|
1
|
International Agency for Research on
Cancer WHO. GLOBOCAN2012: Estimated Cancer Incidence, Mortality and
Prevalence. 2012.
|
|
2
|
American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and
Figures 2014. American Cancer Society. 2014.
|
|
3
|
Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig
AB, Fleshman JM and Matrisian LM: Projecting cancer incidence and
deaths to 2030: The unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and
pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 74:2913–2921.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hidalgo M: Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J
Med. 362:1605–1617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Oettle H, Neuhaus P, Hochhaus A, Hartmann
JT, Gellert K, Ridwelski K, Niedergethmann M, Zülke C, Fahlke J,
Arning MB, et al: Adjuvant chemotherapy with gemcitabine and
long-term outcomes among patients with resected pancreatic cancer:
The CONKO-001 randomized trial. JAMA. 310:1473–1481. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kalser MH and Ellenberg SS: Pancreatic
cancer. Adjuvant combined radiation and chemotherapy following
curative resection. Arch Surg. 120:899–903. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Oettle H, Post S, Neuhaus P, Gellert K,
Langrehr J, Ridwelski K, Schramm H, Fahlke J, Zuelke C, Burkart C,
et al: Adjuvant chemotherapy with gemcitabine vs observation in
patients undergoing curative-intent resection of pancreatic cancer:
A randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 297:267–277. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Uesaka K, Boku N, Fukutomi A, Okamura Y,
Konishi M, Matsumoto I, Kaneoka Y, Shimizu Y, Nakamori S, Sakamoto
