|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
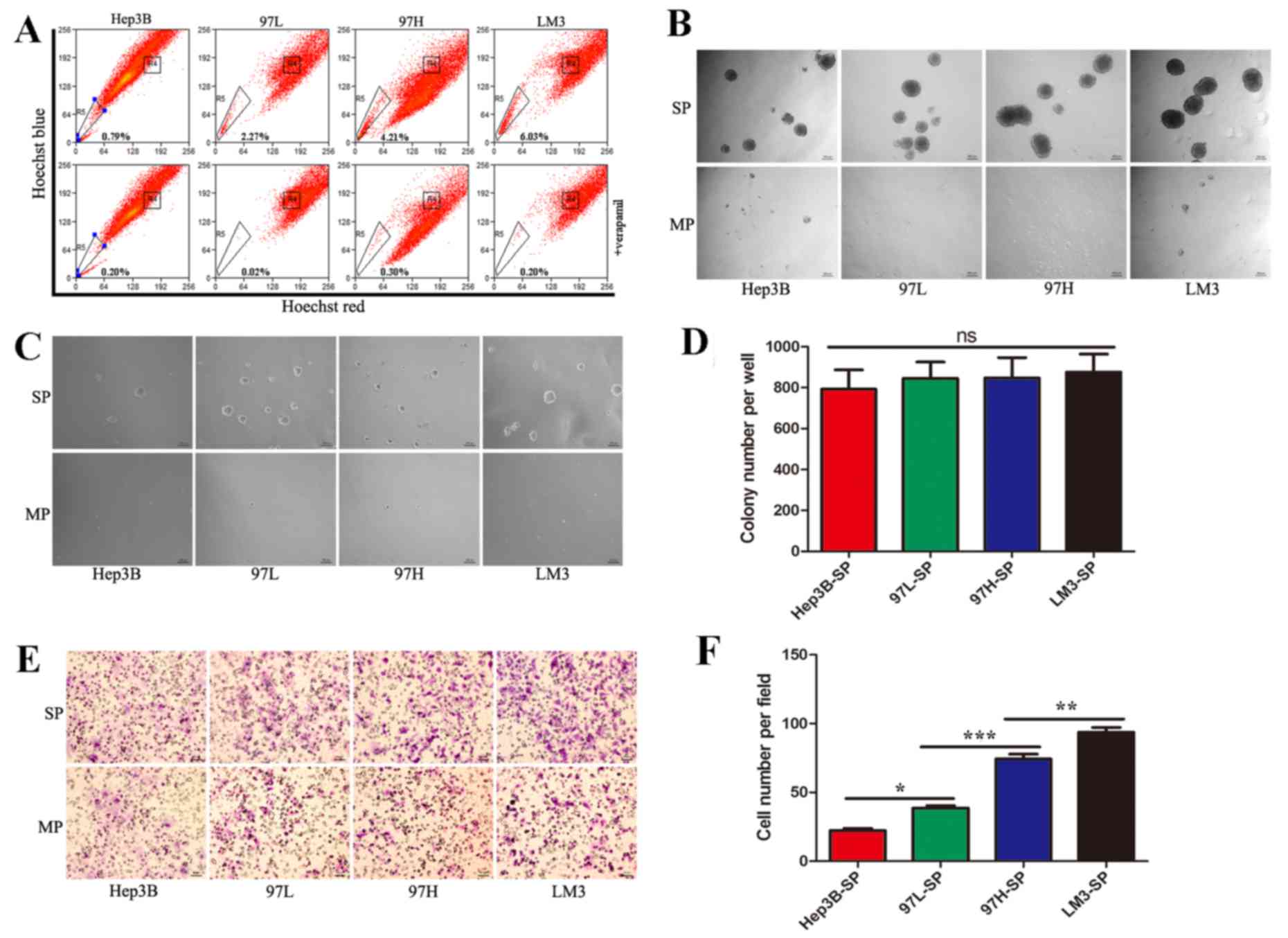
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
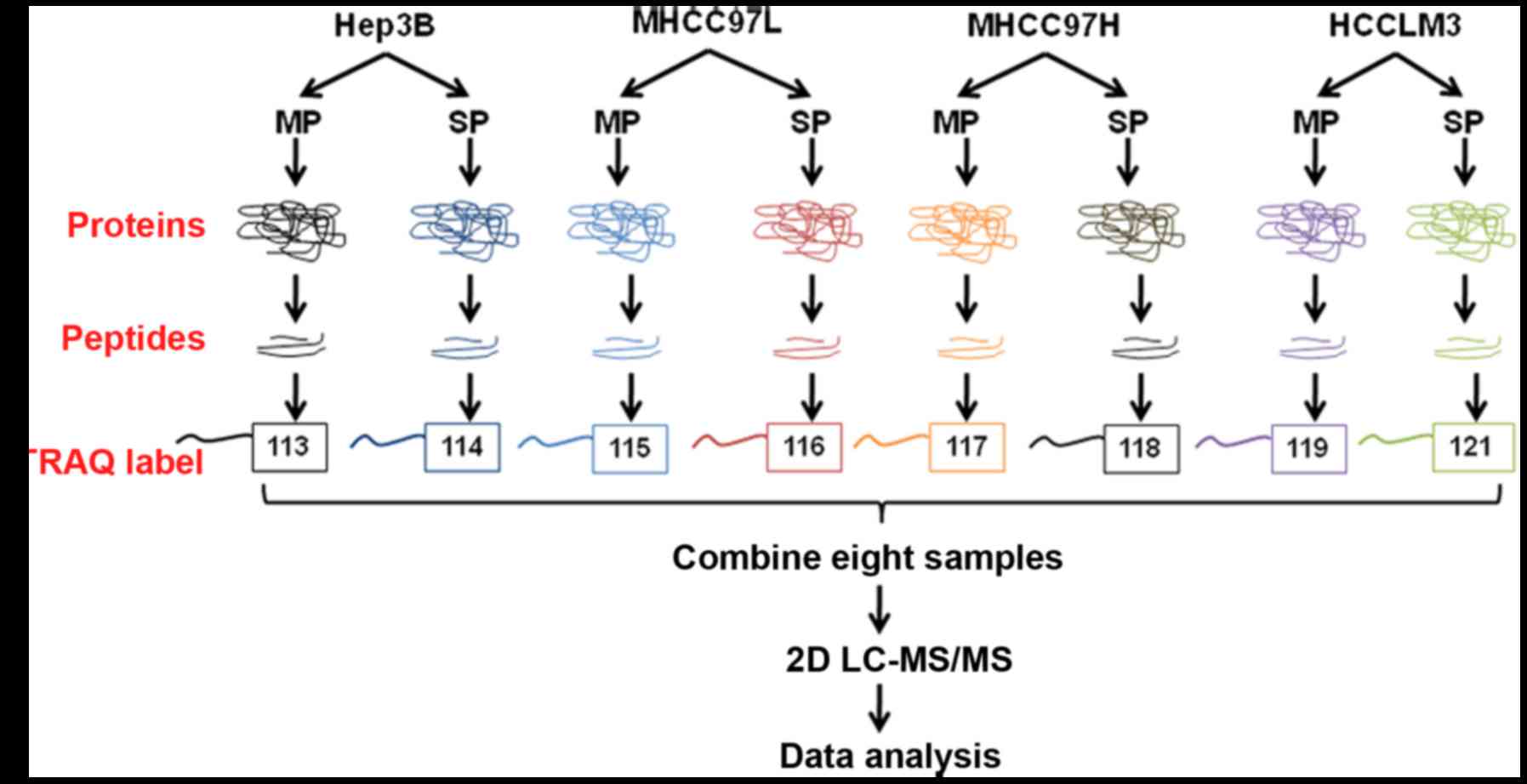
3
|
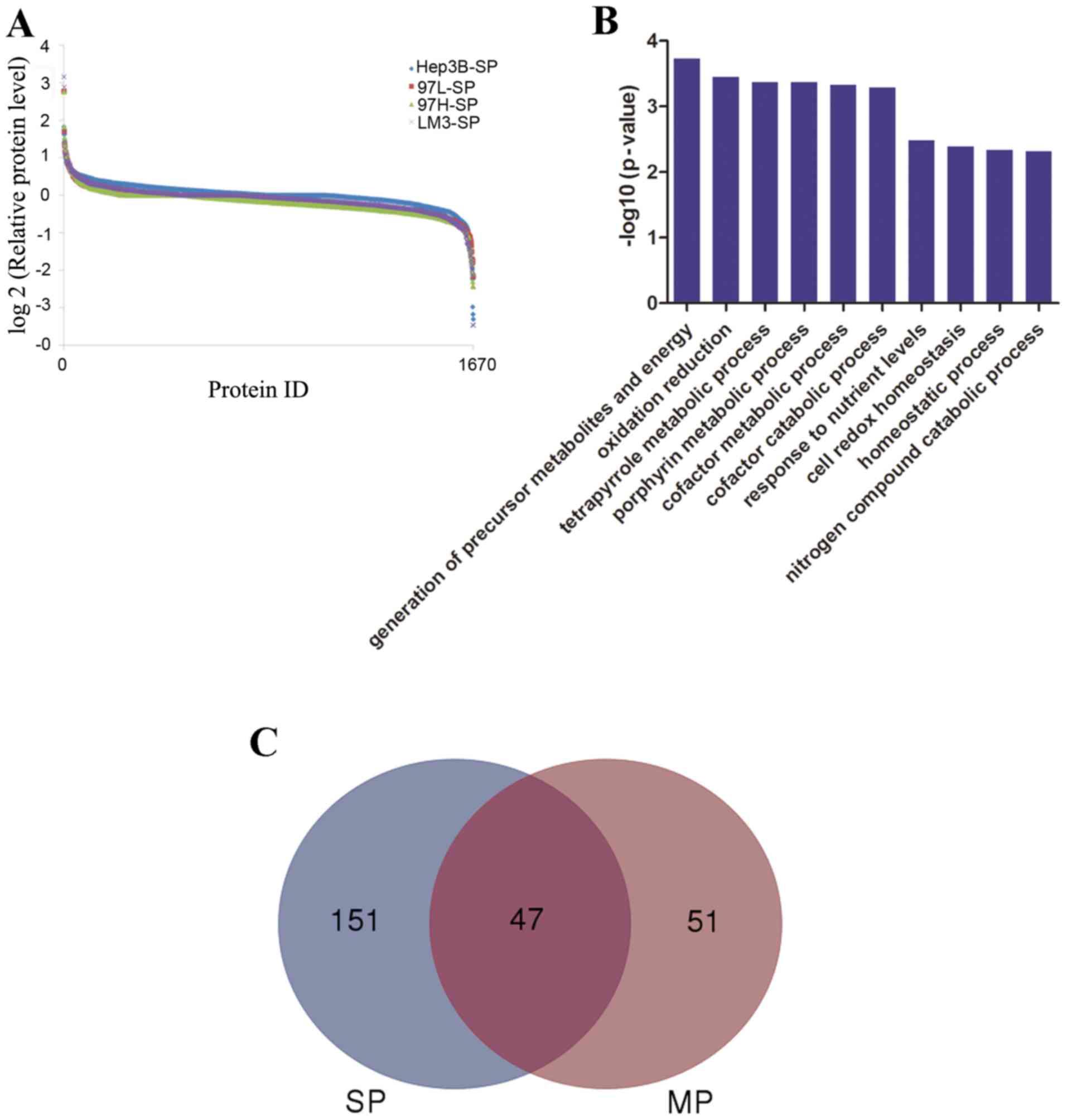
Shah SA, Cleary SP, Wei AC, Yang I, Taylor
