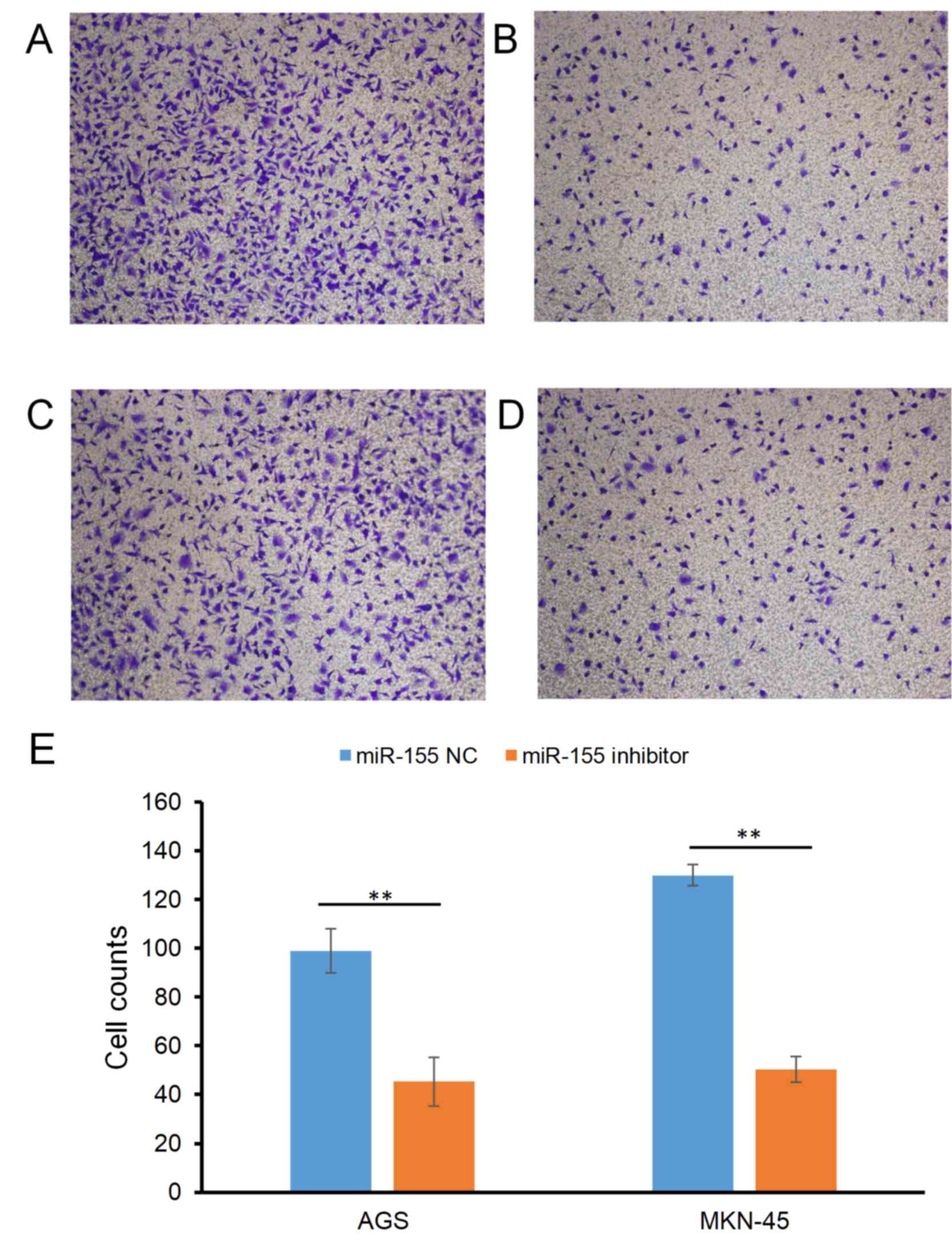
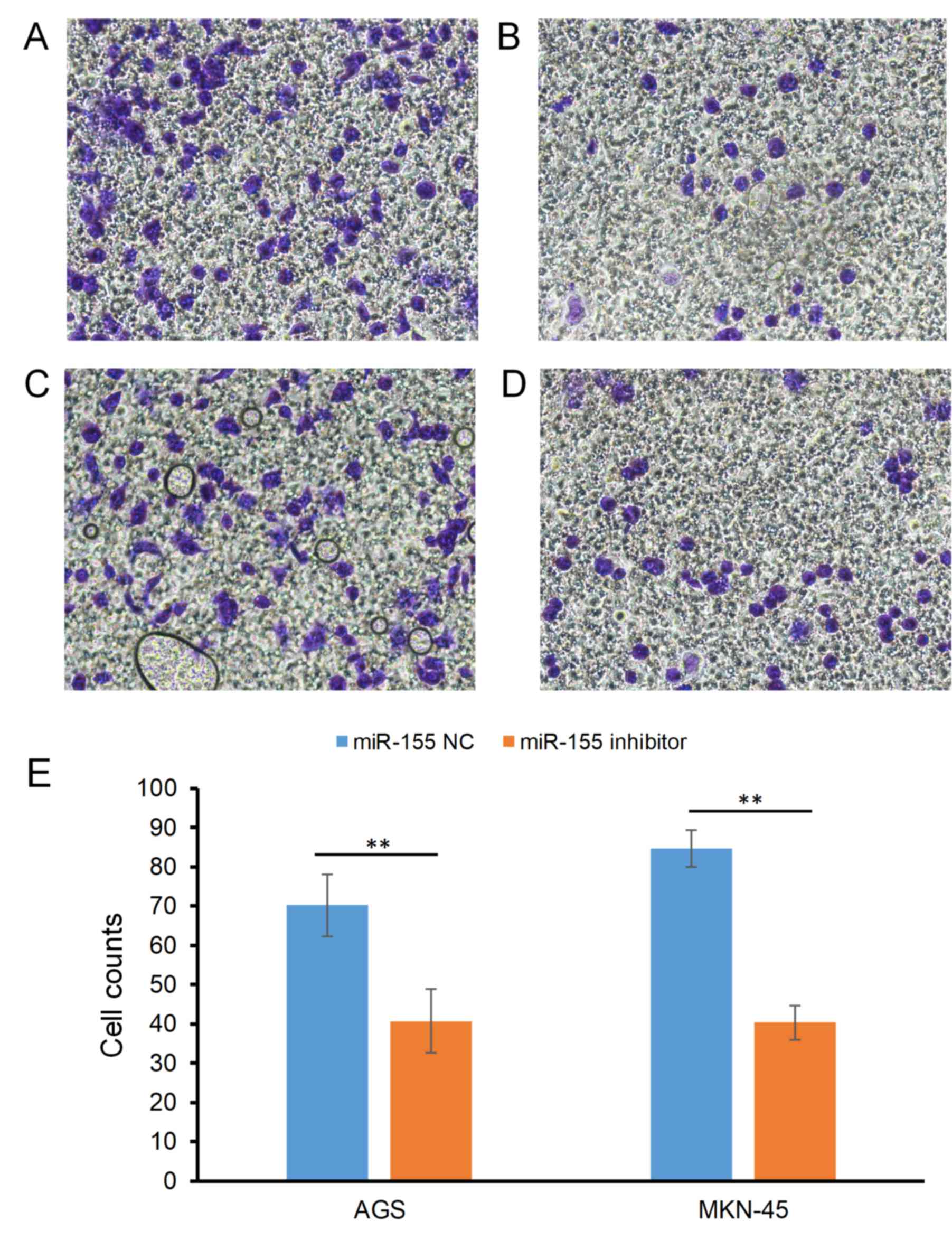
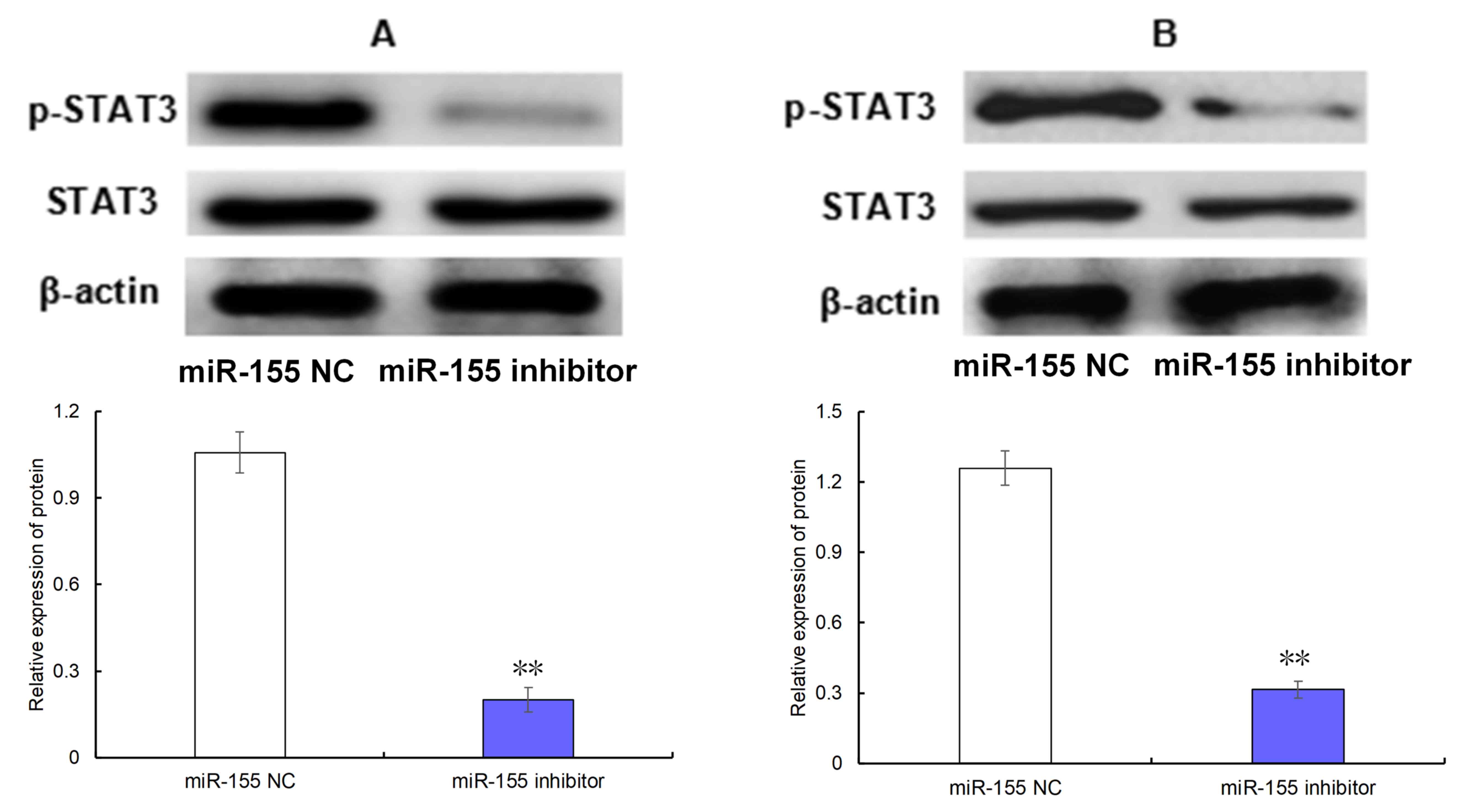
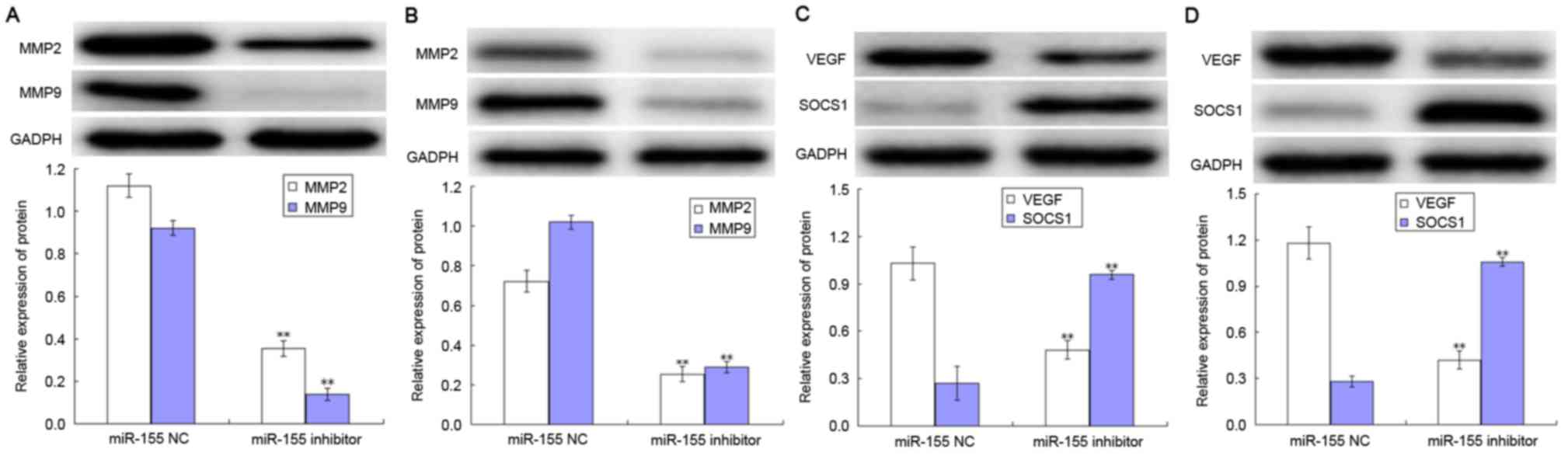
|
1
|
Xia Y, Zhang M, Zhang X and Liu X: A
systematic review and meta-analysis of runt-related transcription
factor 3 gene promoter hypermethylation and risk of gastric cancer.
J Cancer Res Ther. 10 Suppl:S310–S313. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jiang C, Chen X, Alattar M, Wei J and Liu
H: MicroRNAs in tumorigenesis, metastasis, diagnosis and prognosis
of gastric cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 22:291–301. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wu LT, Cui L, Wang YL and Huang LM:
Research progress on miR-155, EMT and tumour invasion/metastasis.
