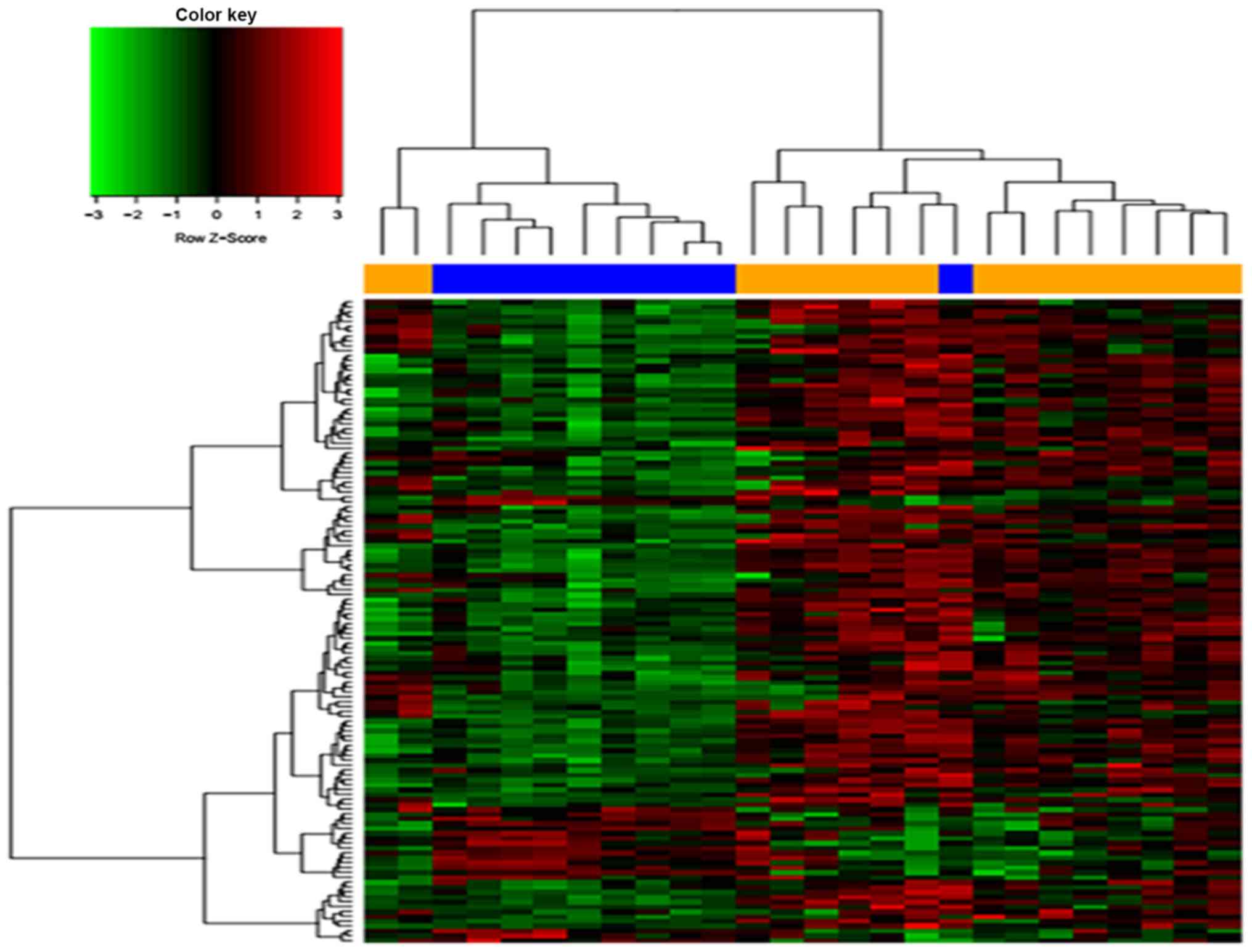
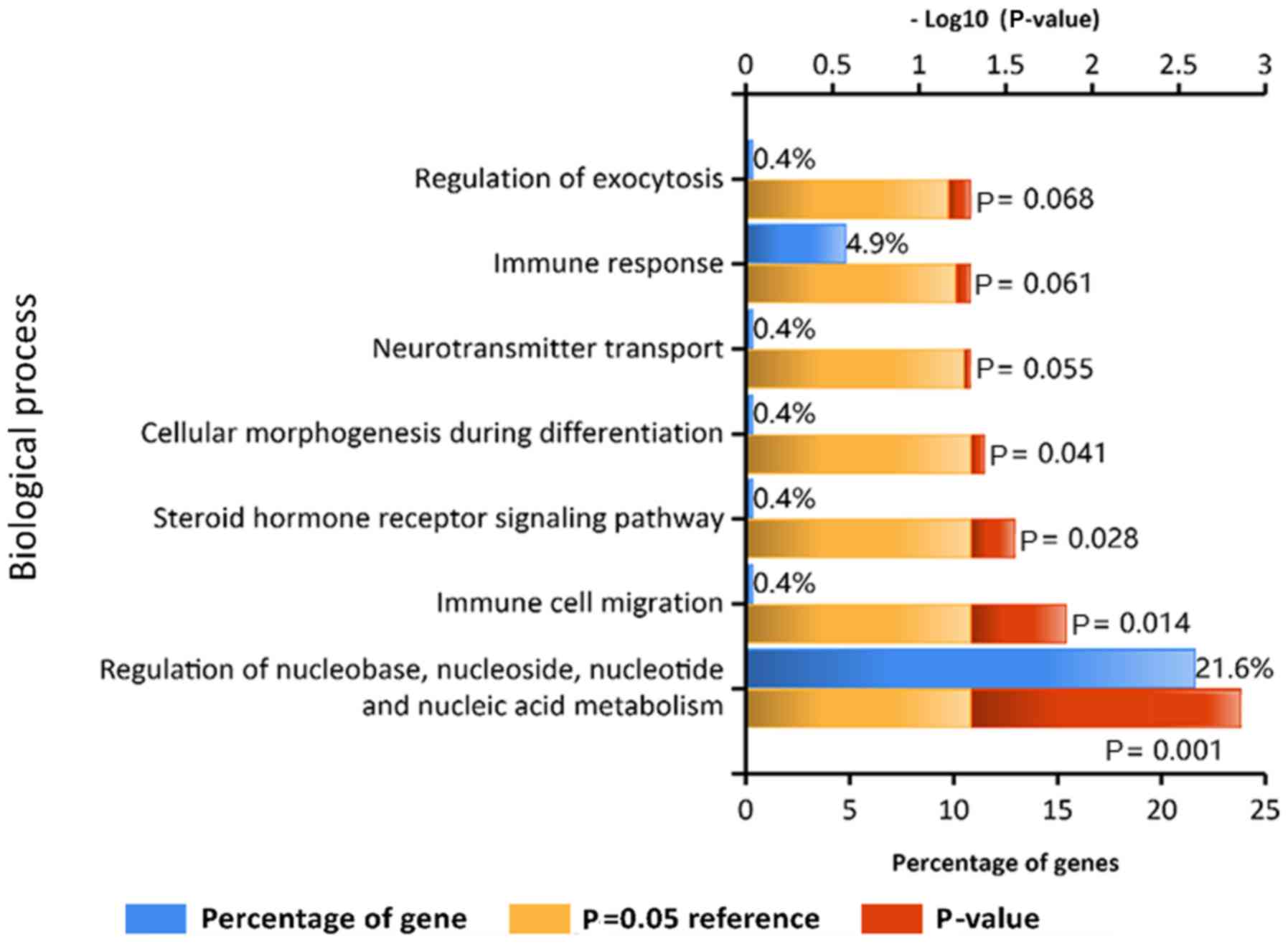
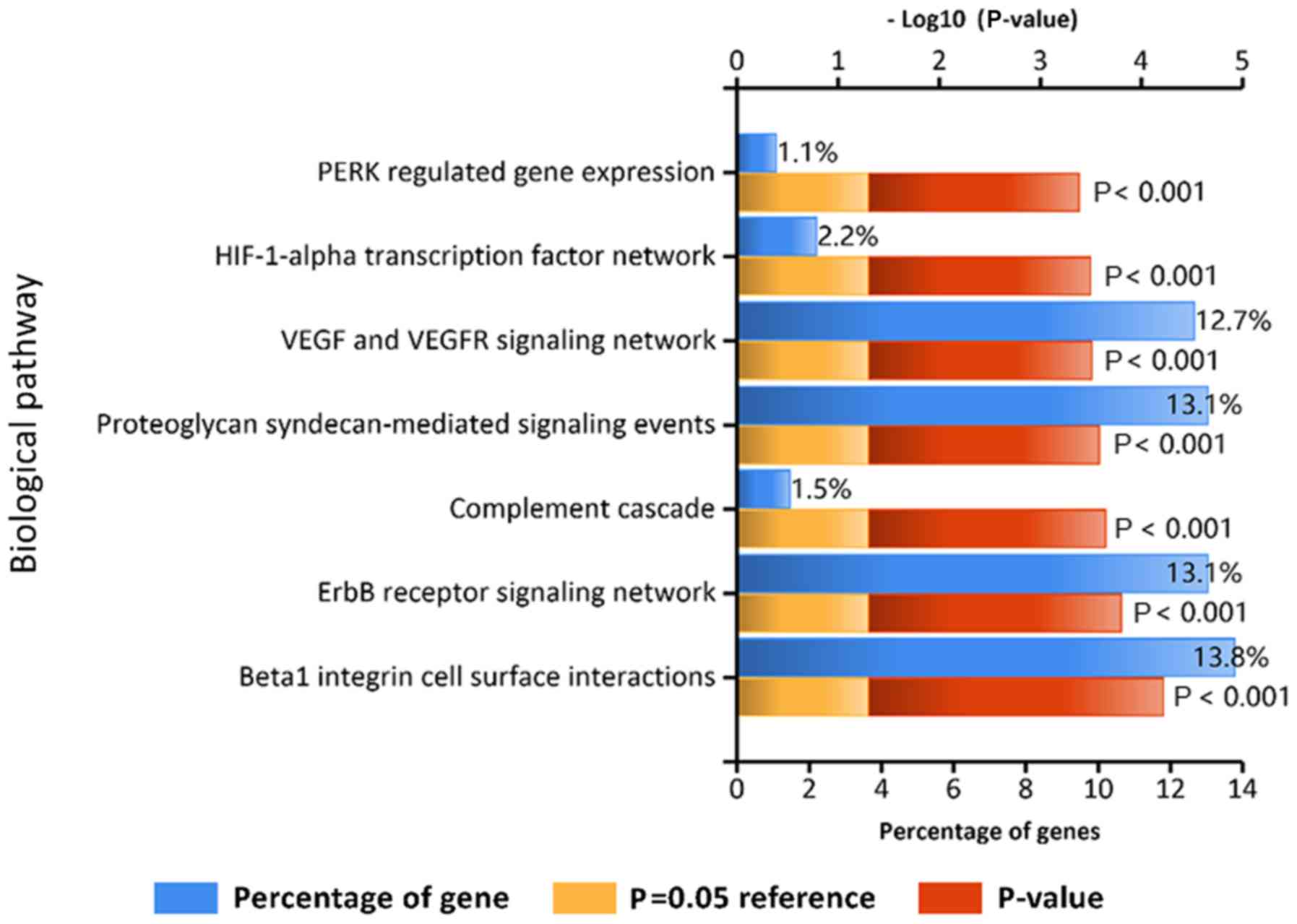
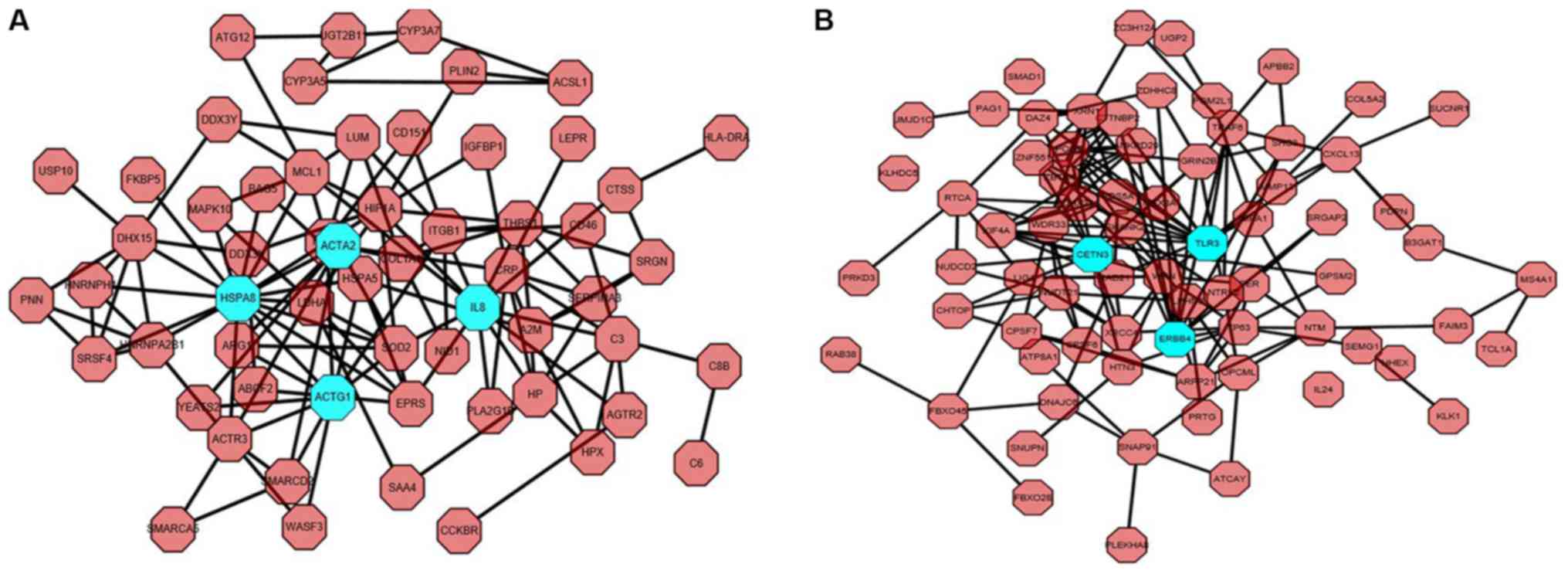
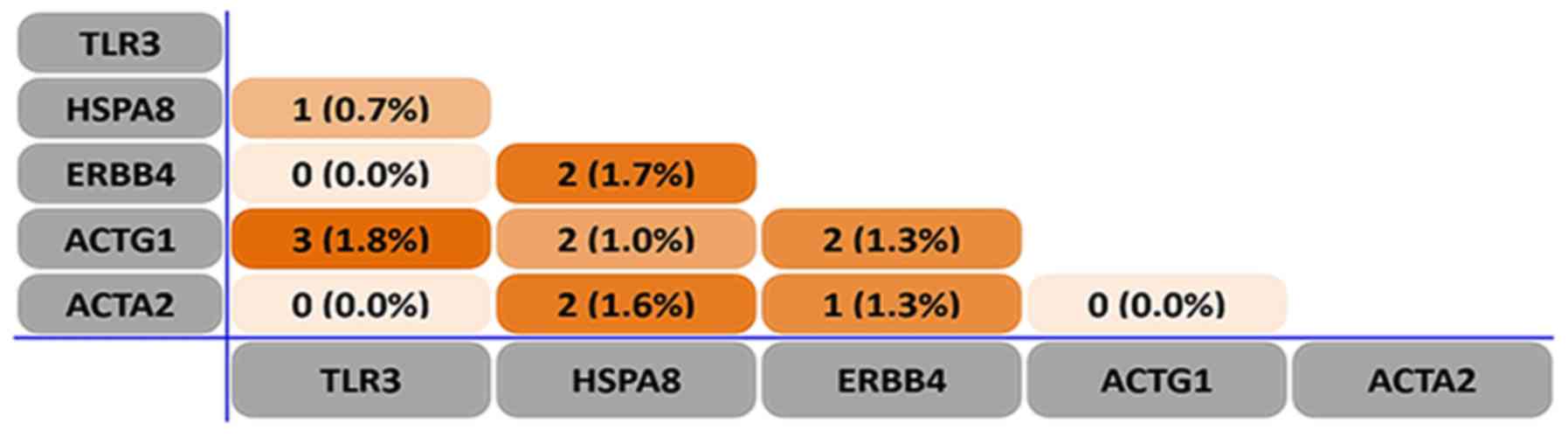
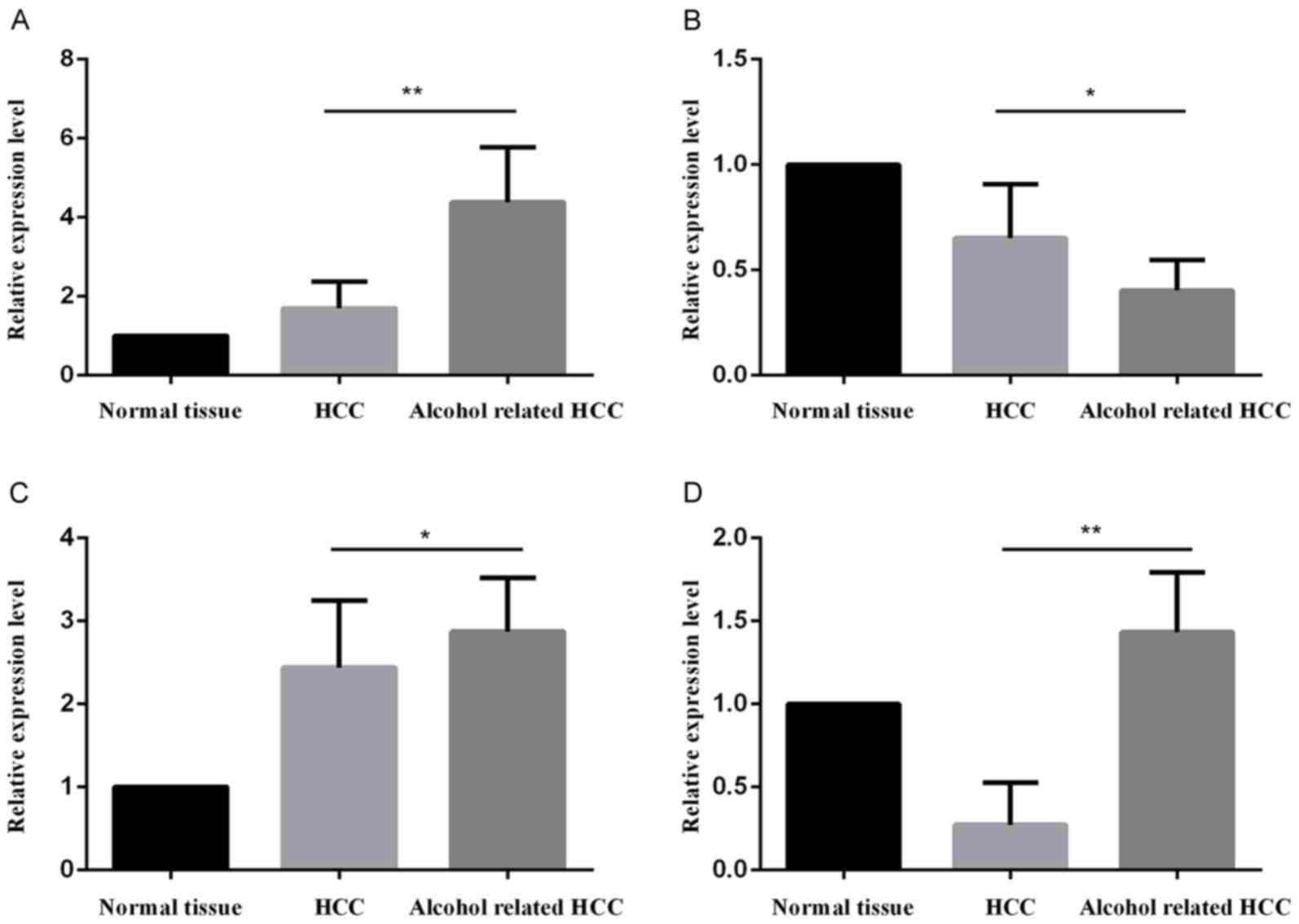
|
1
|
Park JW, Chen M, Colombo M, Roberts LR,
Schwartz M, Chen PJ, Kudo M, Johnson P, Wagner S, Orsini LS and
Sherman M: Global patterns of hepatocellular carcinoma management
from diagnosis to death: The BRIDGE Study. Liver Int. 35:2155–2166.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nahon P and Nault JC: Constitutional and
functional genetics of human alcohol-related hepatocellular
