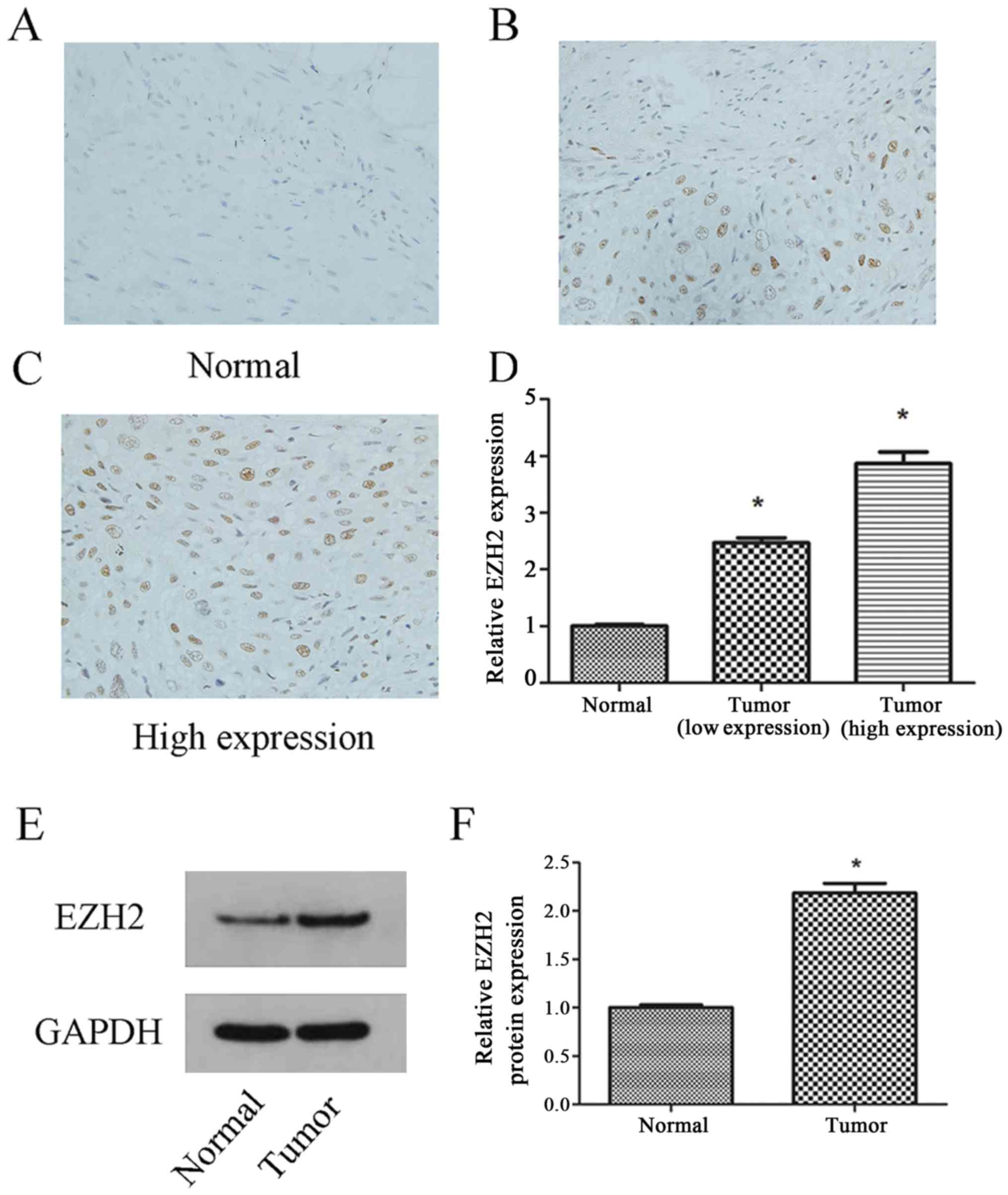
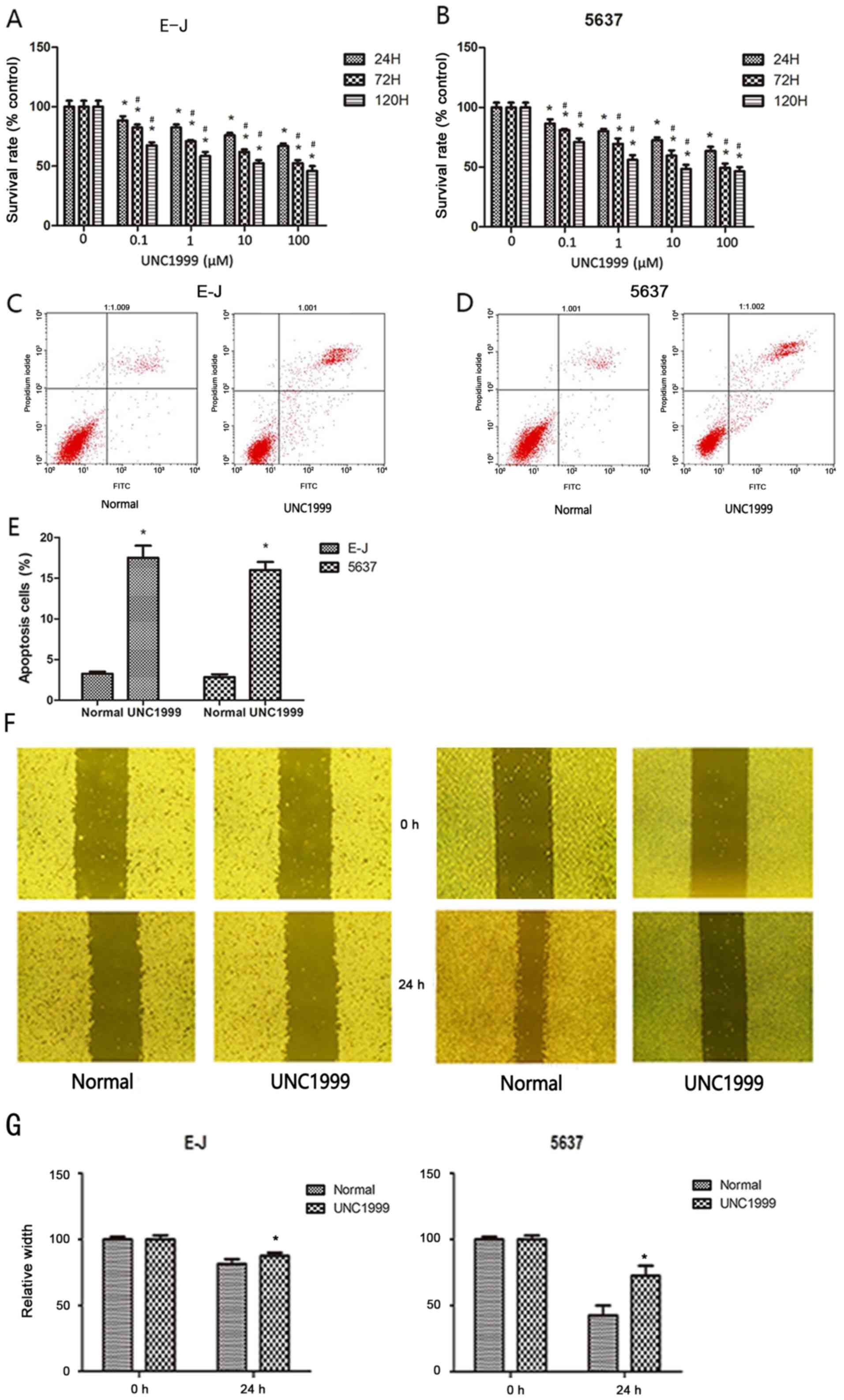
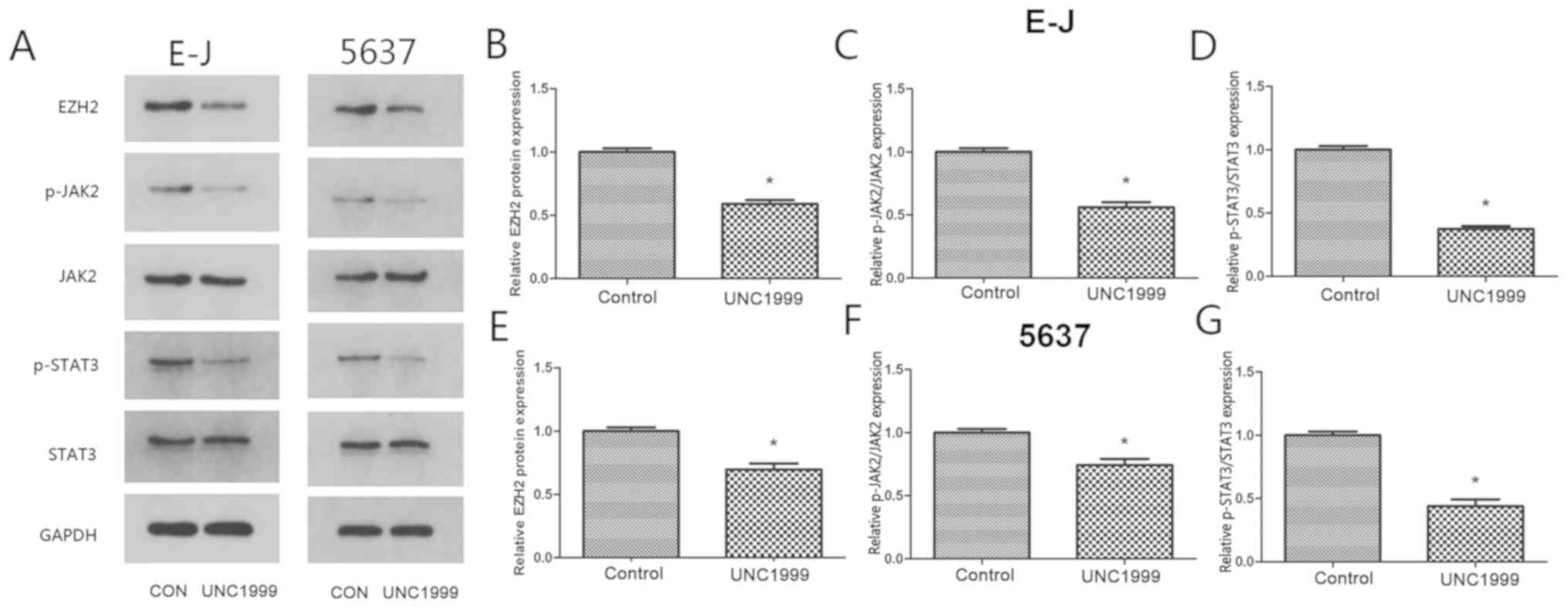
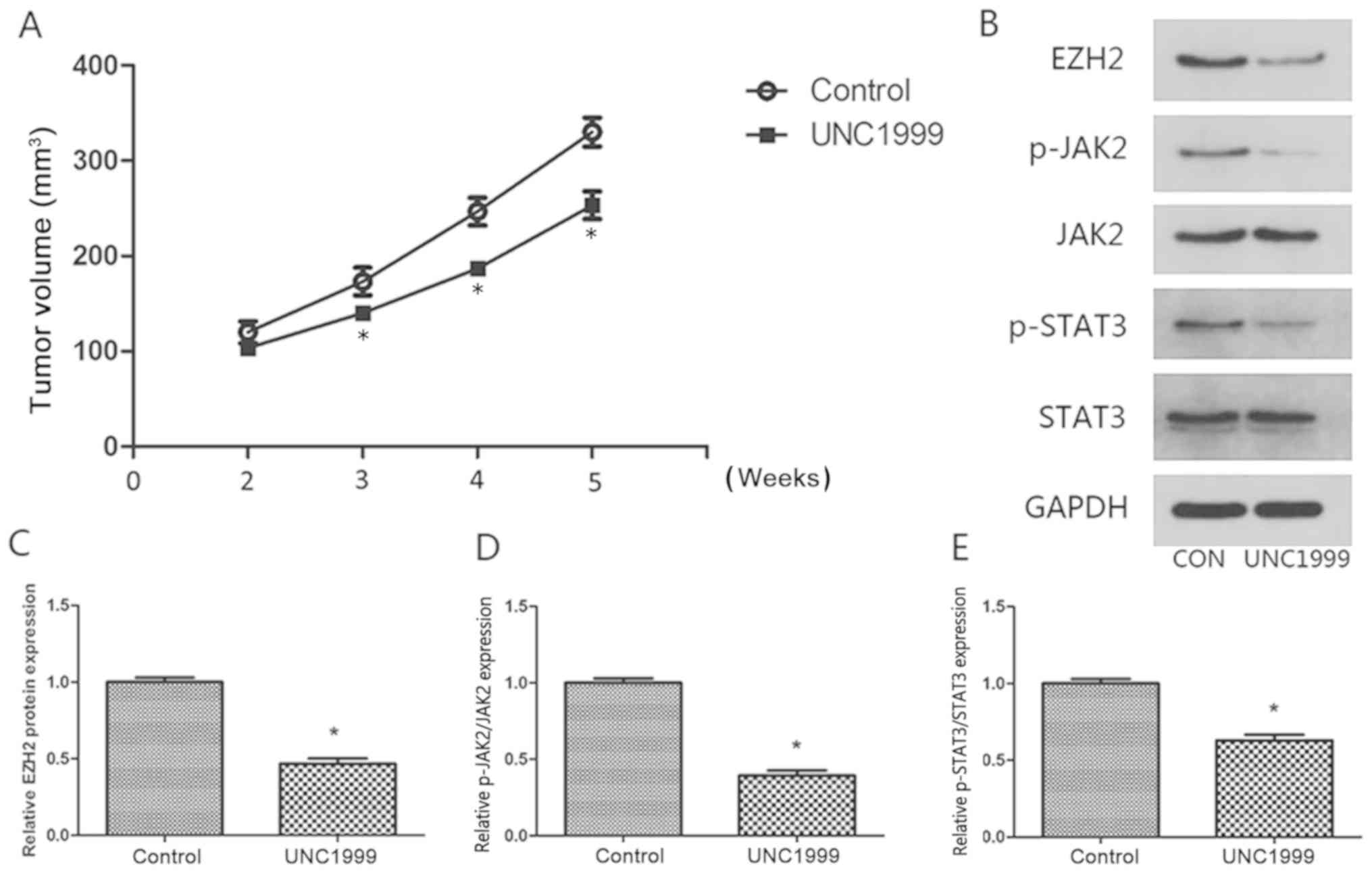
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fedewa SA, Ahnen DJ,
Meester RGS, Barzi A and Jemal A: Colorectal cancer statistics,
2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:177–193. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang Z, Zhang G and Kong C: Targeted
inhibition of polo-like kinase 1 by a novel small-molecule
inhibitor induces mitotic catastrophe and apoptosis in human
bladder cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med. 21:758–767. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yan K, Zhang C, Feng J, Hou L, Yan L, Zhou
Z, Liu Z, Liu C, Fan Y, Zheng B and Xu Z: Induction of G1 cell
