Introduction
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related
mortality in males and females. Advances in the knowledge of tumor
biology and the mechanisms of oncogenesis have led to the selection
of several molecular targets for lung cancer treatment. The
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) has received particular
attention for lung cancer treatment. EGFR is a transmembrane
receptor found on cells of epithelial origin, which is commonly
expressed at a high level in a variety of solid tumors. It is
involved in the control of cell proliferation, metastasis and
angiogenesis (1). The therapeutic
inhibition of EGFR with monoclonal antibodies to antagonize
ligand-receptor binding or small-molecules to inhibit tyrosine
kinase domain activation, is the main pharmacological strategy in
clinical development for therapeutics. Erlotinib, an orally
available inhibitor of EGFR tyrosine kinase, has been shown to
improve survival in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients
following first- or second-line chemotherapy. However, various skin
manifestations have been reported in patients with NSCLC who
received erlotinib therapy. Skin reactions are the most common
adverse events associated with erlotinib, and generally develop
within 7–10 days of treatment initiation. Clinical manifestations
include papulopustular rash, xerosis, paronychia and hair changes
(2). Skin rash may spontaneously
resolve and reappear, and is reversible following drug
discontinuation. However, when it develops, the chronic side-effect
is extremely distressing for patients. We report a patient with
metastatic lung cancer, who was diagnosed with histologically
