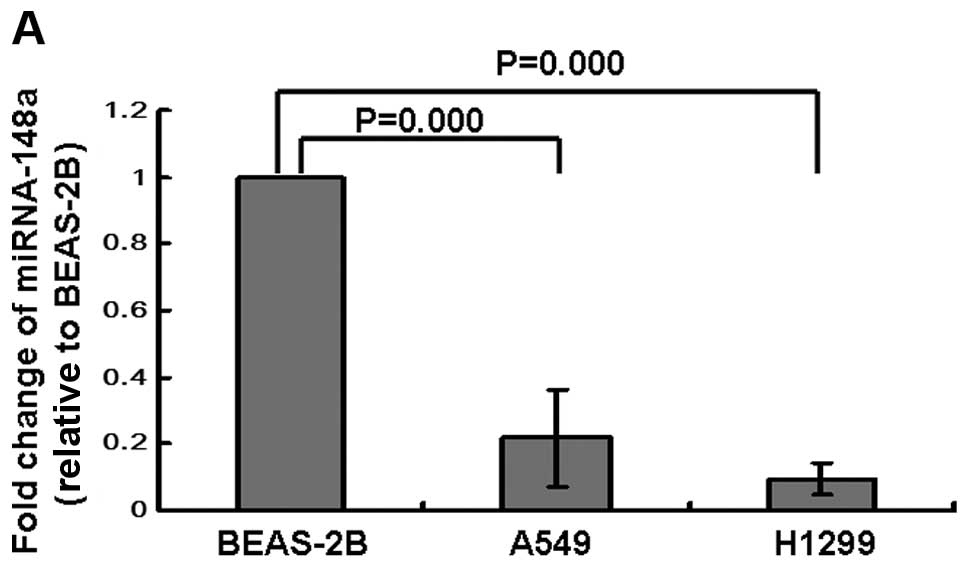
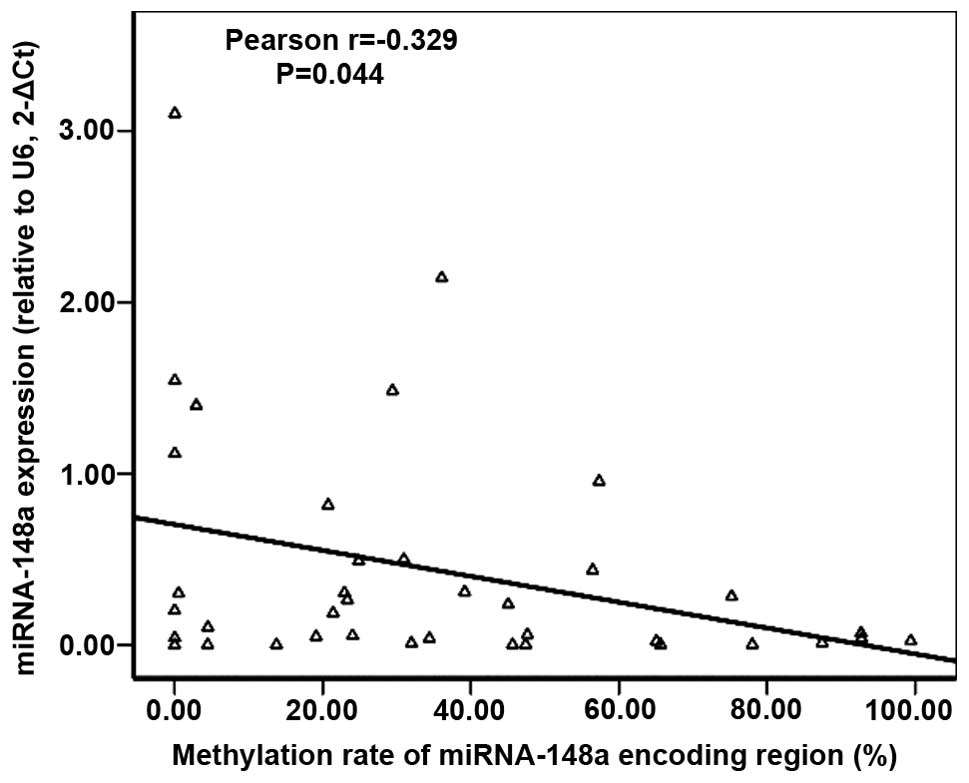
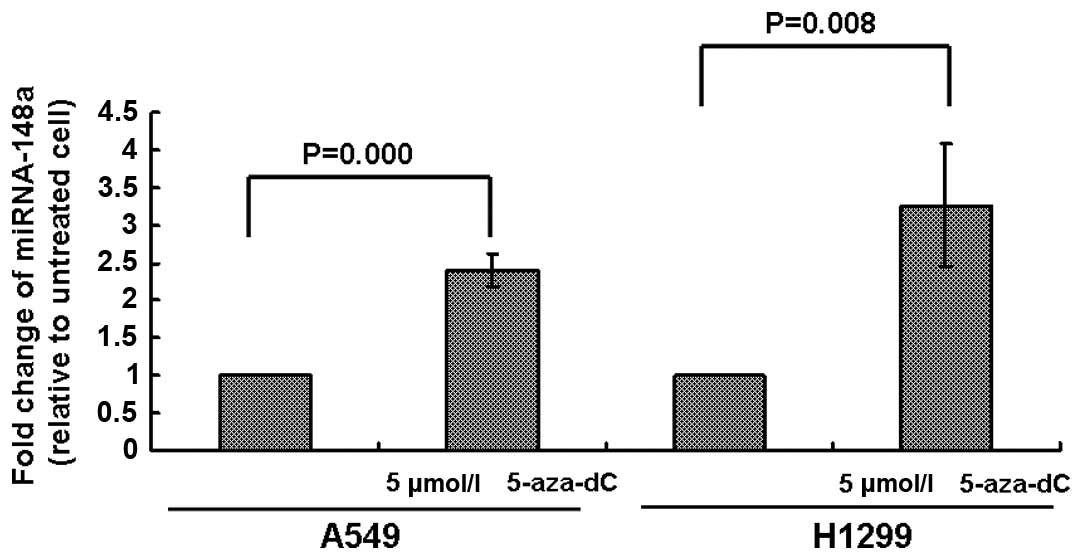
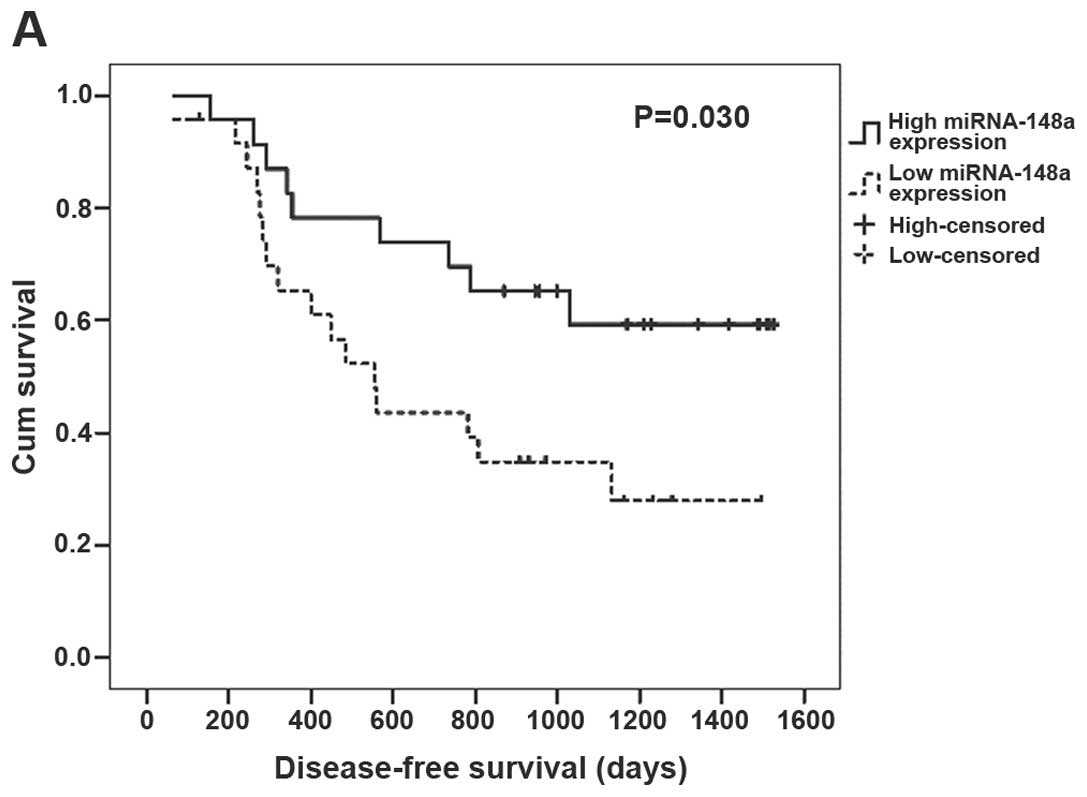
|
1
|
Jemal A, Tiwari RC, Murray T, et al:
Cancer statistics, 2004. CA Cancer J Clin. 54:8–29. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Minna JD, Roth JA and Gazdar AF: Focus on
lung cancer. Cancer Cell. 1:49–52. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Dykxhoorn DM: MicroRNAs and metastasis:
little RNAs go a long way. Cancer Res. 70:6401–6406. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, et al:
Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and
prognosis. Cancer Cell. 9:189–198. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Farazi TA, Spitzer JI, Morozov P and
Tuschl T: miRNAs in human cancer. J Pathol. 223:102–115. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Garzon R, Fabbri M, Cimmino A, Calin GA
and Croce CM: MicroRNA expression and function in cancer. Trends
Mol Med. 12:580–587. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schetter AJ, Leung SY, Sohn JJ, et al:
MicroRNA expression profiles associated with prognosis and
therapeutic outcome in colon adenocarcinoma. JAMA. 299:425–436.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hummel R, Hussey DJ, Michael MZ, et al:
MiRNAs and their association with locoregional staging and survival
following surgery for esophageal carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol.