H, et al: Adjuvant chemotherapy of S-1 versus gemcitabine for
resected pancreatic cancer: A phase 3, open-label, randomised,
non-inferiority trial (JASPAC 01). Lancet. 388:248–257. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Neoptolemos JP, Dunn JA, Stocken DD,
Almond J, Link K, Beger H, Bassi C, Falconi M, Pederzoli P,
Dervenis C, et al: Adjuvant chemoradiotherapy and chemotherapy in
resectable pancreatic cancer: A randomised controlled trial.
Lancet. 358:1576–1585. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim EJ, Ben-Josef E, Herman JM,
Bekaii-Saab T, Dawson LA, Griffith KA, Francis IR, Greenson JK,
Simeone DM, Lawrence TS, et al: A multi-institutional phase 2 study
of neoadjuvant gemcitabine and oxaliplatin with radiation therapy
in patients with pancreatic cancer. Cancer. 119:2692–2700. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW: Cancer genes
and the pathways they control. Nat Med. 10:789–799. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yachida S, Jones S, Bozic I, Antal T,
Leary R, Fu B, Kamiyama M, Hruban RH, Eshleman JR, Nowak MA, et al:
Distant metastasis occurs late during the genetic evolution of
pancreatic cancer. Nature. 467:1114–1117. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Waraya M, Yamashita K, Katagiri H, Ishii
K, Takahashi Y, Furuta K and Watanabe M: Preoperative serum CA19-9
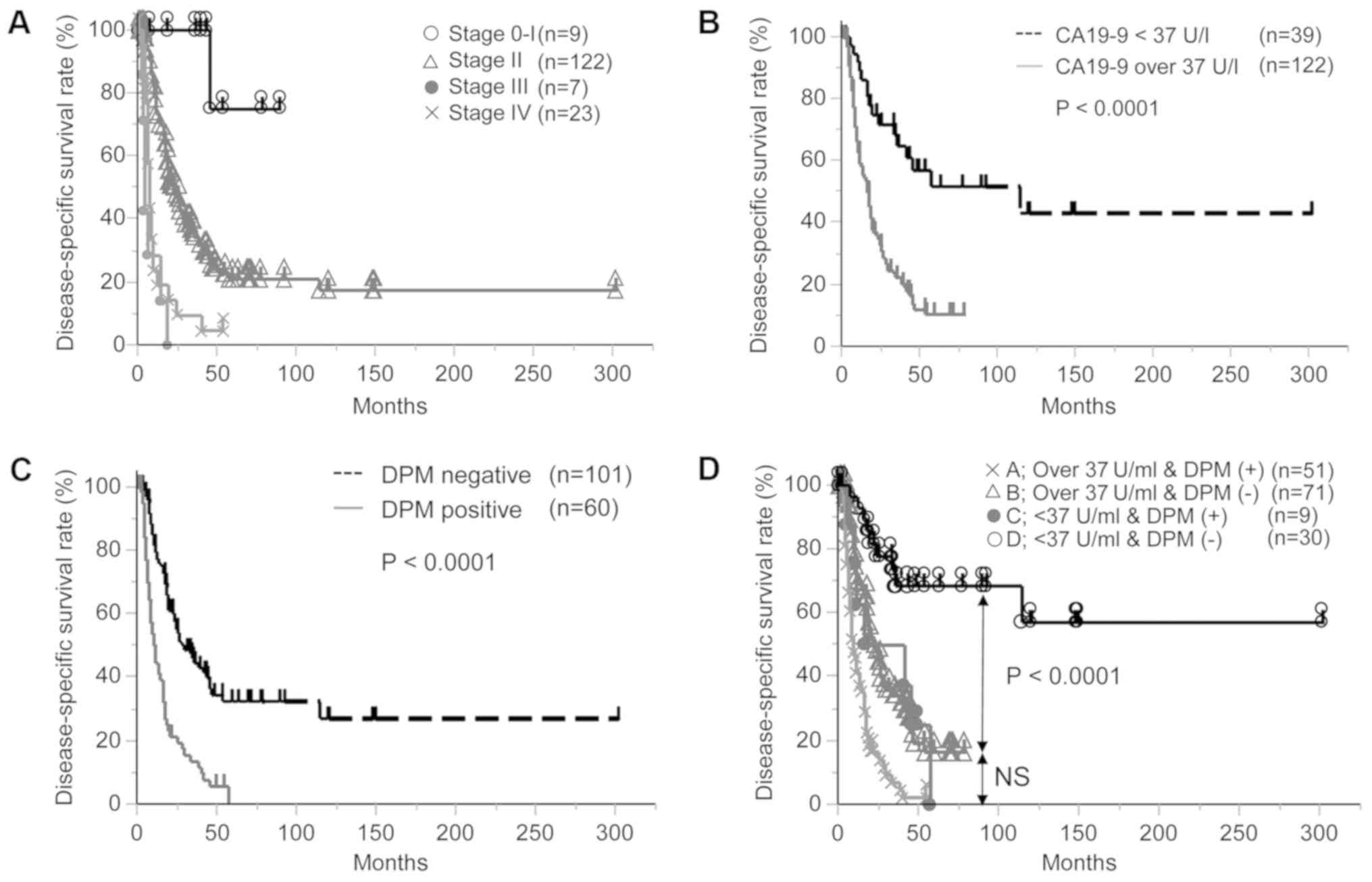
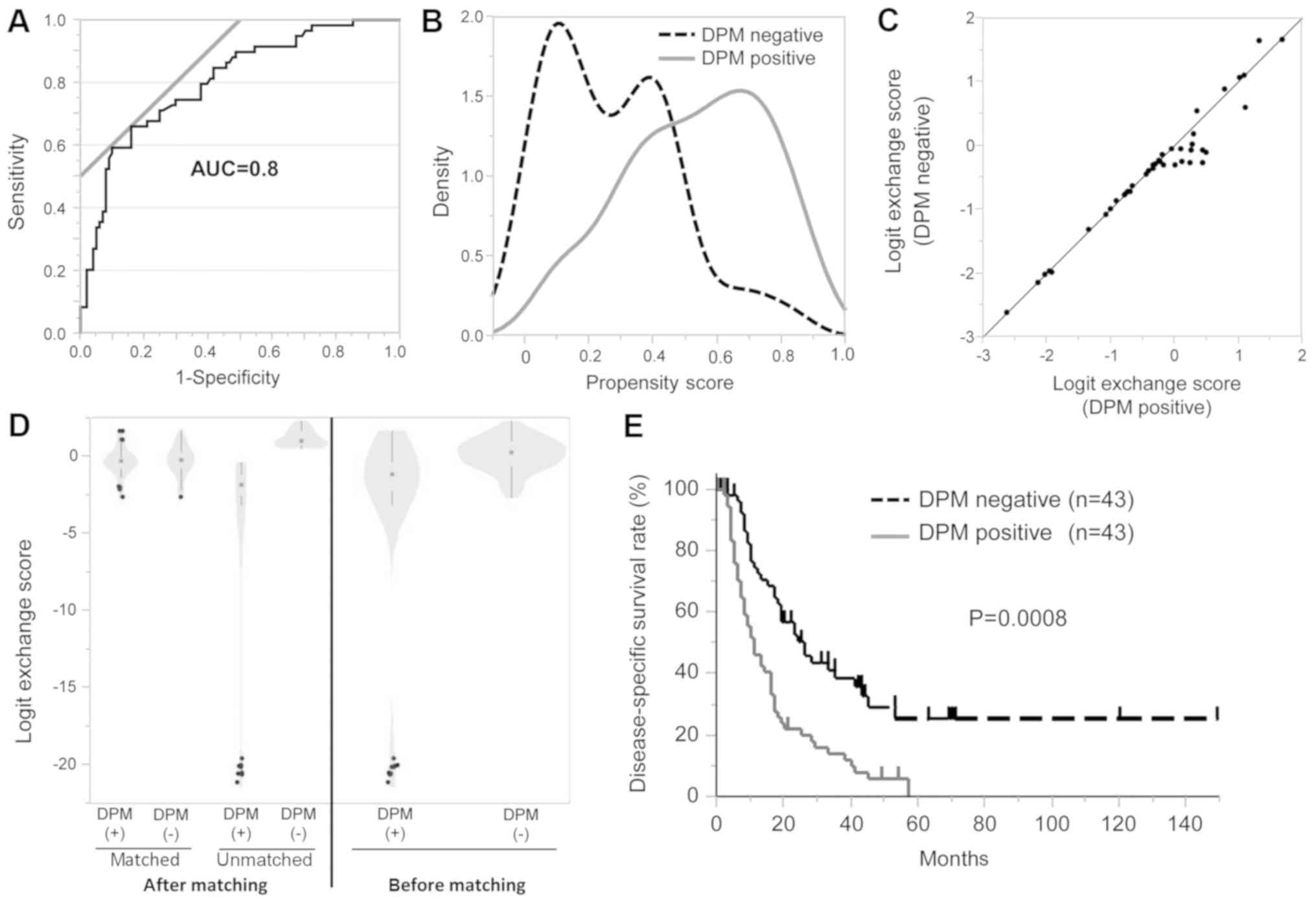
and dissected peripancreatic tissue margin as determiners of
long-term survival in pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg Oncol.
16:1231–1240. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mirkin KA, Hollenbeak CS and Wong J:
