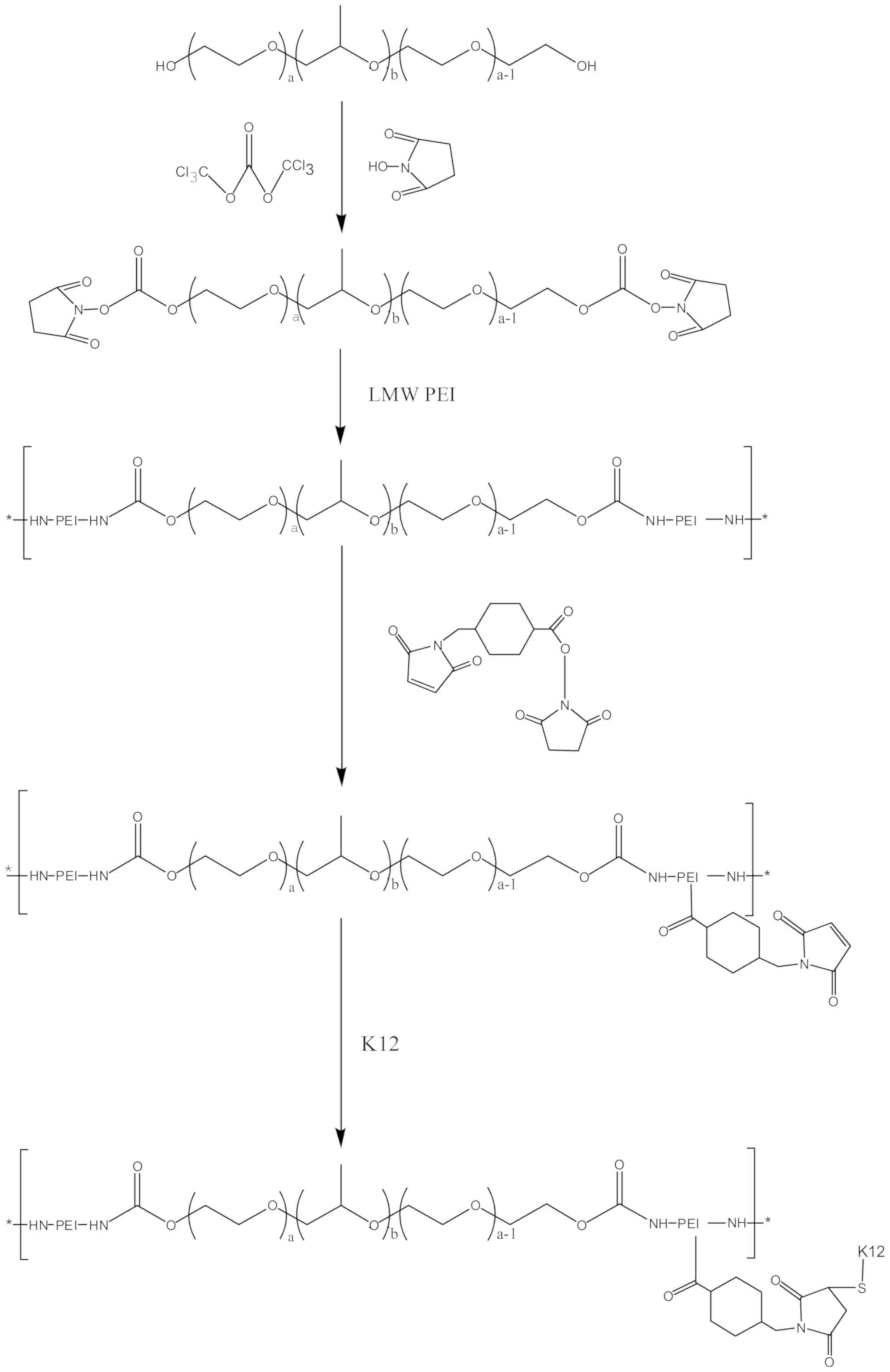
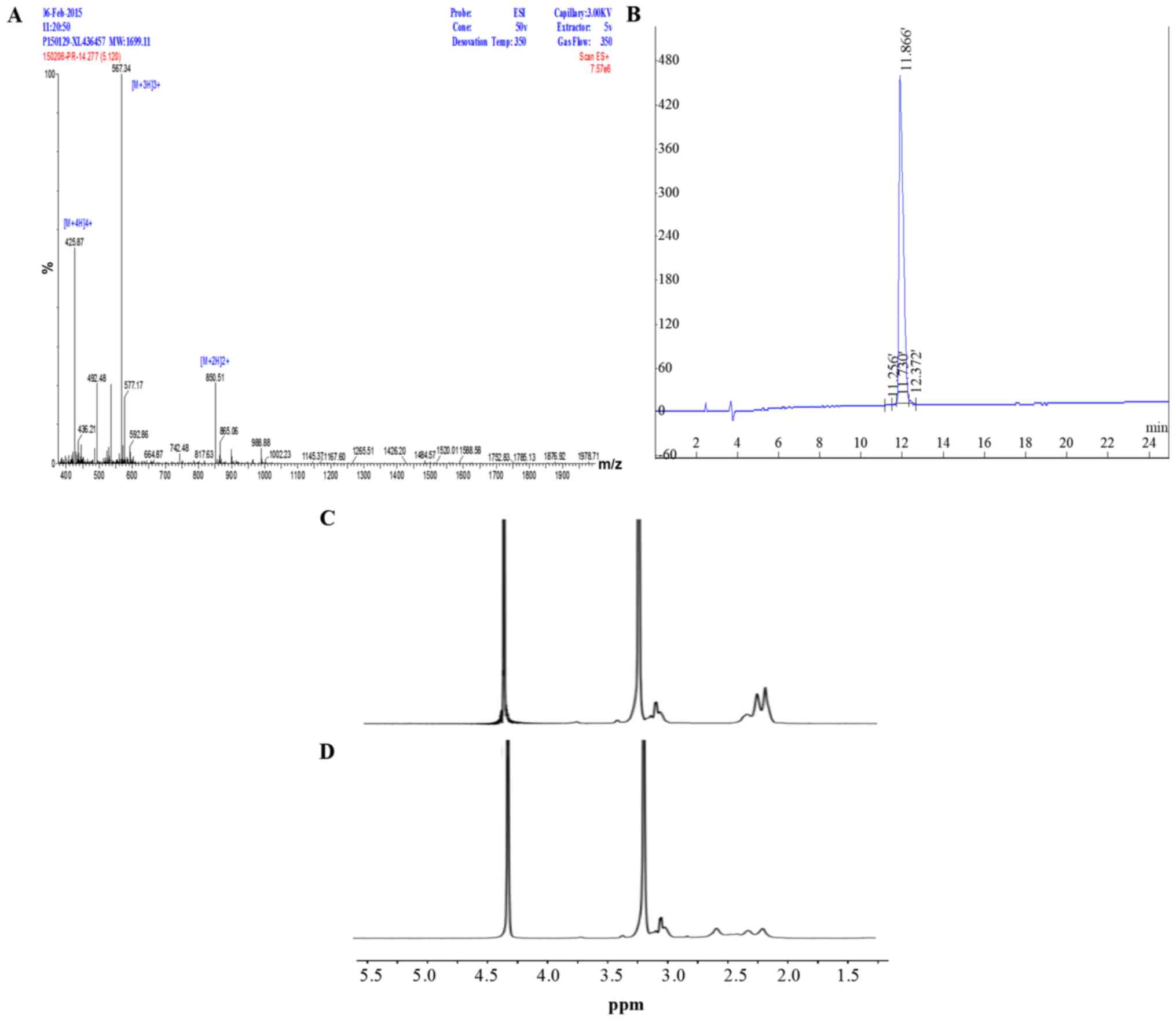
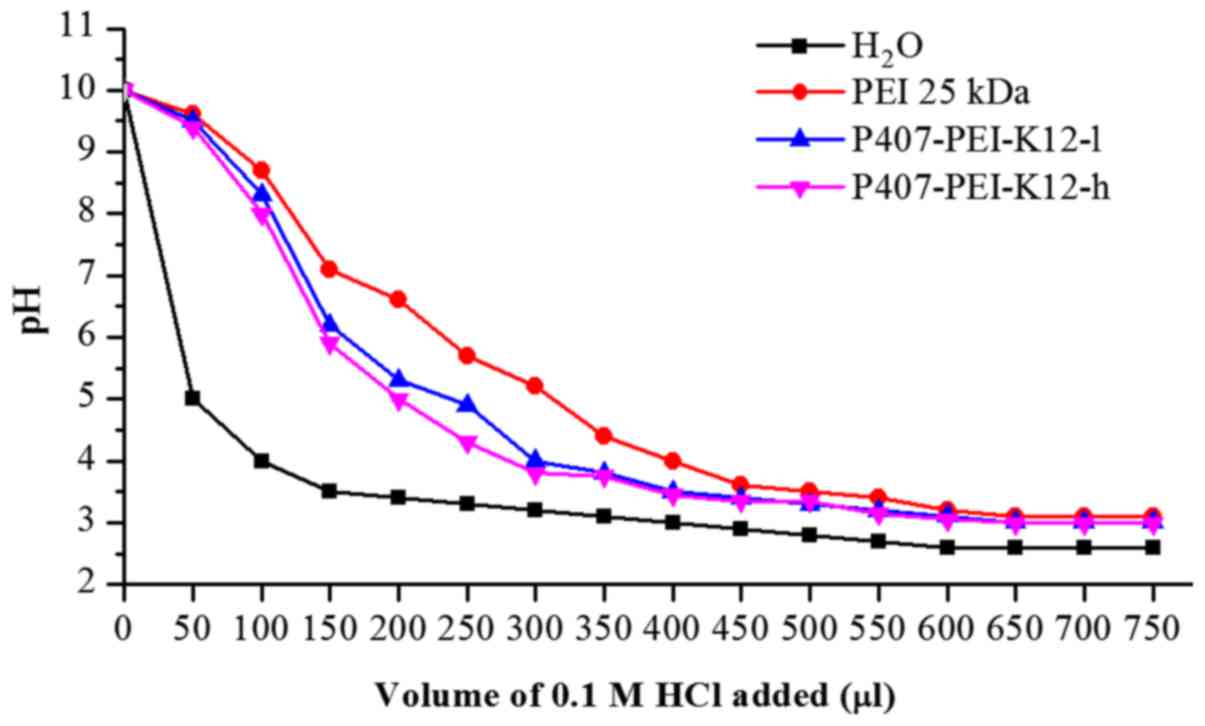
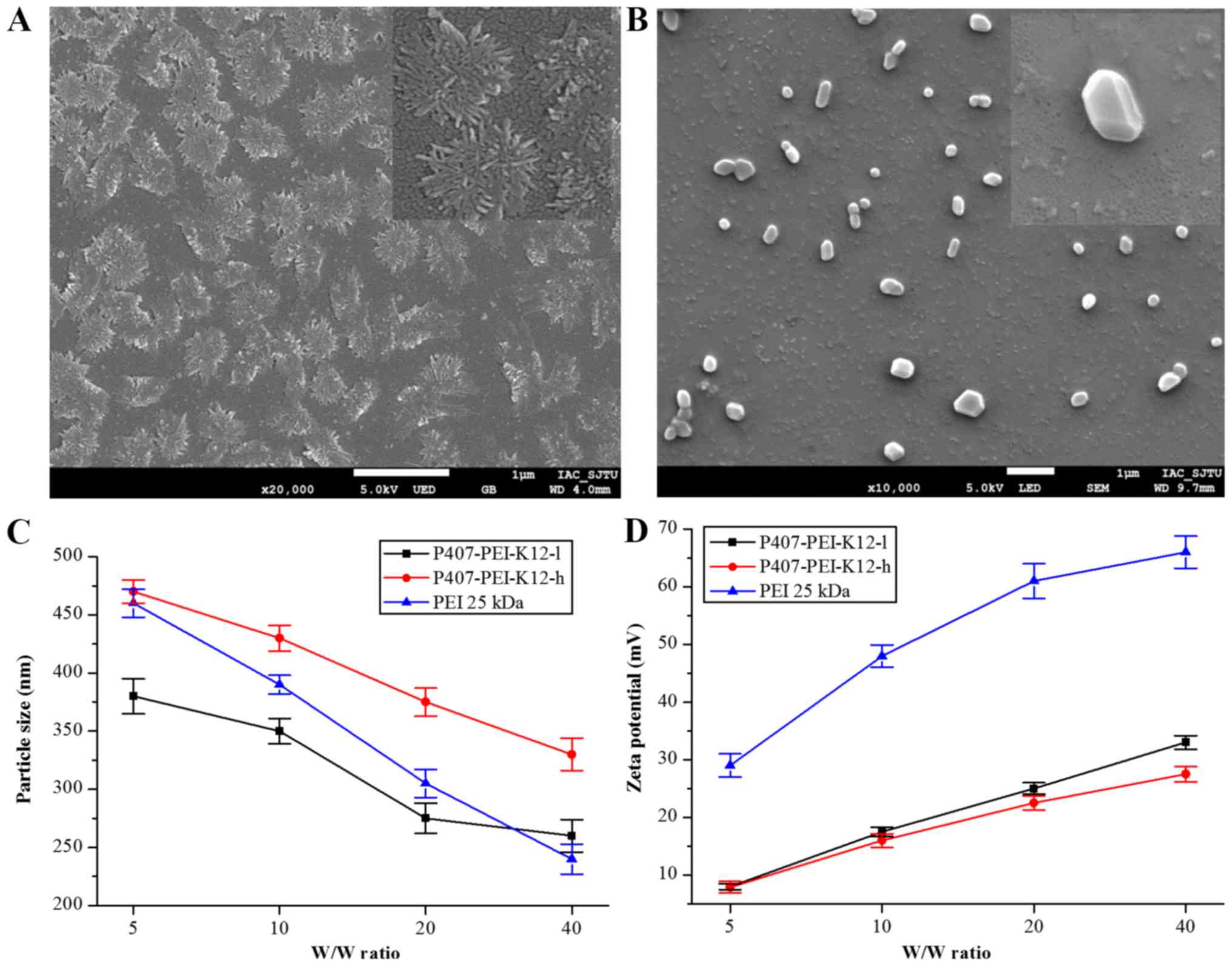
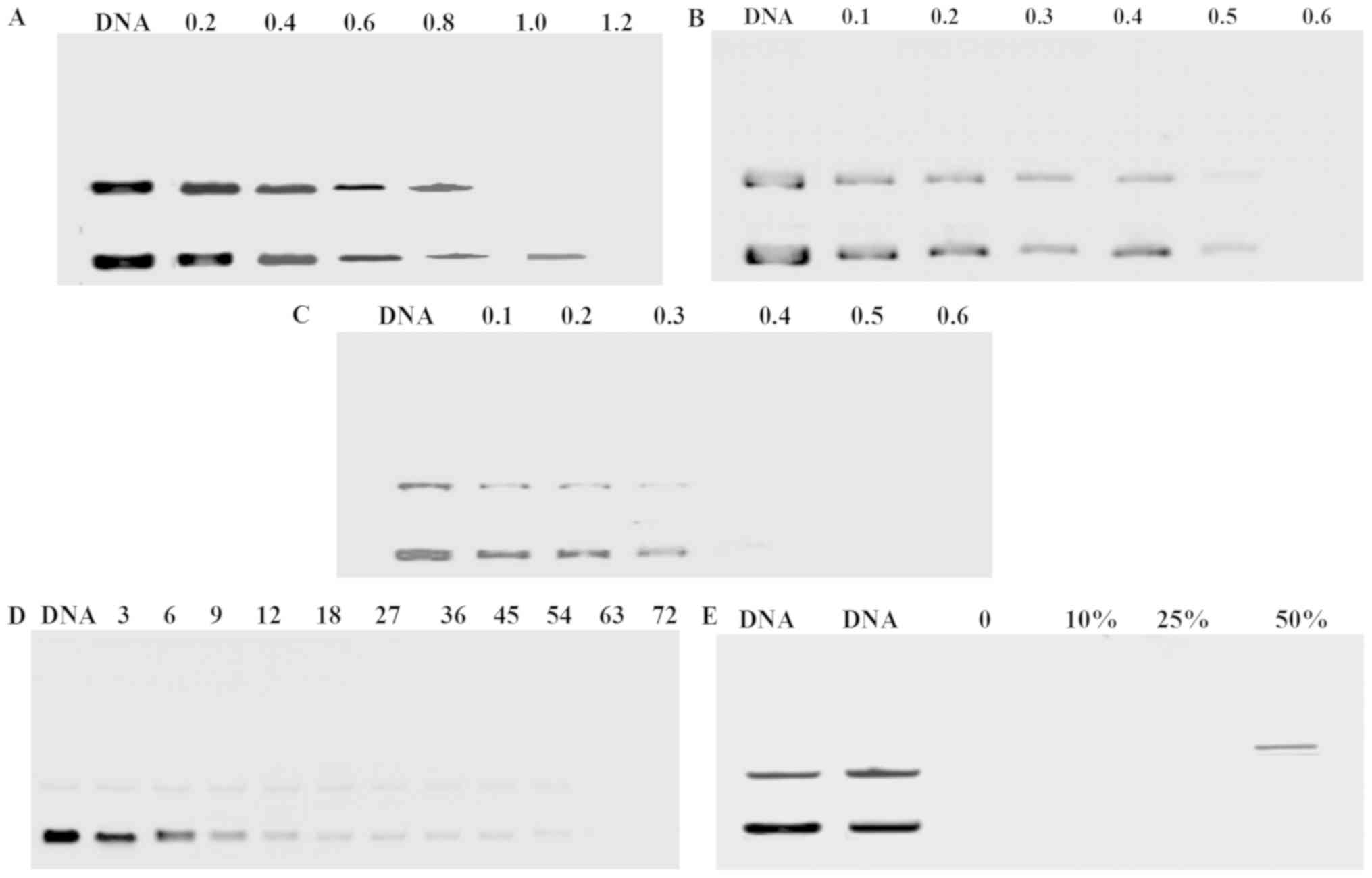
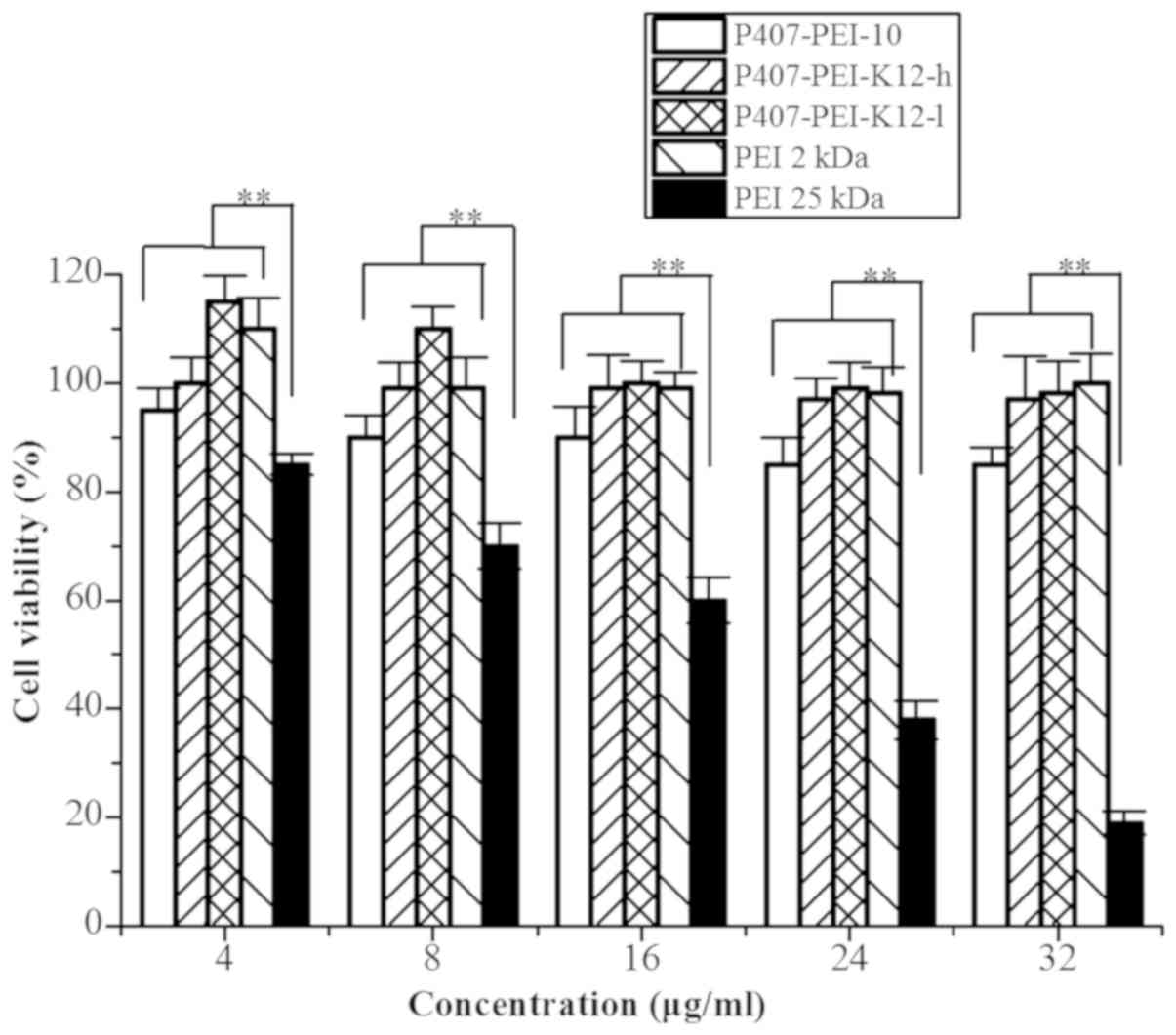
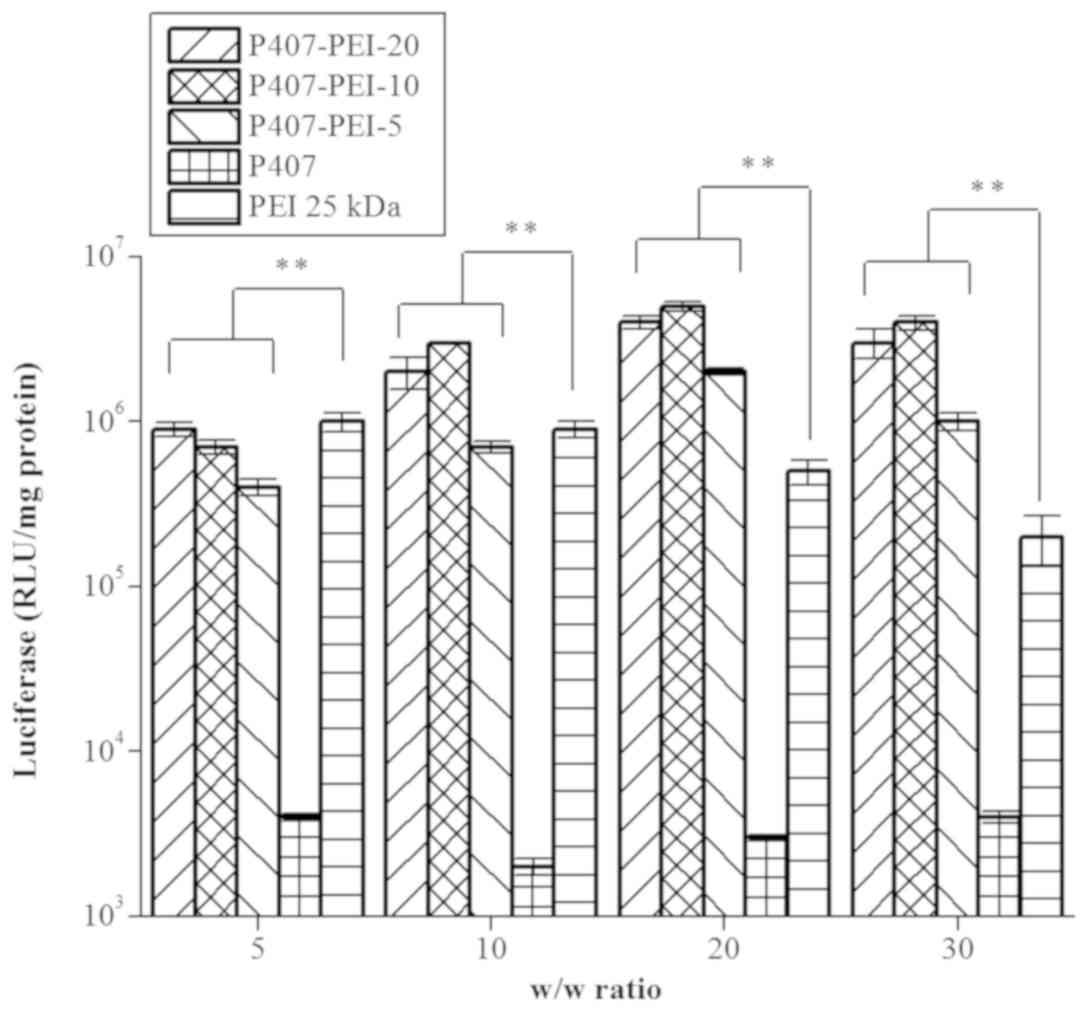
