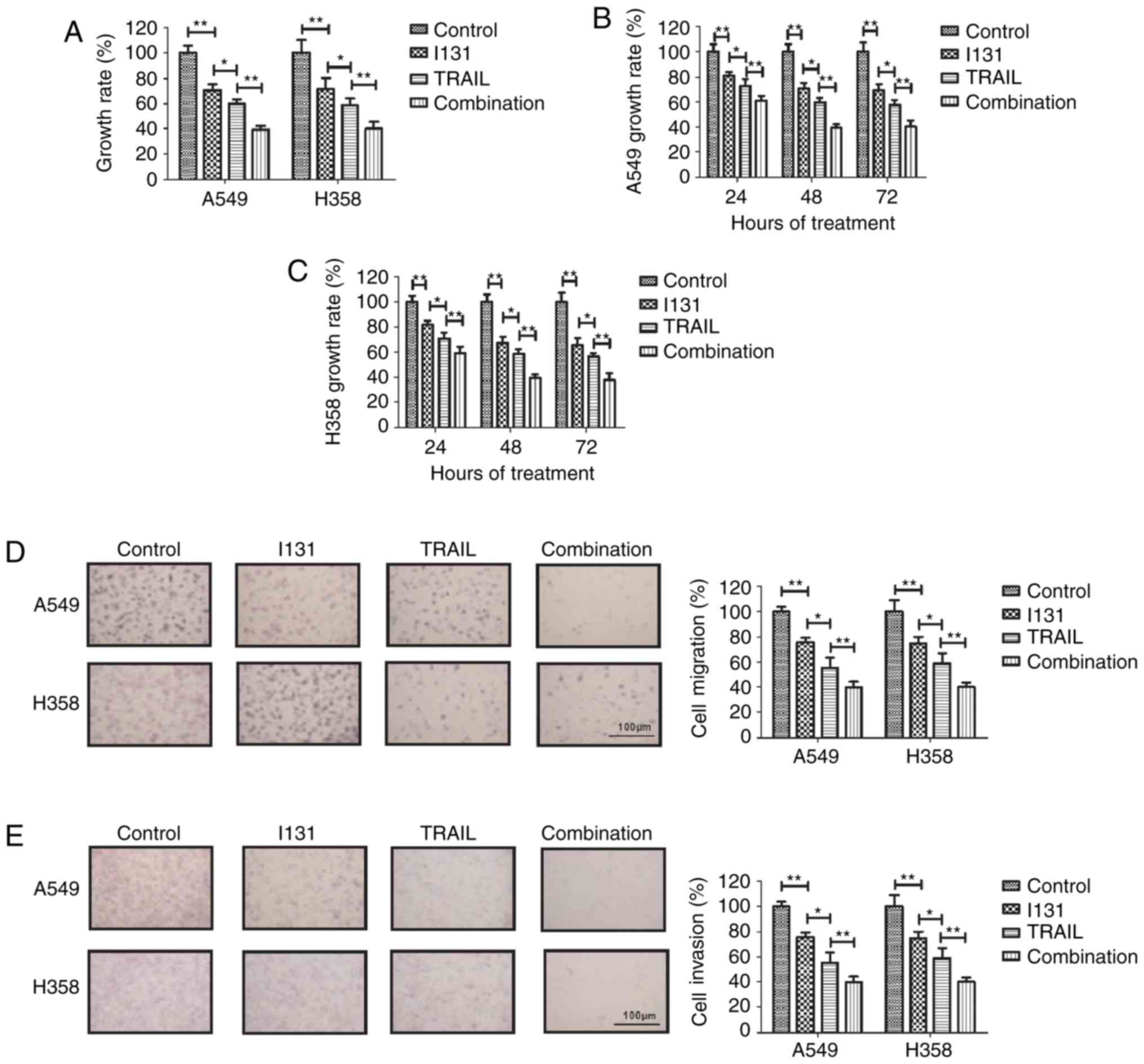
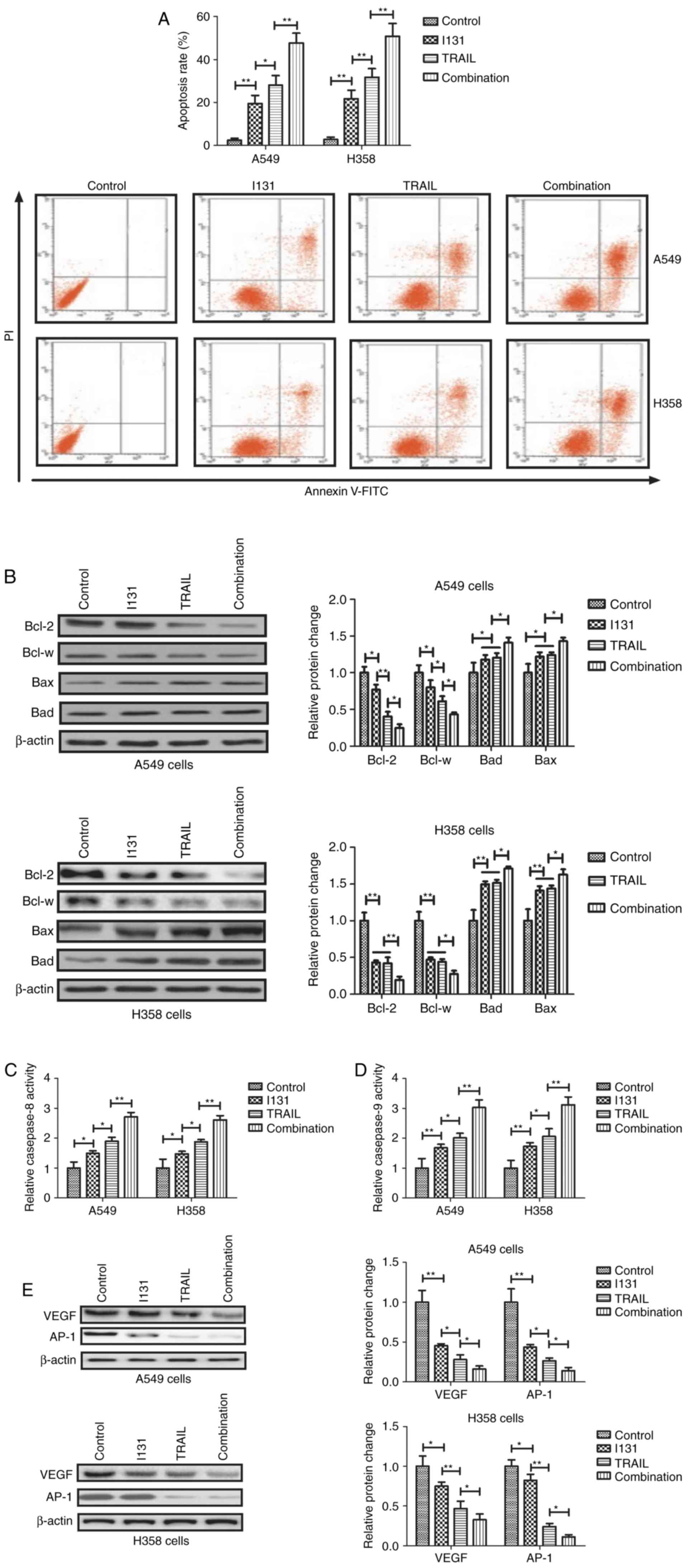
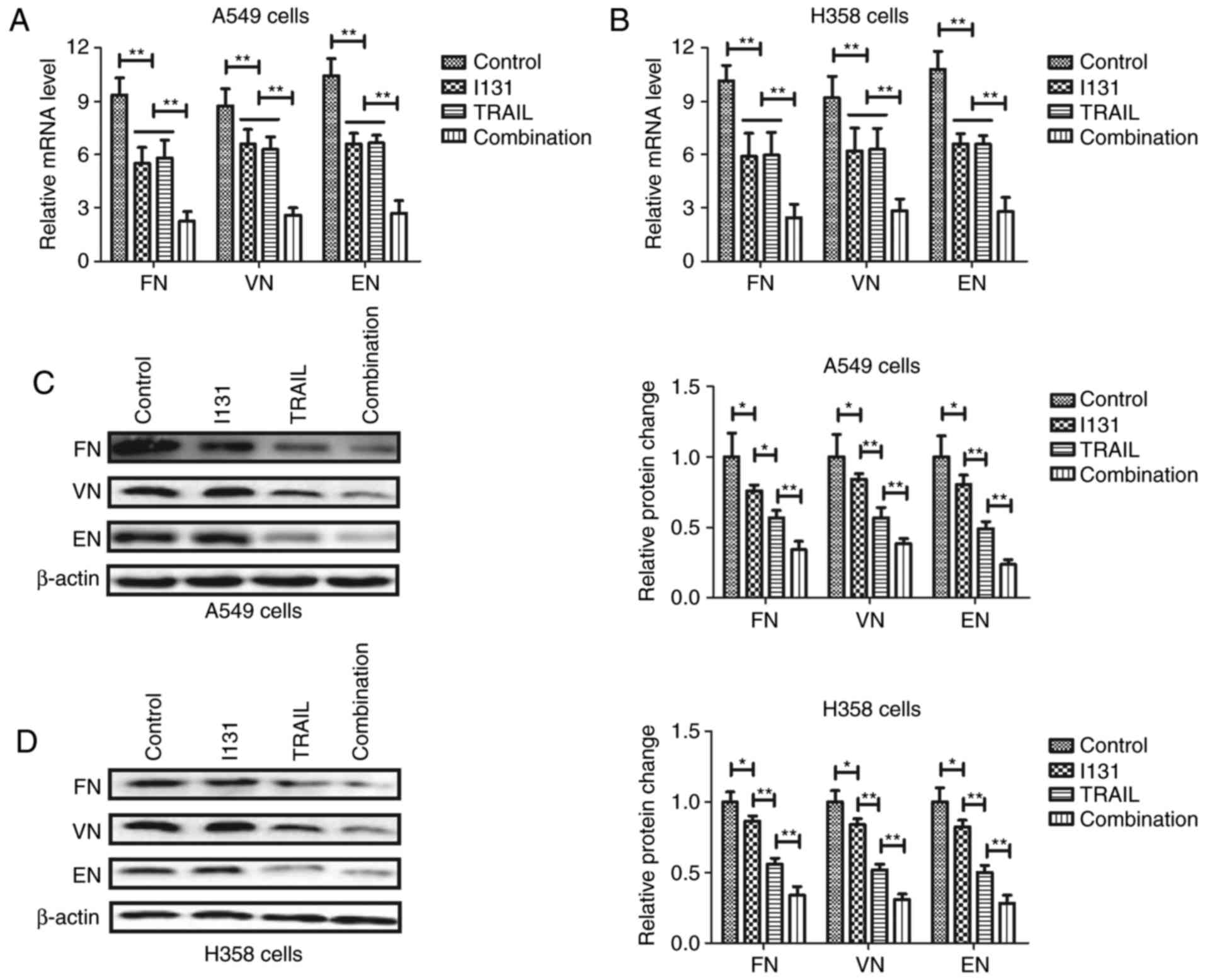
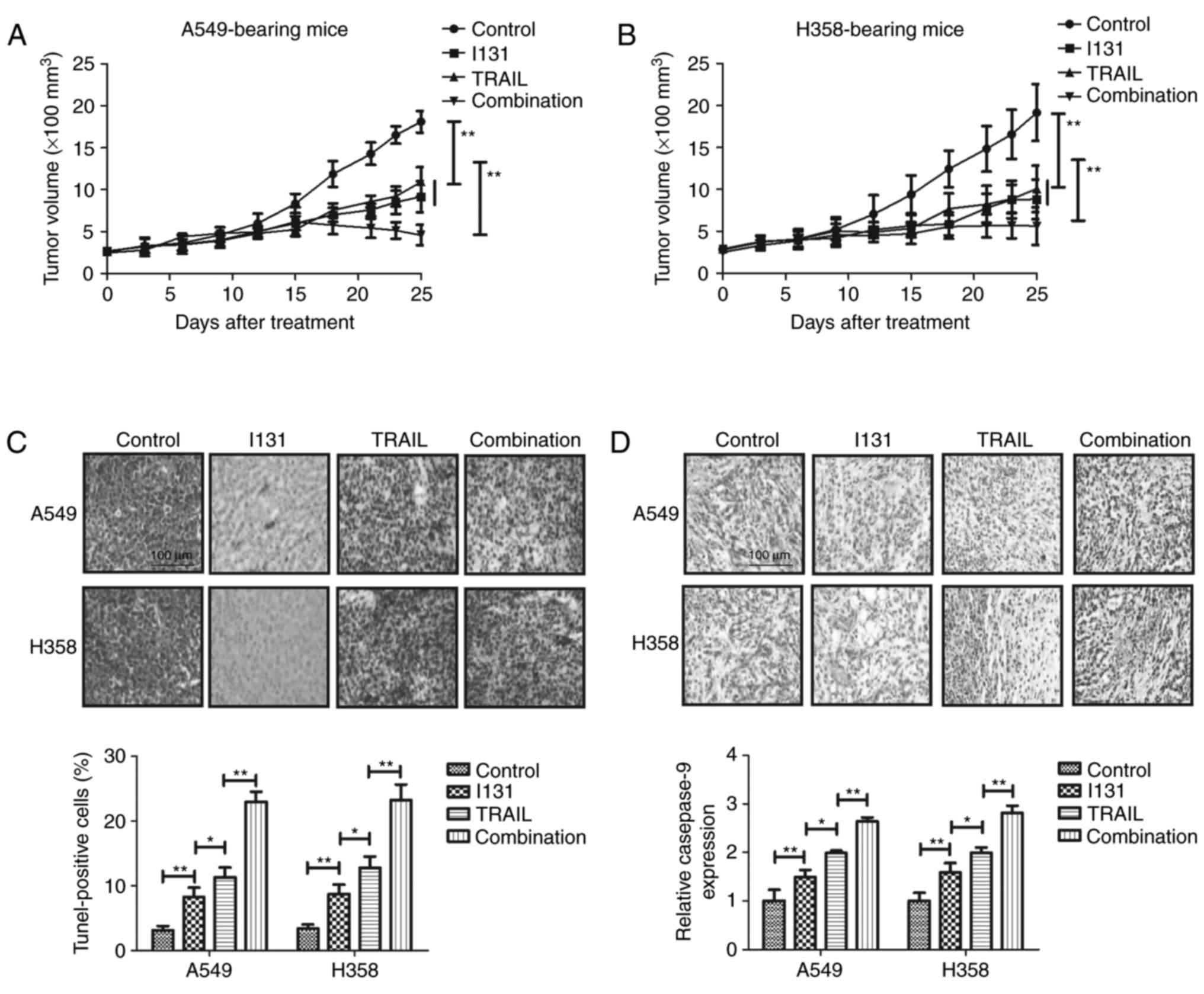
|
1
|
Baker S, Dahele M, Lagerwaard FJ and Senan
S: A critical review of recent developments in radiotherapy for
non-small cell lung cancer. Radiat Oncol. 11:1152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jiang T, Zhai C, Su C, Ren S and Zhou C:
The diagnostic value of circulating cell free DNA quantification in
non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review with meta-analysis.
Lung Cancer. 100:63–70. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhukovsky M, Varaksin A and Pakholkina O:
Statistical analysis of observational study of the influence of
radon and other risk factors on lung cancer incidence. Radiat Prot