Prognostic impact of carbohydrate antigen 19-9 level at diagnosis
in resected stage I–III pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A U.S.
population study. J Gastrointest Oncol. 8:778–788. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Allema JH, Reinders ME, van Gulik TM,
Koelemay MJ, Van Leeuwen DJ, de Wit LT, Gouma DJ and Obertop H:
Prognostic factors for survival after pancreaticoduodenectomy for
patients with carcinoma of the pancreatic head region. Cancer.
75:2069–2076. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wenger FA, Peter F, Zieren J, Steiert A,
Jacobi CA and Müller JM: Prognosis factors in carcinoma of the head
of the pancreas. Dig Surg. 17:29–35. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Japan Pancreas Society. Classification of
pancreatic carcinoma Tokyo: Kanahara; 2011
|
|
18
|
Sobin LH and Wittekind C: International
Union Againt Cancer (UICC): TNM classification of malignant tumors.
6th. New York: Wiley and Liss; 2002
|
|
19
|
National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
Clinical practice guidelines in oncology. Pancreatic
Adenocarcinoma. Version 2. 2016.
|
|
20
|
Yamashita K, Tatebayashi T, Shinoda H and
Okayasu I: Simplified rapid non-radioactive PCR-SSCP method applied
to K-ras mutation analysis. Pathol Int. 46:801–804. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yamashita K, Yoshida T, Shinoda H and
Okayasu I: Novel method for simultaneous analysis of p53 and K-ras
mutations and p53 protein expression in single histologic sections.
Arch Pathol Lab Med. 125:347–352. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kaplan EL and Meier P: Nonparametric
estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc.
