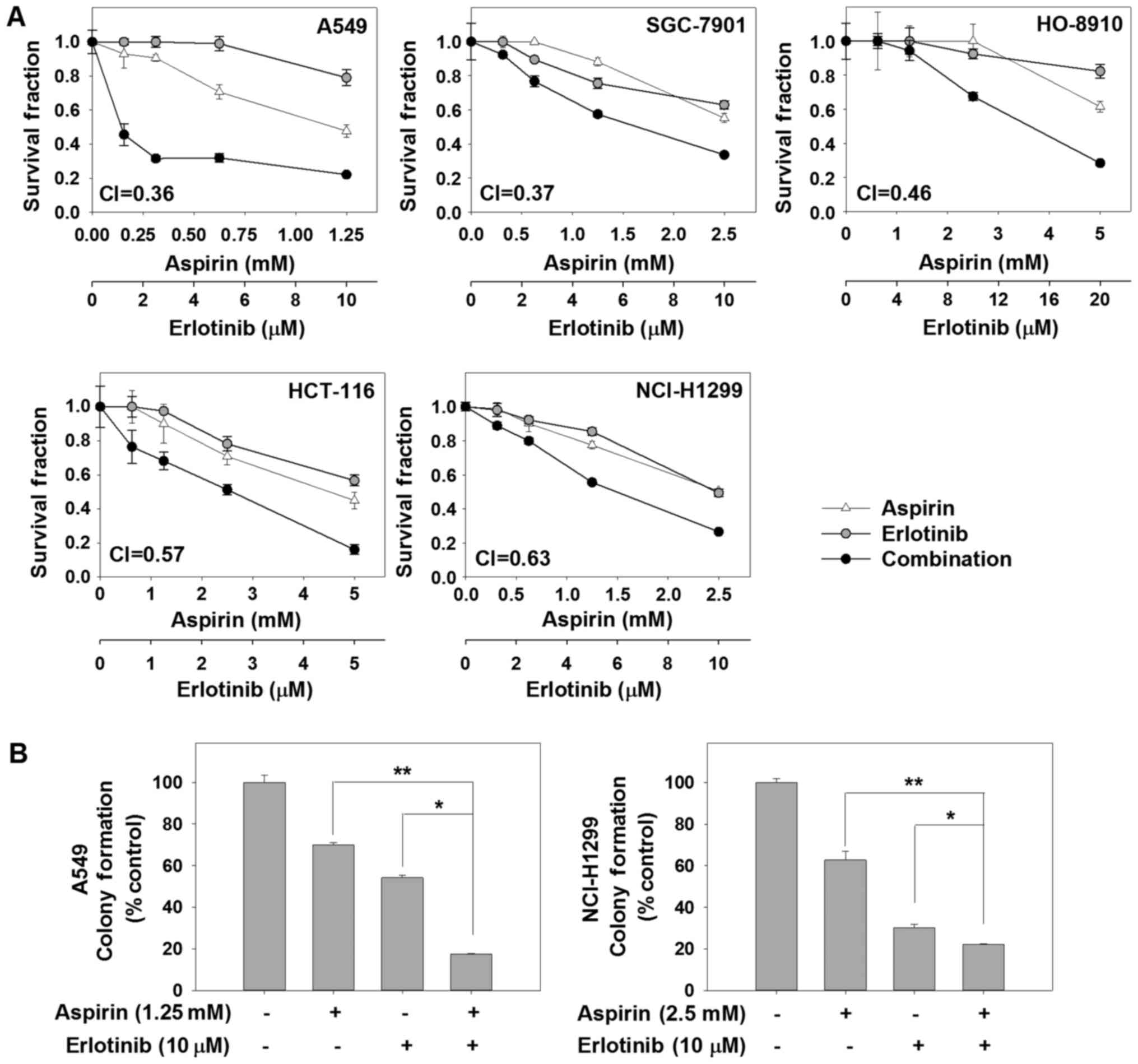
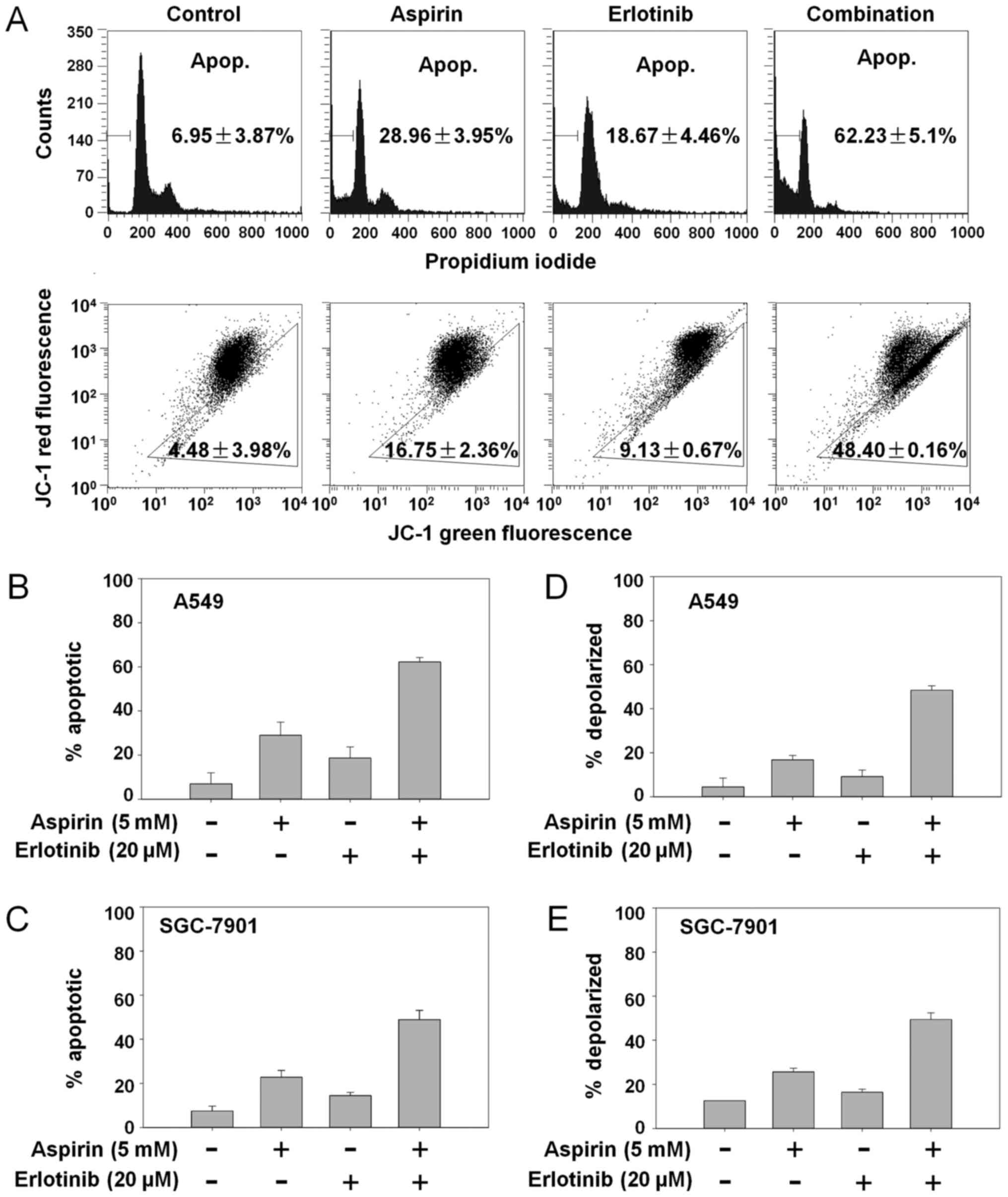
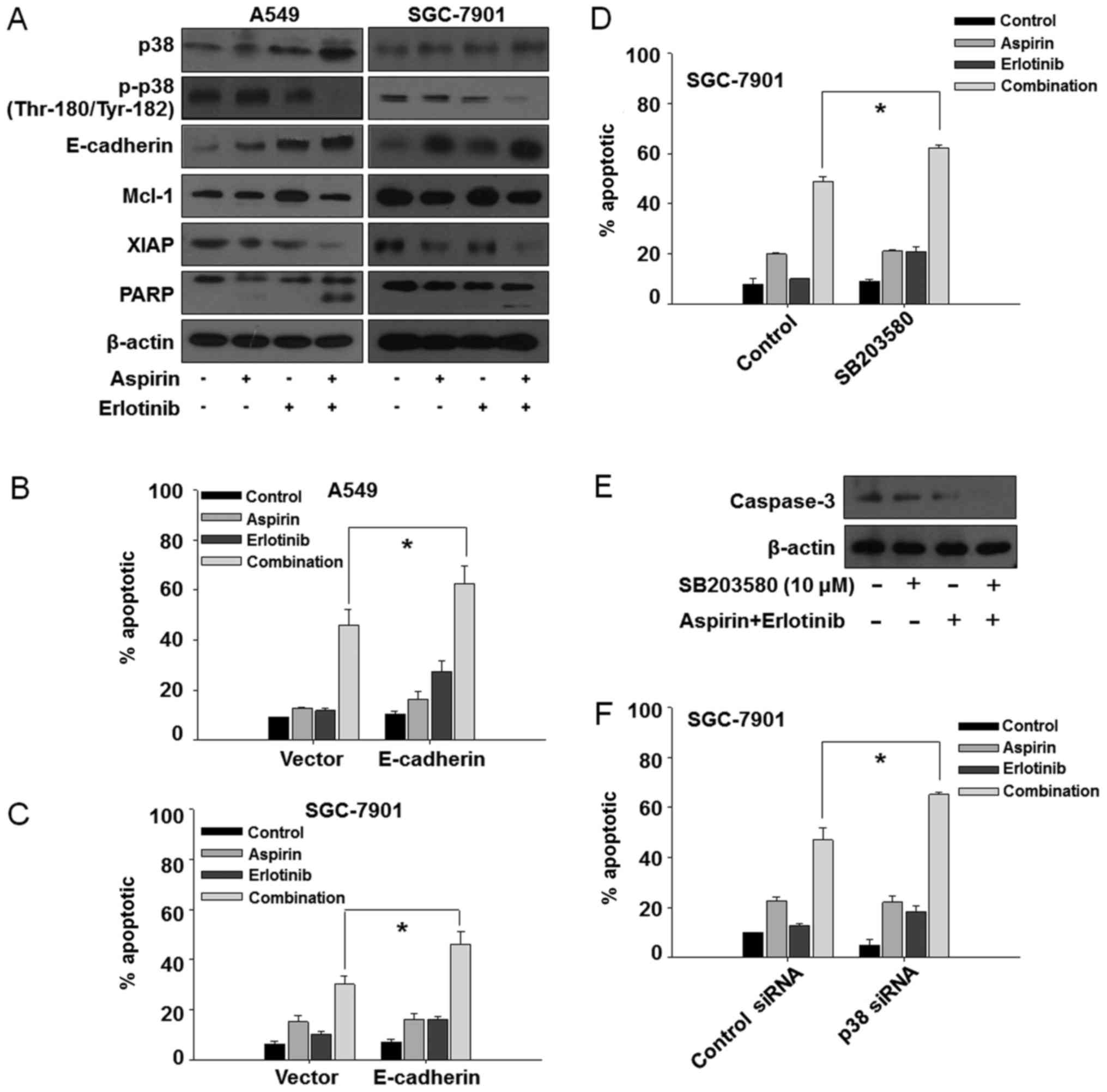
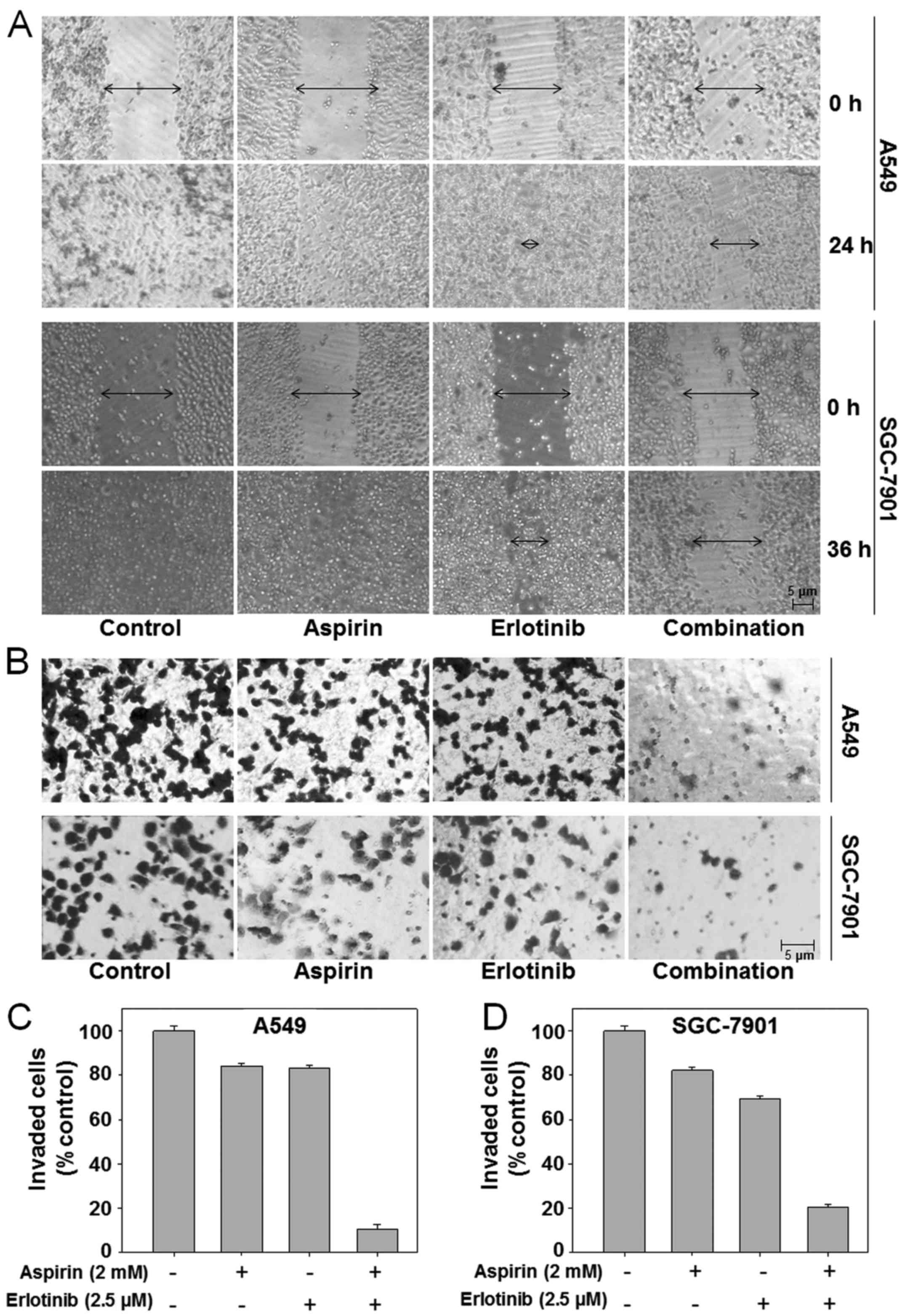
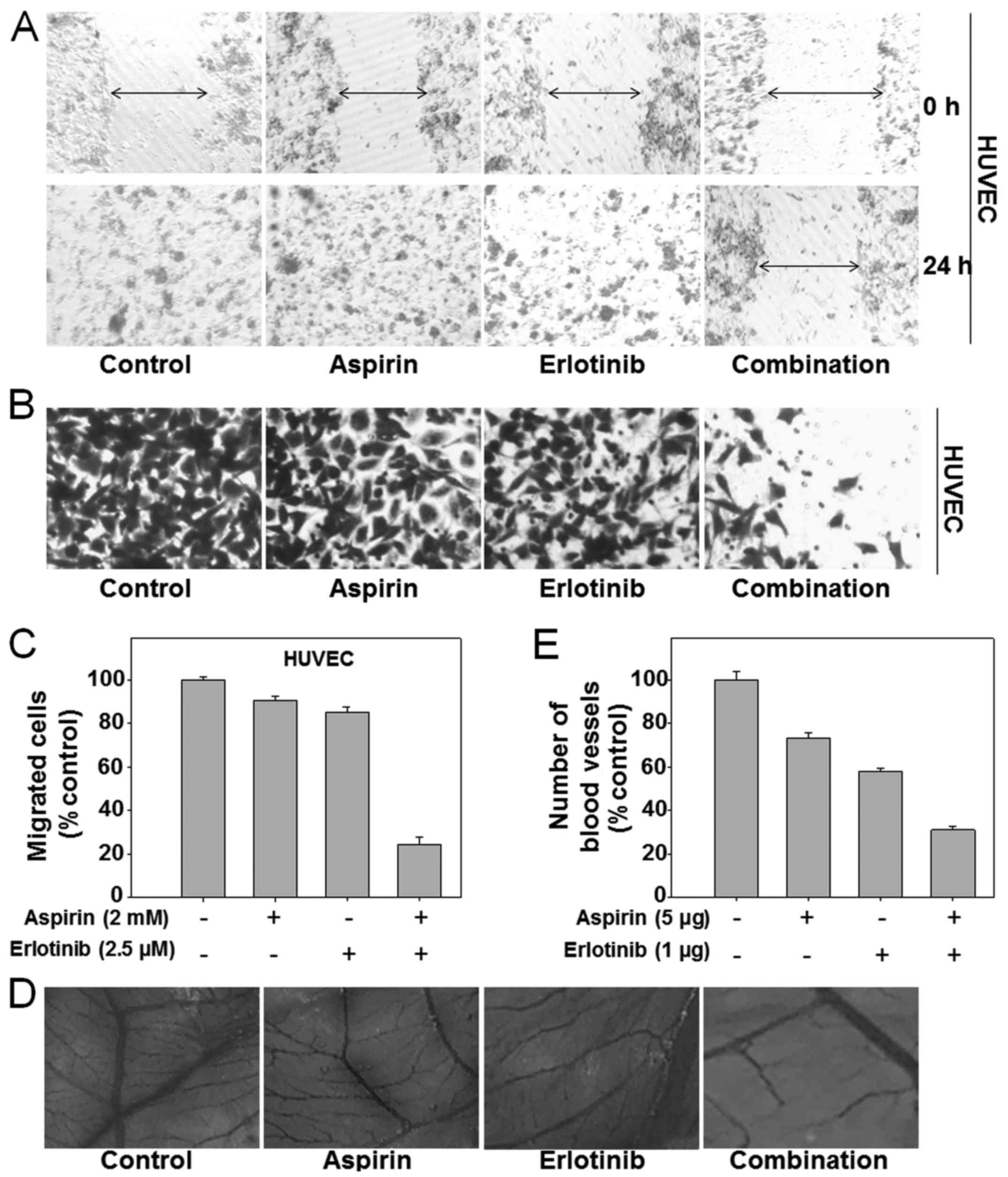
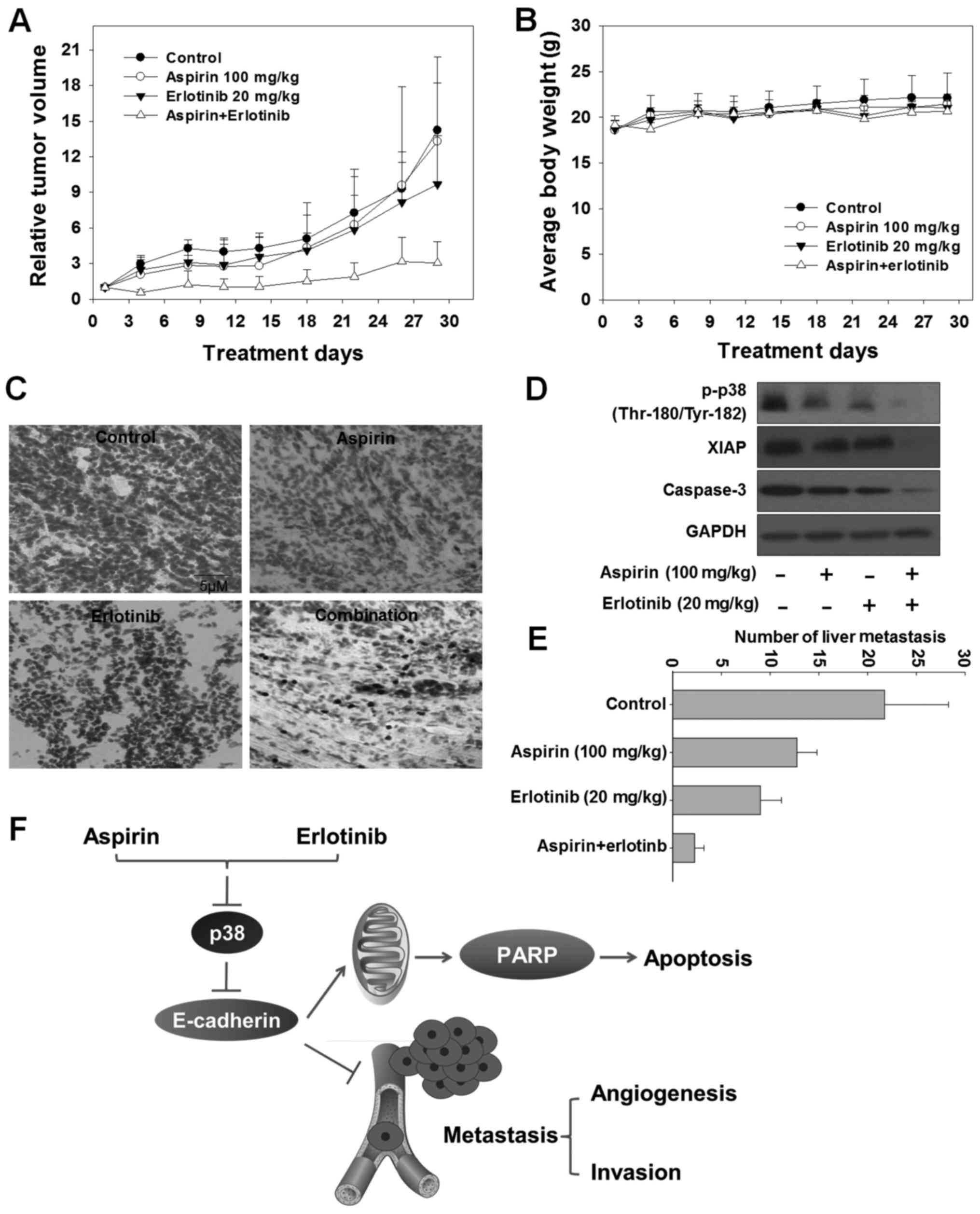
|
1
|
Khan P, Manna A, Saha S, Mohanty S,
Mukherjee S, Mazumdar M, Guha D and Das T: Aspirin inhibits
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and migration of oncogenic
K-ras-expressing non-small cell lung carcinoma cells by
down-regulating E-cadherin repressor Slug. BMC Cancer. 16:392016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kurimoto R, Iwasawa S, Ebata T, Ishiwata
T, Sekine I, Tada Y, Tatsumi K, Koide S, Iwama A and Takiguchi Y:
Drug resistance originating from a TGF-β/FGF-2-driven
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and its reversion in human
lung adenocarcinoma cell lines harboring an EGFR mutation. Int J
Oncol. 48:1825–1836. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Matsuda Y, Miura K, Yamane J, Shima H,
Fujibuchi W, Ishida K, Fujishima F, Ohnuma S, Sasaki H, Nagao M, et
al: SERPINI1 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in an
orthotopic implantation model of colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci.
107:619–628. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Onder TT, Gupta PB, Mani SA, Yang J,
Lander ES and Weinberg RA: Loss of E-cadherin promotes metastasis
via multiple downstream transcriptional pathways. Cancer Res.
