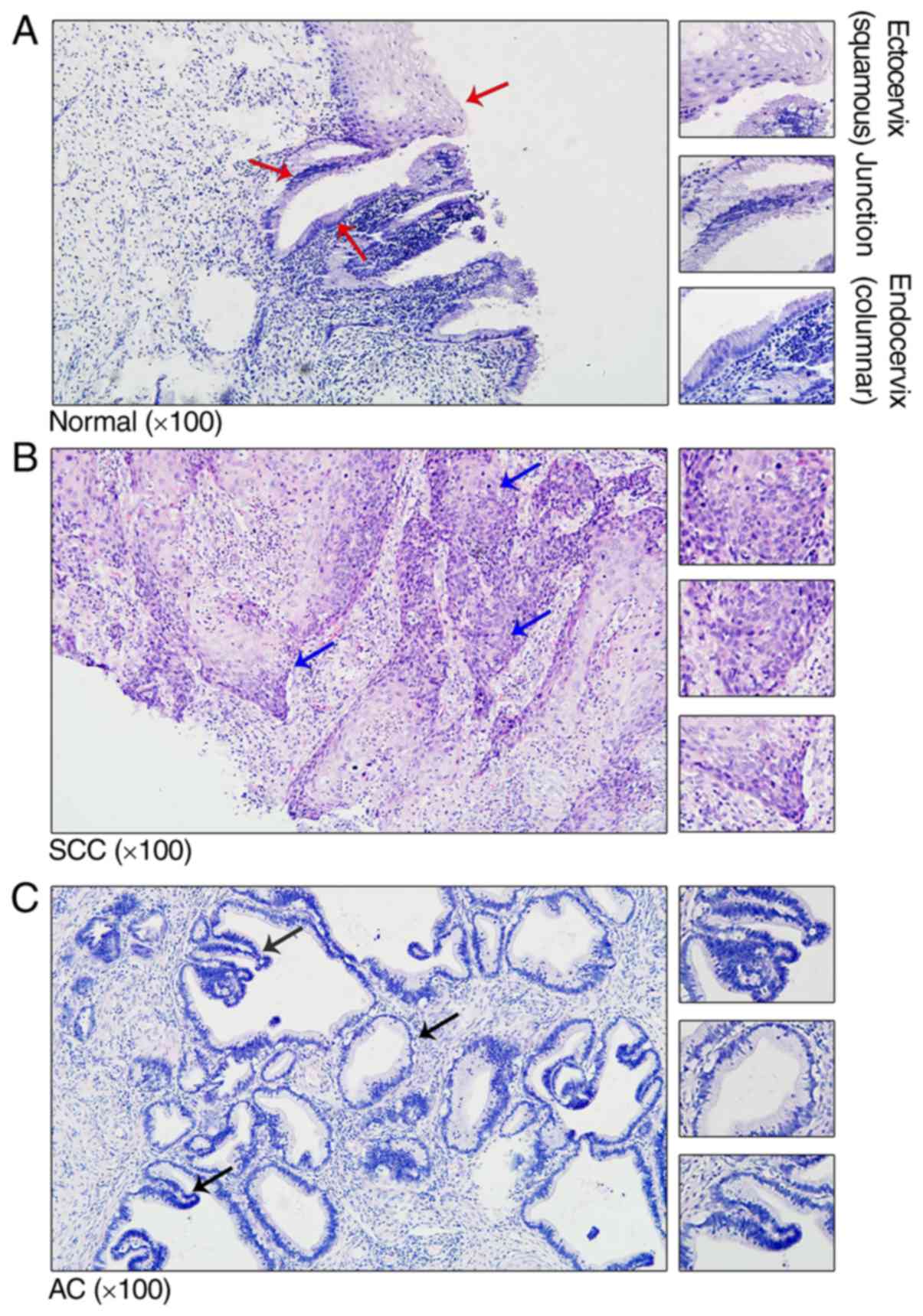
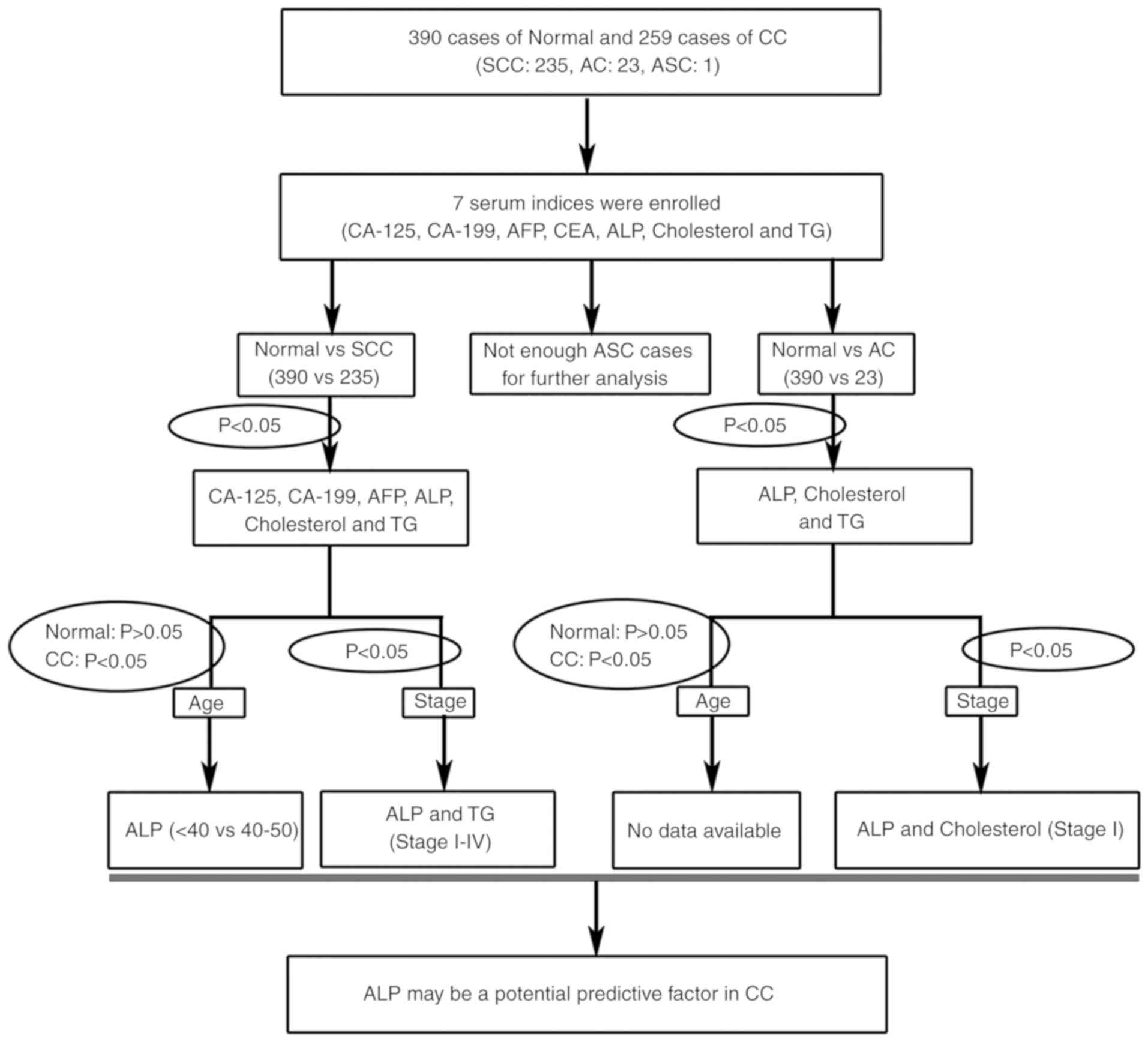
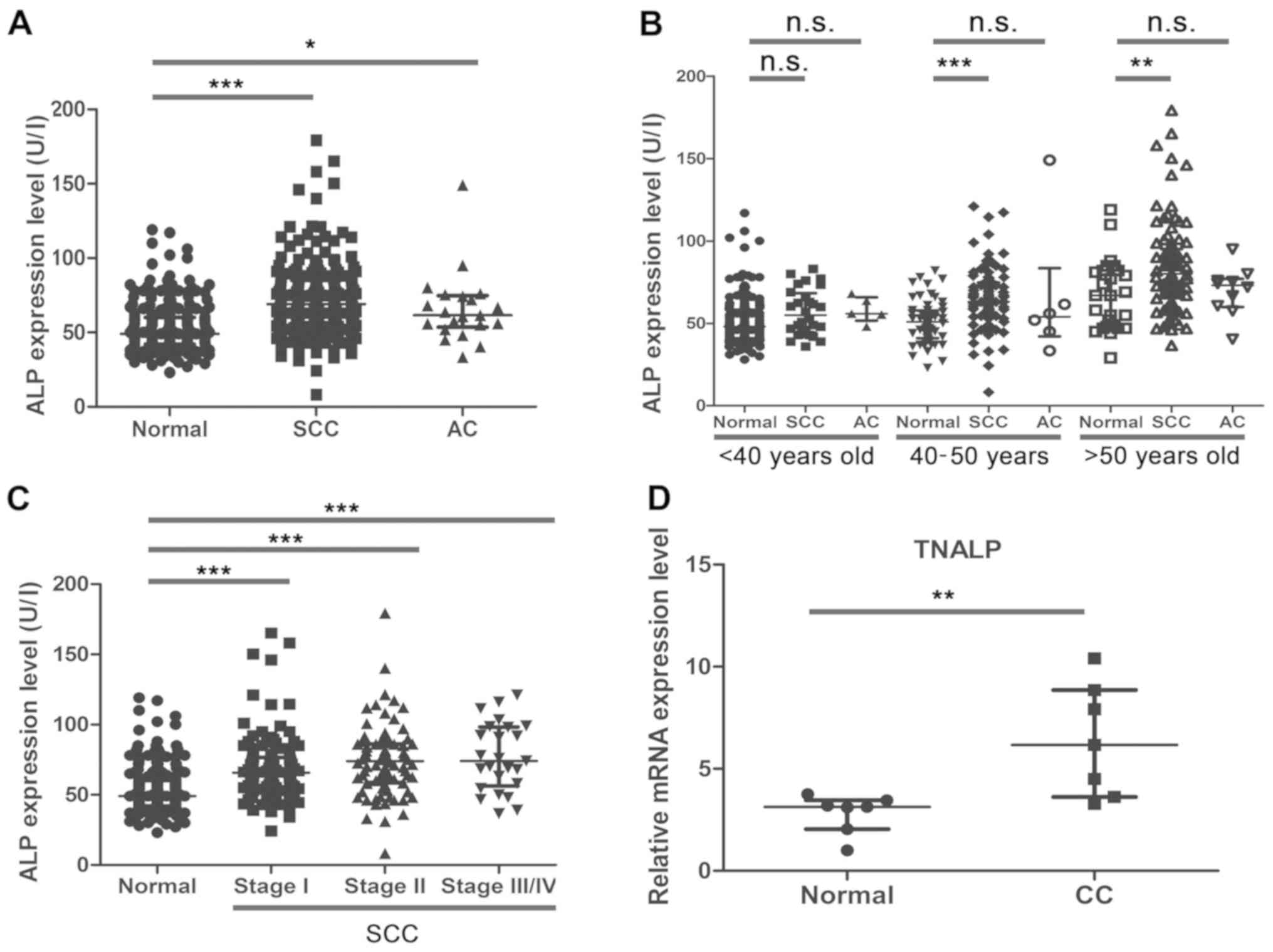
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen P, Jiao L and Wang DB: Squamous cell
carcinoma antigen expression in tumor cells is associated with the
chemosensitivity and survival of patients with cervical cancer
receiving docetaxel-carboplatin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Oncol Lett. 13:1235–1241. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Molina R, Filella X, Augé JM, Fuentes R,
Bover I, Rifa J, Moreno V, Canals E, Viñolas N, Marquez A, et al:
Tumor markers (CEA, CA 125, CYFRA 21-1, SCC and NSE) in patients
with non-small cell lung cancer as an aid in histological diagnosis
and prognosis. Comparison with the main clinical and pathological
prognostic factors. Tumour Biol. 24:209–218. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Catanzaro JM, Guerriero JL, Liu J, Ullman