carcinoma. Liver Int. 37:1591–1601. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li DK, Yan P, Abou-Samra AB, Chung RT and
Butt AA: Proton pump inhibitors are associated with accelerated
development of cirrhosis, hepatic decompensation and hepatocellular
carcinoma in noncirrhotic patients with chronic hepatitis C
infection: Results from ERCHIVES. Aliment pharmacol Ther.
47:246–258. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
David D, Raghavendran A, Goel A Bharath,
Kumar C, Kodiatte TA, Burad D, Abraham P, Ramakrishna B, Joseph P,
Ramachandran J and Eapen CE: Risk factors for non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease are common in patients with non-B non-C
hepatocellular carcinoma in India. Indian J Gastroenterol.
36:373–379. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xin B, Cui Y, Wang Y, Wang L, Yin J, Zhang
L, Pang H, Zhang H and Wang RA: Combined use of alcohol in
conventional chemical-induced mouse liver cancer model improves the
simulation of clinical characteristics of human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 14:4722–4728. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ramadori P, Cubero FJ, Liedtke C,
Trautwein C and Nevzorova YA: Alcohol and hepatocellular carcinoma:
Adding fuel to the flame. Cancers (Basel). 9:E1302017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Neumann O, Kesselmeier M, Geffers R,
Pellegrino R, Radlwimmer B, Hoffmann K, Ehemann V, Schemmer P,
Schirmacher P, Lorenzo Bermejo J and Longerich T: Methylome
analysis and integrative profiling of human HCCs identify novel
protumorigenic factors. Hepatology. 56:1817–1827. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Harbig J, Sprinkle R and Enkemann SA: A
sequence-based identification of the genes detected by probesets on
the Affymetrix U133 plus 2.0 array. Nucleic Acids Res. 33:e312005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wettenhall JM, Simpson KM, Satterley K and
Smyth GK: affylmGUI: A graphical user interface for linear modeling
of single channel microarray data. Bioinformatics. 22:897–899.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Han L, Suzek TO, Wang Y and Bryant SH: The
text-mining based pubchem bioassay neighboring analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 11:5492010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cho E, Lee JE, Rimm EB, Fuchs CS and
Giovannucci EL: Alcohol consumption and the risk of colon cancer by
family history of colorectal cancer. Am J Clin Nut. 95:413–419.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Murugan S, Boyadjieva N and Sarkar DK:
Protective effects of hypothalamic beta-endorphin neurons against
alcohol-induced liver injuries and liver cancers in rat animal
models. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 38:2988–2997. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hidaka A, Sasazuki S, Matsuo K, Ito H,
Sawada N, Shimazu T, Yamaji T, Iwasaki M, Inoue M and Tsugane S:
JPHC Study Group: Genetic polymorphisms of ADH1B, ADH1C and ALDH2,
alcohol consumption, and the risk of gastric cancer: The Japan
Public Health Center-based prospective study. Carcinogenesis.