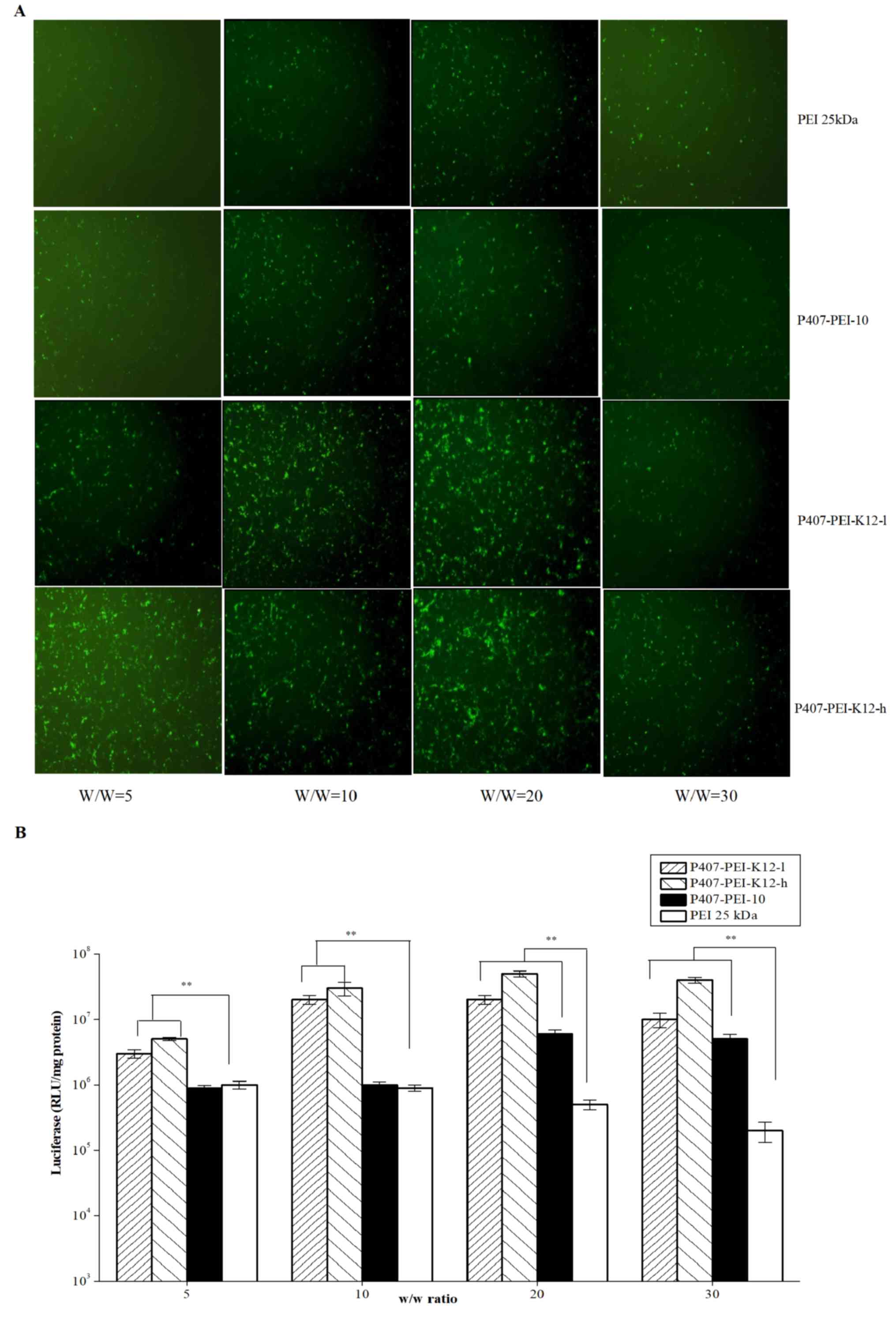
|
1
|
Ambattu LA and Rekha MR: Collagen
synthesis promoting pullulan-PEI-ascorbic acid conjugate as an
efficient anti-cancer gene delivery vector. Carbohydr Polymers.
126:52–61. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tripathi SK, Gupta S, Gupta KC and Kumar