cycle arrest and apoptosis by berberine in bladder cancer cells.
Eur J Pharmacol. 661:1–7. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Daneshmand S, Patel S, Lotan Y, Pohar K,
Trabulsi E, Woods M, Downs T, Huang W, Jones J, O'Donnell M, et al:
Efficacy and safety of blue light flexible cystoscopy with
hexaminolevulinate in the surveillance of bladder cancer: A phase
III, comparative, multicenter study. J Urol. 199:1158–1165. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sun J, Yu M, Lu Y, Thakur C, Chen B, Qiu
P, Zhao H and Chen F: Carcinogenic metalloid arsenic induces
expression of mdig oncogene through JNK and STAT3 activation.
Cancer Lett. 346:257–263. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G,
Zhao Y, Pestell RG, Albanese C and Darnell JE Jr: Stat3 as an
oncogene. Cell. 98:295–303. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Devarajan E and Huang S: STAT3 as a
central regulator of tumor metastases. Curr Mol Med. 9:626–633.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wagner KU and Schmidt JW: The two faces of
Janus kinases and their respective STATs in mammary gland
development and cancer. J Carcinog. 10:322011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gu W, Zhang E, Song L, Tu L, Wang Z, Tian
F, Aikenmu K, Chu G and Zhao J: Long noncoding RNA HOXD-AS1
aggravates osteosarcoma carcinogenesis through epigenetically
inhibiting p57 via EZH2. Biomed Pharmacother. 106:890–895. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pasini D, Bracken AP, Hansen JB, Capillo M
and Helin K: The polycomb group protein Suz12 is required for
embryonic stem cell differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 27:3769–3779.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chamberlain SJ, Yee D and Magnuson T:
Polycomb repressive complex 2 is dispensable for maintenance of
embryonic stem cell pluripotency. Stem Cells. 26:1496–1505. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Labbe DP, Sweeney CJ, Brown M, Galbo P,
Rosario S, Wadosky KM, Ku SY, Sjöström M, Alshalalfa M, Erho N, et
al: TOP2A and EZH2 provide early detection of an aggressive
prostate cancer subgroup. Clin Cancer Res. 23:7072–7083. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu D, Li Y, Luo G, Xiao X, Tao D, Wu X,
Wang M, Huang C, Wang L, Zeng F and Jiang G: LncRNA SPRY4-IT1
sponges miR-101-3p to promote proliferation and metastasis of
bladder cancer cells through up-regulating EZH2. Cancer Lett.