68:3645–3654. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Singh A and Settleman J: EMT, cancer stem
cells and drug resistance: An emerging axis of evil in the war on
cancer. Oncogene. 29:4741–4751. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lu M, Marsters S, Ye X, Luis E, Gonzalez L
and Ashkenazi A: E-cadherin couples death receptors to the
cytoskeleton to regulate apoptosis. Mol Cell. 54:987–998. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
McConkey DJ, Choi W, Marquis L, Martin F,
Williams MB, Shah J, Svatek R, Das A, Adam L, Kamat A, et al: Role
of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in drug sensitivity
and metastasis in bladder cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
28:335–344. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bolos V, Peinado H, Perez-Moreno MA, Fraga
MF, Esteller M and Cano A: The transcription factor Slug represses
E-cadherin expression and induces epithelial to mesenchymal
transitions: A comparison with Snail and E47 repressors. J Cell
Sci. 116:499–511. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Peinado H, Olmeda D and Cano A: Snail, Zeb
and bHLH factors in tumour progression: An alliance against the
epithelial phenotype? Nat rev Cancer. 7:415–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang H, Fang R, Wang XF, Zhang F, Chen DY,
Zhou B, Wang HS, Cai SH and Du J: Stabilization of Snail through
AKT/GSK-3β signaling pathway is required for TNF-α-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer PC3 cells. Eur
J Pharmacol. 714:48–55. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zohn IE, Li Y, Skolnik EY, Anderson KV,
Han J and Niswander L: p38 and a p38-interacting protein are
critical for downregulation of E-cadherin during mouse
gastrulation. Cell. 125:957–969. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen R, Yang Q and Lee JD: BMK1 kinase
suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the Akt/GSK3β
signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 72:1579–1587. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cheng JC, Klausen C and Leung PC: Hydrogen
peroxide mediates EGF-induced down-regulation of E-cadherin
expression via p38 MAPK and snail in human ovarian cancer cells.
Mol Endocrinol. 24:1569–1580. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sui X, Kong N, Ye L, Han W, Zhou J, Zhang
Q, He C and Pan H: p38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of
apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents.
Cancer Lett. 344:174–179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Olson JM and Hallahan AR: p38 MAP kinase:
A convergence point in cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med. 10:125–129.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Limami Y, Pinon A, Leger DY, Pinault E,
Delage C, Beneytout JL, Simon A and Liagre B: The
P2Y2/Src/p38/COX-2 pathway is involved in the resistance to ursolic
acid-induced apoptosis in colorectal and prostate cancer cells.
Biochimie. 94:1754–1763. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Salim H, Akbar NS, Zong D, Vaculova AH,
Lewensohn R, Moshfegh A, Viktorsson K and Zhivotovsky B: miRNA-214
modulates radiotherapy response of non-small cell lung cancer cells
through regulation of p38MAPK, apoptosis and senescence. Br J
Cancer. 107:1361–1373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yan KH, Yao CJ, Chang HY, Lai GM, Cheng AL
and Chuang SE: The synergistic anticancer effect of troglitazone
combined with aspirin causes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in
human lung cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 49:235–246. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chan AT, Ogino S and Fuchs CS: Aspirin and
the risk of colorectal cancer in relation to the expression of
COX-2. N Engl J Med. 356:2131–2142. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bardia A, Keenan TE, Ebbert JO, Lazovich
D, Wang AH, Vierkant RA, Olson JE, Vachon CM, Limburg PJ, Anderson
KE and Cerhan JR: Personalizing aspirin use for targeted breast
cancer chemoprevention in postmenopausal women. Mayo Clin Proc.
91:71–80. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Petrick JL, Sahasrabuddhe VV, Chan AT,
Alavanja MC, Beane-Freeman LE, Buring JE, Chen J, Chong DQ,
Freedman ND, Fuchs CS, et al: NSAID Use and risk of hepatocellular
carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: The liver cancer
pooling project. Cancer Prev Res. 8:1156–1162. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Brasky TM, Baik CS, Slatore CG, Potter JD
and White E: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and small cell
lung cancer risk in the VITAL study. Lung Cancer. 77:260–264. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rothwell PM, Wilson M, Price JF, Belch JF,
Meade TW and Mehta Z: Effect of daily aspirin on risk of cancer
metastasis: A study of incident cancers during randomised
controlled trials. Lancet. 379:1591–1601. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guillem-Llobat P, Dovizio M, Bruno A,
Ricciotti E, Cufino V, Sacco A, Grande R, Alberti S, Arena V,
Cirillo M, et al: Aspirin prevents colorectal cancer metastasis in
mice by splitting the crosstalk between platelets and tumor cells.
