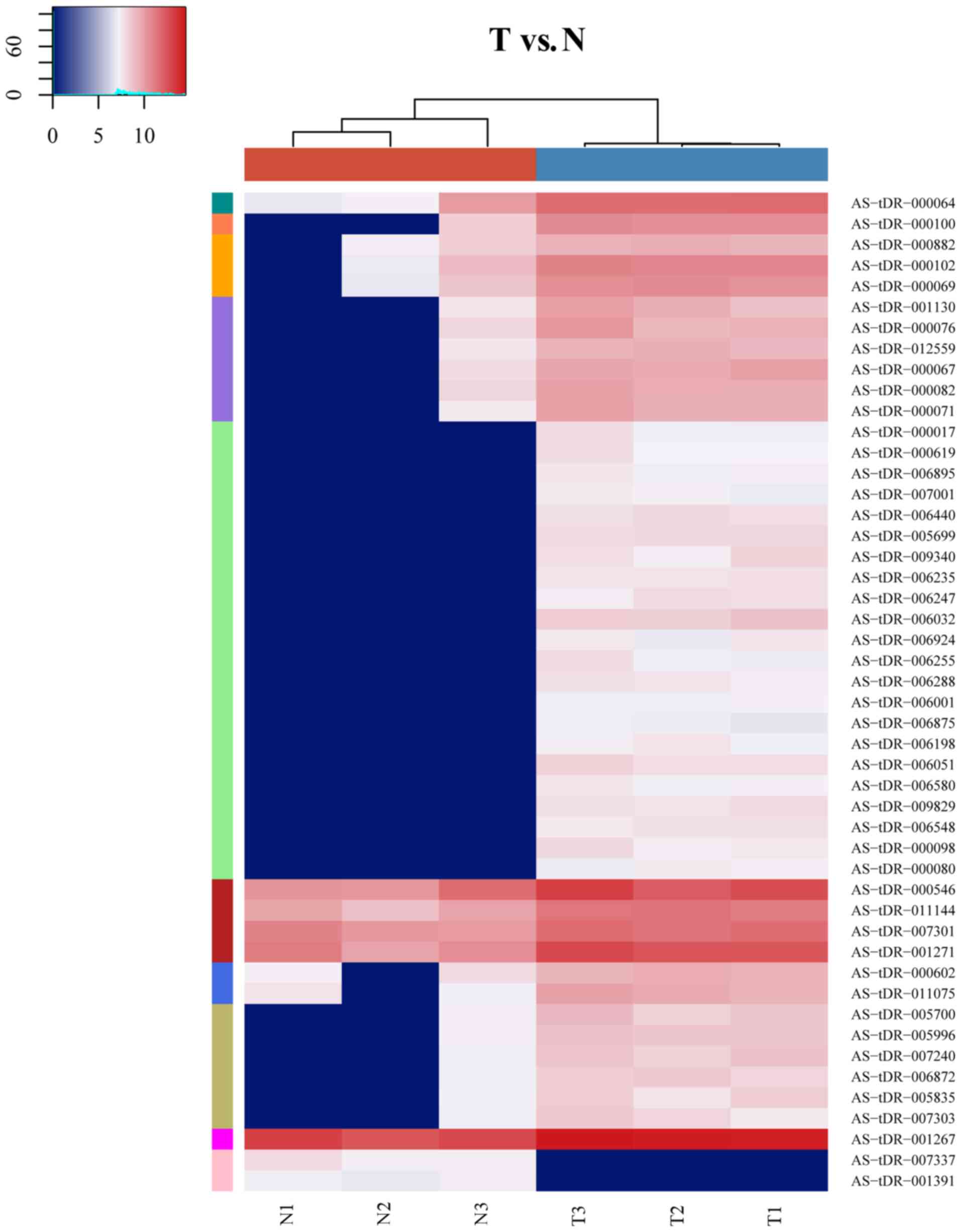
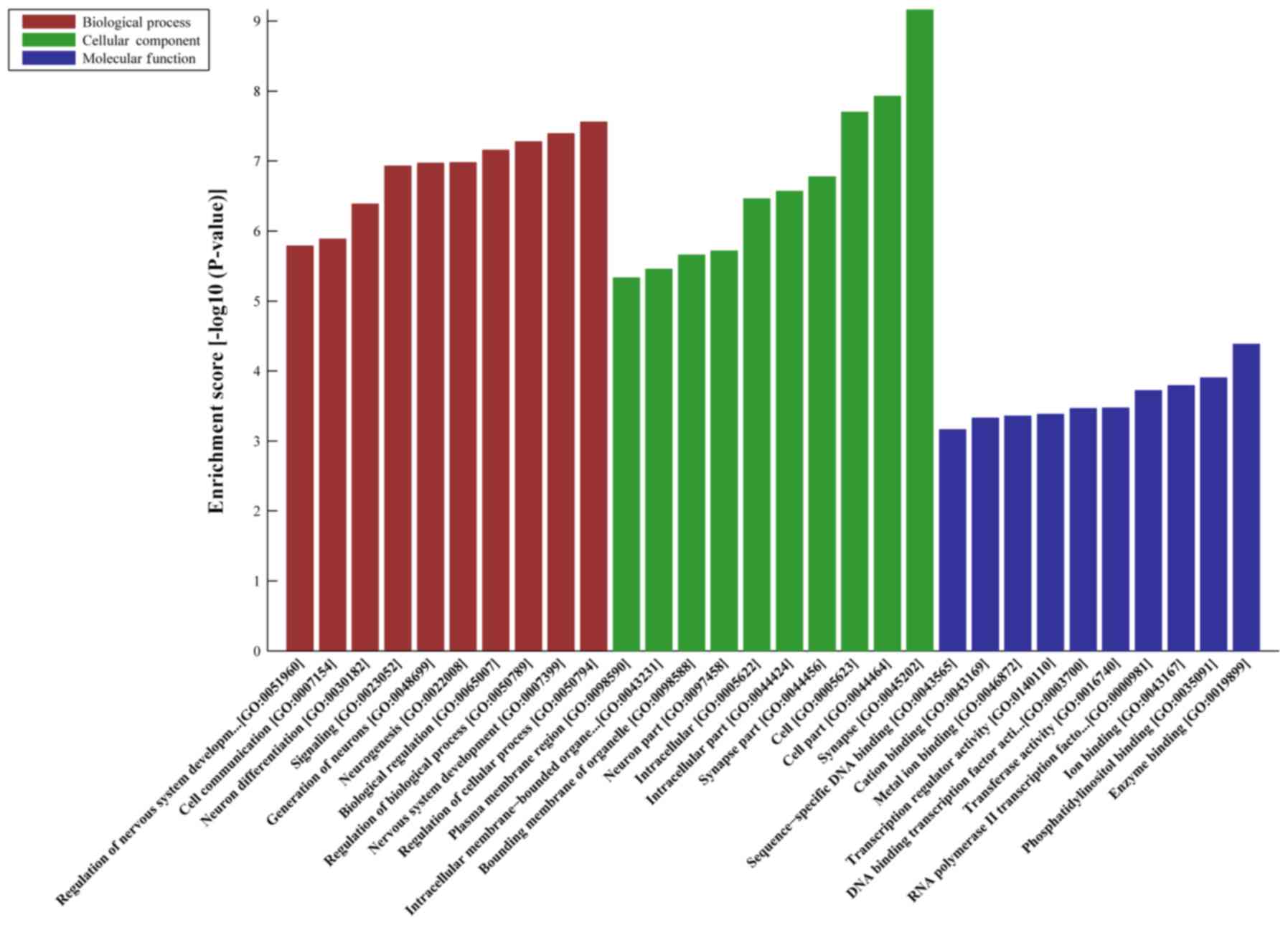
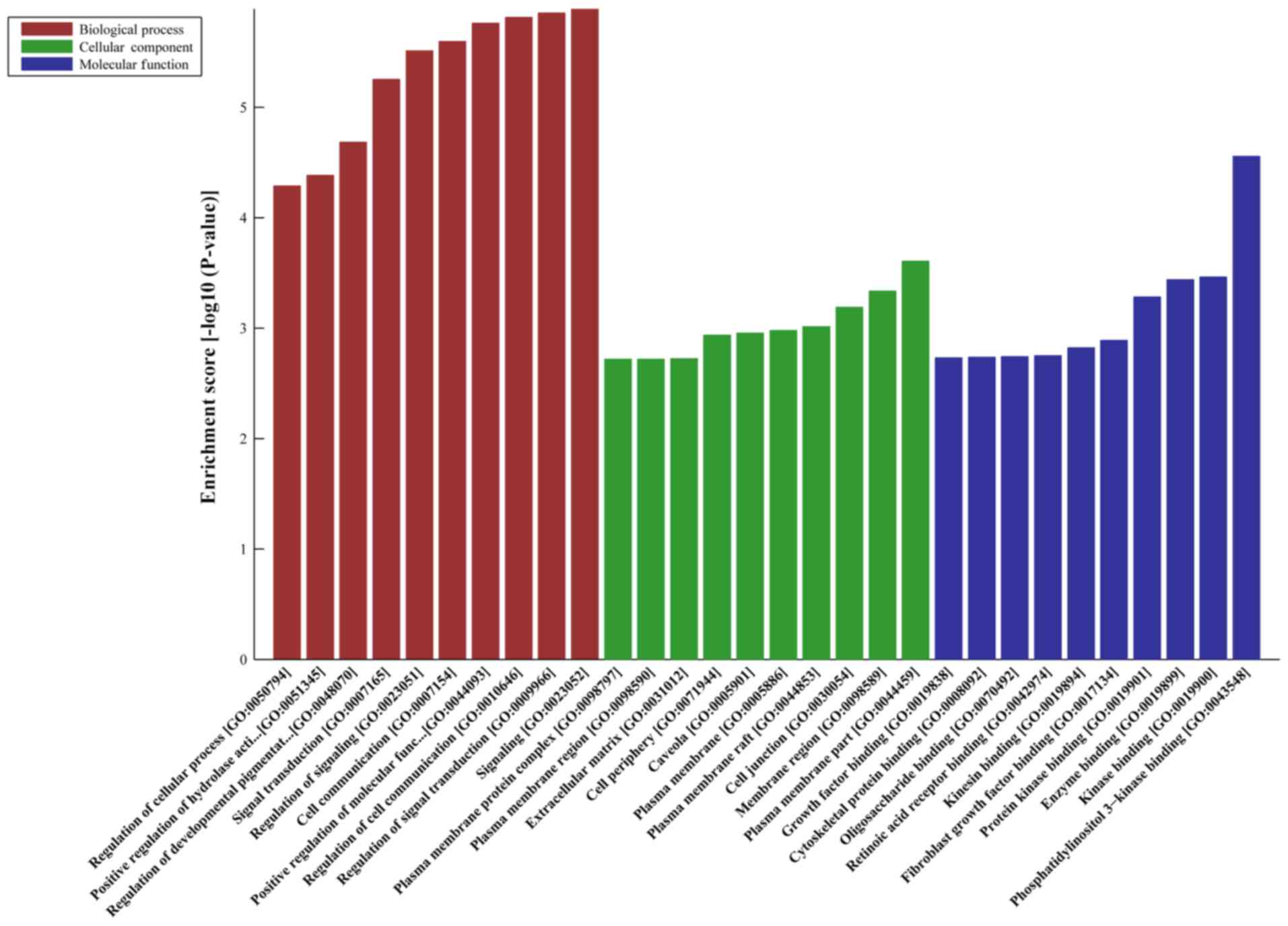
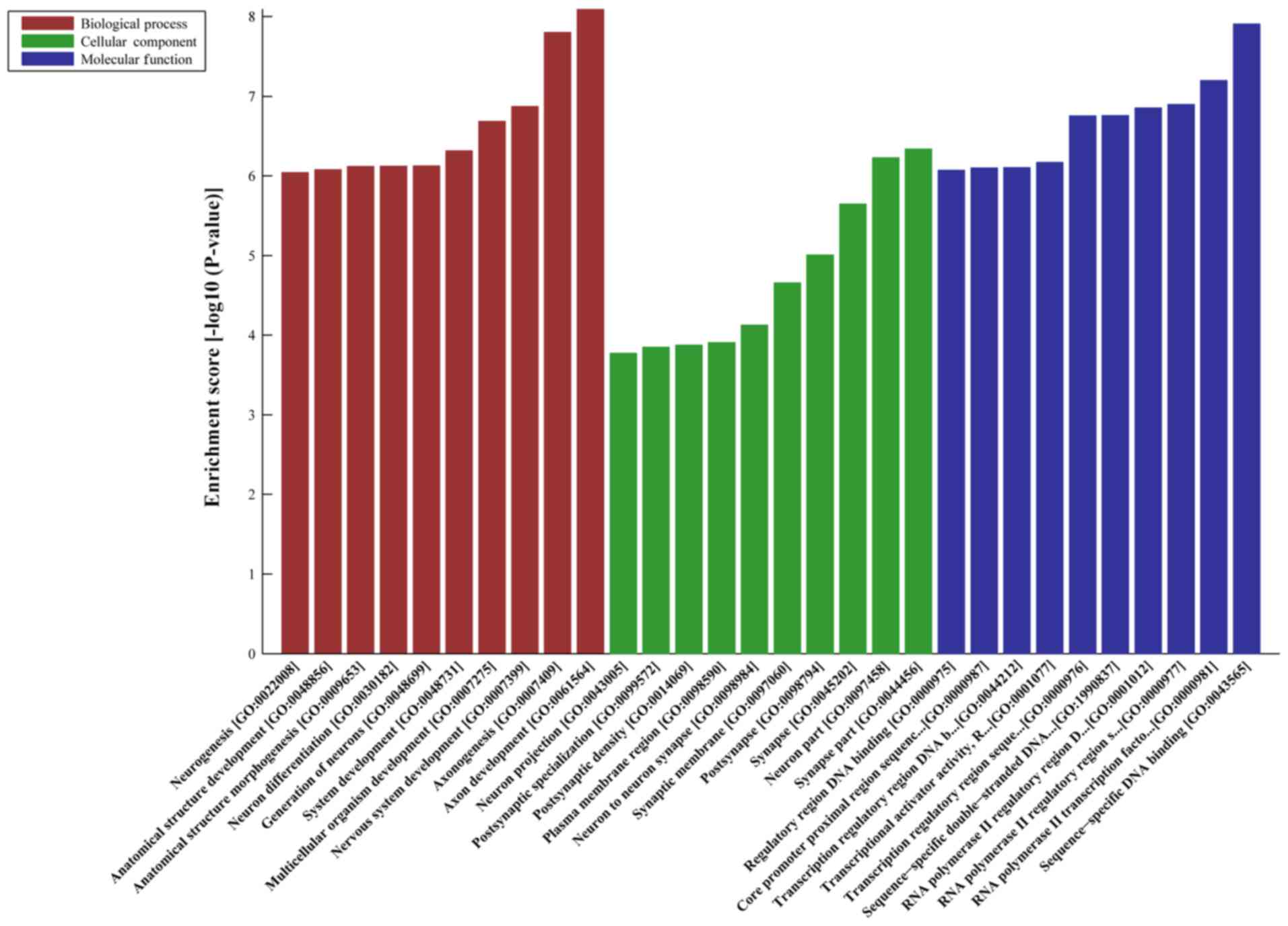
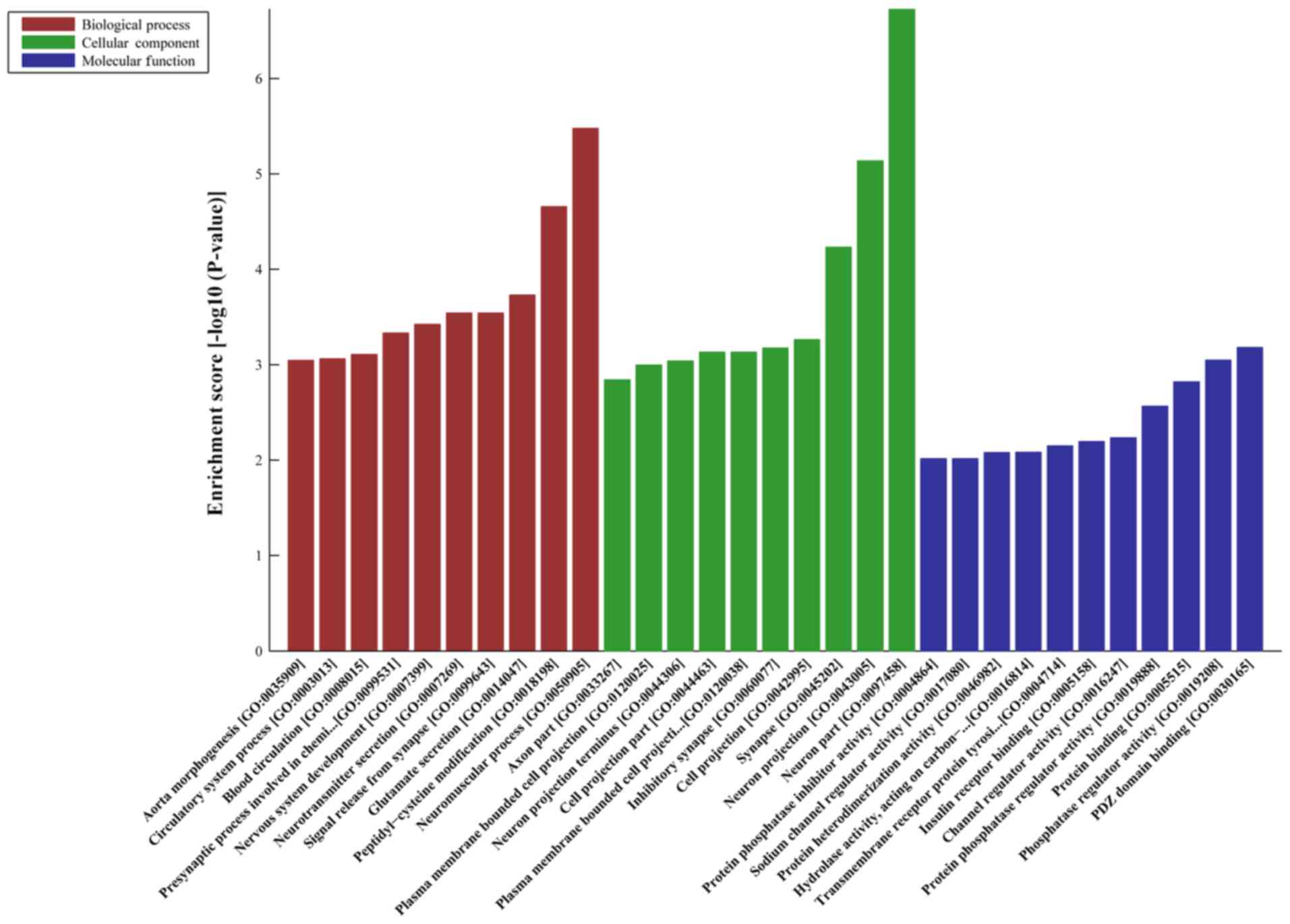
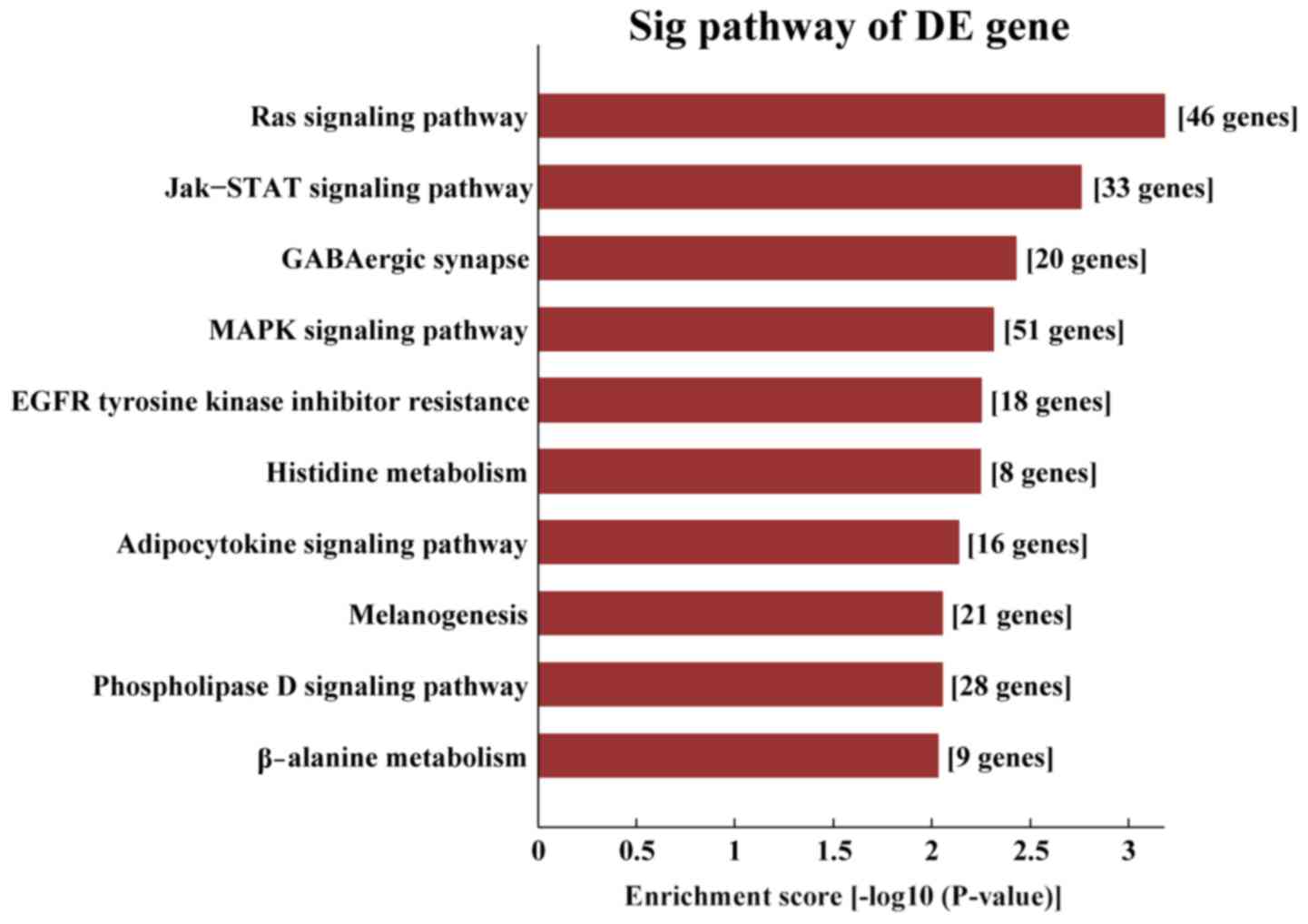
