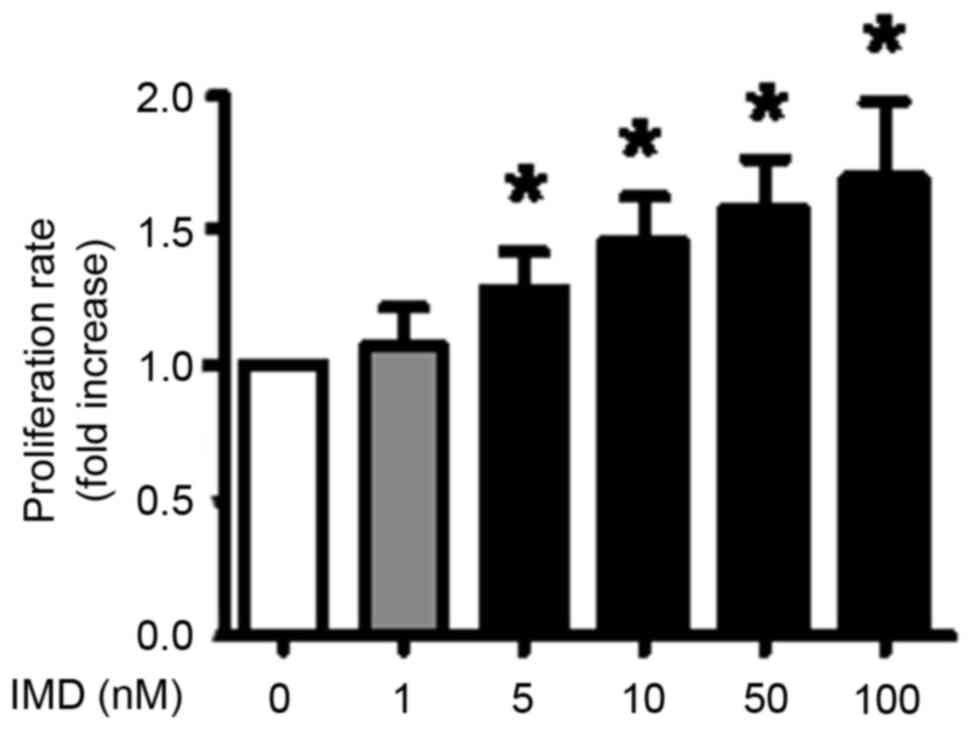
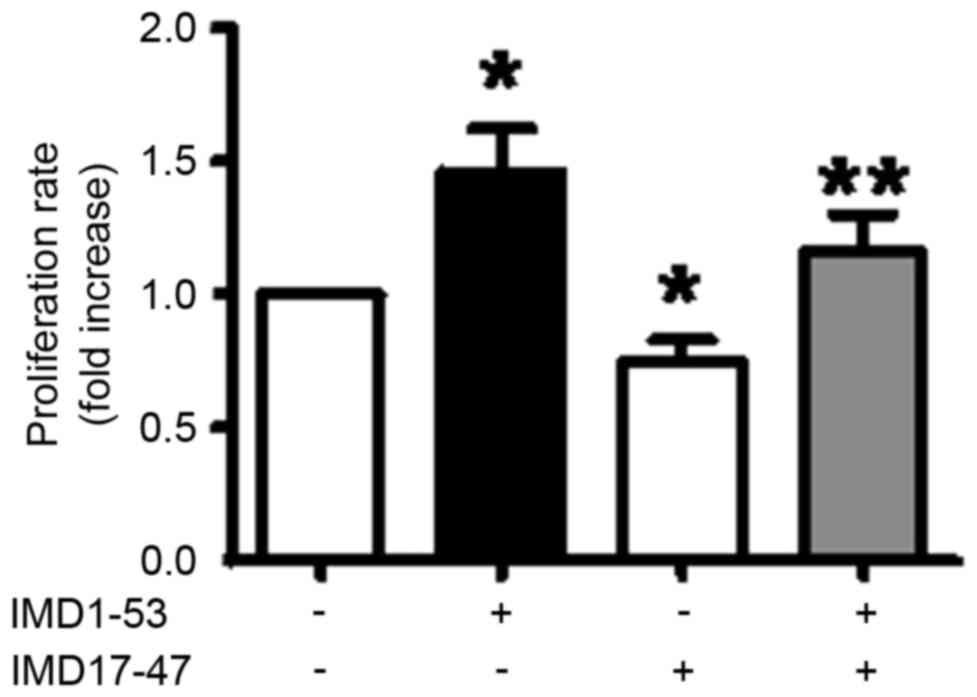
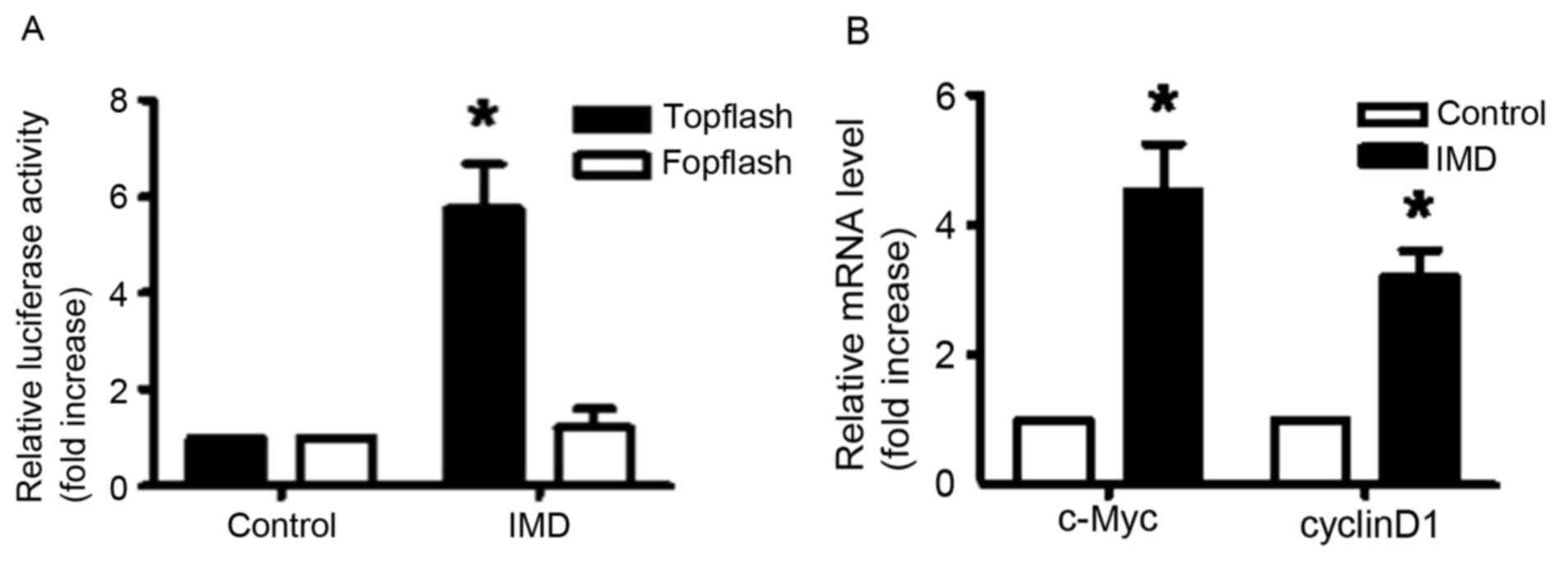
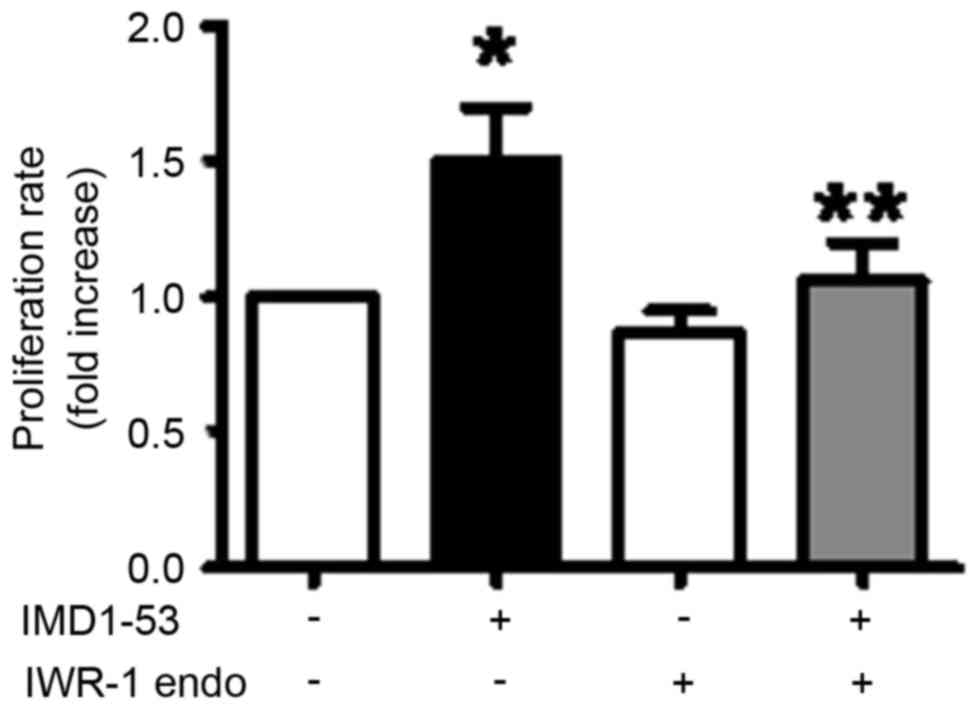
|
1
|
Tang B, Liang X, Tang F, Zhang J, Zeng S,
Jin S, Zhou L, Kudo Y and Qi G: Expression of USP22 and Survivin is
an indicator of malignant behavior in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int
J Oncol. 47:2208–2216. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhuang PH, Xu L, Gao L, Lu W, Ruan LT and
Yang J: Correlations of microvascular blood flow of
contrast-enhanced ultrasound and HGF/c-Met signaling pathway with
clinicopathological features and prognosis of patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 10:847–857. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dai L, Peng XX, Tan EM and Zhang JY:
Tumor-associated antigen CAPERα and microvessel density in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:16985–16995. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bozkaya G, Korhan P, Cokakli M, Erdal E,
Sağol O, Karademir S, Korch C and Atabey N: Cooperative interaction
of MUC1 with the HGF/c-Met pathway during hepatocarcinogenesis. Mol
Cancer. 11:642012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Whittaker S, Marais R and Zhu AX: The role
of signaling pathways in the development and treatment of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 29:4989–5005. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang C: Review on nutrition function of
bioactive pephides. Food Science. 24:153–154. 2003.
|
|
7
|
Holmes D, Campbell M, Harbinson M and Bell
D: Protective effects of intermedin on cardiovascular, pulmonary
and renal diseases: Comparison with adrenomedullin and CGRP. Curr
Protein Pept Sci. 14:294–329. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Takei Y, Inoue K, Ogoshi M, Kawahara T,
Bannai H and Miyano S: Identification of novel adrenomedullin in
mammals: A potent cardiovascular and renal regulator. FEBS Lett.
556:53–58. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Morimoto R, Satoh F, Murakami O, Hirose T,
Totsune K, Imai Y, Arai Y, Suzuki T, Sasano H, Ito S and Takahashi
K: Expression of adrenomedullin 2/intermedin in human adrenal
tumors and attached non-neoplastic adrenal tissues. J Endocrinol.
198:175–183. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hikosaka T, Tsuruda T, Nagata S, Kuwasako
K, Tsuchiya K, Hoshiko S, Inatsu H, Chijiiwa K and Kitamura K:
Adrenomedullin production is increased in colorectal
adenocarcinomas; its relation to matrix metalloproteinase-9.