BR, Hemming AW, Langer B, Grant DR, Greig PD and Gallinger:
Recurrence after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: Risk
factors, treatment, and outcomes. Surgery. 141:330–339. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
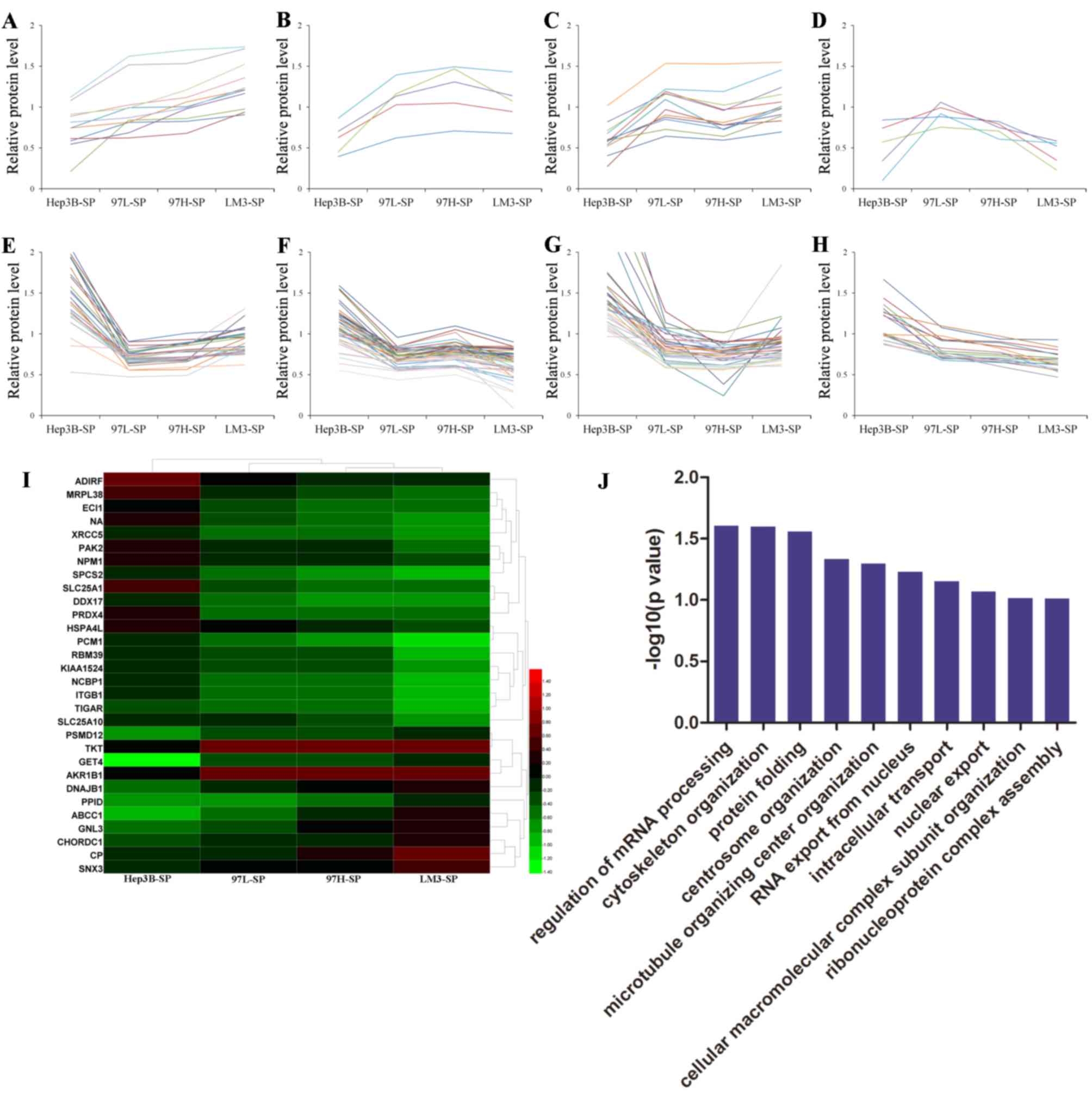
4
|
Bruix J and Sherman M: American
Association for the Study of Liver Diseases: Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology. 53:1020–1022.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tang Z: Hepatocellular carcinoma-cause,
treatment and metastasis. World J Gastroenterol. 7:445–454. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guo Z, Li LQ, Jiang JH, Ou C, Zeng LX and
Xiang BD: Cancer stem cell markers correlate with early recurrence
and survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol.