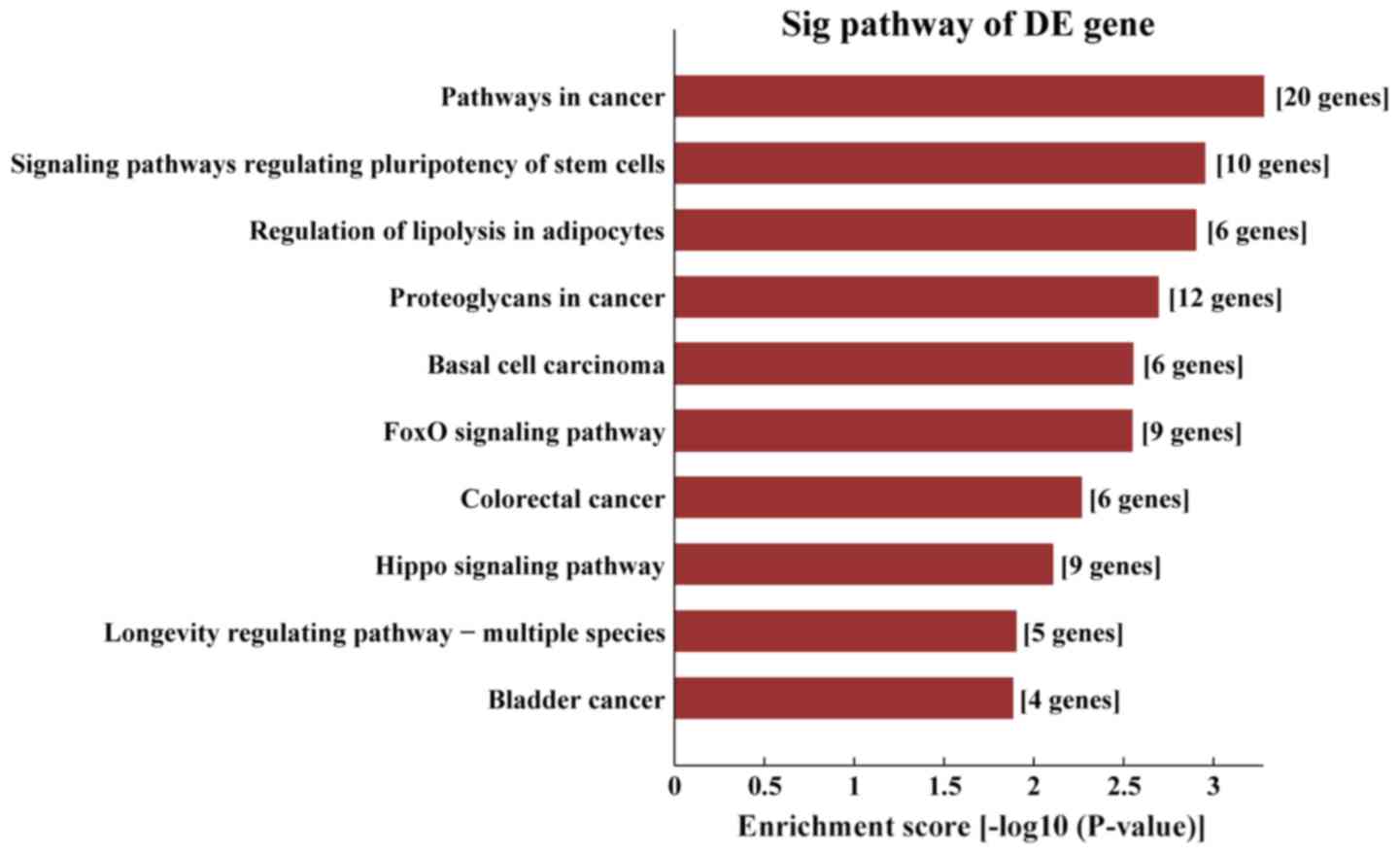
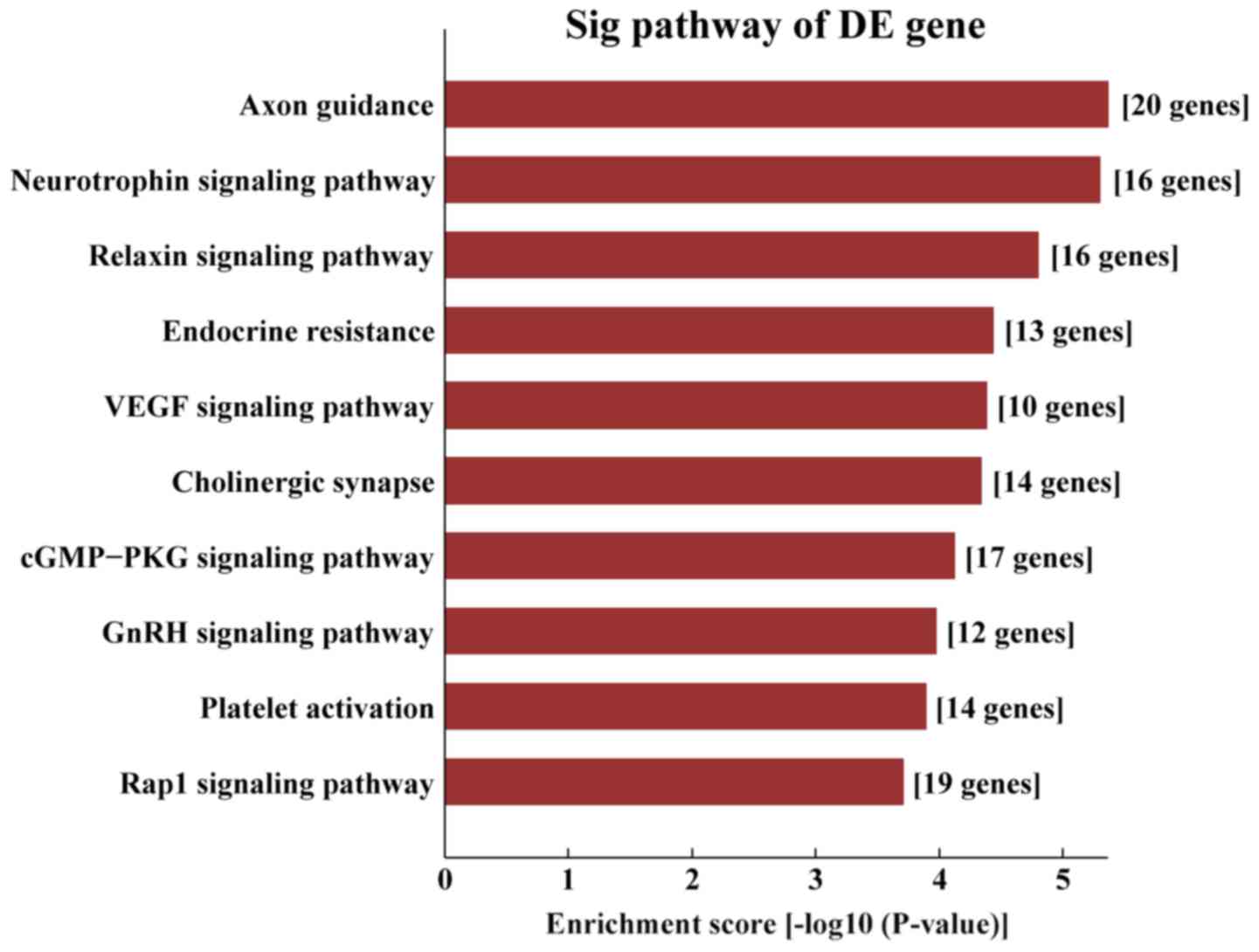
|
1
|
Kleeff J, Korc M, Apte M, La Vecchia C,
Johnson CD, Biankin AV, Neale RE, Tempero M, Tuveson DA, Hruban RH
and Neoptolemos JP: Pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
2:160222016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parker SL, Tong T, Bolden S and Wingo PA:
Cancer statistics, 1997. CA Cancer J Clin. 47:5–27. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig
AB, Fleshman JM and Matrisian LM: Projecting cancer incidence and
deaths to 2030: The unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and
pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 74:2913–2921.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ryan DP, Hong TS and Bardeesy N:
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 371:1039–1049. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kawaji H, Nakamura M, Takahashi Y,
Sandelin A, Katayama S, Fukuda S, Daub CO, Kai C, Kawai J, Yasuda
J, et al: Hidden layers of human small RNAs. BMC Genomics.
9:1572008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cole C, Sobala A, Lu C, Thatcher SR,
Bowman A, Brown JW, Green PJ, Barton GJ and Hutvagner G: Filtering
of deep sequencing data reveals the existence of abundant
Dicer-dependent small RNAs derived from tRNAs. RNA. 15:2147–2160.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee YS, Shibata Y, Malhotra A and Dutta A:
A novel class of small RNAs: tRNA-derived RNA fragments (tRFs).