P: Efficient DNA and siRNA delivery with biodegradable cationic
hyaluronic acid conjugates. R Soc Chem. 3:15687–15697. 2013.
|
|
3
|
Shen J, Zhao DJ, Li W, Hu QL, Wang QW, Xu
FJ and Tang GP: A polyethylenimine-mimetic biodegradable polycation
gene vector and the effect of amine composition in transfection
efficiency. Biomaterials. 34:4520–4531. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pérez-Martínez FC, Carrión B and Ceña V:
The use of nanoparticles for gene therapy in the nervous system. J
Alzheimers Dis. 31:697–710. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu K, Wang X, Fan W, Zhu Q, Yang J, Gao J
and Gao S: Degradable polyethylenimine derivate coupled to a
bifunctional peptide R13 as a new gene delivery vector. Int J
Nanomed. 7:1149–1162. 2012.
|
|
6
|
Thomas M, Ge Q, Lu JJ, Chen J and Klibanov
AM: Cross-linked small polyethylenimines: While still nontoxic,
deliver DNA efficiently to mammalian cells in vitro and in vivo.
Pharm Res. 22:373–380. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang W, Li M, Zhang Z, Cui C, Zhou J, Yin
L and Lv H: Design, synthesis and evaluation of multi-functional
tLyP-1-hyaluronic acid-paclitaxel conjugate endowed with broad
anticancer scope. Carbohydr Polym. 156:97–107. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang HY, Chen JX, Sun YX, Deng JZ, Li C,
Zhang XZ and Zhuo RX: Construction of cell penetrating peptide
vectors with N-terminal stearylated nuclear localization signal for
targeted delivery of DNA into the cell nuclei. J Control Release.