Biotechnol Bull. 30:55–59. 2014.
|
|
4
|
Song J, Wang H, Fu HX, Meng S, Xu YX and
Xu W: MiR-155 expression in gastric cancer tissues and its clinical
significance. Chin J Gen Surg. 21:1236–1239. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
5
|
Liu L, Chen Q, Lai R, Wu X, Wu X, Liu F,
Xu G and Ji Y: Elevated expression of mature miR-21 and miR-155 in
cancerous gastric tissues from Chinese patients with gastric
cancer. J Biomed Res. 24:187–197. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li P, Grgurevic S, Liu Z, Harris D,
Rozovski U, Calin GA, Keating MJ and Estrov Z: Signal transducer
and activator of transcription-3 induces microRNA-155 expression in
chronic lymphocytic leukemia. PLoS One. 8:e646782013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ji K, Zhang L, Zhang M, Chu Q, Li X and
Wang W: Prognostic value and clinicopathological significance of
p-stat3 among gastric carcinoma patients: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e26412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang XM, Zhou C, Gu H, Yan L and Zhang
GY: Correlation of RKIP, STAT3 and cyclin D1 expression in
pathogenesis of gastric cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:5902–5908.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li MX, Bi XY, Huang Z, Zhao JJ, Han Y, Li
ZY, Zhang YF, Li Y, Chen X, Hu XH, et al: Prognostic role of
phospho-STAT3 in patients with cancers of the digestive system: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 10:e01273562015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Inokuchi M, Murayama T, Hayashi M, Takagi
Y, Kato K, Enjoji M, Kojima K, Kumagai J and Sugihara K: Prognostic
value of co-expression of STAT3, mTOR and EGFR in gastric cancer.
Exp Ther Med. 2:251–256. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen J, Liu X, Jiao H, Peng L, Huo Z, Yang
W, Shen Q, Li T and Liu Q: Prognostic and clinical significance of
STAT3 and MMP9 in patients with gastric cancer: A meta-analysis of
a Chinese cohort. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:546–557. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu Y, Deng J, Luo X, Pan Y, Zhang L,
Zhang R and Liang H: Overexpression of SMYD3 was associated with
increased STAT3 activation in gastric cancer. Med Oncol.
