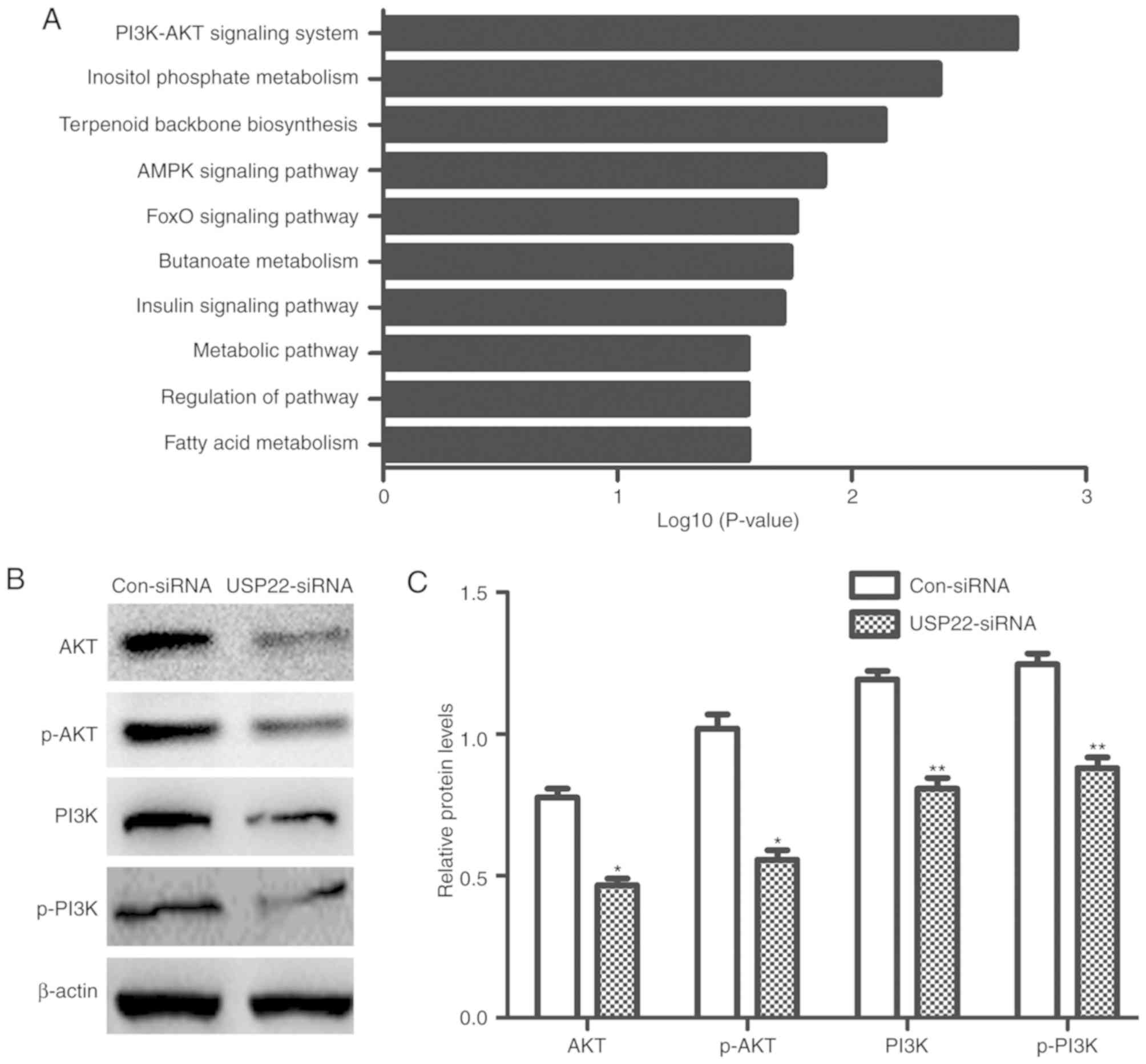
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bao J, Lu Y, Deng Y, Rong C, Liu Y, Huang
X, Song L, Li S and Qin X: Association between IL-18 polymorphisms,
serum levels, and HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma in a Chinese
population: A retrospective case-control study. Cancer Cell Int.
15:722015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun Y, Lu Y, Li T, Xie L, Deng Y, Li S and
Qin X: Interferon gamma +874T/A polymorphism increases the risk of
hepatitis virus-related diseases: Evidence from a meta-analysis.
PLoS One. 10:e01211682015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dastjerdi MN, Kavoosi F, Valiani A,
Esfandiari E, Sanaei M, Sobhanian S, Hakemi MG and Mobarakian M:
Inhibitory effect of genistein on PLC/PRF5 hepatocellular carcinoma
cell line. Int J Prev Med. 6:542015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Peng Q, Yang S, Lao X, Li R, Chen Z, Wang
J, Qin X and Li S: Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms
in VDR and DBP genes with HBV-Related hepatocellular carcinoma risk
in a chinese population. PLoS One. 9:e1160262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang T, Zhang J, You X, Liu Q, Du Y, Gao
Y, Shan C, Kong G, Wang Y, Yang X, et al: Hepatitis B virus X
protein modulates oncogene Yes-associated protein by CREB to
promote growth of hepatoma cells. Hepatology. 56:2051–2059. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hodgson AJ, Hyser JM, Keasler VV, Cang Y
and Slagle BL: Hepatitis B virus regulatory HBx protein binding to
DDB1 is required but is not sufficient for maximal HBV replication.