Peptides. 32:1825–1831. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Smith RS Jr, Gao L, Bledsoe G, Chao L and
Chao J: Intermedin is a new angiogenic growth factor. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 297:H1040–H1047. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu Y, Pang X, Dong M, Wen F and Zhang Y:
Nesfatin-1 inhibits ovarian epithelial carcinoma cell proliferation
in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 440:467–472. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Y, Zhang S, Shang H, Pang X and Zhao
Y: Basic fibroblast growth factor upregulates adrenomedullin
expression in ovarian epithelial carcinoma cells via JNK-AP-1
pathway. Regul Pept. 157:44–50. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bell D and McDermott BJ: Intermedin
(adrenomedullin-2): A novel counter-regulatory peptide in the
cardiovascular and renal systems. Br J Pharmacol. 153 Suppl
1:S247–S262. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Roh J, Chang CL, Bhalla A, Klein C and Hsu
SY: Intermedin is a calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide
family peptide acting through the calcitonin receptor-like
receptor/receptor activity-modifying protein receptor complexes. J
Biol Chem. 279:7264–7274. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dong F, Taylor MM, Samson WK and Ren J:
Intermedin (adrenomedullin-2. enhances cardiac contractile function
via a protein kinase C- and protein kinase A-dependent pathway in
murine ventricular myocytes. J Appl Physiol (1985). 101:778–784.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ren H, Ren H, Li X, Yu D, Mu S, Chen Z and
Fu Q: Effects of intermedin on proliferation, apoptosis and the
expression of OPG/RANKL/M-CSF in the MC3T3-E1 osteoblast cell line.
Mol Med Rep. 12:6711–6717. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hollander LL, Guo X, Salem RR and Cha CH:
The novel tumor angiogenic factor, adrenomedullin-2, predicts
survival in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Surg Res. 197:219–224.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lu YM, Zhong JB, Wang HY, Yu XF and Li ZQ:
The prognostic value of intermedin in patients with breast cancer.
Dis Markers. 2015:8621582015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Billottet C, Janji B, Thiery JP and
Jouanneau J: Rapid tumor development and potent vascularization are
independent events in carcinoma producing FGF-1 or FGF-2. Oncogene.
21:8128–8139. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Di Blasio AM, Cremonesi L, Viganó P,
Ferrari M, Gospodarowicz D, Vignali M and Jaffe RB: Basic
fibroblast growth factor and its receptor messenger ribonucleic
acids are expressed in human ovarian epithelial neoplasms. Am J
Obstet Gynecol. 169:1517–1523. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guo X, Schmitz JC, Kenney BC, Uchio EM,
Kulkarni S and Cha CH: Intermedin is overexpressed in
hepatocellular carcinoma and regulates cell proliferation and
survival. Cancer Sci. 103:1474–1480. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Moon RT, Bowerman B, Boutros M and
Perrimon N: The promise and perils of Wnt signaling through
beta-catenin. Science. 296:1644–1646. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Clevers H: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in
development and disease. Cell. 127:469–480. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wong CM, Fan ST and Ng IO: Beta-catenin
mutation and overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma:
Clinicopathologic and prognostic significance. Cancer. 92:136–145.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Devereux TR, Stern MC, Flake GP, Yu MC,
Zhang ZQ, London SJ and Taylor JA: CTNNB1 mutations and
beta-catenin protein accumulation in human hepatocellular
carcinomas associated with high exposure to aflatoxin B1. Mol
Carcinog. 31:68–73. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hsu HC, Jeng YM, Mao TL, Chu JS, Lai PL
and Peng SY: Beta-catenin mutations are associated with a subset of
low-stage hepatocellular carcinoma negative for hepatitis B virus
and with favorable prognosis. Am J Pathol. 157:763–770. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bienz M and Clevers H: Linking colorectal
cancer to Wnt signaling. Cell. 103:311–320. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tetsu O and McCormick F: Beta-catenin
regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature.
398:422–426. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|