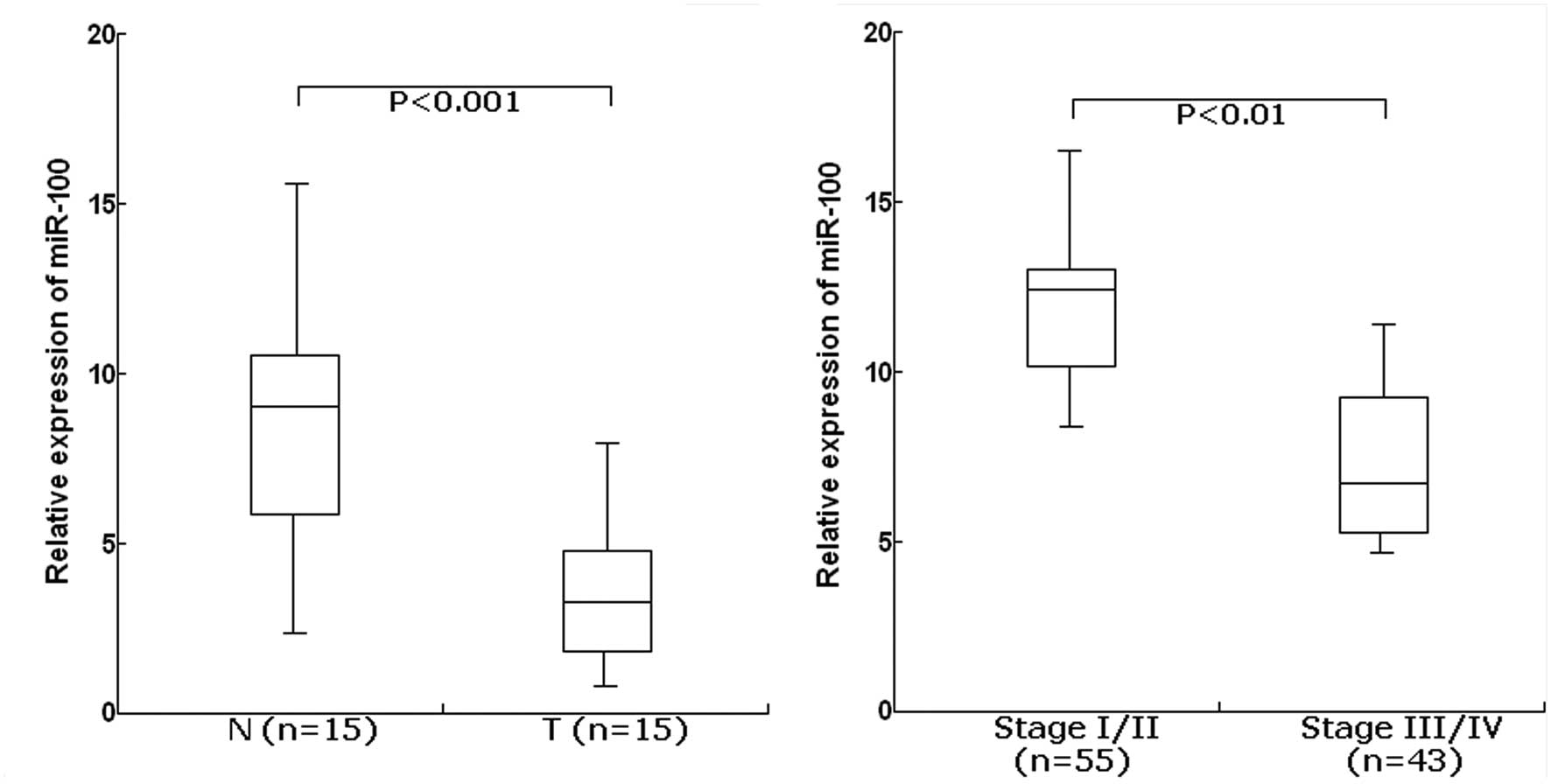
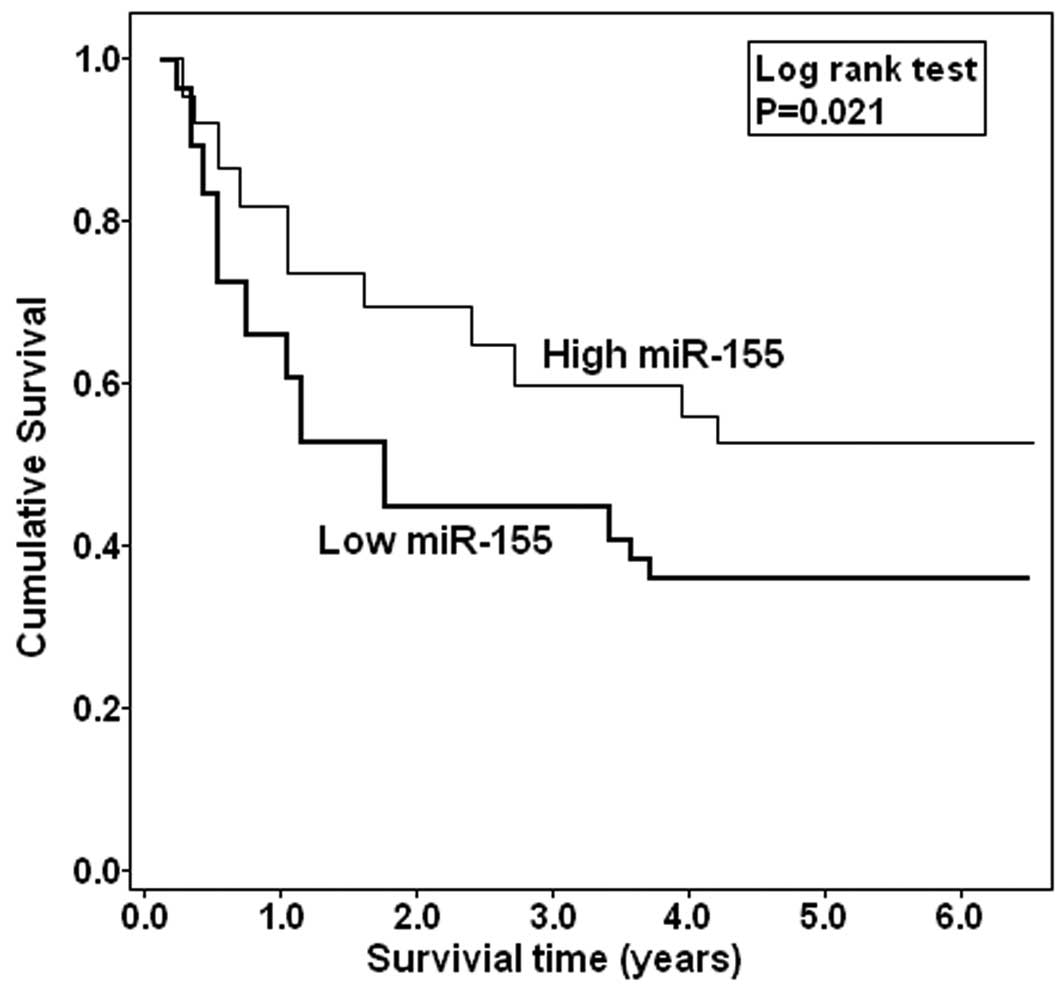
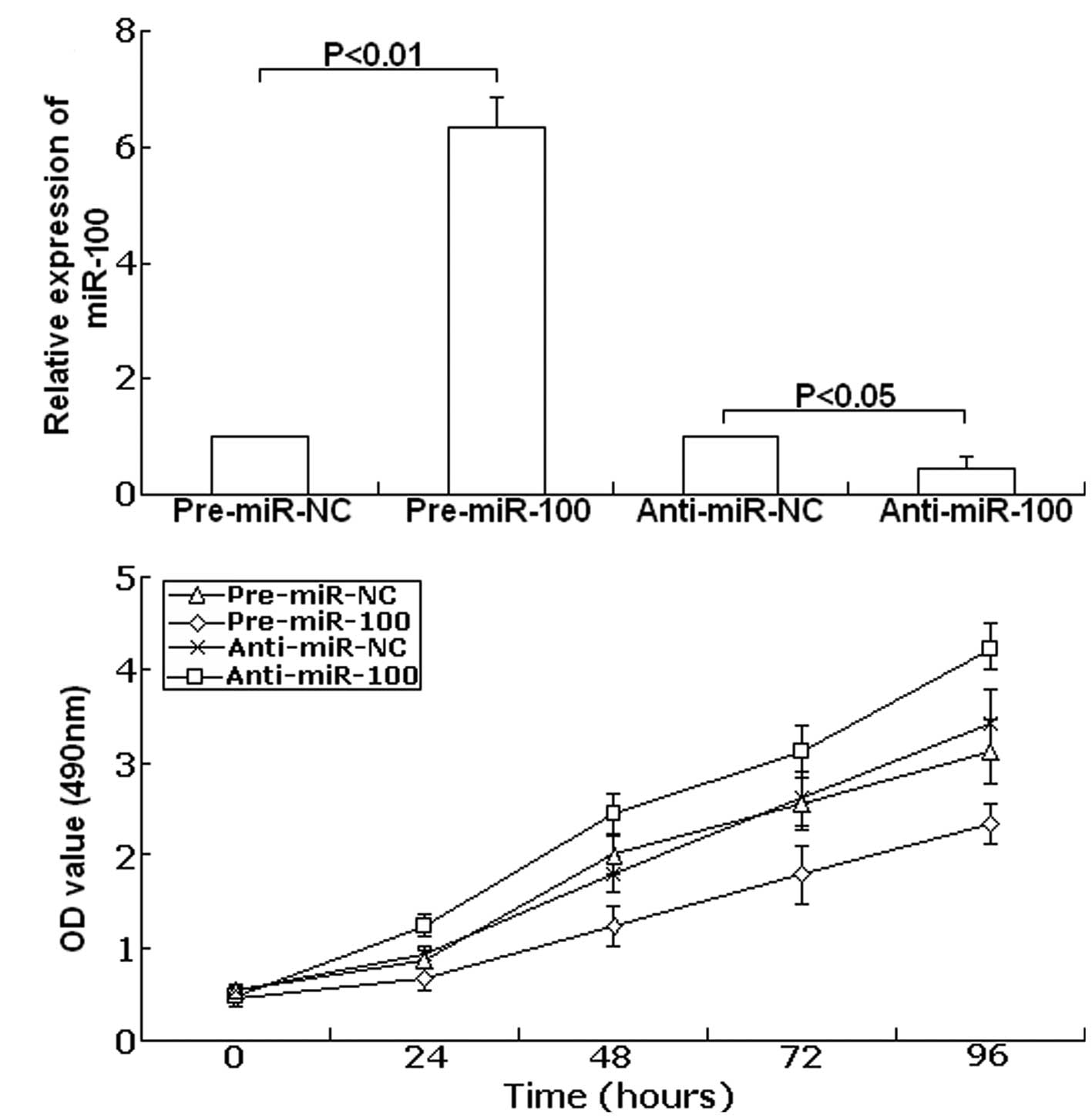
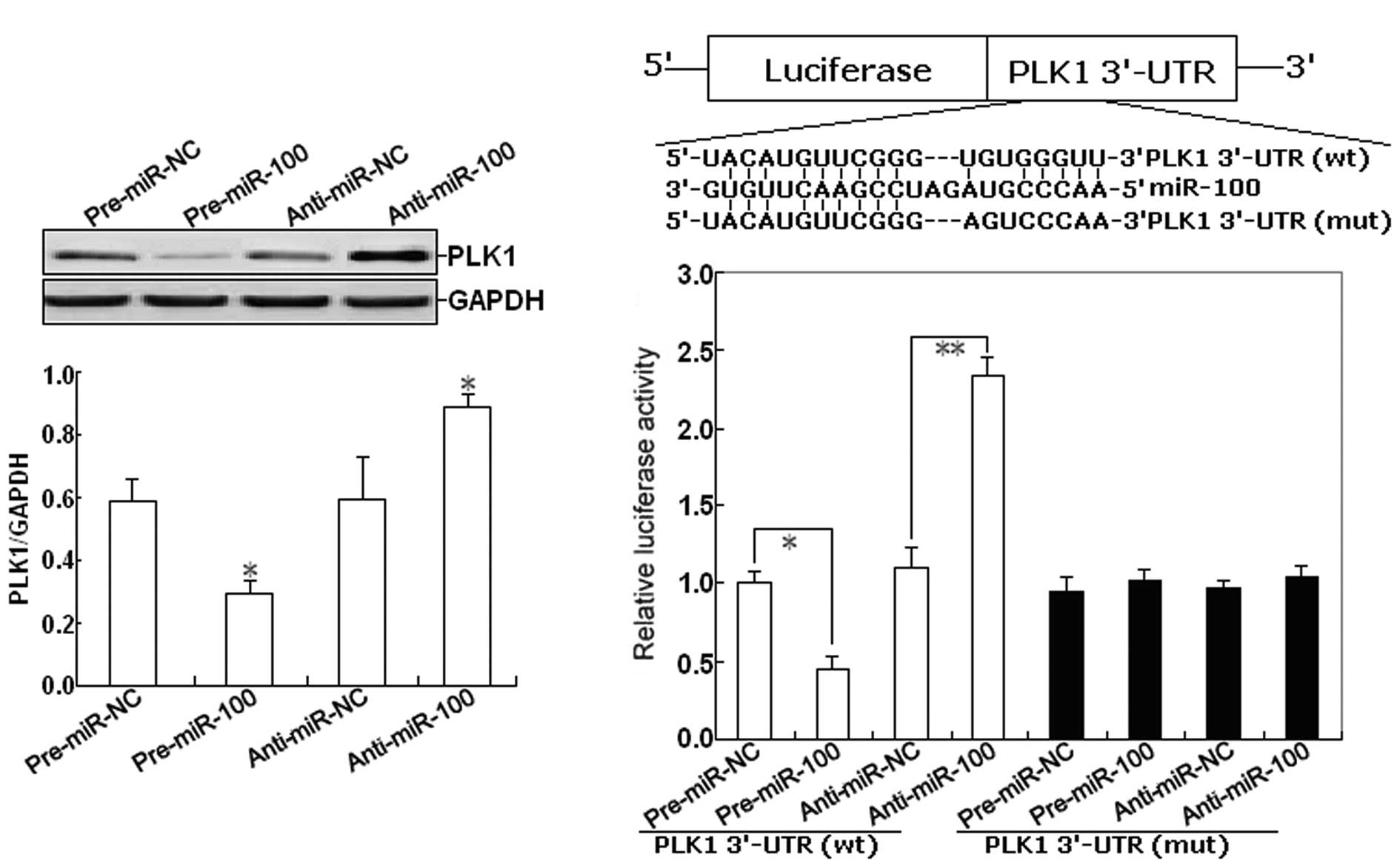
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Armstrong DK: Relapsed ovarian cancer:
challenges and management strategies for a chronic disease.
Oncologist. 7(Suppl 5): 20–28. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huang Y, Shen XJ, Zou Q and Zhao QL:
Biological functions of microRNAs. Bioorg Khim. 36:747–752.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huang Y, Shen XJ, Zou Q, Wang SP, Tang SM
and Zhang GZ: Biological functions of microRNAs: a review. J
Physiol Biochem. 67:129–139. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Perera RJ and Ray A: MicroRNAs in the
search for understanding human diseases. BioDrugs. 21:97–104. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dahiya N and Morin PJ: MicroRNAs in
ovarian carcinomas. Endocr Relat Cancer. 17:77–89. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhang L, Huang J, Yang N, et al: microRNAs
exhibit high frequency genomic alterations in human cancer. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:9136–9141. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang H, Kong W, He L, et al: MicroRNA
expression profiling in human ovarian cancer: miR-214 induces cell
survival and cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN. Cancer Res.