Virology. 426:73–82. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
He P, Zhang D, Li H, Yang X, Li D, Zhai Y,
Ma L and Feng G: Hepatitis B virus X protein modulates apoptosis in
human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells by activating the
JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 31:1017–1029. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Arbuthnot P, Capovilla A and Kew M:
Putative role of hepatitis B virus X protein in
hepatocarcinogenesis: Effects on apoptosis, DNA repair,
mitogen-activated protein kinase and JAK/STAT pathways. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15:357–368. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
El-Serag HB: Hepatocellular carcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 365:1118–1127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin S, Hoffmann K and Schemmer P:
Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review. Liver
Cancer. 1:144–158. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Whittaker S, Marais R and Zhu AX: The role
of signaling pathways in the development and treatment of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 29:4989–5005. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang XY, Pfeiffer HK, Thorne AW and
McMahon SB: USP22, an hSAGA subunit and potential cancer stem cell
marker, reverses the polycomb-catalyzed ubiquitylation of histone
H2A. Cell Cycle. 7:1522–1524. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee HJ, Kim MS, Shin JM, Park TJ, Chung HM
and Baek KH: The expression patterns of deubiquitinating enzymes,
USP22 and Usp22. Gene Expr Patterns. 6:277–284. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Piao S, Ma J, Wang W, Liu Y, Zhang M, Chen
H and Guo F, Zhang B and Guo F: Increased expression of USP22 is
associated with disease progression and patient prognosis of
salivary duct carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 49:796–801. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li ZH, Yu Y, Du C, Fu H, Wang J and Tian
YU: RNA interference-mediated USP22 gene silencing promotes human
brain glioma apoptosis and induces cell cycle arrest. Oncol Lett.
5:1290–1294. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ning J, Zhang J, Liu W, Lang Y, Xue Y and
Xu S: Overexpression of ubiquitin-specific protease 22 predicts
poor survival in patients with early-stage non-small cell lung
cancer. Eur J Histochem. 56:e462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Piao S, Liu Y, Hu J, Guo F, Ma J, Sun Y
and Zhang B: USP22 is m as a novel molecular Marker for predicting
disease progression and patient prognosis of oral squamous cell
carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e425402012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Glinsky GV, Berezovska O and Glinskii AB:
Microarray analysis identifies a death-from-cancer signature
predicting therapy failure in patients with multiple types of
cancer. J Clin Invest. 115:1503–1521. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH and
Theise N: WHO Classification of tumours of the digestive system.
4th. IARC; Lyon: 2010
|
|
23
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American Joint
committee on cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hoeller D and Dikic I: Targeting the
ubiquitin system in cancer therapy. Nature. 458:438–444. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tang B, Tang F, Li B, Yuan S, Xu Q,
Tomlinson S, Jin J, Hu W and He S: High USP22 expression indicates
poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget.
6:12654–12667. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Atanassov BS, Mohan RD, Lan X, Kuang X, Lu
Y, Lin K, McIvor E, Li W, Zhang Y, Florens L, et al: ATXN7L3 and
ENY2 coordinate activity of multiple H2B deubiquitinases important
for cellular proliferation and tumor growth. Mol Cell. 62:558–571.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tang B, Liang X, Tang F, Zhang J, Zeng S,
Jin S, Zhou L, Kudo Y and Qi G: Expression of USP22 and Survivin is
an indicator of malignant behavior in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int
J Oncol. 47:2208–2216. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang XY, Varthi M, Sykes SM, Phillips C,
Warzecha C, Zhu W, Wyce A, Thorne AW, Berger SL and McMahon SB: The
putative cancer stem cell marker USP22 is a subunit of the human
SAGA complex required for activator-driven transcription and cell
cycle progression. Mol Cell. 29:102–111. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu YL, Jiang SX, Yang YM, Xu H, Liu JL
and Wang XS: USP22 acts as an oncogene by the activation of
BMI-1-mediated INK4a/ARF pathway and Akt pathway. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 62:229–235. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Atanassov BS and Dent SY: USP22 regulates
cell proliferation by deubiquitinating the transcriptional
regulator FBP1. EMBO Rep. 12:924–930. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ning Z, Wang A, Liang J, Xie Y, Liu J, Yan
Q and Wang Z: USP22 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition via
the FAK pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
32:1451–1458. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hu J, Yang D, Zhang H, Liu W, Zhao Y, Lu
H, Meng Q, Pang H, Chen X, Liu Y and Cai L: USP22 promotes tumor
progression and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung
adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer. 88:239–245. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu M, Li W, Lu Y, Dong X, Lin B, Chen Y,
Zhang X, Guo J and Li M: HBx drives alpha fetoprotein expression to
promote initiation of liver cancer stem cells through activating
PI3K/AKT signal pathway. Int J Cancer. 140:1346–1355. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu H, Xu J, Zhou L, Yun X, Chen L, Wang
S, Sun L, Wen Y and Gu J: Hepatitis B virus large surface antigen
promotes liver carcinogenesis by activating the Src/PI3K/Akt
pathway. Cancer Res. 71:7547–7557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Iyer SC, Gopal A and Halagowder D:
Myricetin induces apoptosis by inhibiting P21 activated kinase 1
(PAK1) signaling cascade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell
Biochem. 407:223–237. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|