388:281–291. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Y, Chen Y, Geng H, Qi C, Liu Y and
Yue D: Overexpression of YB1 and EZH2 are associated with cancer
metastasis and poor prognosis in renal cell carcinomas. Tumour
Biol. 36:7159–7166. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Reijm EA, Timmermans AM, Look MP,
Meijer-van GM, Stobbe CK, van Deurzen CH, Martens JW, Sleijfer S,
Foekens JA, Berns PM and Jansen MP: High protein expression of EZH2
is related to unfavorable outcome to tamoxifen in metastatic breast
cancer. Ann Oncol. 25:2185–2190. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shen H, Morrison CD, Zhang J, Underwood W
III, Yang N, Frangou C, Eng K, Head K, Bollag RJ, Kavuri SK, et al:
6p22.3 amplification as a biomarker and potential therapeutic
target of advanced stage bladder cancer. Oncotarget. 4:2124–2134.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li Z, Wang Y, Qiu J, Li Q, Yuan C, Zhang
W, Wang D, Ye J, Jiang H, Yang J and Cheng J: The polycomb group
protein EZH2 is a novel therapeutic target in tongue cancer.
Oncotarget. 4:2532–2549. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Magers MJ, Lopez-Beltran A, Montironi R,
Williamson SR, Kaimakliotis HZ and Cheng L: Staging of bladder
cancer. Histopathology. 74:112–134. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Moon JH, Hong SW, Kim JE, Shin JS, Kim JS,
Jung SA, Ha SH, Lee S, Kim J, Lee DH, et al: Targeting β-catenin
overcomes MEK inhibition resistance in colon cancer with KRAS and
PIK3CA mutations. Br J Cancer. 4–April;2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen J, Weihs D and Vermolen FJ: A model
for cell migration in non-isotropic fibrin networks with an
application to pancreatic tumor islets. Biomech Model Mechanobiol.
17:367–386. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao JM, Cheng W, He XG, Liu YL, Wang FF
and Gao YF: Long non-coding RNA PICART1 suppresses proliferation
and promotes apoptosis in lung cancer cells by inhibiting
JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Neoplasma. 65:779–789. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dehayni Y, Tetou M, Khdach Y, Janane A,
Alami M and Ameur A: Prognostic of older age for patients with
invasive-muscle-bladder cancer and treated by radical cystectomy.
Prog Urol. 28:166–172. 2018.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Racioppi M, D'Agostino D, Totaro A, Pinto
F, Sacco E, D'Addessi A, Marangi F, Palermo G and Bassi PF: Value
of current chemotherapy and surgery in advanced and metastatic
bladder cancer. Urol Int. 88:249–258. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hammerle M, Gutschner T, Uckelmann H,
Ozgur S, Fiskin E, Gross M, Skawran B, Geffers R, Longerich T,
Breuhahn K, et al: Posttranscriptional destabilization of the
liver-specific long noncoding RNA HULC by the IGF2 mRNA-binding
protein 1 (IGF2BP1). Hepatology. 58:1703–1712. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Muller J, Hart CM, Francis NJ, Vargas ML,
Sengupta A, Wild B, Miller EL, O'Connor MB, Kingston RE and Simon
JA: Histone methyltransferase activity of a drosophila polycomb
group repressor complex. Cell. 111:197–208. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shahabipour F, Caraglia M, Majeed M,
Derosa G, Maffioli P and Sahebkar A: Naturally occurring
anti-cancer agents targeting EZH2. Cancer Lett. 400:325–335. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Varambally S, Dhanasekaran SM, Zhou M,
Barrette TR, Kumar-Sinha C, Sanda MG, Ghosh D, Pienta KJ, Sewalt
RG, Otte AP, et al: The polycomb group protein EZH2 is involved in
progression of prostate cancer. Nature. 419:624–629. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Karanikolas BD, Figueiredo ML and Wu L:
Polycomb group protein enhancer of zeste 2 is an oncogene that
promotes the neoplastic transformation of a benign prostatic
epithelial cell line. Mol Cancer Res. 7:1456–1465. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yamamoto I, Nosho K, Kanno S, Igarashi H,
Kurihara H, Ishigami K, Ishiguro K, Mitsuhashi K, Maruyama R, Koide
H, et al: EZH2 expression is a prognostic biomarker in patients
with colorectal cancer treated with anti-EGFR therapeutics.
