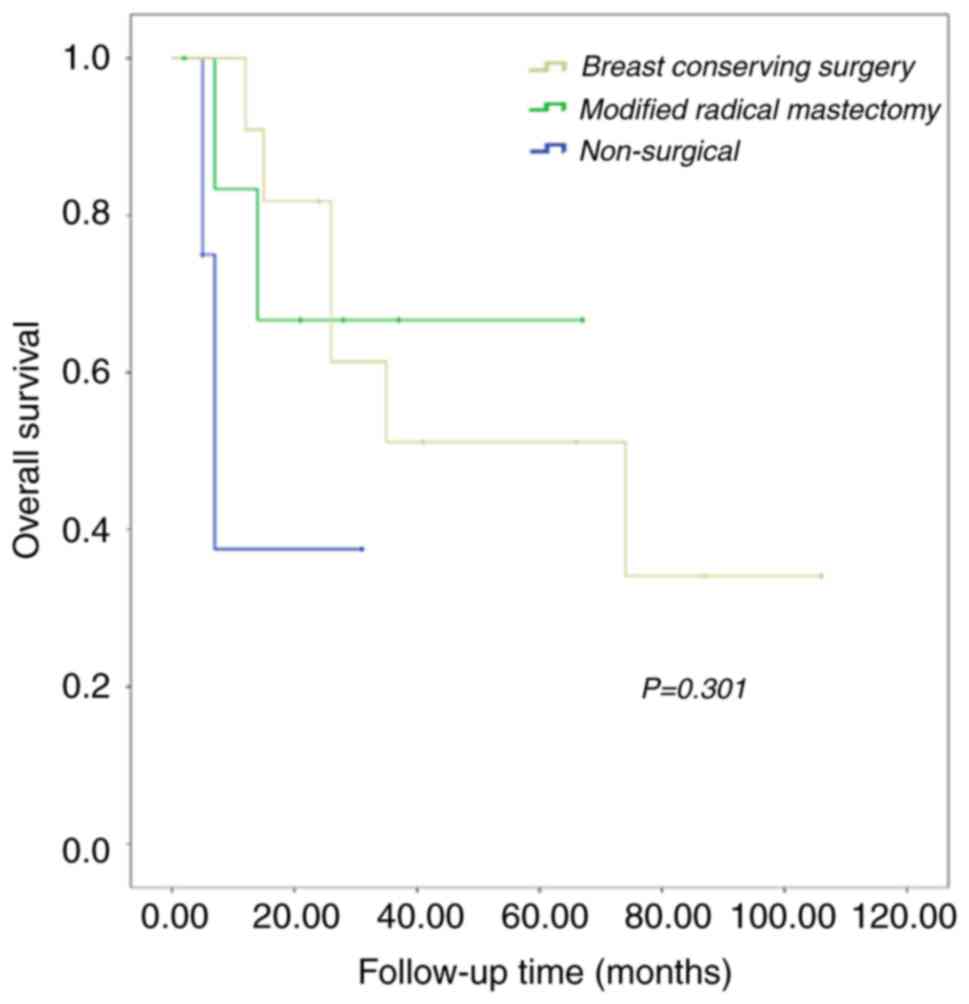
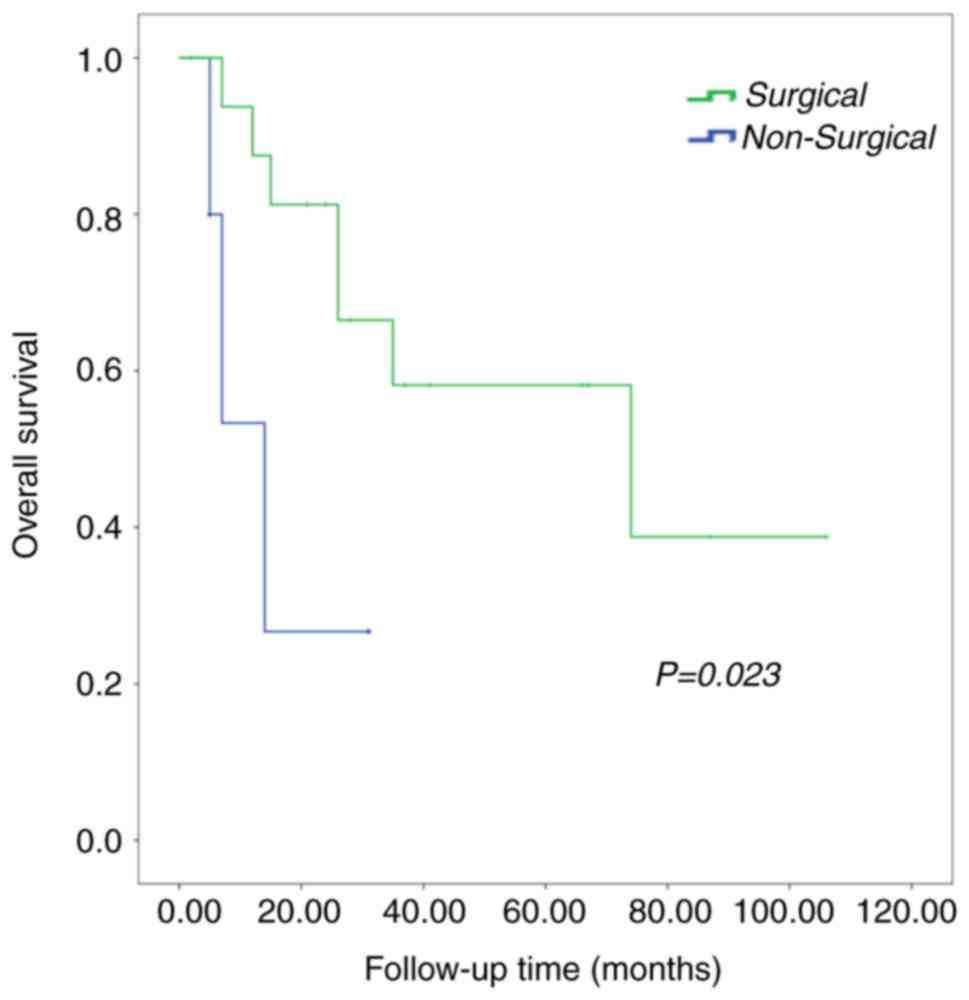
|
1
|
Alva S and Shetty-Alva N: An update of
tumor metastasis to the breast data. Arch Surg. 134:4501999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Akçay MN: Metastatic disease in the
breast. Breast. 11:526–528. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Williams SA, Ehlers RA II, Hunt KK, Yi M,
Kuerer HM, Singletary SE, Ross MI, Feig BW, Symmans WF and
Meric-Bernstam F: Metastases to the breast from nonbreast solid
neoplasms: Presentation and determinants of survival. Cancer.
110:731–737. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee SK, Kim WW, Kim SH, Hur SM, Kim S,
Choi JH, Cho EY, Han SY, Hahn BK, Choe JH, et al: Characteristics
of metastasis in the breast from extramammary malignancies. J Surg
Oncol. 101:137–140. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sippo DA, Kulkarni K, Carlo PD, Lee B,
Eisner D, Cimino-Mathews A and Harvey SC: Metastatic disease to the
breast from extramammary malignancies: A multimodality pictorial
review. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 45:225–232. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Manini C, Pietribiasi F, Sapino A and
Donadio S: Serous cystadenocarcinoma of the ovary with simultaneous
breast metastases. Description of a case. Pathologica. 90:152–155.
1998.(In Italian).
|
|
7
|
Hanna NN, O'Donnell K and Wolfe GR:
Alveolar soft part sarcoma metastatic to the breast. J Surg Oncol.
61:159–162. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Oksüzoğlu B, Abali H, Güler N, Baltali E
and Ozişik Y: Metastasis to the breast from nonmammarian solid
neoplasms: A report of five cases. Med Oncol. 20:295–300. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liberman L and Menell JH: Breast imaging
reporting and data system (BI-RADS). Radiol Clin North Am.
40:409–430, v. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hajdu SI and Urban JA: Cancers metastatic
to the breast. Cancer. 29:1691–1696. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hamby LS, McGrath PC, Cibull ML and