confirmed cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis during erlotinib
treatment. After a short period of erlotinib withdrawal,
leukocytoclastic vasculitis was not reproduced following successful
restoration of a reduced dose of erlotinib.
Approval for the study was obtained from the
Institutional Review Board of the Chi-Mei Medical Center, Tainan,
Taiwan. Patient consent was obtained.
Case report
The patient was a 50-year-old female with metastatic
lung adenocarcinoma, who had initial symptoms of multiple bone pain
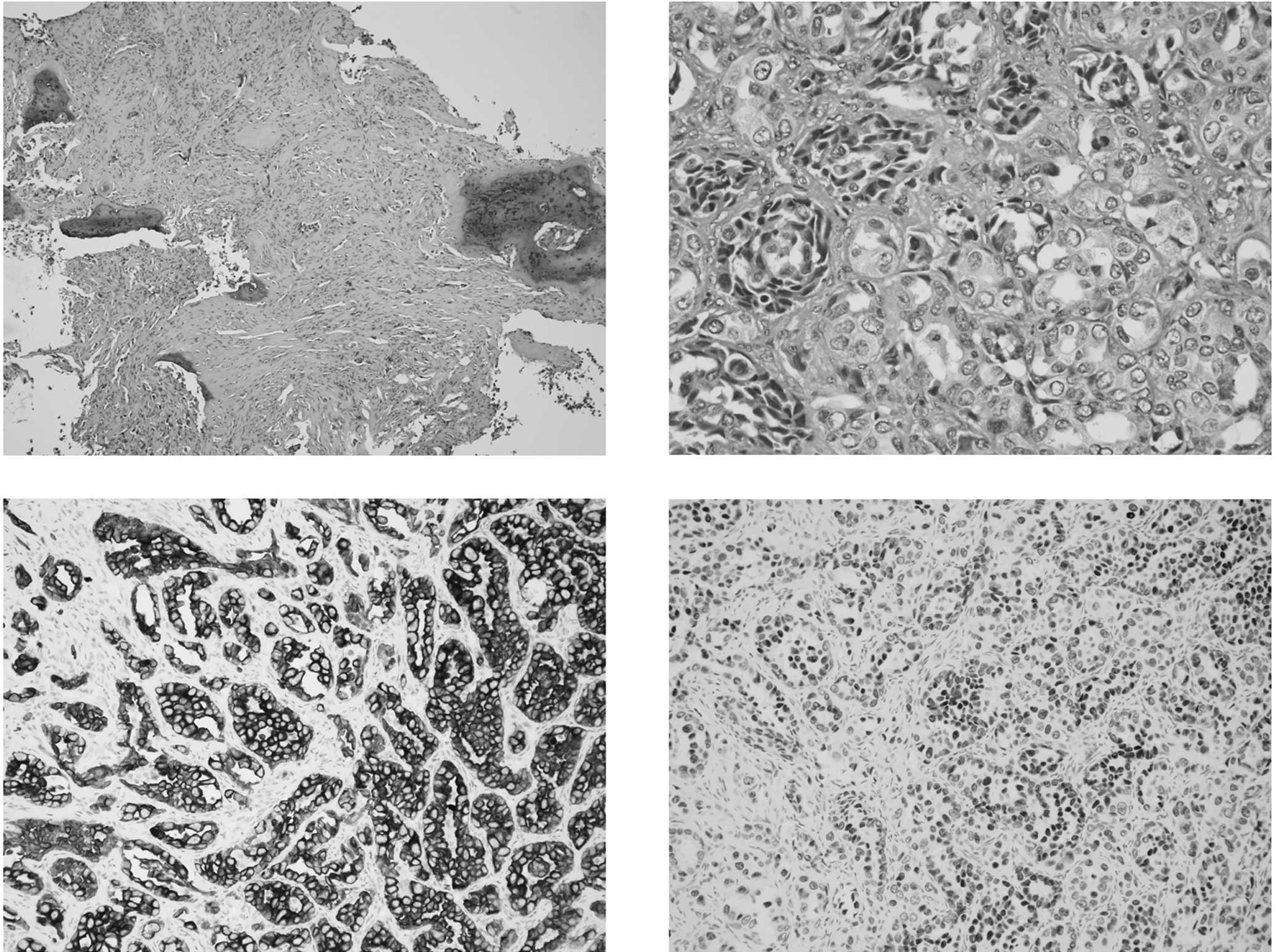
and a cough. The diagnosis of lung cancer was determined from the
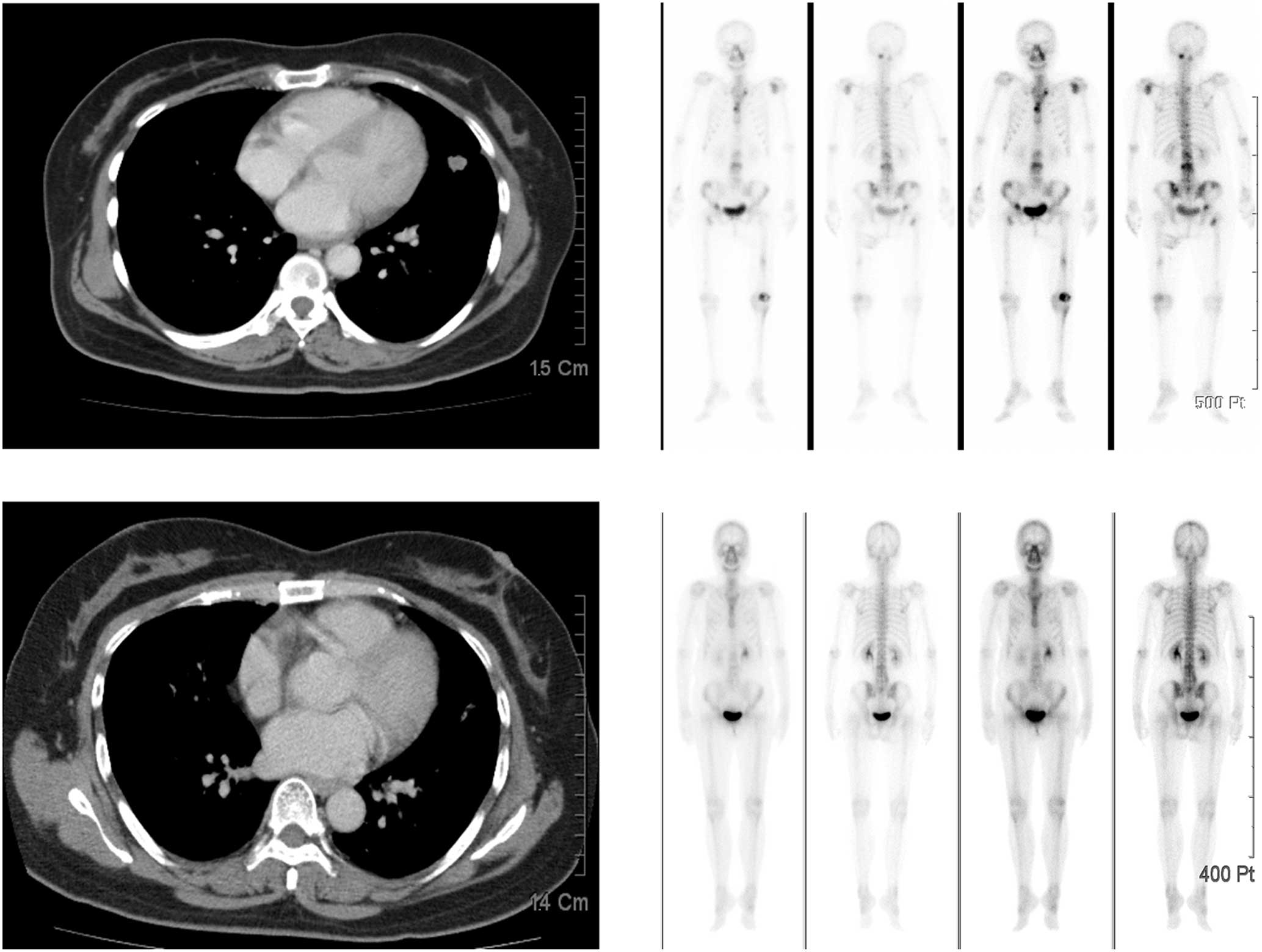
biopsied pathology from bone metastasis (Fig. 1), and a computed tomography of the
chest. The patient initiated first-line treatment with erlotinib
(150 mg daily) and bevacizumab (15 mg/kg every 3 weeks) in