20:2098–2106. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu Z, Pestell TG, Lisanti MP and Pestell
RG: Cancer stem cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:2144–2151. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Giannelli G, Bergamini C, Fransvea E,
Marinosci F, Quaranta V and Antonaci S: Human hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC) cells require both alpha3beta1 integrin and matrix
metalloproteinases activity for migration and invasion. Lab Invest.
81:613–617. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen W, Chen L, Cai Z, Liang D, Zhao B,
Zeng Y, Liu X and Liu J: Overexpression of annexin A4 indicates
poor prognosis and promotes tumor metastasis of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 37:9343–9355. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hermann PC, Huber SL, Herrler T, Aicher A,
Ellwart JW, Guba M, Bruns CJ and Heeschen C: Distinct populations
of cancer stem cells determine tumor growth and metastatic activity
in human pancreatic cancer. Cell Stem Cell. 1:313–323. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shi GM, Xu Y, Fan J, Zhou J, Yang XR, Qiu
SJ, Liao Y, Wu WZ, Ji Y, Ke AW, et al: Identification of side
population cells in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with
stepwise metastatic potentials. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
134:1155–1163. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Goodell MA, Brose K, Paradis G, Conner AS
and Mulligan RC: Isolation and functional properties of murine
hematopoietic stem cells that are replicating in vivo. J Exp Med.
183:1797–1806. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chiba T, Kita K, Zheng YW, Yokosuka O,
Saisho H, Iwama A, Nakauchi H and Taniguchi H: Side population
purified from hepatocellular carcinoma cells harbors cancer stem
cell-like properties. Hepatology. 44:240–251. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang J, Guo LP, Chen LZ, Zeng YX and Lu
SH: Identification of cancer stem cell-like side population cells
in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line. Cancer Res.
67:3716–3724. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ho MM, Ng AV, Lam S and Hung JY: Side
population in human lung cancer cell lines and tumors is enriched
with stem-like cancer cells. Cancer Res. 67:4827–4833. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Haraguchi N, Utsunomiya T, Inoue H, Tanaka
F, Mimori K, Barnard GF and Mori M: Characterization of a side
population of cancer cells from human gastrointestinal system. Stem
Cells. 24:506–513. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ross PL, Huang YN, Marchese JN, Williamson
B, Parker K, Hattan S, Khainovski N, Pillai S, Dey S, Daniels S, et
al: Multiplexed protein quantitation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
using amine-reactive isobaric tagging reagents. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 3:1154–1169. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Aggarwal K, Choe LH and Lee KH: Shotgun
proteomics using the iTRAQ isobaric tags. Brief Funct Genomic
Proteomic. 5:112–120. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xing X, Huang Y, Wang S, Chi M, Zeng Y,
Chen L, Li L, Zeng J, Lin M, Han X, et al: Comparative analysis of
primary hepatocellular carcinoma with single and multiple lesions
by iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics. J Roteomics. 128:262–271.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wei D, Zeng Y, Xing X, Liu H, Lin M, Liu X
and Liu J: Proteome differences between hepatitis B virus
genotype-B- and genotype-C-induced hepatocellular carcinoma
revealed by iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics. J Proteome Res.