68:425–433. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wyman SK, Parkin RK, Mitchell PS, Fritz
BR, et al: Repertoire of microRNAs in epithelial ovarian cancer as
determined by next generation sequencing of small RNA cDNA
libraries. PLoS One. 4:e53112009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang R, Wang ZX, Yang JS, Pan X, De W and
Chen LB: MicroRNA-451 functions as a tumor suppressor in human
non-small cell lung cancer by targeting ras-related protein 14
(RAB14). Oncogene. 30:2644–2658. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rui W, Bing F, Hai-Zhu S, Wei D and
Long-Bang C: Identification of microRNA profiles in
docetaxel-resistant human non-small cell lung carcinoma cells
(SPC-A1). J Cell Mol Med. 14:206–214. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bovicelli A, D’Andrilli G and Giordano A:
New players in ovarian cancer. J Cell Physiol. 226:2500–2504. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li SD, Zhang JR, Wang YQ and Wan XP: The
role of microRNAs in ovarian cancer initiation and progression. J
Cell Mol Med. 14:2240–2249. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lima RT, Busacca S, Almeida GM, Gaudino G,
Fennell DA and Vasconcelos MH: MicroRNA regulation of core
apoptosis pathways in cancer. Eur J Cancer. 47:163–174. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dykxhoorn DM: MicroRNAs and metastasis:
little RNAs go a long way. Cancer Res. 70:6401–6406. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
van Jaarsveld MT, Helleman J, Berns EM and
Wiemer EA: MicroRNAs in ovarian cancer biology and therapy
resistance. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 42:1282–1290. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lu L, Katsaros D, de la Longrais IA,
Sochirca O and Yu H: Hypermethylation of let-7a-3 in epithelial
ovarian cancer is associated with low insulin-like growth factor-II
expression and favorable prognosis. Cancer Res. 67:10117–10122.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lu L, Schwartz P, Scarampi L, et al:
MicroRNA let-7a: a potential marker for selection of paclitaxel in
ovarian cancer management. Gynecol Oncol. 122:366–371. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lou Y, Yang X, Wang F, Cui Z and Huang Y:
MicroRNA-21 promotes the cell proliferation, invasion and migration
abilities in ovarian epithelial carcinomas through inhibiting the
expression of PTEN protein. Int J Mol Med. 26:819–827.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang H, Kong W, He L, et al: MicroRNA
expression profiling in human ovarian cancer: miR-214 induces cell
survival and cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN. Cancer Res.
68:425–433. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sorrentino A, Liu CG, Addario A, Peschle
C, Scambia G and Ferlini C: Role of microRNAs in drug-resistant
ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 2111:478–486. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li Z, Hu S, Wang J, et al: MiR-27a
modulates MDR1/P-glycoprotein expression by targeting HIPK2 in
human ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 119:125–130. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shi W, Alajez NM, Bastianutto C, et al:
Significance of Plk1 regulation by miR-100 in human nasopharyngeal
cancer. Int J Cancer. 126:2036–2048. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Leite KR, Tomiyama A, Reis ST, et al:
MicroRNA-100 expression is independently related to biochemical
recurrence of prostate cancer. J Urol. 185:1118–1122. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zheng YS, Zhang H, Zhang XJ, et al:
MiR-100 regulates cell differentiation and survival by targeting
RBSP3, a phosphatase-like tumor suppressor in acute myeloid
leukemia. Oncogene. June 6–2011.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
28
|
Takaki T, Trenz K, Costanzo V and
Petronczki M: Polo-like kinase 1 reaches beyond
mitosis-cytokinesis, DNA damage response, and development. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 20:650–660. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Weichert W, Denkert C, Schmidt M, et al:
Polo-like kinase isoform expression is a prognostic factor in
ovarian carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 90:815–821. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Degenhardt Y and Lampkin T: Targeting
Polo-like kinase in cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 16:384–389.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Strebhardt K and Ullrich A: Targeting
polo-like kinase 1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:321–330.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gao Q, Huang X, Tang D, et al: Influence
of chk1 and plk1 silencing on radiation- or cisplatin-induced
cytotoxicity in human malignant cells. Apoptosis. 11:1789–1800.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|