E, Sheshadri N, Chen JJ and Zong WX: Elevated expression of
squamous cell carcinoma antigen (SCCA) is associated with human
breast carcinoma. PLoS One. 6:e190962011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sánchez Vega JF, Murillo Bacilio MDR,
Vintimilla Condoy AS, Palta González AM, Crespo Astudillo JA and
Mora-Bravo FG: Predictive equation of metastasis in patients with
malignant ovarian epithelial tumors with the Ca-125 marker. BMC
Cancer. 18:5872018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Malati T: Tumour markers: An overview.
Indian J Clin Biochem. 22:17–31. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lebrecht A, Ludwig E, Huber A, Klein M,
Schneeberger C, Tempfer C, Koelbl H and Hefler L: Serum vascular
endothelial growth factor and serum leptin in patients with
cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 85:32–35. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fuso L, Mazzola S, Marocco F, Ferrero A,
Dompè D, Carus AP and Zola P: Pretreatment serum hemoglobin level
as a predictive factor of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in
patients with locally advanced squamous cervical carcinoma: A
preliminary report. Gynecol Oncol. 99 (Suppl 1):S187–S191. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bhatla N, Aoki D, Sharma DN and
Sankaranarayanan R: Cancer of the cervix uteri. Int J Gynaecol
Obstet. 143 (Suppl 2):S22–S36. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
US Preventive Services Task Force, ; Curry
SJ, Krist AH, Owens DK, Barry MJ, Caughey AB, Davidson KW, Doubeni
CA, Epling JW Jr, Kemper AR, et al: Screening for cervical cancer:
US preventive services task force recommendation statement. JAMA.