15:487–498. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Huang X, Zeng Y, Xing X, Zeng J, Gao Y,
Cai Z, Xu B, Liu X, Huang A and Liu J: Quantitative proteomics
analysis of early recurrence/metastasis of huge hepatocellular
carcinoma following radical resection. Proteome Sci. 12:222014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ko CH, Cheng CF, Lai CP, Tzu TH, Chiu CW,
Lin MW, Wu SY, Sun CY, Tseng HW, Wang CC, et al: Differential
proteomic analysis of cancer stem cell properties in hepatocellular
carcinomas by isobaric tag labeling and mass spectrometry. J
Proteome Res. 12:3573–3585. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu Y, Xie Y, Wang X, Chen X, Liu Q, Ying M
and Zheng Q: Identification of cancer stem cells from
hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines and their related microRNAs.
Oncol Rep. 30:2056–2062. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu Y, Shen H, Yu H, Zhong F, Zhang Y,
Zhang C, Zhao J, Li H, Chen J, Liu Y and Yang P: Systematic
proteomic analysis of human hepotacellular carcinoma cells reveals
molecular pathways and networks involved in metastasis. Mol
Biosyst. 7:1908–1916. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen N, Sun W, Deng X, Hao Y, Chen X, Xing
B, Jia W, Ma J, Wei H, Zhu Y, et al: Quantitative proteome analysis
of HCC cell lines with different metastatic potentials by SILAC.
Proteomics. 8:5108–5118. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ricciardelli C, Lokman NA, Cheruvu S, Tan
IA, Ween MP, Pyragius CE, Ruszkiewicz A, Hoffmann P and Oehler MK:
Transketolase is upregulated in metastatic peritoneal implants and
promotes ovarian cancer cell proliferation. Clin Exp Metastasis.
32:441–455. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li J, Zhu SC, Li SG, Zhao Y, Xu JR and
Song CY: TKTL1 promotes cell proliferation and metastasis in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 74:71–76.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tan GS, Lim KH, Tan HT, Khoo ML, Tan SH,
Toh HC and Chung Ching Ming M: Novel proteomic biomarker panel for
prediction of aggressive metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma
relapse in surgically resectable patients. J Proteome Res.
13:4833–4846. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu IM, Lai RK, Lin SH, Tse AP, Chiu DK,
Koh HY, Law CT, Wong CM, Cai Z, Wong CC and Ng IO: Transketolase
counteracts oxidative stress to drive cancer development. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 113:E725–E734. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chow AK, Ng L, Lam CS, Wong SK, Wan TM,
Cheng NS, Yau TC, Poon RT and Pang RW: The Enhanced metastatic
potential of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells with sorafenib
resistance. PLoS One. 8:e786752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lu Y, Hu J, Sun W, Li S, Deng S and Li M:
MiR-29c inhibits cell growth, invasion, and migration of pancreatic
cancer by targeting ITGB1. Onco Targets Ther. 9:992015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Broustas CG and Lieberman HB: RAD9
enhances radioresistance of human prostate cancer cells through
regulation of ITGB1 protein levels. Prostate. 74:1359–1370. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nakarai C, Osawa K, Akiyama M, Matsubara
N, Ikeuchi H, Yamano T, Hirota S, Tomita N, Usami M and Kido Y:
Expression of AKR1C3 and CNN3 as markers for detection of lymph
node metastases in colorectal cancer. Clin Exp Med. 15:333–341.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dan S, Shirakawa M, Mukai Y, Yoshida Y,
Yamazaki K, Kawaguchi T, Matsuura M, Nakamura Y and Yamori T:
Identification of candidate predictive markers of anticancer drug
sensitivity using a panel of human cancer cell lines. Cancer Sci.
