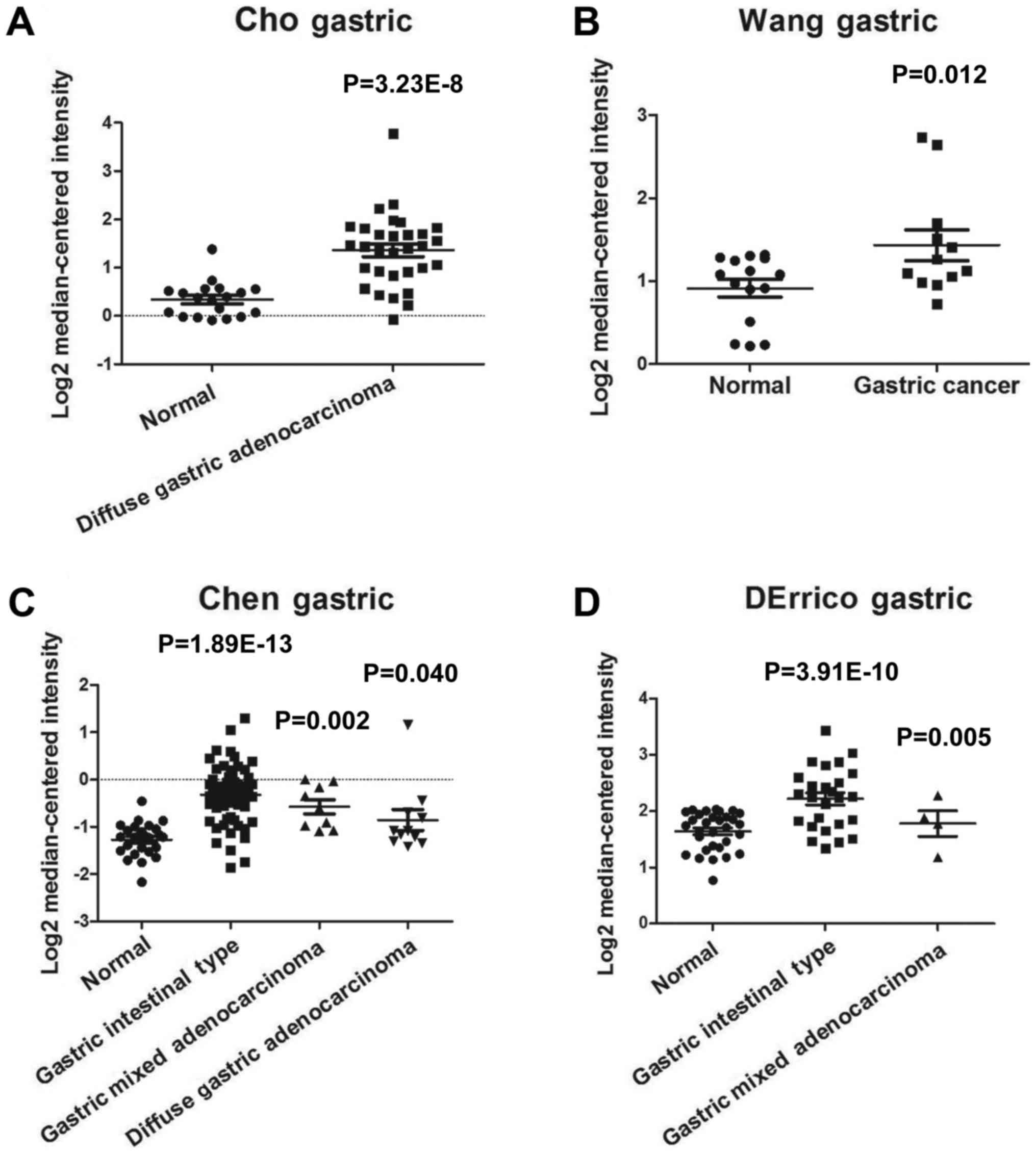
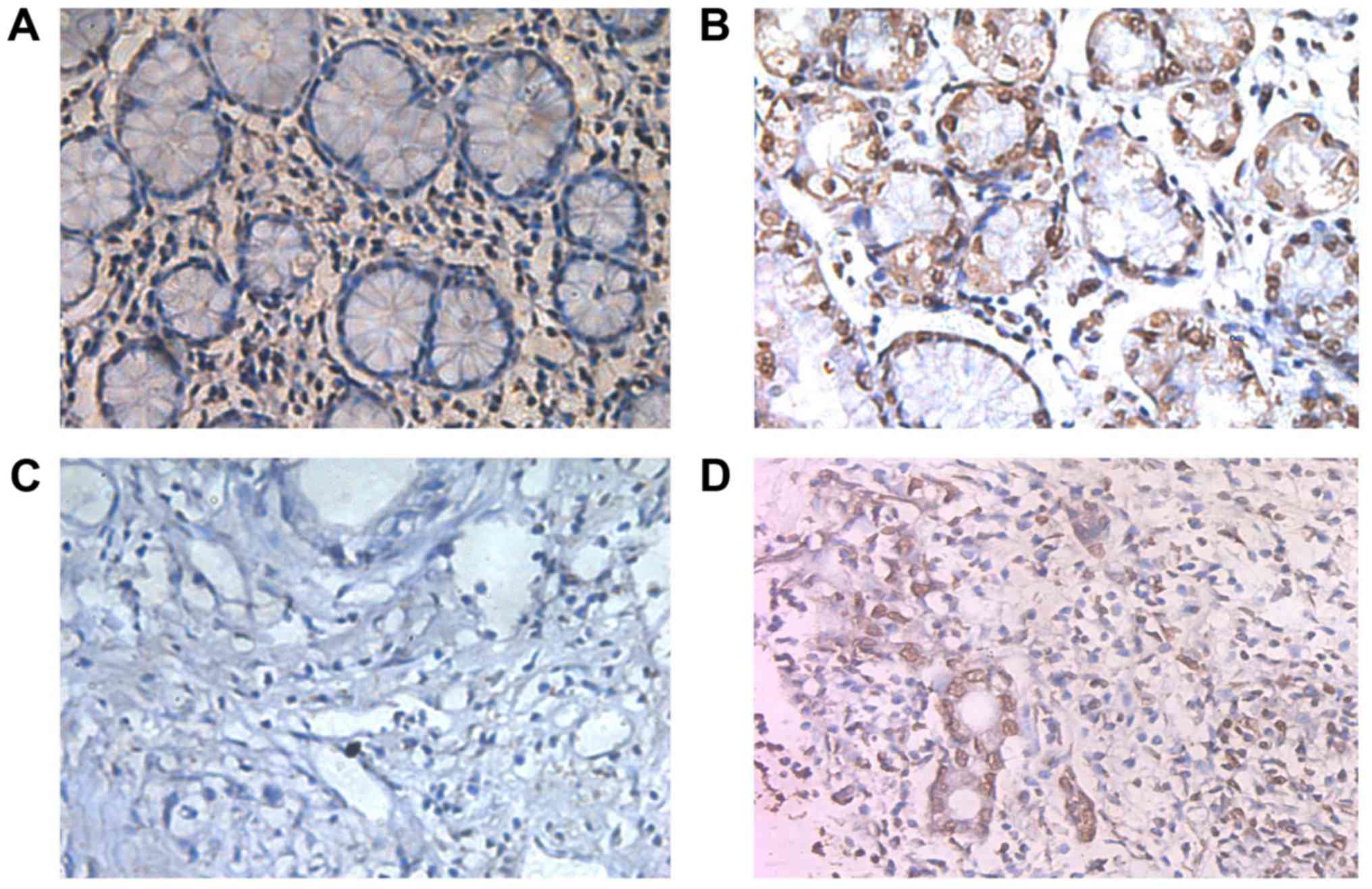
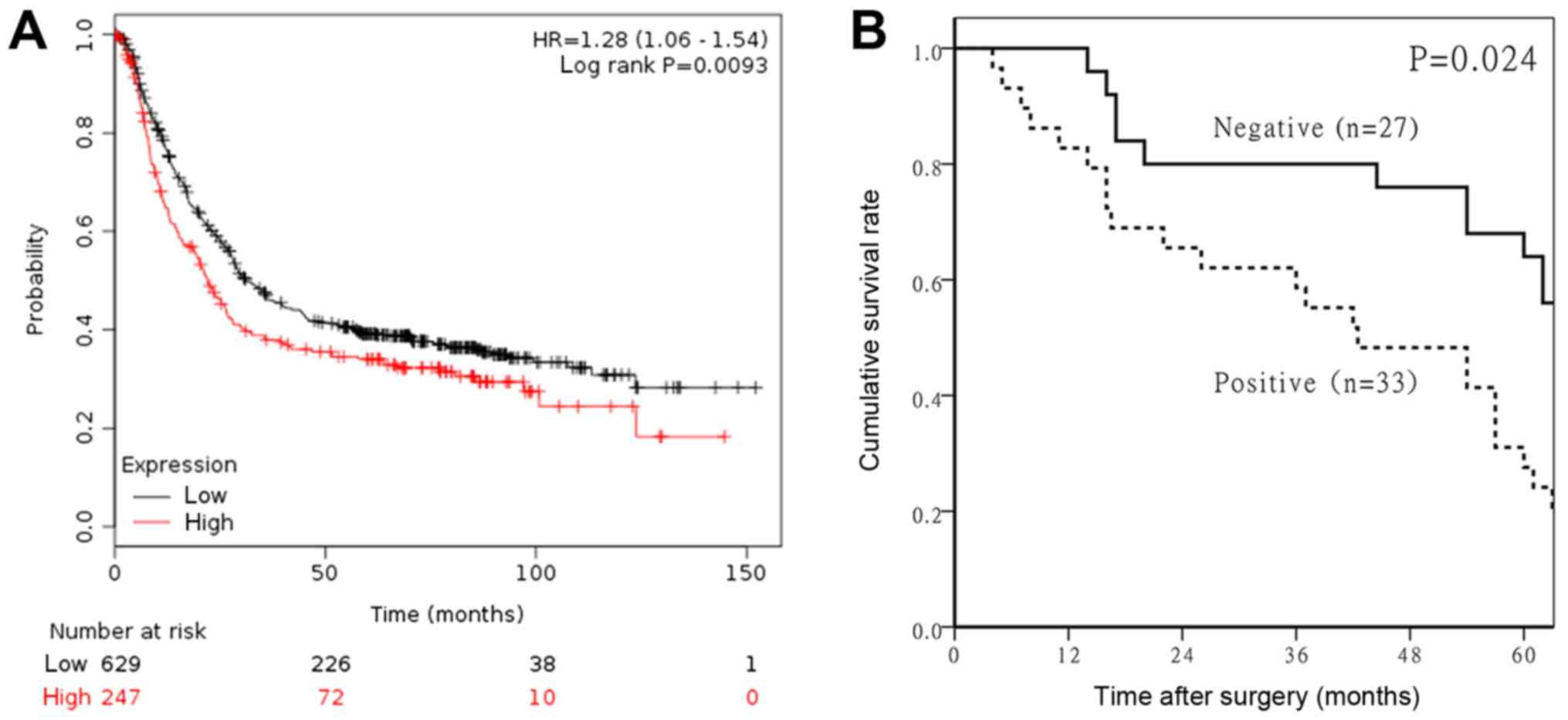
|
1
|
Chen W: Cancer statistics: Updated cancer
burden in China. Chin J Cancer Res. 27:12015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shen GS, Zhao JD, Zhao JH, Ma XF, Du F,
Kan J, Ji FX, Ma F, Zheng FC, Wang ZY and Xu BH: Association of
HER2 status with prognosis in gastric cancer patients undergoing R0
resection: A large-scale multicenter study in China. World J
Gastroenterol. 22:5406–5414. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mahu C, Purcarea AP, Gheorghe CM and
Purcarea MR: Molecular events in gastric carcinogenesis. J Med
Life. 7:375–378. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bernstein KA, Gangloff S and Rothstein R:
The RecQ DNA helicases in DNA repair. Annu Rev Genet. 44:393–417.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gupta S, De S, Srivastava V, Hussain M,
Kumari J, Muniyappa K and Sengupta S: RECQL4 and p53 potentiate the
activity of polymerase γ and maintain the integrity of the human
mitochondrial genome. Carcinogenesis. 35:34–45. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Croteau DL, Singh DK, Hoh Ferrarelli L, Lu
H and Bohr VA: RECQL4 in genomic instability and aging. Trends
Genet. 28:624–631. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Croteau DL, Popuri V, Opresko PL and Bohr
VA: Human RecQ helicases in DNA repair, recombination, and
replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 83:519–552. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chi Z, Nie L, Peng Z, Yang Q, Yang K, Tao
J, Mi Y, Fang X, Balajee AS and Zhao Y: RecQL4 cytoplasmic
localization: Implications in mitochondrial DNA oxidative damage
repair. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:1942–1951. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Singh DK, Popuri V, Kulikowicz T, Shevelev
I, Ghosh AK, Ramamoorthy M, Rossi ML, Janscak P, Croteau DL and
Bohr VA: The human RecQ helicases BLM and RECQL4 cooperate to
preserve genome stability. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:6632–6648. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Capp C, Wu J and Hsieh TS: RecQ4: The
second replicative helicase? Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 45:233–242.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yin J, Kwon YT, Varshavsky A and Wang W:
RECQL4, mutated in the Rothmund-Thomson and RAPADILINO syndromes,
interacts with ubiquitin ligases UBR1 and UBR2 of the N-end rule
pathway. Hum Mol Genet. 13:2421–2430. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fang H, Nie L, Chi Z, Liu J, Guo D, Lu X,
Hei TK, Balajee AS and Zhao Y: RecQL4 helicase amplification is
involved in human breast tumorigenesis. PLoS One. 8:e696002013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lao VV, Welcsh P, Luo Y, Carter KT,
Dzieciatkowski S, Dintzis S, Meza J, Sarvetnick NE, Monnat RJ Jr,
