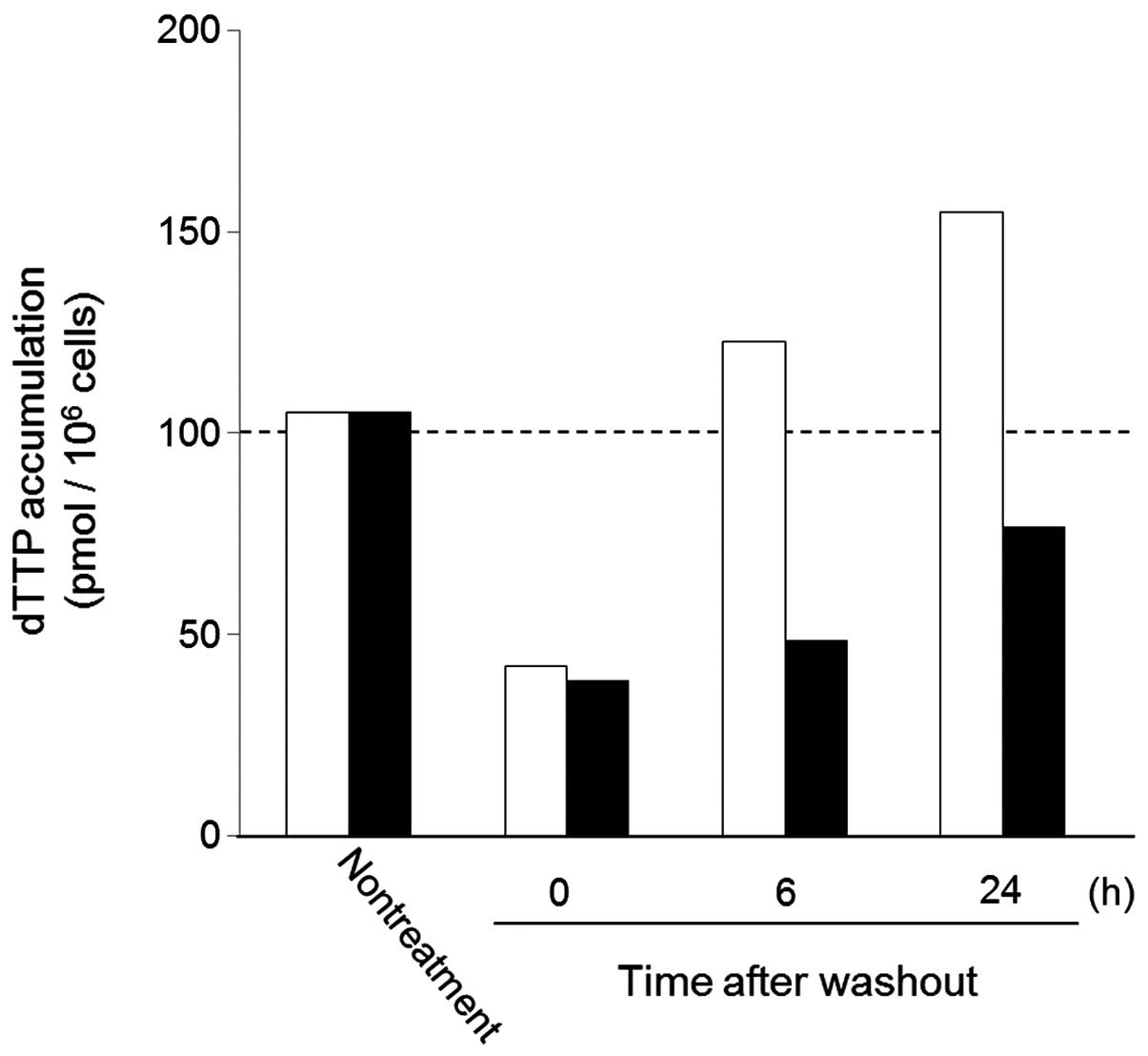
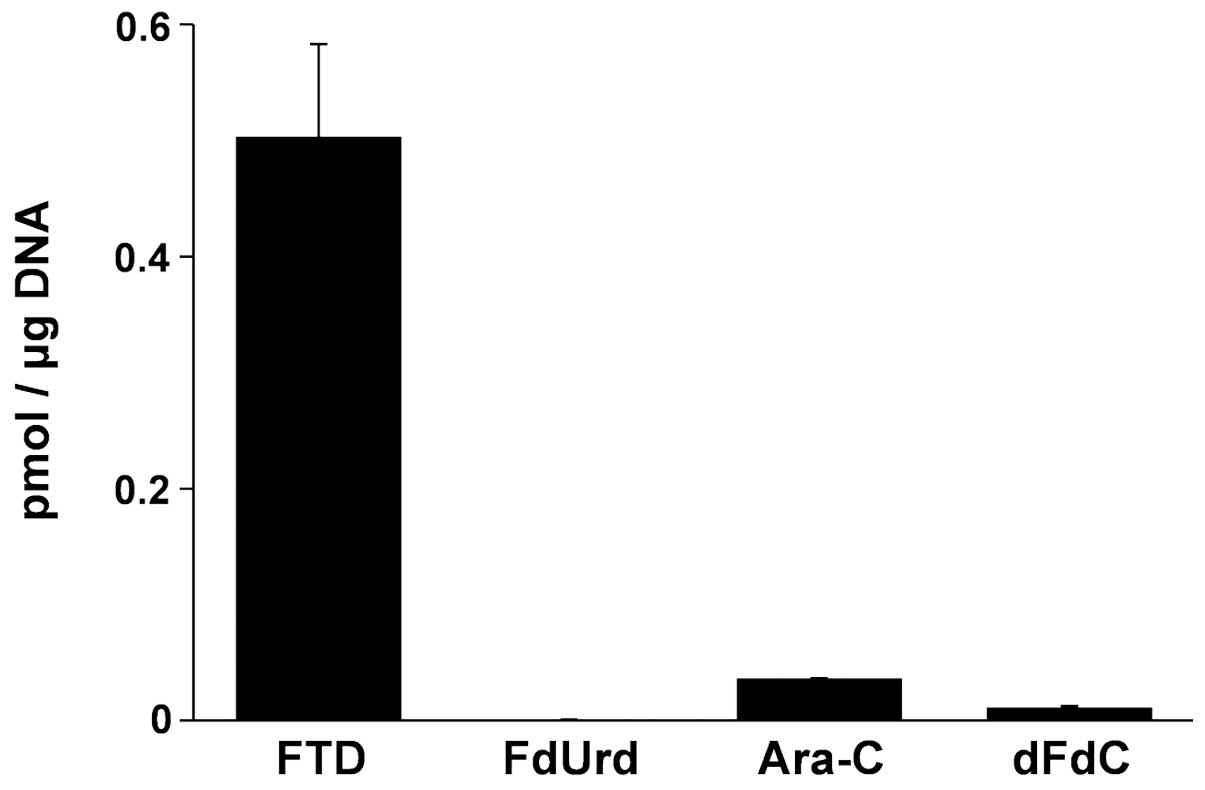
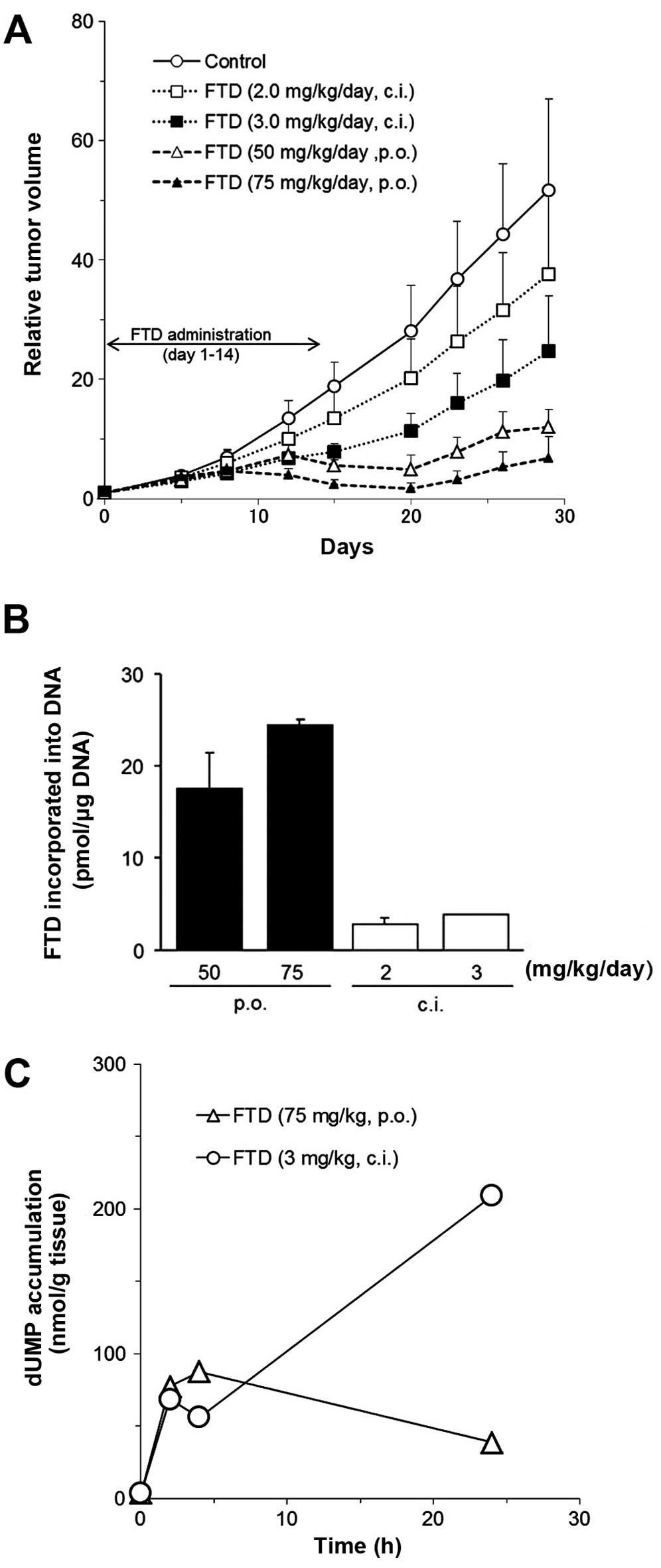
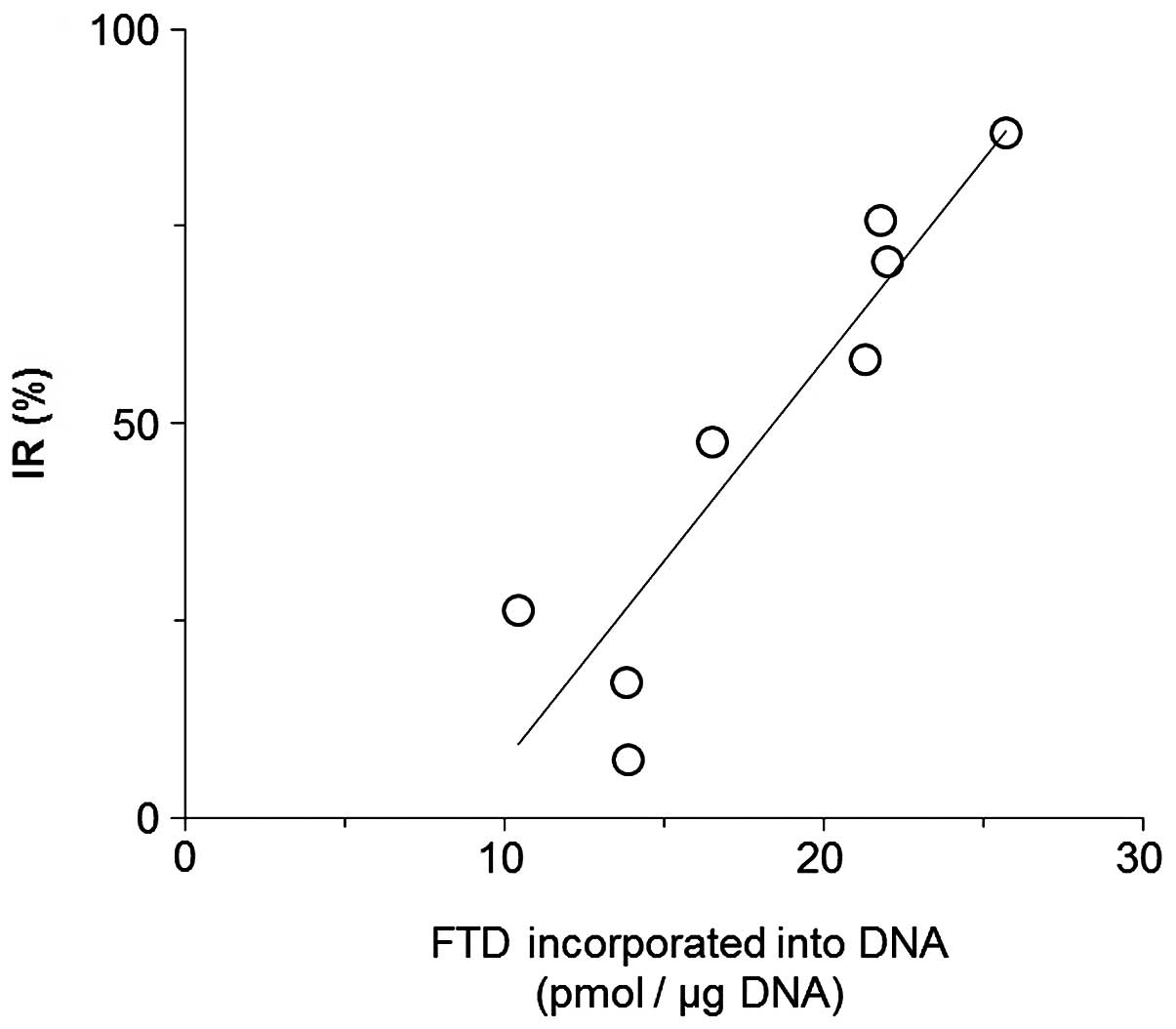
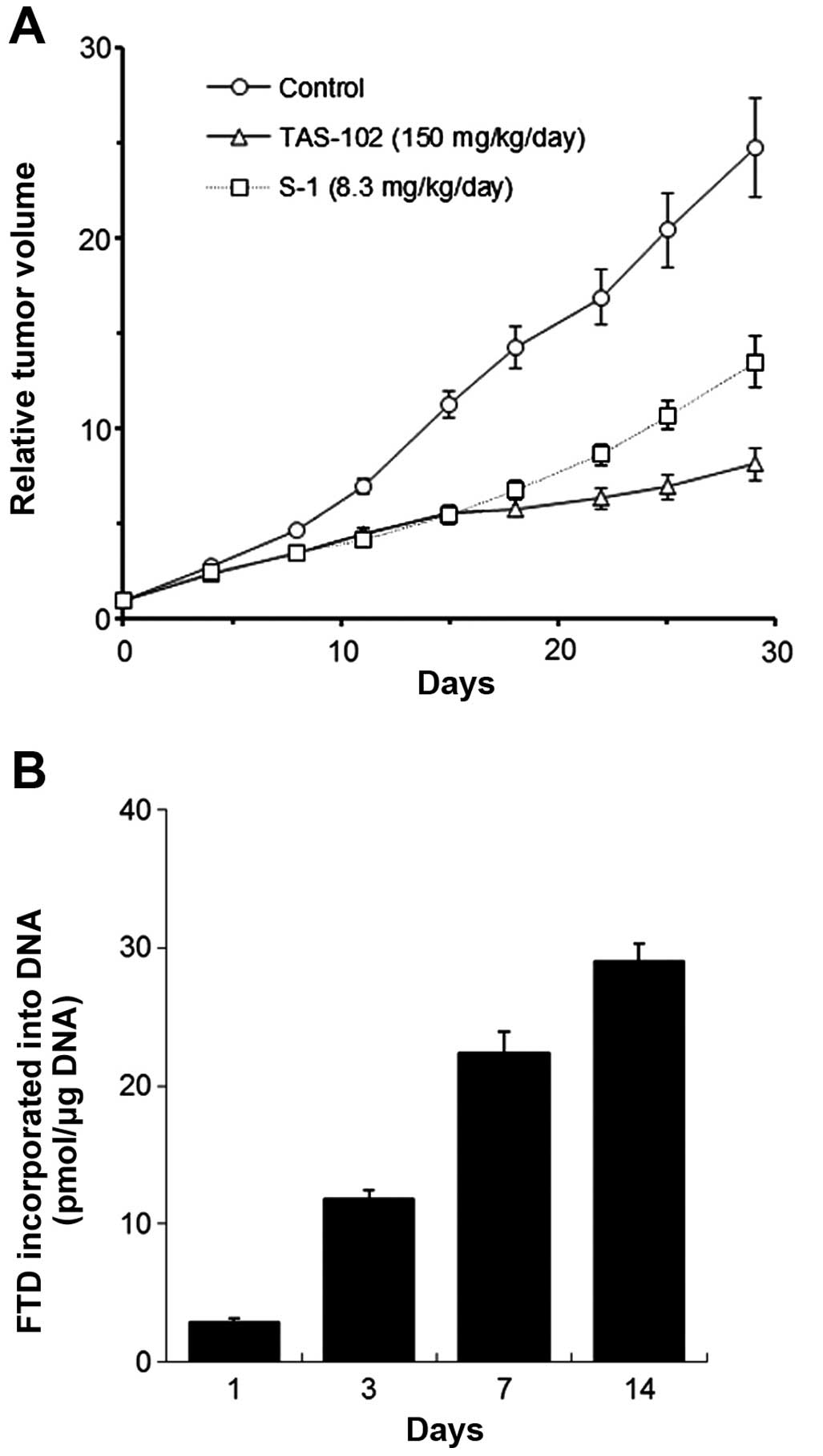
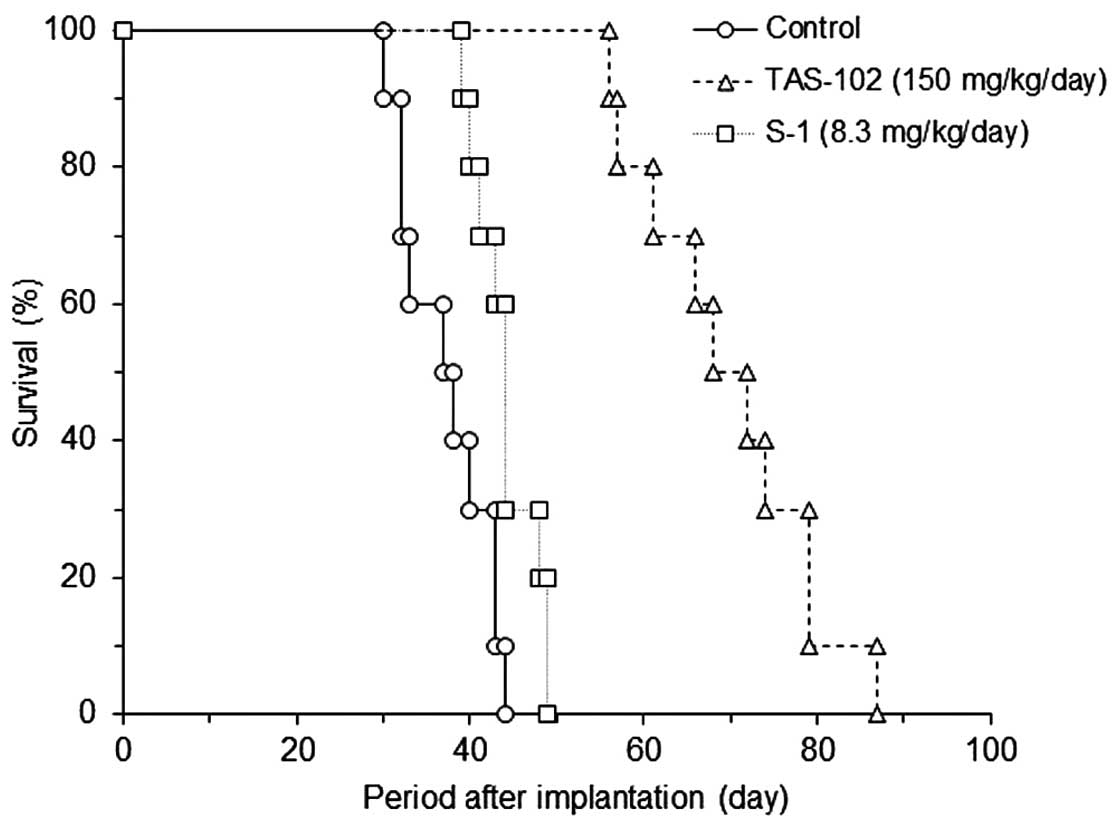
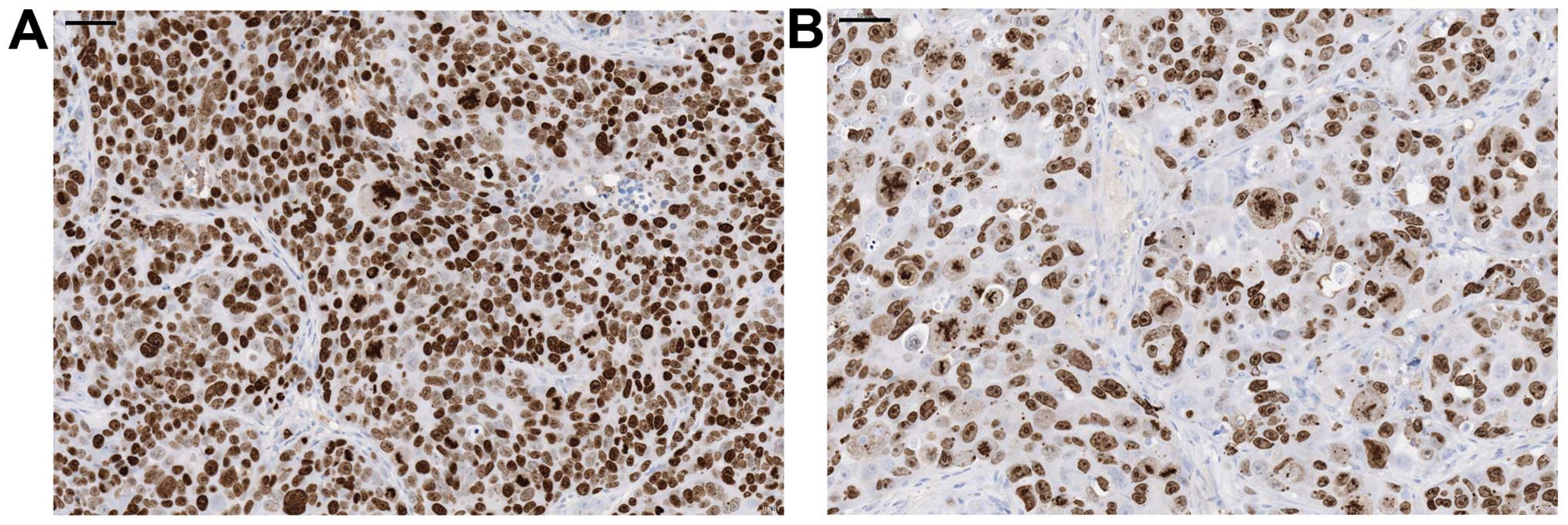