Genes Dev. 23:2639–2649. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thompson DM and Parker AR: Stressing out
over tRNA cleavage. Cell. 138:215–219. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Martens-Uzunova ES, Olvedy M and Jenster
G: Beyond microRNA-novel RNAs derived from small non-coding RNA and
their implication in cancer. Cancer Lett. 340:2012013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kumar P, Anaya J, Mudunuri SB and Dutta A:
Meta-analysis of tRNA derived RNA fragments reveals that they are
evolutionarily conserved and associate with AGO proteins to
recognize specific RNA targets. BMC Biol. 12:782014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Thompson DM and Parker R: The RNase Rny1p
cleaves tRNAs and promotes cell death during oxidative stress in
Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 185:43–50. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yamasaki S, Ivanov P, Hu GF and Anderson
P: Angiogenin cleaves tRNA and promotes stress-induced
translational repression. J Cell Biol. 185:35–42. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Haussecker D, Huang YA, Parameswaran P,
Fire AZ and Kay MA: Human tRNA-derived small RNAs in the global
regulation of RNA silencing. RNA. 16:673–695. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kumar P, Mudunuri SB, Anaya J and Dutta A:
tRFdb: A database for transfer RNA fragments. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:(Database Issue). D141–D145. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen Q, Yan M, Cao Z, Li X, Zhang Y, Shi
J, Feng GH, Peng H, Zhang X, Zhang Y, et al: Sperm tsRNAs
contribute to intergenerational inheritance of an acquired
metabolic disorder. Science. 351:397–400. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Goodarzi H, Liu X, Nguyen HC, Zhang S,
Fish L and Tavazoie SF: Endogenous tRNA-derived fragments suppress
breast cancer progression via YBX1 displacement. Cell. 161:790–802.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Blanco S, Dietmann S, Flores JV, Hussain
S, Kutter C, Humphreys P, Lukk M, Lombard P, Treps L, Popis M, et
al: Aberrant methylation of tRNAs links cellular stress to
neuro-developmental disorders. EMBO J. 33:2020–2039. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shao Y, Sun Q, Liu X, Wang P, Wu R and Ma
Z: tRF-Leu-CAG promotes cell proliferation and cell cycle in
non-small cell lung cancer. Chem Biol Drug Des. 90:730–738. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang B, Yang H, Cheng X, Wang D, Fu S,
Shen W, Zhang Q, Zhang L, Xue Z, Li Y, et al: tRF/miR-1280
suppresses stem cell-like cells and metastasis in colorectal
cancer. Cancer Res. 77:3194–3206. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gebetsberger J, Zywicki M, Künzi A and
Polacek N: tRNA-derived fragments target the ribosome and function
as regulatory non-coding RNA in Haloferax volcanii. Archaea.
2012:2609092012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ivanov P, Emara MM, Villen J, Gygi SP and
Anderson P: Angiogenin-induced tRNA fragments inhibit translation
initiation. Mol Cell. 43:613–623. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang S, Sun L and Kragler F: The
phloem-delivered RNA pool contains small noncoding RNAs and
interferes with translation. Plant Physiol. 150:378–387. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Maute RL, Schneider C, Sumazin P, Holmes
A, Califano A, Basso K and Dalla-Favera R: tRNA-derived microRNA
modulates proliferation and the DNA damage response and is
downregulated in B cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:1404–1409. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American Joint
Committee on Cancer the 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Durdevic Z and Schaefer M: tRNA
modifications: Necessary for correct tRNA-derived fragments during
the recovery from stress? Bioessays. 35:323–327. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Martens-Uzunova ES, Jalava SE, Dits NF,
van Leenders GJ, Møller S, Trapman J, Bangma CH, Litman T,
Visakorpi T and Jenster G: Diagnostic and prognostic signatures
from the small non-coding RNA transcriptome in prostate cancer.
Oncogene. 31:978–991. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mishima E, Inoue C, Saigusa D, Inoue R,
Ito K, Suzuki Y, Jinno D, Tsukui Y, Akamatsu Y, Araki M, et al:
Conformational change in transfer RNA is an early indicator of
acute cellular damage. J Am Soc Nephrol. 25:2316–2326. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Greenway MJ, Andersen PM, Russ C, Ennis S,
Cashman S, Donaghy C, Patterson V, Swingler R, Kieran D, Prehn J,
et al: ANG mutations segregate with familial and ‘sporadic’
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Genet. 38:411–413. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Olvedy M, Scaravilli M, Hoogstrate Y,
Visakorpi T, Jenster G and Martens-Uzunova ES: A comprehensive
repertoire of tRNA-derived fragments in prostate cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:24766–24777. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|