September 2008. Following eight days of treatment with erlotinib
and bevacizumab, the patient presented with papulopustules over the
scalp, face, trunk and extremities. Topical steroids and
antibiotics were administered to alleviate her discomfort. Five
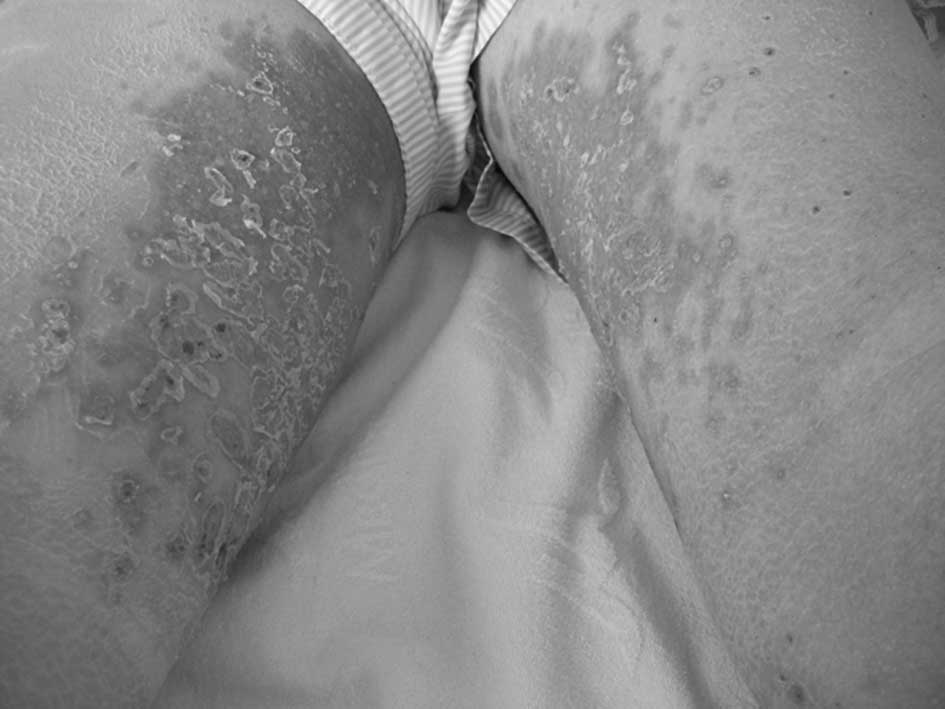
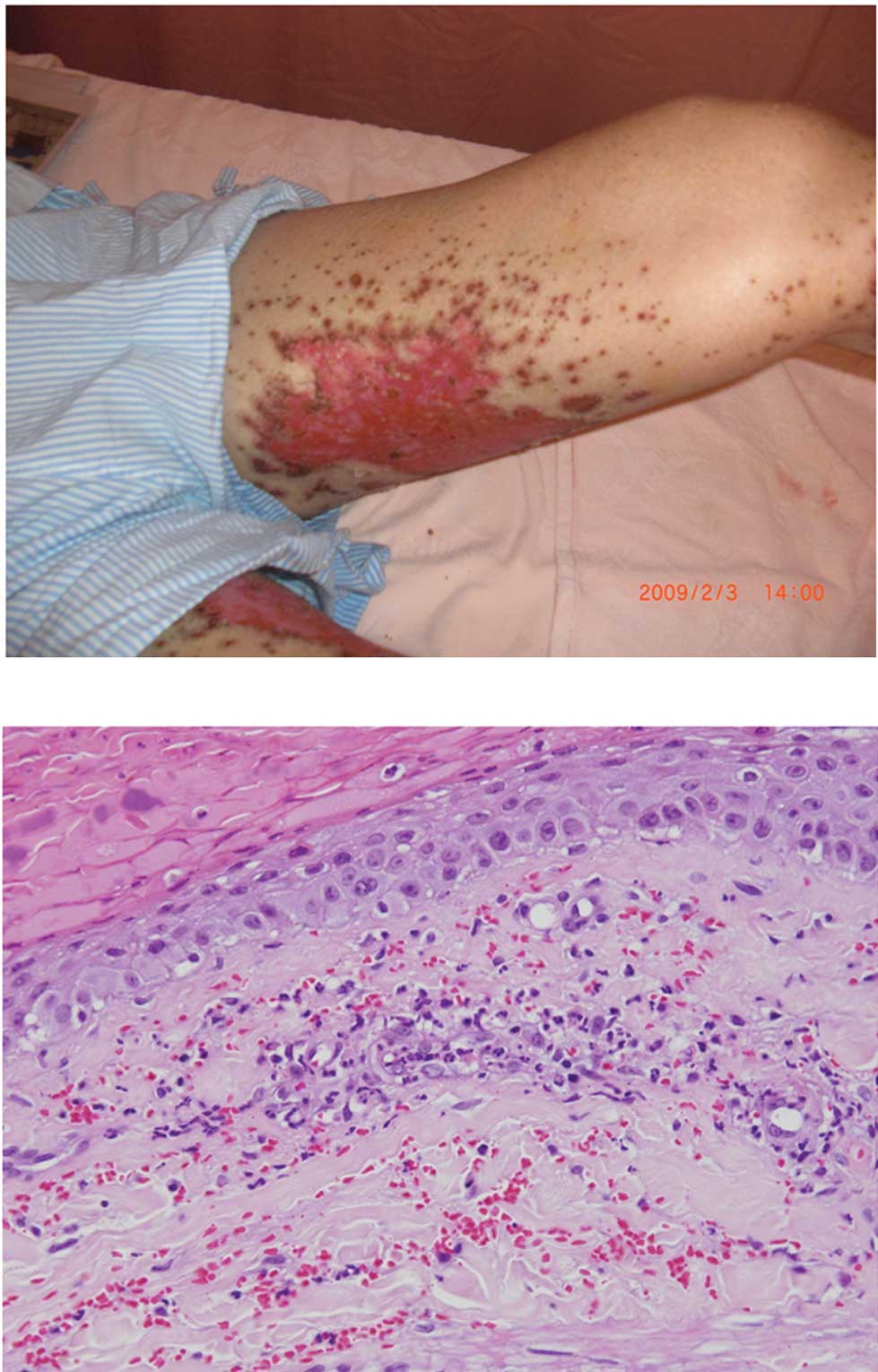
weeks later, purpuric lesions surrounding the red areas of necrosis
were located mostly at the extremities. The patient’s skin
reactions progressed to extensive ulcerations (Fig. 2A). A skin biopsy was performed on
the patient’s leg four months after the initiation of erlotinib,
which revealed an infiltration of neutrophils and red blood cells
surrounding the vessels in the upper dermis (Fig. 2B). A histological diagnosis of
leukocytoclastic vasculitis was determined based on these findings.