Dosimetry. 160:108–111. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Falkson CB, Vella ET, Yu E, El-Mallah M,
Mackenzie R, Ellis PM and Ung YC: Radiotherapy with curative intent
in patients with Early-stage, medically inoperable, non-small-cell
lung cancer: A systematic review. Clin Lung Cancer. 18:105–121.e5.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Onesti CE, Iacono D, Angelini S, Lauro S,
Mazzotta M, Occhipinti MA, Giusti R and Marchetti P: Unexpected
long survival of brain oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer
(NSCLC) treated with multimodal treatment: A single-center
experience and review of the literature. Transl Lung Cancer Res.
5:712–719. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cadranel J, Park K, Arrieta O, Pless M,
Bendaly E, Patel D, Sasane M, Nosal A, Swallow E, Galebach P, et
al: Characteristics, treatment patterns, and survival among ALK+
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with
crizotinib: A chart review study. Lung Cancer. 98:9–14. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
McKay C, Knight KA and Wright C: Beyond
cancer treatment-a review of total lymphoid irradiation for heart
and lung transplant recipients. J Med Radiat Sci. 61:202–209. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Han RX, Liu X, Pan P, Jia YJ and Yu JC:
Effectiveness and safety of chemotherapy combined with dendritic
cells co-cultured with cytokine-induced killer cells in the
treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 9:e1089582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kuykendall A and Chiappori A: Advanced
EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Case report,
literature review, and treatment recommendations. Cancer Control.
21:67–73. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Grosse-Wilde A, Voloshanenko O, Bailey SL,
Longton GM, Schaefer U, Csernok AI, Schütz G, Greiner EF, Kemp CJ
and Walczak H: TRAIL-R deficiency in mice enhances lymph node
metastasis without affecting primary tumor development. J Clin
Invest. 118:100–110. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dai X, Zhang J, Arfuso F, Chinnathambi A,
Zayed ME, Alharbi SA, Kumar AP, Ahn KS and Sethi G: Targeting
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor by natural
products as a potential therapeutic approach for cancer therapy.
Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 240:760–773. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang F, Shi P, Xi X, Yi S, Li H, Sun Q and
Sun M: Recombinant adenoviruses expressing TRAIL demonstrate
antitumor effects on non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Med Oncol.
23:191–204. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang X, Cheung RM, Komaki R, Fang B and
Chang JY: Radiotherapy sensitization by tumor-specific TRAIL gene
targeting improves survival of mice bearing human non-small cell
lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 11:6657–6668. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Odoux C, Albers A, Amoscato AA, Lotze MT
and Wong MK: TRAIL, FasL and a blocking anti-DR5 antibody augment
paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in human non-small-cell lung cancer.
Int J Cancer. 97:458–465. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Voortman J, Resende TP, El Hassan Abou MA,
Giaccone G and Kruyt FA: TRAIL therapy in non-small cell lung
cancer cells: Sensitization to death receptor-mediated apoptosis by
proteasome inhibitor bortezomib. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:2103–2112.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Guo L, Fan L, Ren J, Pang Z, Ren Y, Li J,
Wen Z, Qian Y, Zhang L, Ma H and Jiang X: Combination of TRAIL and
actinomycin D liposomes enhances antitumor effect in non-small cell
lung cancer. Int J Nanomedicine. 7:1449–1460. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cho C, Horzempa C, Jones D and
McKeown-Longo PJ: The fibronectin III-1 domain activates a
PI3-Kinase/Akt signaling pathway leading to αvβ5 integrin
activation and TRAIL resistance in human lung cancer cells. BMC
Cancer. 16:5742016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kao PF, Chang HY, Tsai MF, Lin KJ, Tzen KY
and Chang CN: Breast uptake of iodine-131 mimicking lung metastases
in a thyroid cancer patient with a pituitary tumour. Br J Radiol.
74:378–381. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu S, Feng F, Wang K, Men C, Lin C, Liu Q,
Yang D and Gao Z: The therapeutic efficacy of I131-PSCA-mAb in
orthotopic mouse models of prostate cancer. Eur J Med Res.
18:562013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schachter P, Shimonov M and Lorberboim M:
Combined radioiodine (I-131) treatment and radio-guided surgery for
recurrent cervical well-differentiated thyroid cancer. Harefuah.
144(168–172): 231–232. 2005.
|
|
21
|
van Ginkel RJ, Limburg PC, Piers DA, Koops
HS and Hoekstra HJ: Value of continuous leakage monitoring with
radioactive iodine-131-labeled human serum albumin during
hyperthermic isolated limb perfusion with tumor necrosis
factor-alpha and melphalan. Ann Surg Oncol. 9:355–363. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dewaraja YK, Ljungberg M and Koral KF:
Monte Carlo evaluation of object shape effects in iodine-131 SPET
tumor activity quantification. Eur J Nucl Med. 28:900–906. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen S, Yu L, Jiang C, Zhao Y, Sun D, Li
S, Liao G, Chen Y, Fu Q, Tao Q, et al: Pivotal study of
iodine-131-labeled chimeric tumor necrosis treatment
radioimmunotherapy in patients with advanced lung cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 23:1538–1547. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Song JJ, Lin YS, Zhu L and Li F: Efficacy
of iodine-131 in treating hyperthyroid heart disease. Zhongguo Yi
Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 35:166–170. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gultekin SS and Sahmaran T: The efficacy
of patient-dependent practices on exposure rate in patients
undergoing iodine-131 ablation. Health Phys. 104:454–458. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Burvenich I, Schoonooghe S, Cornelissen B,
Blanckaert P, Coene E, Cuvelier C, Mertens N and Slegers G: In
vitro and in vivo targeting properties of iodine-123- or
iodine-131-labeled monoclonal antibody 14C5 in a non-small cell
lung cancer and colon carcinoma model. Clin Cancer Res.
11:7288–7296. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jin CY, Park C, Hong SH, Han MH, Jeong JW,
Xu H, Liu H, Kim GY, Kim WJ, Yoo YH and Choi YH: Synergistic
induction of TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by anisomycin in human
hepatoma cells via the BH3-only protein Bid and c-Jun/AP-1
signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 67:321–328. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Na HJ, Hwang JY, Lee KS, Choi YK, Choe J,
Kim JY, Moon HE, Kim KW, Koh GY, Lee H, et al: TRAIL negatively
regulates VEGF-induced angiogenesis via caspase-8-mediated
enzymatic and non-enzymatic functions. Angiogenesis. 17:179–194.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bai FL, Yu YH, Tian H, Ren GP, Wang H,
Zhou B, Han XH, Yu QZ and Li DS: Genetically engineered Newcastle
disease virus expressing interleukin-2 and TNF-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand for cancer therapy. Cancer Biol Ther.