94:1074–1082. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sato M, Matsuda Y, Wakai T, Kubota M,
Osawa M, Fujimaki S, Sanpei A, Takamura M, Yamagiwa S and Aoyagi Y:
p21-activated kinase-2 is a critical mediator of transforming
growth factor-β-induced hepatoma cell migration. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 28:1047–1055. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee M, Williams KA, Hu Y, Andreas J, Patel
SJ, Zhang S and Crawford NP: GNL3 and SKA3 are novel prostate
cancer metastasis susceptibility genes. Clin Exp Metastasis.
32:769–782. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ching RH, Lau EY, Ling PM, Lee JMF, Ma MK,
Cheng BY, Lo RC, Ng IO and Lee TK: Phosphorylation of Nucleophosmin
at Threonine 234/237 is associated with HCC metastasis. Oncotarget.
6:43483–43495. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ueo H, Takano Y, Matsumura T, Kurashige J,
Shinden Y, Eguchi H, Sudo T, Sugimachi K, Saeki H, Oki E, et al:
Identification of genes that predict lymph node metastasis in
colorectal cancer cases. Fukuoka Igaku Zasshi. 104:559–563.
2013.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Song G, Ouyang G and Bao S: The activation
of Akt/PKB signaling pathway and cell survival. J Cell Mol Med.
9:59–71. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Martini M, De Santis MC, Braccini L,
Gulluni F and Hirsch E: PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: An
updated review. Ann Med. 46:372–383. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li C, Wang C, Xing Y, Zhen J and Ai Z:
CD133 promotes gallbladder carcinoma cell migration through
activating Akt phosphorylation. Oncotarget. 7:17751–17759.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang H, Zhang G, Zhang H, Zhang F, Zhou B,
Ning F, Wang HS, Cai SH and Du J: Acquisition of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype and cancer stem
cell-like properties in cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells
through AKT/β-catenin/Snail signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol.
723:156–166. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rinkenbaugh AL and Baldwin AS: The NF-κB
pathway and cancer stem cells. Cells. 5:pii: E16. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang FS, Fan JG, Zhang Z, Gao B and Wang
HY: The global burden of liver disease: The major impact of China.
Hepatology. 60:2099–2108. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Margonis GA, Sasaki K, Andreatos N,
Nishioka Y, Sugawara T, Amini N, Buettner S, Hashimoto M, Shindoh J
and Pawlik TM: Prognostic impact of complications after resection
of early stage hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 115:791–804.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chiba T, Iwama A and Yokosuka O: Cancer
stem cells in hepatocellular carcinoma: Therapeutic implications
based on stem cell biology. Hepatol Res. 46:50–57. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE,
Hawkins C, Squire J and Dirks PB: Identification of a cancer stem
cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 63:5821–5828.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Collins AT, Berry PA, Hyde C, Stower MJ
and Maitland NJ: Prospective identification of tumorigenic prostate
cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 65:10946–10951. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kim CF, Jackson EL, Woolfenden AE,
Lawrence S, Babar I, Vogel S, Crowley D, Bronson RT and Jacks T:
Identification of bronchioalveolar stem cells in normal lung and
lung cancer. Cell. 121:823–835. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Takaishi S, Okumura T, Tu S, Wang SS,
Shibata W, Vigneshwaran R, Gordon SA, Shimada Y and Wang TC:
Identification of gastric cancer stem cells using the cell surface
marker CD44. Stem Cells. 27:1006–1020. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ricci-Vitiani L, Lombardi DG, Pilozzi E,
Biffoni M, Todaro M, Peschle C and De Maria R: Identification and
expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature.