32:4042015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhao XD, Zhang W, Liang HJ and Ji WY:
Overexpression of miR-155 promotes proliferation and invasion of
human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via targeting SOCS1 and
STAT3. PLoS One. 8:e563952013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang C, Li H, Wu W, Jiang T and Qiu Z:
Regulation of miR-155 affects pancreatic cancer cell invasiveness
and migration by modulating the STAT3 signaling pathway through
SOCS1. Oncol Rep. 30:1223–1230. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wan J, Xia L, Xu W and Lu N: Expression
and function of miR-155 in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Int J Mol Sci. 17:E7092016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Seddiki N, Brezar V, Ruffin N, Lévy Y and
Swaminathan S: Role of miR-155 in the regulation of lymphocyte
immune function and disease. Immunology. 142:32–38. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jurkovicova D, Magyerkova M, Kulcsar L,
Krivjanska M, Krivjansky V, Gibadulinova A, Oveckova I and Chovanec
M: miR-155 as a diagnostic and prognostic marker in hematological
and solid malignancies. Neoplasma. 61:241–251. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Buettner R, Mora LB and Jove R: Activated
STAT signaling in human tumors provides novel molecular targets for
therapeutic intervention. Clin Cancer Res. 8:945–954.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang L, Li J, Wang Q, Meng G, Lv X, Zhou
H, Li W and Zhang J: The relationship between microRNAs and the
STAT3-related signaling pathway in cancer. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283177198692017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Alexander WS, Starr R, Metcalf D,
Nicholson SE, Farley A, Elefanty AG, Brysha M, Kile BT, Richardson
R, Baca M, et al: Suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS):
Negative regulators of signal transduction. J Leukoc Biol.
66:588–592. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Souma Y, Nishida T, Serada S, Iwahori K,
Takahashi T, Fujimoto M, Ripley B, Nakajima K, Miyazaki Y, Mori M,
et al: Antiproliferative effect of SOCS-1 through the suppression
of STAT3 and p38 MAPK activation in gastric cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 131:1287–1296. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wei D, Le X, Zheng L, Wang L, Frey JA, Gao
AC, Peng Z, Huang S, Xiong HQ, Abbruzzese JL and Xie K: Stat3
activation regulates the expression of vascular endothelial growth
factor and human pancreatic cancer angiogenesis and metastasis.
Oncogene. 22:319–329. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Niu G, Wright KL, Huang M, Song L, Haura
E, Turkson J, Zhang S, Wang T, Sinibaldi D, Coppola D, et al:
Constitutive Stat3 activity up-regulates VEGF expression and tumor
angiogenesis. Oncogene. 21:2000–2008. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li S, Priceman SJ, Xin H, Zhang W, Deng J,
Liu Y, Huang J, Zhu W, Chen M, Hu W, et al: Icaritin inhibits
JAK/STAT3 signaling and growth of renal cell carcinoma. PLoS One.
8:e816572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xie TX, Huang FJ, Aldape KD, Kang SH, Liu
M, Gershenwald JE, Xie K, Sawaya R and Huang S: Activation of stat3
in human melanoma promotes brain metastasis. Cancer Res.
66:3188–3196. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gupta MK and Qin RY: Mechanism and its
regulation of tumor-induced angiogenesis. World J Gastroenterol.
9:1144–1155. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Deng J, Cui J, Jiang N, Zhang R, Zhang L,
Hao X and Liang H: STAT3 regulation the expression of VEGF-D in
HGC-27 gastric cancer cell. Am J Transl Res. 6:756–767.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fofaria NM and Srivastava SK: Critical
role of STAT3 in melanoma metastasis through anoikis resistance.
Oncotarge. 5:7051–7064. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Deryugina EI and Quigley JP: Tumor
angiogenesis: MMP-mediated induction of intravasation- and
metastasis-sustaining neovasculature. Matrix Biol. 44-46:1–112.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mook OR, Frederiks WM and Van Noorden CJ:
The role of gelatinases in colorectal cancer progression and
metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1705:69–89. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yoon J, Cho SJ, Ko YS, Park J, Shin DH,
Hwang IC, Han SY, Nam SY, Kim MA, Chang MS, et al: A synergistic
interaction between transcription factors nuclear factor-κB and
signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 promotes
gastric cancer cell migration and invasion. BMC Gastroenterol.
13:292013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|