Oncotarget. 8:17810–17818. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gonzalez ME, Li X, Toy K, DuPrie M,
Ventura AC, Banerjee M, Ljungman M, Merajver SD and Kleer CG:
Downregulation of EZH2 decreases growth of estrogen
receptor-negative invasive breast carcinoma and requires BRCA1.
Oncogene. 28:843–853. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu B, On DM, Ma A, Parton T, Konze KD,
Pattenden SG, Allison DF, Cai L, Rockowitz S, Liu S, et al:
Selective inhibition of EZH2 and EZH1 enzymatic activity by a small
molecule suppresses MLL-rearranged leukemia. Blood. 125:346–357.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee SR, Roh YG, Kim SK, Lee JS, Seol SY,
Lee HH, Kim WT, Kim WJ, Heo J, Cha HJ, et al: Activation of EZH2
and SUZ12 regulated by E2F1 predicts the disease progression and
aggressive characteristics of bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
21:5391–5403. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang S, Zhong G, He W, Yu H, Huang J and
Lin T: lncRNA Up-regulated in nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer
facilitates tumor growth and acts as a negative prognostic factor
of recurrence. J Urol. 196:1270–1278. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xu B, Chen X, Tan J and Xu X: Effect of
AG490 on JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in human retinoblastoma
HXO-RB44 cell lines. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.
43:1061–1067. 2018.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Heinrich PC, Behrmann I, Haan S, Hermanns
HM, Muller-Newen G and Schaper F: Principles of interleukin
(IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem J.
374:1–20. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zheng L, Chen J, Zhou Z and He Z:
Knockdown of long non-coding RNA HOXD-AS1 inhibits gastric cancer
cell growth via inactivating the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283177053352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim MJ, Nam HJ, Kim HP, Han SW, Im SA, Kim
TY, Oh DY and Bang YJ: OPB-31121, a novel small molecular
inhibitor, disrupts the JAK2/STAT3 pathway and exhibits an
antitumor activity in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
335:145–152. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Song Y, Kong L, Sun B, Gao L, Chu P, Ahsan
A, Qaed E, Lin Y, Peng J, Ma X, et al: Induction of autophagy by an
oleanolic acid derivative, SZC017, promotes ROS-dependent apoptosis
through Akt and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in human lung cancer
cells. Cell Biol Int. 41:1367–1378. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lei J, Xiao JH, Zhang SH, Liu ZQ, Huang K,
Luo ZP, Xiao XL and Hong ZD: Non-coding RNA 886 promotes renal cell
carcinoma growth and metastasis through the Janus kinase 2/signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling pathway. Mol
Med Rep. 16:4273–4278. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang Z, Wang F, Du C, Guo H, Ma L, Liu X,
Kornmann M, Tian X and Yang Y: BRM/SMARCA2 promotes the
proliferation and chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer cells by
targeting JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Cancer Lett. 402:213–224. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yang X, Li F, Konze KD, Meslamani J, Ma A,
Brown PJ, Zhou MM, Arrowsmith CH, Kaniskan HÜ, Vedadi M and Jin J:
Structure-activity relationship studies for enhancer of zeste
homologue 2 (EZH2) and enhancer of zeste homologue 1 (EZH1)
inhibitors. J Med Chem. 59:7617–7633. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|