Erlotinib was discontinued one week after the skin biopsy without
interruption of bevacizumab. The skin ulceration healed 10 days
after the discontinuation of erlotinib (Fig. 3), and resolved completely seven
weeks later. Erlotinib at a dose of 100 mg daily was challenged in
this patient after almost complete resolution of the skin reaction.
The patient’s lung malignancy remains responsive to the reduced
dose of erlotinib and bevacizumab more than 2 years later, without
recurrence of skin ulcerations (Fig.
4).
Discussion
Among skin manifestations associated with erlotinib
therapy, acneiform eruption usually consisting of follicular
papules and pustules without comedones or propionibacterium acne is
observed in more than 90% of patients (3). Vasculitis is a histological diagnosis
defined as inflammation targeting the blood vessel walls, which
compromises their function, leading to hemorrhagic or ischemic
events. Etiologically, vasculitis can be separated into primary or
secondary vasculitis following the determination of offending
factors, including connective tissue disease, infection, adverse
drug reaction or a paraneoplastic phenomenon.
Inflammation of the small blood vessels, most
commonly postcapillary venules, is the cardinal histological
feature of leukocytoclastic vasculitis. Other characteristic
features include fibrinoid necrosis of the vessel walls,
leukocytoclastosis and hemorrhage. The inflammatory infiltrate is
typically neutrophilic; other studies have demonstrated a
predominance of mononuclear cells and eosinophils distributed in
all vessel layers (4). The skin is
the most commonly involved organ in leukocytoclastic vasculitis,
predominantly in the lower extremities. Up to one-third of patients
have trunk and upper extremity involvement, typically sparing the
palmar, plantar and mucosal surfaces. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis
is rarely observed in patients treated with erlotinib. Boeck et
al have reported two patients treated with erlotinib who
developed hemorrhagic-necrotic type leukocytoclastic vasculitis
(5). None of these reported
patients were challenged with erlotinib again. However, Asian
patients with lung adenocarcinoma have been reported to benefit
from erlotinib therapy (6).
Concerning the incidence of erlotinib-related skin rash, data from
a phase III randomized clinical trial of erlotinib versus a placebo
in pretreated NSCLC patients revealed that rash developed in 75% of
patients who received erlotinib, but only 1% definitively
discontinued erlotinib therapy (BR.21 trial, conducted by NCIC CTG
(National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group).
It is very difficult to determine the permanent
withdrawal of erlotinib, particularly when patients benefit from
erlotinib. Skin rash may spontaneously resolve and reappear during
erlotinib discontinuation. The chronic side effect of skin rash is
extremely distressing for patients. However, whether or not to
continue erlotinib therapy when facing this clinical challenge has
yet to be determined. This is the first report to assess whether to
rechallenge with erlotinib when encountering a severe degree of
leukocytoclastic vasculitis. To ensure the safety of a lower dose
of erlotinib in erlotinib-associated leukocytoclastic vasculitis,
we therefore strongly suggest that preclinical and clinical
investigations of this syndrome associated with erlotinib are
significant in making clinical decisions.
References
|
1
|
Ciardiello F, De Vita F, Orditura M, De
Placido S and Tortora G: Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine
kinase inhibitors in late stage clinical trials. Expert Opin Emerg
Drugs. 8:501–514. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Segaert S and Van Cutsem E: Clinical
signs, pathophysiology and management of skin toxicity during
therapy with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. Ann
Oncol. 16:1425–1433. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Segaert S, Tabernero J, Chosidow O, et al:
The management of skin reactions in cancer patients receiving
epidermal growth factor receptor targeted therapies. J Dtsch
Dermatol Ges. 3:599–606. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Carlson JA: The histological assessment of
cutaneous vasculitis. Histopathology. 56:3–23. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Boeck S, Wollenberg A and Heinemann V:
Leukocytoclastic vasculitis during treatment with the oral EGFR
tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib. Ann Oncol. 18:1582–1583. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kubota K, Nishiwaki Y, Tamura T, et al:
Efficacy and safety of erlotinib monotherapy for Japanese patients
with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a phase II study. J
Thorac Oncol. 3:1439–1445. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|