18:253–260. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Langevin SM, Stone RA, Bunker CH, et al:
MicroRNA-137 promoter methylation is associated with poorer overall
survival in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and
neck. Cancer. 117:1454–1462. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Watanabe K, Emoto N, Hamano E, et al:
Genome structure-based screening identified epigenetically silenced
microRNA associated with invasiveness in non-small-cell lung
cancer. Int J Cancer. 130:2580–2590. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Visone R, Rassenti LZ, Veronese A, et al:
Karyotype-specific microRNA signature in chronic lymphocytic
leukemia. Blood. 114:3872–3879. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Magrelli A, Azzalin G, Salvatore M, et al:
Altered microRNA expression patterns in hepatoblastoma patients.
Transl Oncol. 2:157–163. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu Q, Jiang Y, Yin Y, et al: A regulatory
circuit of miR-148a/152 and DNMT1 in modulating cell transformation
and tumor angiogenesis through IGF-IR and IRS1. J Mol Cell Biol.
5:3–13. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ueda T, Volinia S, Okumura H, et al:
Relation between microRNA expression and progression and prognosis
of gastric cancer: a microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol.
11:136–146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Katada T, Ishiguro H, Kuwabara Y, et al:
microRNA expression profile in undifferentiated gastric cancer. Int
J Oncol. 34:537–542. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen Y, Song Y, Wang Z, et al: Altered
expression of MiR-148a and MiR-152 in gastrointestinal cancers and
its clinical significance. J Gastrointest Surg. 14:1170–1179. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang H, Li Y, Huang Q, et al: MiR-148a
promotes apoptosis by targeting Bcl-2 in colorectal cancer. Cell
Death Differ. 18:1702–1710. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhu A, Xia J, Zuo J, et al: MicroRNA-148a
is silenced by hypermethylation and interacts with DNA
methyltransferase 1 in gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 29:2701–2709.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liffers ST, Munding JB, Vogt M, et al:
MicroRNA-148a is down-regulated in human pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinomas and regulates cell survival by targeting CDC25B.
Lab Invest. 91:1472–1479. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lujambio A, Calin GA, Villanueva A, et al:
A microRNA DNA methylation signature for human cancer metastasis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:13556–13561. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zheng B, Liang L, Wang C, et al:
MicroRNA-148a suppresses tumor cell invasion and metastasis by
downregulating ROCK1 in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
17:7574–7583. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Reddel RR, Ke Y, Gerwin BI, et al:
Transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells by infection
with SV40 or adenovirus-12 SV40 hybrid virus, or transfection via
strontium phosphate coprecipitation with a plasmid containing SV40
early region genes. Cancer Res. 48:1904–1909. 1988.
|
|
24
|
Hanoun N, Delpu Y, Suriawinata AA, et al:
The silencing of microRNA 148a production by DNA hypermethylation
is an early event in pancreatic carcinogenesis. Clin Chem.
56:1107–1118. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang G, Hu X, Lu C, Su C, Luo S and Luo
ZW: Promoter-hypermethylation associated defective expression of
E-cadherin in primary non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
62:162–172. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pan W, Zhu S, Yuan M, et al: MicroRNA-21
and microRNA-148a contribute to DNA hypomethylation in lupus
CD4+ T cells by directly and indirectly targeting DNA
methyltransferase 1. J Immunol. 184:6773–6781. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xi Y, Nakajima G, Gavin E, et al:
Systematic analysis of microRNA expression of RNA extracted from
fresh frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples. RNA.
13:1668–1674. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang X, Chen J, Radcliffe T, Lebrun DP,
Tron VA and Feilotter H: An array-based analysis of microRNA
expression comparing matched frozen and formalin-fixed
paraffin-embedded human tissue samples. J Mol Diagn. 10:513–519.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Leite KR, Canavez JM, Reis ST, et al:
miRNA analysis of prostate cancer by quantitative real time PCR:
comparison between formalin-fixed paraffin embedded and
fresh-frozen tissue. Urol Oncol. 29:533–537. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA-cancer
connection: the beginning of a new tale. Cancer Res. 66:7390–7394.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Qiu X, Qiao F, Su X, Zhao Z and Fan H:
Epigenetic activation of E-cadherin is a candidate therapeutic
target in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp Ther Med. 1:519–523.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huang J, Wang Y, Guo Y and Sun S:
Down-regulated microRNA-152 induces aberrant DNA methylation in
hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting DNA
methyltransferase 1. Hepatology. 52:60–70. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shimamoto T, Ohyashiki JH, Hirano T, Kato
H and Ohyashiki K: Hypermethylation of E-cadherin gene is frequent
and independent of p16INK4A methylation in non-small
cell lung cancer: Potential prognostic implication. Oncol Rep.
12:389–395. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|