|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stenzl A, Cowan NC, De Santis M, Jakse G,
Kuczyk MA, Merseburger AS, Ribal MJ, Sherif A and Witjes JA: The
updated EAU guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder
cancer. Eur Urol. 55:815–825. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Babjuk M, Oosterlinck W, Sylvester R,
Kaasinen E, Böhle A and Palou-Redorta J: European Association of
Urology (EAU): EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial
carcinoma of the bladder. Eur Urol. 54:303–314. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kao LT, Huang CY, Lin HC and Chu CM: No
increased risk of fracture in patients receiving antimuscarinics
for overactive bladder syndrome: A retrospective cohort study. J
Clin Pharmacol. Jan 9–2018.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Balachandran AA and Duckett J: Metastatic
breast cancer presenting as detrusor overactivity. BMJ Case Rep.
2014:pii: bcr2014207920. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Haferkamp A, Schurch B, Reitz A, Krengel
U, Grosse J, Kramer G, Schumacher S, Bastian PJ, Büttner R, Müller
SC and Stöhrer M: Lack of ultrastructural detrusor changes
following endoscopic injection of botulinum toxin type a in
overactive neurogenic bladder. Eur Urol. 46:784–791. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ito Y, Kashiwabara M, Yoshida A, Hikiyama
E, Onoue S and Yamada S: Muscarinic receptor binding in rat bladder
urothelium and detrusor muscle by intravesical solifenacin. Biol
Pharm Bull. 39:1167–1171. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hawthorn MH, Chapple CR, Cock M and
Chess-Williams R: Urothelium-derived inhibitory factor(s)
influences on detrusor muscle contractility in vitro. Br J
Pharmacol. 129:416–419. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang CT, Chen TM, Mei CT, Chang CF, Liu
LL, Chiu KH, Wu TM, Lan YC, Liu WS and Chen YH: The Functional
Haplotypes of CHRM3 Modulate mRNA Expression and Associate
with Bladder Cancer among a Chinese Han Population in Kaohsiung
City. Biomed Res Int. 2016:40528462016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
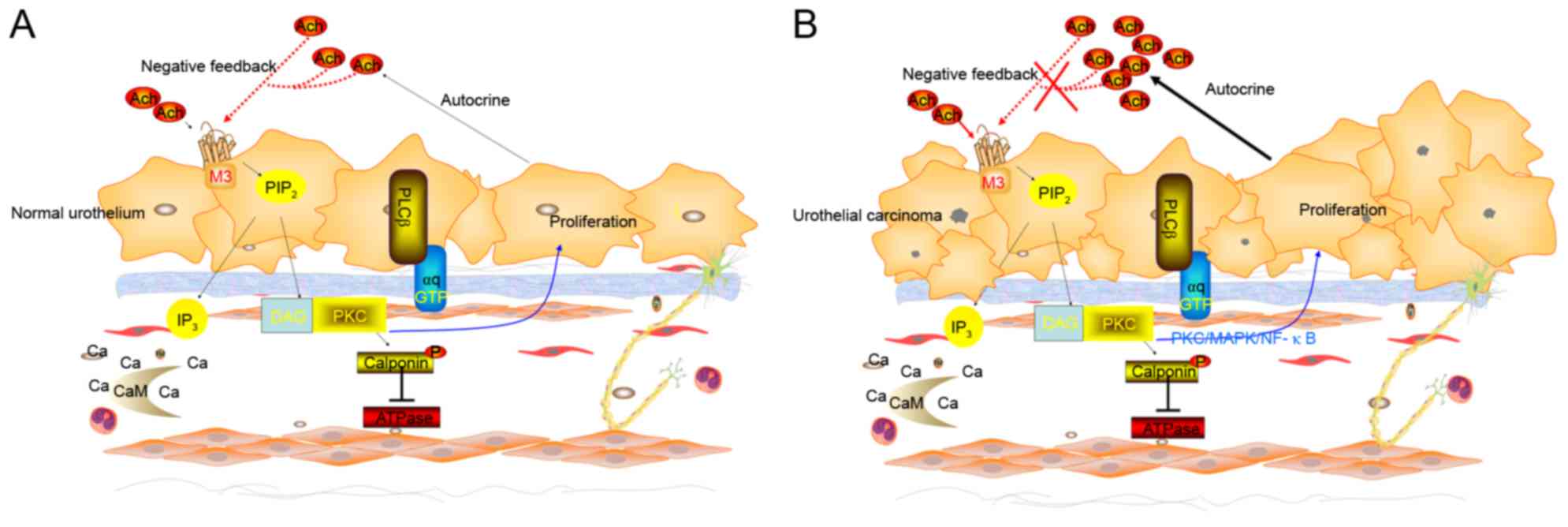
Sun Y and Chai T: 319 the role of m3
muscarinic signaling in bladder urothelial cancer cell
proliferation and apoptosis. J Urol. 183:2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Gutkind JS, Novotny EA, Brann MR and
Robbins KC: Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes as
agonist-dependent oncogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 88:4703–4707.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ashkenazi A, Ramachandran J and Capon DJ:
Acetylcholine analogue stimulates DNA synthesis in brain-derived
cells via specific muscarinic receptor subtypes. Nature.