320:674–686. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Herfs M, Yamamoto Y, Laury A, Wang X,
Nucci MR, McLaughlin-Drubin ME, Münger K, Feldman S, McKeon FD,
Xian W and Crum CP: A discrete population of squamocolumnar
junction cells implicated in the pathogenesis of cervical cancer.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:10516–10521. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Quinn BA, Deng X, Colton A, Bandyopadhyay
D, Carter JS and Fields EC: Increasing age predicts poor cervical
cancer prognosis with subsequent effect on treatment and overall
survival. Brachytherapy. 18:29–37. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang C, Wang H, Ning Z, Xu L, Zhuang L,
Wang P and Meng Z: Serum liver enzymes serve as prognostic factors
in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Onco Targets
Ther. 10:1441–1449. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fuchs CS, Muro K, Tomasek J, Van Cutsem E,
Cho JY, Oh SC, Safran H, Bodoky G, Chau I, Shimada Y, et al:
Prognostic factor analysis of overall survival in gastric cancer
from two phase III studies of second-line ramucirumab (REGARD and
RAINBOW) using pooled patient data. J Gastric Cancer. 17:132–144.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Haarhaus M, Brandenburg V, Kalantar-Zadeh
K, Stenvinkel P and Magnusson P: Alkaline phosphatase: A novel
treatment target for cardiovascular disease in CKD. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 13:429–442. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Magnusson P, Degerblad M, Sääf M, Larsson
L and Thorén M: Different responses of bone alkaline phosphatase
isoforms during recombinant insulin-like growth factor-i (IGF-I)
and during growth hormone therapy in adults with growth hormone
deficiency. J Bone Miner Res. 12:210–220. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Metwalli AR, Rosner IL, Cullen J, Chen Y,
Brand T, Brassell SA, Lesperance J, Porter C, Sterbis J and McLeod
DG: Elevated alkaline phosphatase velocity strongly predicts
overall survival and the risk of bone metastases in
castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Urol Oncol. 32:761–768. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sonpavde G, Pond GR, Berry WR, de Wit R,
Armstrong AJ, Eisenberger MA and Tannock IF: Serum alkaline
phosphatase changes predict survival independent of PSA changes in
men with castration-resistant prostate cancer and bone metastasis
receiving chemotherapy. Urol Oncol. 30:607–613. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fedde KN, Lane CC and Whyte MP: Alkaline
phosphatase is an ectoenzyme that acts on micromolar concentrations
of natural substrates at physiologic pH in human osteosarcoma
(SAOS-2) cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 264:400–409. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Rao SR, Snaith AE, Marino D, Cheng X, Lwin
ST, Orriss IR, Hamdy FC and Edwards CM: Tumour-derived alkaline
phosphatase regulates tumour growth, epithelial plasticity and
disease-free survival in metastatic prostate cancer. Br J Cancer.
116:227–236. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Millán JL: The role of phosphatases in the
initiation of skeletal mineralization. Calcif Tissue Int.
93:299–306. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nam HK, Sharma M, Liu J and Hatch NE:
Tissue nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNAP) regulates cranial
base growth and synchondrosis maturation. Front Physiol. 8:1612017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shao J, Wang C, Li L, Liang H, Dai J, Ling
X and Tang H: Luteoloside inhibits proliferation and promotes
intrinsic and extrinsic pathway-mediated apoptosis involving MAPK
and mTOR signaling pathways in human cervical cancer cells. Int J
Mol Sci. 19:E16642018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hua FF, Liu SS, Zhu LH, Wang YH, Liang X,
Ma N and Shi HR: MiRNA-338-3p regulates cervical cancer cells
proliferation by targeting MACC1 through MAPK signaling pathway.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:5342–5352. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun Q, Liang Y, Zhang T, Wang K and Yang
X: ER-α36 mediates estrogen-stimulated MAPK/ERK activation and
regulates migration, invasion, proliferation in cervical cancer
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 487:625–632. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li S, Ma YM, Zheng PS and Zhang P: GDF15
promotes the proliferation of cervical cancer cells by
phosphorylating AKT1 and Erk1/2 through the receptor ErbB2. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 37:802018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang XL, Liu KY, Lin FJ, Shi HM and Ou ZL:
CCL28 promotes breast cancer growth and metastasis through
MAPK-mediated cellular anti-apoptosis and pro-metastasis. Oncol
Rep. 38:1393–1401. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang C, Li P, Xuan J, Zhu C, Liu J, Shan
L, Du Q, Ren Y and Ye J: Cholesterol enhances colorectal cancer
progression via ROS elevation and MAPK signaling pathway
activation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 42:729–742. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang Z, Wang L, Du J, Li Y, Yang H, Li C,
Li H and Hu H: Lipid raft localization of epidermal growth factor
receptor alters matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression in SiHa cells
via the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 12:4991–4998. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cohen PA, Jhingran A, Oaknin A and Denny
L: Cervical cancer. Lancet. 393:169–182. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|