36:223–231. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu M, Wang S, Qi Y, Chen L, Frank JA, Yang
XH, Zhang Z, Shi X and Luo J: Role of MCP-1 in alcohol-induced
aggressiveness of colorectal cancer cells. Mol Carcinog.
55:1002–1011. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brooks PJ and Zakhari S: Moderate alcohol
consumption and breast cancer in women: From epidemiology to
mechanisms and interventions. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 37:23–30. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rendtorff ND, Zhu M, Fagerheim T, Antal
TL, Jones M, Teslovich TM, Gillanders EM, Barmada M, Teig E, Trent
JM, et al: A novel missense mutation in ACTG1 causes dominant
deafness in a Norwegian DFNA20/26 family, but ACTG1 mutations are
not frequent among families with hereditary hearing impairment. Eur
J Hum Genet. 14:1097–1105. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
van Wijk E, Krieger E, Kemperman MH, De
Leenheer EM, Huygen PL, Cremers CW, Cremers FP and Kremer H: A
mutation in the gamma actin 1 (ACTG1) gene causes autosomal
dominant hearing loss (DFNA20/26). J Med Genet. 40:879–884. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Morín M, Bryan KE, Mayo-Merino F, Goodyear
R, Mencía A, Modamio-Høybjør S, del Castillo I, Cabalka JM,
Richardson G, Moreno F, et al: In vivo and in vitro effects of two
novel gamma-actin (ACTG1) mutations that cause DFNA20/26 hearing
impairment. Hum Mol Genet. 18:3075–3089. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Park G, Gim J, Kim AR, Han KH, Kim HS, Oh
SH, Park T, Park WY and Choi BY: Multiphasic analysis of whole
exome sequencing data identifies a novel mutation of ACTG1 in a
nonsyndromic hearing loss family. BMC Genomics. 14:1912013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wei Q, Zhu H, Qian X, Chen Z, Yao J, Lu Y,
Cao X and Xing G: Targeted genomic capture and massively parallel
sequencing to identify novel variants causing Chinese hereditary
hearing loss. J Transl Med. 12:3112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bunnell TM and Ervasti JM: Delayed
embryonic development and impaired cell growth and survival in
Actg1 null mice. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 67:564–572. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mutai H, Suzuki N, Shimizu A, Torii C,
Namba K, Morimoto N, Kudoh J, Kaga K, Kosaki K and Matsunaga T:
Diverse spectrum of rare deafness genes underlies early-childhood
hearing loss in Japanese patients: A cross-sectional, multi-center
next-generation sequencing study. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 8:1722013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang S, Cai M, Zheng Y, Zhou L, Wang Q
and Chen L: miR-888 in MCF-7 side population sphere cells directly
targets E-cadherin. J Genet Genomics. 41:35–42. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dong X, Han Y, Sun Z and Xu J: Actin Gamma
1, a new skin cancer pathogenic gene, identified by the biological
feature-based classification. J Cell Biochem. 119:1406–1419. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gan TQ, Xie ZC, Tang RX, Zhang TT, Li DY,
Li ZY and Chen G: Clinical value of miR-145-5p in NSCLC and
potential molecular mechanism exploration: A retrospective study
based on GEO, qRT-PCR, and TCGA data. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283176916832017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Wu H, Li Y, Zhang Y, Liu
M, Li X and Tang H: miR-10a suppresses colorectal cancer metastasis
by modulating the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and anoikis.