Schwartz RW: Gastric carcinoma metastatic to the breast. J Surg
Oncol. 48:117–121. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Toombs BD and Kalisher L: Metastatic
disease to the breast: Clinical, pathologic, and radiographic
features. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 129:673–676. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mihai R, Christie-Brown J and Bristol J:
Breast metastases from colorectal carcinoma. Breast. 13:155–158.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brouckaert O, Rudolph A, Laenen A, Keeman
R, Bolla MK, Wang Q, Soubry A, Wildiers H, Andrulis IL, Arndt V, et
al: Reproductive profiles and risk of breast cancer subtypes: A
multi-center case-only study. Breast Cancer Res. 19:1192017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vergier B, Trojani M, de Mascarel I,
Coindre JM and Le Treut A: Metastases to the breast: Differential
diagnosis from primary breast carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 48:112–116.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nayar M, Chandra M, Aggarwal R and Chander
S: Carcinoma cervix presenting as primary breast malignancy. Indian
J Pathol Microbiol. 30:283–286. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
DeLair DF, Corben AD, Catalano JP, Vallejo
CE, Brogi E and Tan LK: Non-mammary metastases to the breast and
axilla: A study of 85 cases. Mod Pathol. 26:343–349. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yeh CN, Lin CH and Chen MF: Clinical and
ultrasonographic characteristics of breast metastases from
extramammary malignancies. Am Surg. 70:287–290. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mun SH, Ko EY, Han BK, Shin JH, Kim SJ and
Cho EY: Breast metastases from extramammary malignancies: Typical
and atypical ultrasound features. Korean J Radiol. 15:20–28. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bohman LG, Bassett LW, Gold RH and Voet R:
Breast metastases from extramammary malignancies. Radiology.