53:457–481. 1958. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Piagnerelli R, Marrelli D, Roviello G,
Ferrara F, Di Mare G, Voglino C, Petrioli R, Marini M, Macchiarelli
R and Roviello F: Clinical value and impact on prognosis of
peri-operative CA 19-9 serum levels in stage I and II
adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Tumour Biol. 37:1959–1966. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chan A, Prassas I, Dimitromanolakis A,
Brand RE, Serra S, Diamandis EP and Blasutig IM: Validation of
biomarkers that complement CA19.9 in detecting early pancreatic
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 20:5787–5795. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kondo N, Murakami Y, Uemura K, Hayashidani
Y, Sudo T, Hashimoto Y, Nakashima A, Sakabe R, Shigemoto N, Kato Y,
et al: Prognostic impact of perioperative serum CA 19-9 levels in
patients with resectable pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg Oncol.
17:2321–2329. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Harsha HC, Kandasamy K, Ranganathan P,
Rani S, Ramabadran S, Gollapudi S, Balakrishnan L, Dwivedi SB,
Telikicherla D, Selvan LD, et al: A compendium of potential
biomarkers of pancreatic cancer. PLoS Med. 6:e10000462009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Berger AC, Garcia M Jr, Hoffman JP, Regine
WF, Abrams RA, Safran H, Konski A, Benson AB III, MacDonald J and
Willett CG: Postresection CA 19-9 predicts overall survival in
patients with pancreatic cancer treated with adjuvant
chemoradiation: A prospective validation by RTOG 9704. J Clin
Oncol. 26:5918–5922. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hess V, Glimelius B, Grawe P, Dietrich D,
Bodoky G, Ruhstaller T, Bajetta E, Saletti P, Figer A, Scheithauer
W and Herrmann R: CA 19-9 tumour-marker response to chemotherapy in
patients with advanced pancreatic cancer enrolled in a randomised
controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 9:132–138. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ohigashi H, Ishikawa O, Sasaki Y, Yamada
T, Furukawa H, Imaoka S, Kasugai T, Ishiguro S, Ueda K, Miyoshi Y
and Nakamura Y: K-ras point mutation in the nerve plexuses around
the superior mesenteric artery in resectable adenocarcinoma of the
pancreatic head: Distribution pattern and related factors. Arch
Surg. 135:1450–1455. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim J, Reber HA, Dry SM, Elashoff D, Chen
SL, Umetani N, Kitago M, Hines OJ, Kazanjian KK, Hiramatsu S, et
al: Unfavourable prognosis associated with K-ras gene mutation in
pancreatic cancer surgical margins. Gut. 55:1598–1605. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ijichi H, Chytil A, Gorska AE, Aakre ME,
Fujitani Y, Fujitani S, Wright CV and Moses HL: Aggressive
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mice caused by