155:26–33. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hu J, Zhao W, Liu K, Yu Q, Mao Y, Lu Z,
Zhang Y and Zhu M: Low-molecular weight polyethylenimine modified
with pluronic 123 and RGD- or chimeric RGD-NLS peptide:
Characteristics and transfection efficacy of their complex with
plasmid DNA. Molecules. 21(pii): E6552016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kabanov AV, Lemieux P, Vinogradov S and
Alakhov V: Pluronic block copolymers: Novel functional molecules
for gene therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 54:223–233. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Amir F, Marta C and Alexander S:
Thermogelling properties of purified poloxamer 407. Heliyon.
3:e003902017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ci L, Huang Z, Liu Y, Liu Z, Wei G and Lu
W: Amino-functionalized poloxamer 407 with both mucoadhesive and
thermosensitive properties: Preparation, characterization and
application in a vaginal drug delivery system. Acta Pharm Sin B.
7:593–602. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wannis B, Vimon T, Namon H, Suppalak P and
Thitima U: The effect of the preservative methylparaben on the
thermoresponsive gelation behavior of aqueous solutions of
poloxamer 407. J Mol Liquids. 240:622–629. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Cespi M, Bonacucina G, Pucciarelli S,
Cocci P, Perinelli DR, Casettari L, Illum L, Palmieri GF, Palermo
FA and Mosconi G: Evaluation of thermosensitive poloxamer 407 gel
systems for the sustained release of estradiol in a fish model. Eur
J Pharm Biopharm. 88:954–961. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hamoudi-Ben Yelles MC, Tran Tan V, Danede
F, Willart JF and Siepmann J: PLGA implants: How Poloxamer/PEO
addition slows down or accelerates polymer degradation and drug
release. J Control Release. 253:19–29. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Puligujja P, Balkundi SS, Kendrick LM,
Baldridge HM, Hilaire JR, Bade AN, Dash PK, Zhang G, Poluektova LY,
Gorantla S, et al: Pharmacodynamics of long-acting folic
acid-receptor targeted ritonavir-boosted atazanavir
nanoformulations. Biomaterials. 41:141–150. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chung TW, Liu DZ and Yang JS: Effects of
interpenetration of thermo-sensitive gels by crosslinking of
chitosan on nasal delivery of insulin: In vitro characterization
and in vivo study. Carbohydrate Polymers. 82:316–322. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
M A Fathalla Z, Vangala A, Longman M,
Khaled KA, Hussein AK, El-Garhy OH and Alany RG: Poloxamer-based
thermoresponsive ketorolac tromethamine in situ gel preparations:
Design, characterisation, toxicity and transcorneal permeation
studies. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 114:119–134. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang FL, Jia SQ, Zheng SP and Ding W:
Celastrol enhances AAV1-mediated gene expression in mice adipose
tissues. Gene Ther. 18:128–134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tsoneva I, Iordanov I, Berger AJ, Tomov T,
Nikolova B, Mudrov N and Berger MR: Electro delivery of drugs into
cancer cells in the presence of poloxamer 188. Biomed Biotechnol.
10:1–11. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhu M, Liu K, Zhu Q, Chen S, Lv H, Zhao W,
Mao Y and Hu J: Intracellular disassembly and localization of a new
P123-PEI-R13/DNA complex. Biomed Mater Eng. 24:1925–1931.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pujari-Palmer S, Chen S, Rubino S, Weng H,
Xia W, Engqvist H, Tang L and Ott MK: In vivo and in vitro
evaluation of hydroxyapatite nanoparticle morphology on the acute
inflammatory response. Biomaterials. 90:1–11. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ma K, Hu MX, Qi Y, Zou JH, Qiu LY, Jin Y,
Ying XY and Sun HY: PAMAM-Triamcinolone acetonide conjugate as a
nucleus-targeting gene carrier for enhanced transfer activity.
Biomalerials. 30:6109–6118. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kim TH, Cook SE, Arote RB, Cho MH, Nah JW,
Choi YJ and Cho CS: A degradable hyperbranched poly(ester amine)
based on poloxamer diacrylate and polyethylenimine as a gene
carrier. Macromol Biosci. 7:611–619. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dewan M, Sarkar G, Bhowmik M, Das B,
Chattoapadhyay AK, Rana D and Chattopadhyay D: Effect of gellan gum
on the thermogelation property and drug release profile of
Poloxamer 407 based ophthalmic formulation. Int J Biol Macromol.
102:258–265. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang M, Hu J, Zou Y, Wu J, Yao Y, Fan H,
Liu K, Wang J and Gao S: Modification of degradable nonviral
delivery vehicle with a novel bifunctional peptide to enhance
transfection in vivo. Nanomedicine (Lond). 13:9–24. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|