Cell Death Dis. 8:e27392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun Q, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Liu F, Cheng X,
Hou N, Zhao X and Yang X: Expression profiling reveals
dysregulation of cellular cytoskeletal genes in HBx–induced
hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Biol Ther. 6:668–674. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu YY, Chen L, Wang GL, Zhou JM, Zhang YX,
Wei YZ, Zhu YY and Qin J: A synthetic dsRNA, as a TLR3
pathwaysynergist, combined with sorafenib suppresses HCC in vitro
and in vivo. BMC Cancer. 13:5272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang SY, Herman M, Ciancanelli MJ, Pérez
de Diego R, Sancho-Shimizu V, Abel L and Casanova JL: TLR3 immunity
to infection in mice and humans. Curr Opin Immunol. 25:19–33. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen C, Feng Y, Zou L, Wang L, Chen HH,
Cai JY, Xu JM, Sosnovik DE and Chao W: Role of extracellular RNA
and TLR3-Trif signaling in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
J Am Heart Assoc. 3:e0006832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen XL, Xu YY, Chen L, Wang GL and Shen
Y: TLR3 plays significant roles against HBV-associated HCC.
Gastroenterol Res Prac. 2015:5721712015.
|
|
33
|
Das A, Chai JC, Kim SH, Lee YS, Park KS,
Jung KH and Chai YG: Transcriptome sequencing of microglial cells
stimulated with TLR3 and TLR4 ligands. BMC Genomics. 16:5172015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Szeles L, Meissner F, Dunand-Sauthier I,
Thelemann C, Hersch M, Singovski S, Haller S, Gobet F, Fuertes
Marraco SA, Mann M, et al: TLR3-mediated CD8+ dendritic cell
activation is coupled with establishment of a cell-intrinsic
antiviral state. J Immunol. 195:1025–1033. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Qiu X, Dong Y, Cao Y and Luo Y:
Correlation between TLR2, TLR3, TLR4, and TLR9 polymorphisms and
susceptibility to and prognosis of severe hepatitis among the
newborns. J Clin Lab Anal. 32:2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yuan MM, Xu YY, Chen L, Li XY, Qin J and
Shen Y: TLR3 expression correlates with apoptosis, proliferation
and angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma and predicts
prognosis. BMC Cancer. 15:2452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kar P, Kumar D, Gumma PK, Chowdhury SJ and
Karra VK: Down regulation of TRIF TLR3, and MAVS in HCV infected
liver correlates with the outcome of infection. J Med Virol.
89:2165–2172. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hu X, Ye J, Qin A, Zou H, Shao H and Qian
K: Both microRNA-155 and virus-encoded MiR-155 ortholog regulate
TLR3 expression. PLoS One. 10:e01260122015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ho V, Lim TS, Lee J, Steinberg J, Szmyd R,
Tham M, Yaligar J, Kaldis P, Abastado JP and Chew V: TLR3 agonist
and Sorafenib combinatorial therapy promotes immune activation and
controls hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Oncotarget.
6:27252–27266. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Guo Z, Chen L, Zhu Y, Zhang Y, He S, Qin
J, Tang X, Zhou J and Wei Y: Double-stranded RNA-induced TLR3
activation inhibits angiogenesis and triggers apoptosis of human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 27:396–402.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yoneda K, Sugimoto K, Shiraki K, Tanaka J,
Beppu T, Fuke H, Yamamoto N, Masuya M, Horie R, Uchida K and Takei
Y: Dual topology of functional Toll-like receptor 3 expression in
human hepatocellular carcinoma: Differential signaling mechanisms
of TLR3-induced NF-kappaB activation and apoptosis. Int J Oncol.
33:929–936. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|