Loeb LA and Grady WM: Altered RECQ helicase expression in sporadic
primary colorectal cancers. Transl Oncol. 6:458–469. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Su Y, Meador JA, Calaf GM, Proietti
De-Santis L, Zhao Y, Bohr VA and Balajee AS: Human RecQL4 helicase
plays critical roles in prostate carcinogenesis. Cancer Res.
70:9207–9217. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Martin JW, Chilton-Mac Neill S, Koti M,
van Wijnen AJ, Squire JA and Zielenska M: Digital expression
profiling identifies RUNX2, CDC5L, MDM2, RECQL4, and CDK4 as
potential predictive biomarkers for neo-adjuvant chemotherapy
response in paediatric osteosarcoma. PLoS One. 9:e958432014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Maire G, Yoshimoto M, Chilton-Mac Neill S,
Thorner PS, Zielenska M and Squire JA: Recurrent RECQL4 imbalance
and increased gene expression levels are associated with structural
chromosomal instability in sporadic osteosarcoma. Neoplasia.
11:260–268, 3p following 268. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Szász AM, Lánczky A, Nagy Á, Förster S,
Hark K, Green JE, Boussioutas A, Busuttil R, Szabó A and Győrffy B:
Cross-validation of survival associated biomarkers in gastric
cancer using transcriptomic data of 1,065 patients. Oncotarget.
7:49322–49333. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Singh DK, Ahn B and Bohr VA: Roles of RECQ
helicases in recombination based DNA repair, genomic stability and