15:1226–1238. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shivapurkar N, Reddy J, Chaudhary PM and
Gazdar AF: Apoptosis and lung cancer: A review. J Cell Biochem.
88:885–898. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ouyang W, Yang C, Liu Y, Xiong J, Zhang J,
Zhong Y, Zhang G, Zhou F, Zhou Y and Xie C: Redistribution of DR4
and DR5 in lipid rafts accounts for the sensitivity to TRAIL in
NSCLC cells. Int J Oncol. 39:1577–1586. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Howard DM, Kearfott KJ, Wilderman SJ and
Dewaraja YK: Comparison of I-131 radioimmunotherapy tumor
dosimetry: Unit density sphere model versus patient-specific Monte
Carlo calculations. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 26:615–621. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
De Miguel D, Gallego-Lleyda A, Ayuso JM,
Erviti-Ardanaz S, Pazo-Cid R, del Agua C, Fernández LJ, Ochoa I,
Anel A and Martinez-Lostao L: TRAIL-coated lipid-nanoparticles
overcome resistance to soluble recombinant TRAIL in non-small cell
lung cancer cells. Nanotechnology. 27:1851012016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zidan J, Hefer E, Iosilevski G, Drumea K,
Stein ME, Kuten A and Israel O: Efficacy of I131 ablation therapy
using different doses as determined by postoperative thyroid scan
uptake in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 59:1330–1336. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Castellani MR, Aktolun C, Buzzoni R,
Seregni E, Chiesa C, Maccauro M, Aliberti GL, Vellani C, Lorenzoni
A and Bombardieri E: Iodine-131 metaiodobenzylguanidine (I-131
MIBG) diagnosis and therapy of pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma:
Current problems, critical issues and presentation of a sample
case. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 57:146–152. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Harisankar CN, Mittal BR, Bhattacharya A,
Kashyap R and Bhansali A: Iodine-131 meta-iodobezylguanidine single
photon emission computed tomography/computerized tomography in
diagnosis of neuro-endocrine tumors. Indian J Nucl Med. 27:55–58.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shao H, Zhang J, Sun Z, Chen F, Dai X, Li
Y, Ni Y and Xu K: Necrosis targeted radiotherapy with
iodine-131-labeled hypericin to improve anticancer efficacy of
vascular disrupting treatment in rabbit VX2 tumor models.
Oncotarget. 6:14247–14259. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kaewput C and Pusuwan P: Severe
hyponatremia: A comorbidity with I131 therapy in a patient with
papillary thyroid cancer. J Med Assoc Thai. 97:886–890.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Grimminger PP, Schneider PM, Metzger R,
Vallböhmer D, Danenberg KD, Danenberg PV, Hölscher AH and Brabender
J: The prognostic role of Bcl-2 mRNA expression in curatively
resected non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Lung Cancer. 70:82–87.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Checinska A, Giaccone G, Rodriguez JA,
Kruyt FA and Jimenez CR: Comparative proteomics analysis of
caspase-9-protein complexes in untreated and cytochrome c/dATP
stimulated lysates of NSCLC cells. J Proteomics. 72:575–585. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ballas MS and Chachoua A: Rationale for
targeting VEGF, FGF, and PDGF for the treatment of NSCLC. Onco
Targets Ther. 4:43–58. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rades D, Setter C, Dunst J, Dahl O, Schild
SE and Noack F: Prognostic impact of VEGF and VEGF receptor 1
(FLT1) expression in patients irradiated for stage II/III non-small
cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Strahlenther Onkol. 186:307–314. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li J, Wang Y, Liu L, Yuan Y and Bao Y:
Thioridazine sensitizes apoptotic effect of TRAIL in human lung
cancer PC9 cells through ER stress mediated upregulation of DR5.
Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 20:80–87. 2017.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nazim UM, Moon JH, Lee YJ, Seol JW and
Park SY: PPARγ activation by troglitazone enhances human lung
cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via autophagy flux.
Oncotarget. 8:26819–26831. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|