445:111–115. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li C, Heidt DG, Dalerba P, Burant CF,
Zhang L, Adsay V, Wicha M, Clarke MF and Simeone DM: Identification
of pancreatic cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 67:1030–1037. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Schatton T, Murphy GF, Frank NY, Yamaura
K, Waaga-Gasser AM, Gasser M, Zhan Q, Jordan S, Duncan LM,
Weishaupt C, et al: Identification of cells initiating human
melanomas. Nature. 451:345–349. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yang ZF, Ngai P, Ho DW, Yu WC, Ng MN, Lau
CK, Li ML, Tam KH, Lam CT, Poon RT and Fan ST: Identification of
local and circulating cancer stem cells in human liver cancer.
Hepatology. 47:919–928. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ma S, Chan KW, Hu L, Lee TK, Wo JY, Ng IO,
Zheng BJ and Guan XY: Identification and characterization of
tumorigenic liver cancer stem/progenitor cells. Gastroenterology.
132:2542–2556. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yang ZF, Ho DW, Ng MN, Lau CK, Yu WC, Ngai
P, Chu PW, Lam CT, Poon RT and Fan ST: Significance of CD90+ cancer
stem cells in human liver cancer. Cancer Cell. 13:153–166. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhu Z, Hao X, Yan M, Yao M, Ge C, Gu J and
Li J: Cancer stem/progenitor cells are highly enriched in
CD133+CD44+ population in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer.
126:2067–2078. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yamashita T, Ji J, Budhu A, Forgues M,
Yang W, Wang HY, Jia H, Ye Q, Qin LX, Wauthier E, et al:
EpCAM-positive hepatocellular carcinoma cells are tumor-initiating
cells with stem/progenitor cell features. Gastroenterology.
136:1012–1024. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yang W, Wang C, Lin Y, Liu Q, Yu LX, Tang
L, Yan HX, Fu J, Chen Y, Zhang HL, et al: OV6+ tumor-initiating
cells contribute to tumor progression and invasion in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 57:613–620. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ma S, Chan KW, Lee TK-W, Tang KH, Wo JY,
Zheng BJ and Guan XY: Aldehyde dehydrogenase discriminates the
CD133 liver cancer stem cell populations. Mol Cancer Res.
6:1146–1153. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ma S: Biology and clinical implications of
CD133(+) liver cancer stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 319:126–132. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Yang X, Wang J, Qu S, Zhang H, Ruan B, Gao
Y, Ma B, Wang X, Wu N, Li X, et al: MicroRNA-200a suppresses
metastatic potential of side population cells in human
hepatocellular carcinoma by decreasing ZEB2. Oncotarget.
6:7918–7929. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhou L, Yang ZX, Song WJ, Li QJ, Yang F,
Wang DS, Zhang N and Dou KF: MicroRNA-21 regulates the migration
and invasion of a stem-like population in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Int J Oncol. 43:661–669. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Li J, Deng Z, Wang Z, Wang D, Zhang L, Su
Q, Lai Y, Li B, Luo Z, Chen X, et al: Zipper-interacting protein
kinase promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and
metastasis through AKT and NF-kB signaling and is associated with
metastasis and poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients.
Oncotarget. 6:8323–8338. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Tang Y, Lv P, Sun Z, Han L and Zhou W:
14-3-3β promotes migration and invasion of human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells by modulating expression of MMP2 and MMP9 through
PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway. PLoS One. 11:e01460702016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wang YH, Dong YY, Wang WM, Xie XY, Wang
ZM, Chen RX, Chen J, Gao DM, Cui JF and Ren ZG: Vascular
endothelial cells facilitated HCC invasion and metastasis through
the Akt and NF-κB pathways induced by paracrine cytokines. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 32:512013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Chen Y, Yu D, Zhang H, He H, Zhang C, Zhao
W and Shao R: CD133(+)EpCAM(+) phenotype possesses more
characteristics of tumor initiating cells in hepatocellular
carcinoma Huh7 cells. Int J Biol Sci. 8:992–1004. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Moitra K: Overcoming multidrug resistance
in cancer stem cells. Bio Med Res Int. 2015:6357452015.
|