aging. Biogerontology. 10:235–252. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Thangavel S, Mendoza-Maldonado R, Tissino
E, Sidorova JM, Yin J, Wang W, Monnat RJ Jr, Falaschi A and
Vindigni A: Human RECQ1 and RECQ4 helicases play distinct roles in
DNA replication initiation. Mol Cell Biol. 30:1382–1396. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lu L, Harutyunyan K, Jin W, Wu J, Yang T,
Chen Y, Joeng KS, Bae Y, Tao J, Dawson BC, et al: RECQL4 regulates
p53 function in vivo during skeletogenesis. J Bone Miner Res.
30:1077–1089. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Arora A, Agarwal D, Abdel-Fatah TM, Lu H,
Croteau DL, Moseley P, Aleskandarany MA, Green AR, Ball G, Rakha
EA, et al: RECQL4 helicase has oncogenic potential in sporadic
breast cancers. J Pathol. 238:495–501. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mo D, Fang H, Niu K, Liu J, Wu M, Li S,
Zhu T, Aleskandarany MA, Arora A, Lobo DN, et al: Human helicase
RECQL4 drives cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer by activating
an AKT-YB1-MDR1 signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 76:3057–3066. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Croteau DL, Rossi ML, Canugovi C, Tian J,
Sykora P, Ramamoorthy M, Wang ZM, Singh DK, Akbari M,
Kasiviswanathan R, et al: RECQL4 localizes to mitochondria and
preserves mitochondrial DNA integrity. Aging Cell. 11:456–466.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|