Oncotarget. 7:32462–32477. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ito K, Semba T, Uenaka T, Wakabayashi T,
Asada M and Funahashi Y: Enhanced anti-angiogenic effect of E7820
in combination with erlotinib in epidermal growth factor
receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung
cancer xenograft models. Cancer Sci. 105:1023–1031. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hirai F, Edagawa M, Shimamatsu S, Toyozawa
R, Toyokawa G, Nosaki K, Yamaguchi M, Seto T, Takenoyama M and
Ichinose Y: Evaluation of erlotinib for the treatment of patients
with non-small cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor
receptor wild type. Oncol Lett. 14:306–312. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li YL, Sun J, Hu X, Pan YN, Yan W, Li QY,
Wang F, Lin NM and Zhang C: Epothilone B induces apoptosis and
enhances apoptotic effects of ABT-737 on human cancer cells via
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 142:2281–2289.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang C, Shi J, Mao SY, Xu YS, Zhang D,
Feng LY, Zhang B, Yan YY, Wang SC, Pan JP, et al: Role of p38 MAPK
in enhanced human cancer cells killing by the combination of
aspirin and ABT-737. J Cell Mol Med. 19:408–417. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang C, Cai TY, Zhu H, Yang LQ, Jiang H,
Dong XW, Hu YZ, Lin NM, He QJ and Yang B: Synergistic antitumor
activity of gemcitabine and ABT-737 in vitro and in vivo through
disrupting the interaction of USP9X and Mcl-1. Mol Cancer Ther.
10:1264–1275. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fernando RI, Hamilton DH, Dominguez C,
David JM, McCampbell KK and Palena C: IL-8 signaling is involved in
resistance of lung carcinoma cells to erlotinib. Oncotarget.
7:42031–42044. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Witta SE, Gemmill RM, Hirsch FR, Coldren
CD, Hedman K, Ravdel L, Helfrich B, Dziadziuszko R, Chan DC, Sugita
M, et al: Restoring E-cadherin expression increases sensitivity to
epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in lung cancer cell
lines. Cancer Res. 66:944–950. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yauch RL, Januario T, Eberhard DA, Cavet
G, Zhu W, Fu L, Pham TQ, Soriano R, Stinson J, Seshagiri S, et al:
Epithelial versus mesenchymal phenotype determines in vitro
sensitivity and predicts clinical activity of erlotinib in lung
cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 11:8686–8698. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Heerboth S, Housman G, Leary M, Longacre
M, Byler S, Lapinska K, Willbanks A and Sarkar S: EMT and tumor
metastasis. Clin Transl Med. 4:62015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bhat TA, Nambiar D, Tailor D, Pal A,
Agarwal R and Singh RP: Acacetin inhibits in vitro and in vivo
angiogenesis and downregulates Stat signaling and VEGF expression.
Cancer Prev Res. 6:1128–1139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Liao X, Lochhead P, Nishihara R, Morikawa
T, Kuchiba A, Yamauchi M, Imamura Y, Qian ZR, Baba Y, Shima K, et
al: Aspirin use, tumor PIK3CA mutation and colorectal-cancer
survival. N Engl J Med. 367:1596–1606. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Turturro SB, Najor MS, Ruby CE, Cobleigh
MA and Abukhdeir AM: Mutations in PIK3CA sensitize breast cancer
cells to physiologic levels of aspirin. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
156:33–43. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Burotto M, Manasanch EE, Wilkerson J and
Fojo T: Gefitinib and erlotinib in metastatic non-small cell lung
cancer: A meta-analysis of toxicity and efficacy of randomized
clinical trials. Oncologist. 20:400–410. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang B, Jiao J, Liu Y, Guo LX, Zhou B, Li
GQ, Yao ZJ and Zhou GB: Gefitinib analogue induces apoptosis of
T790M EGFR-harboring lung cancer cells by up-regulation of the BH-3
only protein Noxa. PLoS One. 7:e487482012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rastogi I, Rajanna S, Webb A, Chhabra G,
Foster B, Webb B and Puri N: Mechanism of c-Met and EGFR tyrosine
kinase inhibitor resistance through epithelial mesenchymal
transition in non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 477:937–944. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang Y, Sheng Q, Spillman MA, Behbakht K
and Gu H: Gab2 regulates the migratory behaviors and E-cadherin
expression via activation of the PI3K pathway in ovarian cancer
cells. Oncogene. 31:2512–2520. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jain RK: Normalization of tumor
vasculature: An emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy.
Science. 307:58–62. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lamalice L, Le Boeuf F and Huot J:
Endothelial cell migration during angiogenesis. Circ Res.
100:782–794. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|