340:146–150. 1989. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Von Rosenvinge EC and Raufman JP:
Muscarinic receptor signaling in colon cancer. Cancers (Basel).
3:971–981. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Parnell EA, Calleja-Macias IE, Kalantari
M, Grando SA and Bernard HU: Muscarinic cholinergic signaling in
cervical cancer cells affects cell motility via ERK1/2 signaling.
Life Sci. 91:1093–1098. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Homma Y, Yoshida M, Seki N, Yokoyama O,
Kakizaki H, Gotoh M, Yamanishi T, Yamaguchi O, Takeda M and
Nishizawa O: Symptom assessment tool for overactive bladder
syndrome-overactive bladder symptom score. Urology. 68:318–323.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
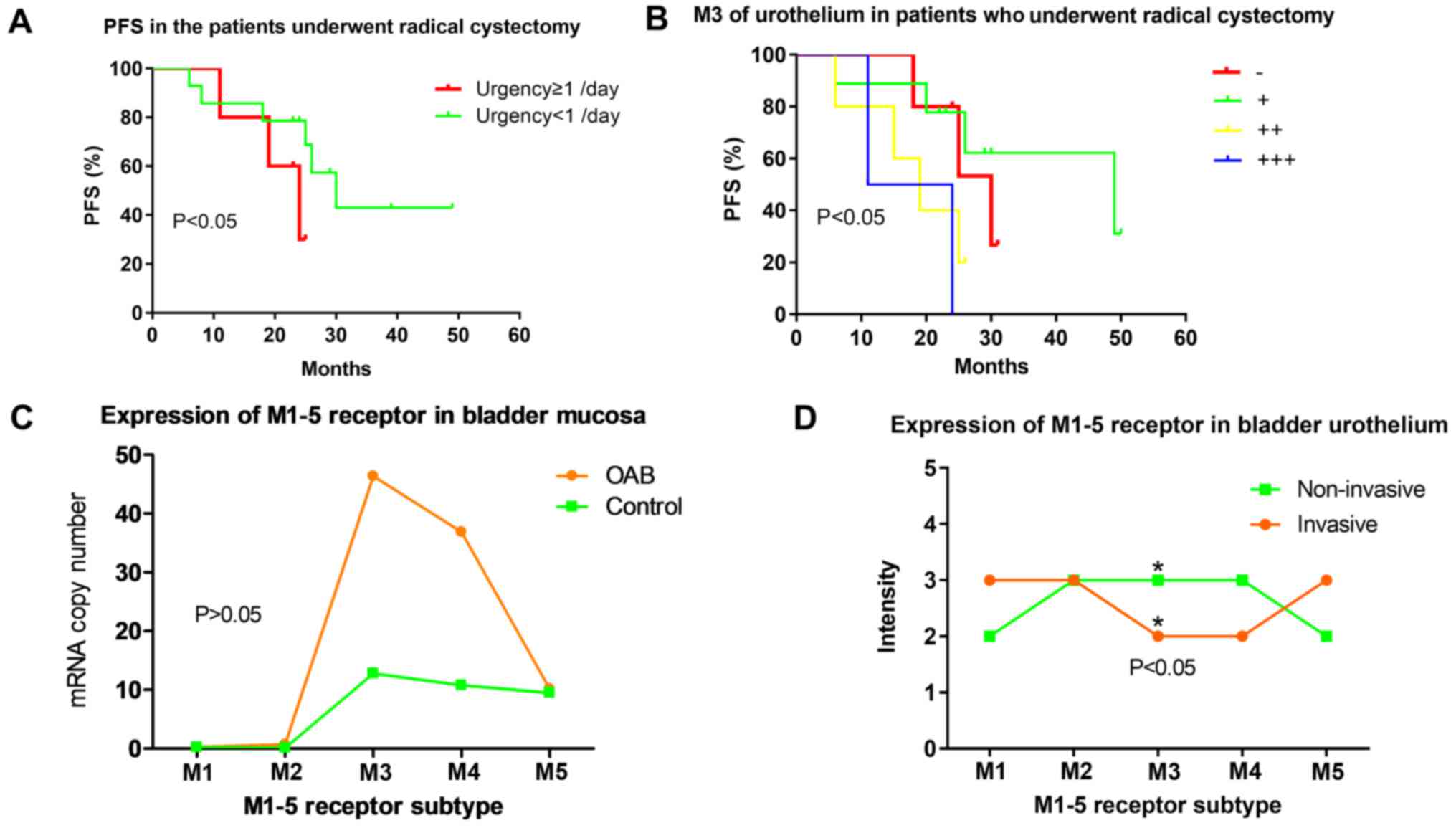
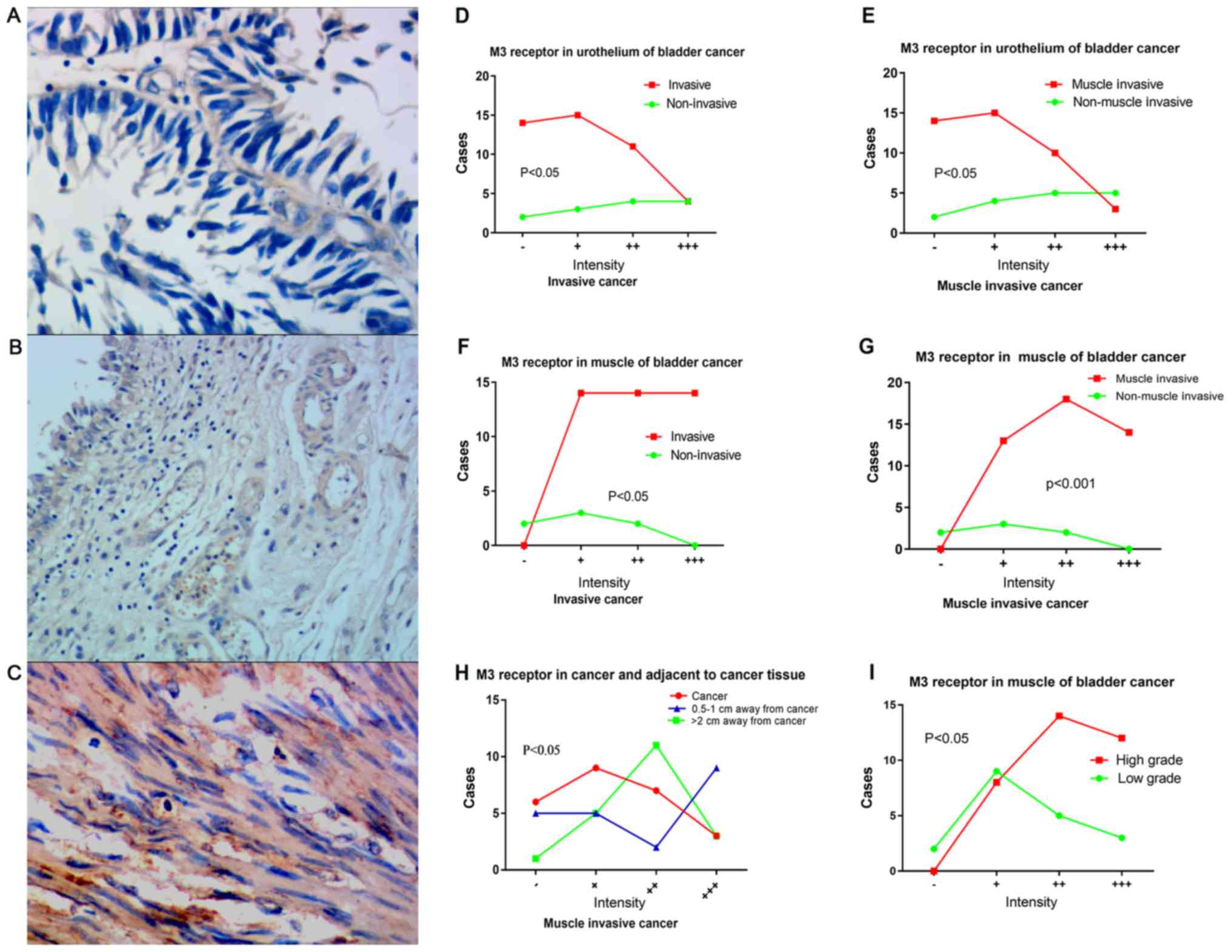
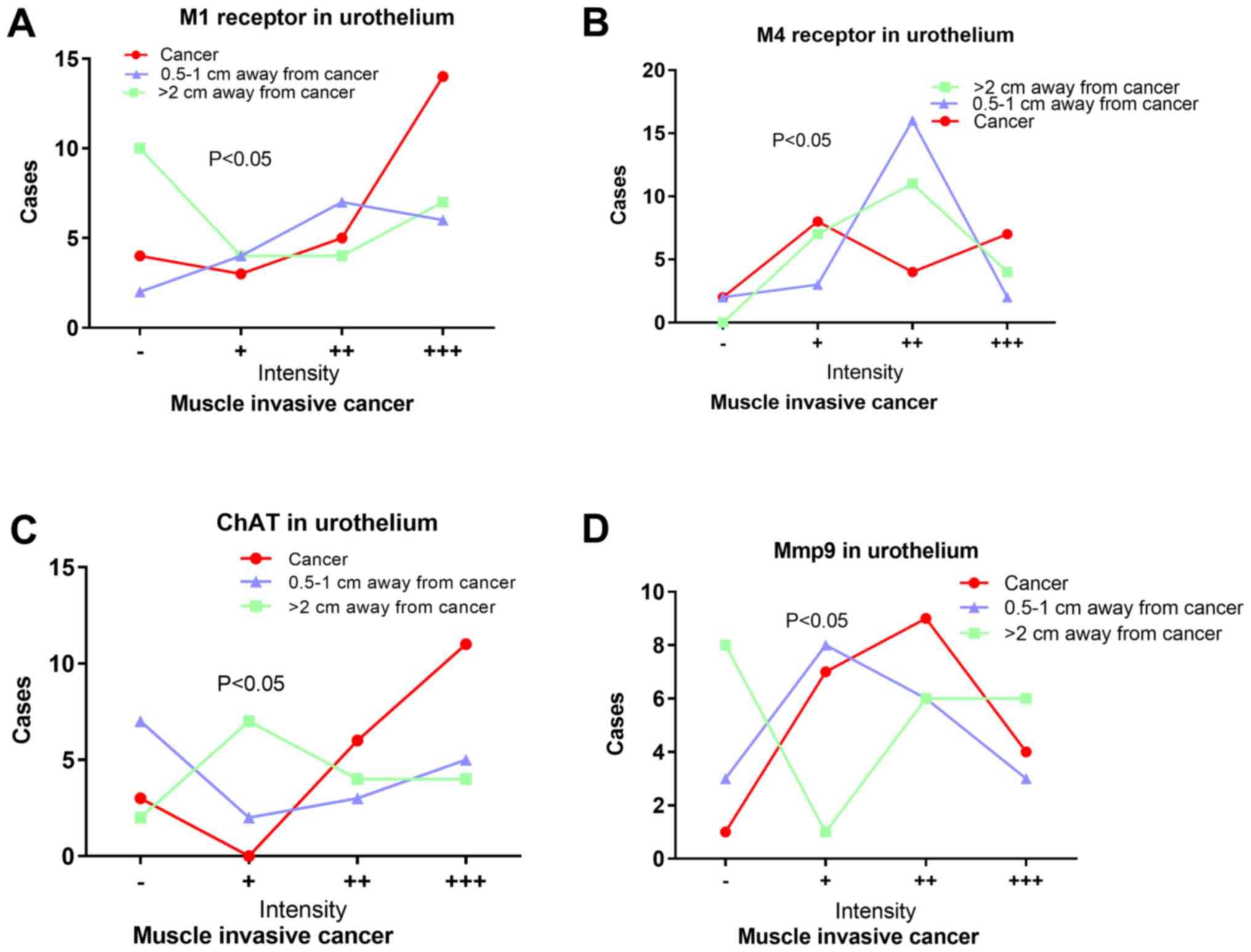
Yi X: Expression and clinical significance
of M1-5 receptor subtype of bladder mucosa in patients with OAB
[D]. Guang Zhou South Med Univ. 2011.