pancreas-specific blockade of transforming growth factor-beta
signaling in cooperation with active Kras expression. Genes Dev.
20:3147–3160. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jones S, Zhang X, Parsons DW, Lin JC,
Leary RJ, Angenendt P, Mankoo P, Carter H, Kamiyama H, Jimeno A, et
al: Core signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancers revealed by
global genomic analyses. Science. 321:1801–1806. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Biankin AV, Waddell N, Kassahn KS, Gingras
MC, Muthuswamy LB, Johns AL, Miller DK, Wilson PJ, Patch AM, Wu J,
et al: Pancreatic cancer genomes reveal aberrations in axon
guidance pathway genes. Nature. 491:399–405. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
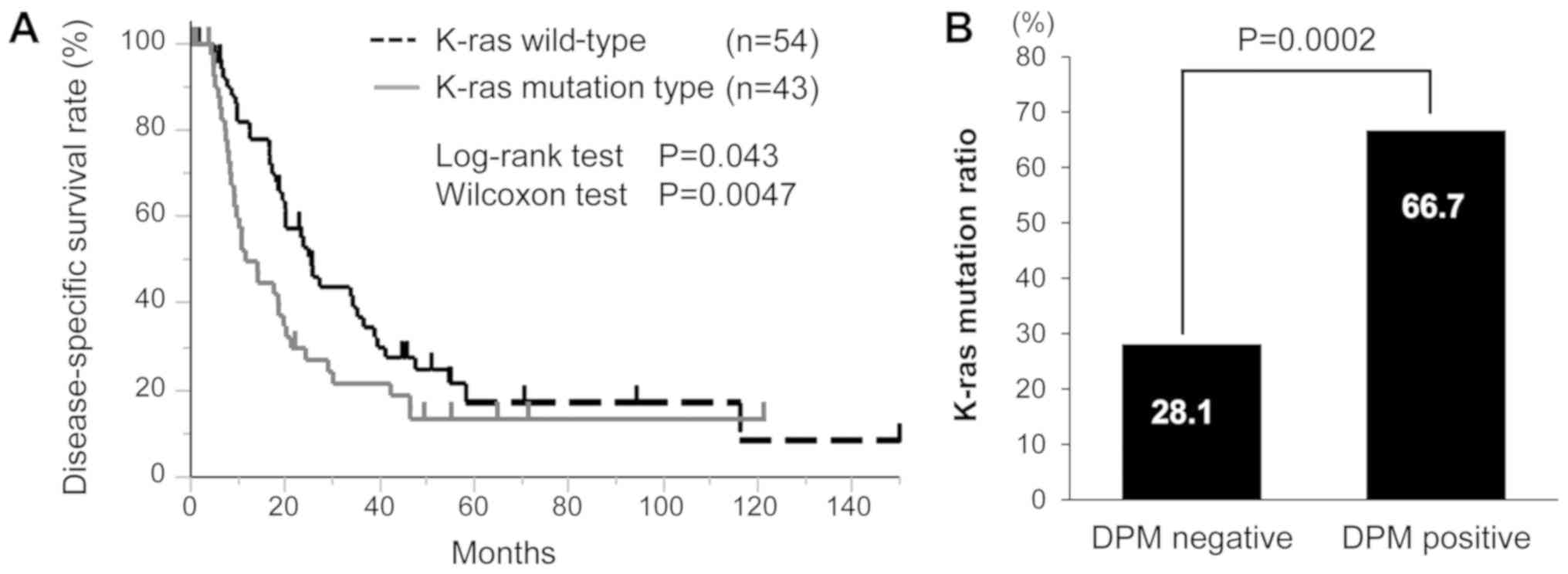
Tao LY, Zhang LF, Xiu DR, Yuan CH, Ma ZL
and Jiang B: Prognostic significance of K-ras mutations in
pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis. World J Surg Oncol. 14:1462016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Knijn N, Mekenkamp LJ, Klomp M,
Vink-Börger ME, Tol J, Teerenstra S, Meijer JW, Tebar M, Riemersma
S, van Krieken JH, et al: KRAS mutation analysis: A comparison
between primary tumours and matched liver metastases in 305
colorectal cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 104:1020–1026. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Collins MA, Bednar F, Zhang Y, Brisset JC,
Galbán S, Galbán CJ, Rakshit S, Flannagan KS, Adsay NV and Pasca di
Magliano M: Oncogenic Kras is required for both the initiation and
maintenance of pancreatic cancer in mice. J Clin Invest.
122:639–653. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Onozato W, Yamashita K, Yamashita K, Kuba
T, Katoh H, Nakamura T, Sato T, Ihara A, Okayasu I and Watanabe M:
Genetic alterations of K-ras may reflect prognosis in stage III
colon cancer patients below 60 years of age. J Surg Oncol.
103:25–33. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yamashita K, Kuba T, Shinoda H, Takahashi
E and Okayasu I: Detection of K-ras point mutations in the
supernatants of peritoneal and pleural effusions for diagnosis
complementary to cytologic examination. Am J Clin Pathol.
109:704–711. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yamashita K, Kida Y, Shinoda H, Kida M and
Okayasu I: K-ras point mutations in the supernatants of pancreatic
juice and bile are reliable for diagnosis of pancreas and biliary
tract carcinomas complementary to cytologic examination. Jpn J
Cancer Res. 90:240–248. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kawamata H, Yamashita K, Kojo K, Ushiku H,
Ooki A and Watanabe M: Discrepancies between the K-ras mutational
status of primary colorectal cancers and corresponding liver
metastases are found in codon 13. Genomics. 106:71–75. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|