144:309–312. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
McCrea ES, Johnston C and Haney PJ:
Metastases to the breast. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 141:685–690. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee SH, Park JM, Kook SH, Han BK and Moon
WK: Metastatic tumors to the breast: Mammographic and
ultrasonographic findings. J Ultrasound Med. 19:257–262. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vizcaíno I, Torregrosa A, Higueras V,
Morote V, Cremades A, Torres V, Olmos S and Molins C: Metastasis to
the breast from extramammary malignancies: A report of four cases
and a review of literature. Eur Radiol. 11:1659–1665. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Surov A, Fiedler E, Holzhausen HJ, Ruschke
K, Schmoll HJ and Spielmann RP: Metastases to the breast from
non-mammary malignancies: Primary tumors, prevalence, clinical
signs, and radiological features. Acad Radiol. 18:565–574. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Torjesen I: Adding ultrasound to
mammography could increase breast cancer detection in Asian women.
BMJ. 351:h59262015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Phadke S, Thomas A, Yang L, Moore C, Xia C
and Schroeder MC: Frequency and clinical significance of
extramammary findings on breast magnetic resonance imaging. Clin
Breast Cancer. 16:424–429. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Benveniste AP, Marom EM, Benveniste MF,
Mawlawi OR, Miranda RN and Yang W: Metastases to the breast from
extramammary malignancies-PET/CT findings. Eur J Radiol.
83:1106–1112. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Buisman FE, van Gelder L, Menke-Pluijmers
MB, Bisschops BH, Plaisier PW and Westenend PJ: Non-primary breast
malignancies: A single institution's experience of a diagnostic
challenge with important therapeutic consequences-a retrospective
study. World J Surg Oncol. 14:1662016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Leach BI, Sun B, Petrovic L and Liu SV:
Breast metastasis from nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report and
review of the literature. Oncol Lett. 5:1859–1861. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li S and Yang J: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
metastasis to the mammary gland: A case report. Oncol Lett.
9:275–277. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Georgiannos SN, Chin J, Goode AW and
Sheaff M: Secondary neoplasms of the breast: A survey of the 20th
century. Cancer. 92:2259–2266. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tornos C, Soslow R, Chen S, Akram M,
Hummer AJ, Abu-Rustum N, Norton L and Tan LK: Expression of WT1, CA
125, and GCDFP-15 as useful markers in the differential diagnosis
of primary ovarian carcinomas versus metastatic breast cancer to
the ovary. Am J Surg Pathol. 29:1482–1489. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dennis JL, Hvidsten TR, Wit EC, Komorowski
J, Bell AK, Downie I, Mooney J, Verbeke C, Bellamy C, Keith WN and
Oien KA: Markers of adenocarcinoma characteristic of the site of
origin: Development of a diagnostic algorithm. Clin Cancer Res.
11:3766–3772. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Moritani S, Ichihara S, Hasegawa M, Endo
T, Oiwa M, Yoshikawa K, Sato Y, Aoyama H, Hayashi T and Kushima R:
Serous papillary adenocarcinoma of the female genital organs and
invasive micropapillary carcinoma of the breast. Are WT1, CA125,
and GCDFP-15 useful in differential diagnosis? Hum Pathol.
39:666–671. 2008.
|
|
35
|
Lagendijk JH, Mullink H, van Diest PJ,
Meijer GA and Meijer CJ: Immunohistochemical differentiation
between primary adenocarcinomas of the ovary and ovarian metastases
of colonic and breast origin. Comparison between a statistical and
an intuitive approach. J Clin Pathol. 52:283–290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Recine MA, Deavers MT, Middleton LP, Silva
EG and Malpica A: Serous carcinoma of the ovary and peritoneum with
metastases to the breast and axillary lymph nodes: A potential
pitfall. Am J Surg Pathol. 28:1646–1651. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee BH, Hecht JL, Pinkus JL and Pinkus GS:
WT1, estrogen receptor, and progesterone receptor as markers for
breast or ovarian primary sites in metastatic adenocarcinoma to
body fluids. Am J Clin Pathol. 117:745–750. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Espinosa I, Gallardo A, D'Angelo E, Mozos
A, Lerma E and Prat J: Simultaneous carcinomas of the breast and
ovary: Utility of Pax-8, WT-1, and GATA3 for distinguishing
independent primary tumors from metastases. Int J Gynecol Pathol.
34:257–265. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tempfer CB, El Fizazi N, Ergonenc H and
Solass W: Metastasis of ovarian cancer to the breast: A report of
two cases and a review of the literature. Oncol Lett. 11:4008–4012.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rossfeld KK and Carson WE III: Surgical
management of ovarian carcinoma metastatic to the breast and
axilla: A role for metastasectomy? J Surg Oncol. 112:581–584. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|