Spandidos Publications style
Tanaka N, Sakamoto K, Okabe H, Fujioka A, Yamamura K, Nakagawa F, Nagase H, Yokogawa T, Oguchi K, Ishida K, Ishida K, et al: Repeated oral dosing of TAS-102 confers high trifluridine incorporation into DNA and sustained antitumor activity in mouse models. Oncol Rep 32: 2319-2326, 2014.
APA
Tanaka, N., Sakamoto, K., Okabe, H., Fujioka, A., Yamamura, K., Nakagawa, F. ... Matsuo, K. (2014). Repeated oral dosing of TAS-102 confers high trifluridine incorporation into DNA and sustained antitumor activity in mouse models. Oncology Reports, 32, 2319-2326. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2014.3487
MLA
Tanaka, N., Sakamoto, K., Okabe, H., Fujioka, A., Yamamura, K., Nakagawa, F., Nagase, H., Yokogawa, T., Oguchi, K., Ishida, K., Osada, A., Kazuno, H., Yamada, Y., Matsuo, K."Repeated oral dosing of TAS-102 confers high trifluridine incorporation into DNA and sustained antitumor activity in mouse models". Oncology Reports 32.6 (2014): 2319-2326.
Chicago
Tanaka, N., Sakamoto, K., Okabe, H., Fujioka, A., Yamamura, K., Nakagawa, F., Nagase, H., Yokogawa, T., Oguchi, K., Ishida, K., Osada, A., Kazuno, H., Yamada, Y., Matsuo, K."Repeated oral dosing of TAS-102 confers high trifluridine incorporation into DNA and sustained antitumor activity in mouse models". Oncology Reports 32, no. 6 (2014): 2319-2326. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2014.3487