|
|
17
|
Humphrey PA, Moch H, Cubilla AL, Ulbright
TM and Reuter VE: The 2016 WHO classification of tumours of the
urinary system and male genital organs-part B: Prostate and bladder
tumours. Eur Urol. 70:106–119. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tully BT, Li M, Sun Y, Berkowitz J and
Chai TC: Defects in muscarinic receptor cell signaling in bladder
urothelial cancer cell lines. Urology. 74:467–473. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pacini L, De Falco E, Di Bari M, Coccia A,
Siciliano C, Ponti D, Pastore AL, Petrozza V, Carbone A, Tata AM
and Calogero A: M2muscarinic receptors inhibit cell proliferation
and migration in urothelial bladder cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther.
15:1489–1498. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bschleipfer T, Schukowski K, Weidner W,
Grando S, Schwantes U, Kummer W and Lips K: Expression and
distribution of cholinergic receptors in the human urothelium. Life
Sci. 80:2303–2307. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yamanishi T, Kaga K, Fuse M, Shibata C,
Kamai T and Uchiyama T: The role of muscarinic receptor subtypes on
carbachol-induced contraction of normal human detrusor and
overactive detrusor associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia. J
Pharmacol Sci. 128:65–70. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Park YS and Cho NJ: Enhanced proliferation
of SNU-407 human colon cancer cells by muscarinic acetylcholine
receptors. BMB Rep. 41:803–807. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Feng YJ, Zhang BY, Yao RY and Lu Y:
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M3 in proliferation and
perineural invasion of cholangiocarcinoma cells. Hepatobiliary
Pancreat Dis Int. 11:418–423. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Arrighi N, Bodei S, Lucente A, Michel MC,
Zani D, Simeone C, Cunico SC, Spano PF and Sigala S: Muscarinic
receptors stimulate cell proliferation in the human
urothelium-derived cell line UROtsa. Pharmacol Res. 64:420–425.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Arrighi N, Bodei S, Zani D, Michel MC,
Simeone C, Cunico Cosciani S, Spano P and Sigala S: Different
muscarinic receptor subtypes modulate proliferation of primary
human detrusor smooth muscle cells via Akt/PI3K and map kinases.
Pharmacol Res. 74:1–6. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Campoy FJ, Vidal CJ, Muñoz-Delgado E,
Montenegro MF, Cabezas-Herrera J and Nieto-Cerón S: Cholinergic
system and cell proliferation. Chem Biol Interact. 259:257–265.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Spindel ER: Muscarinic receptor agonists
and antagonists: Effects on cancer. Handb Exp Pharmacol.
208:451–468. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Peng Z, Heath J, Drachenberg C, Raufman JP
and Xie G: Cholinergic muscarinic receptor activation augments
murine intestinal epithelial cell proliferation and tumorigenesis.
BMC Cancer. 13:2042013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu WT, Huang KY, Lu MC, Huang HL, Chen
CY, Cheng YL, Yu HC, Liu SQ, Lai NS and Huang HB: TGF-β upregulates
the translation of USP15 via the PI3K/AKT pathway to promote p53
stability. Oncogene. 36:2715–2723. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|