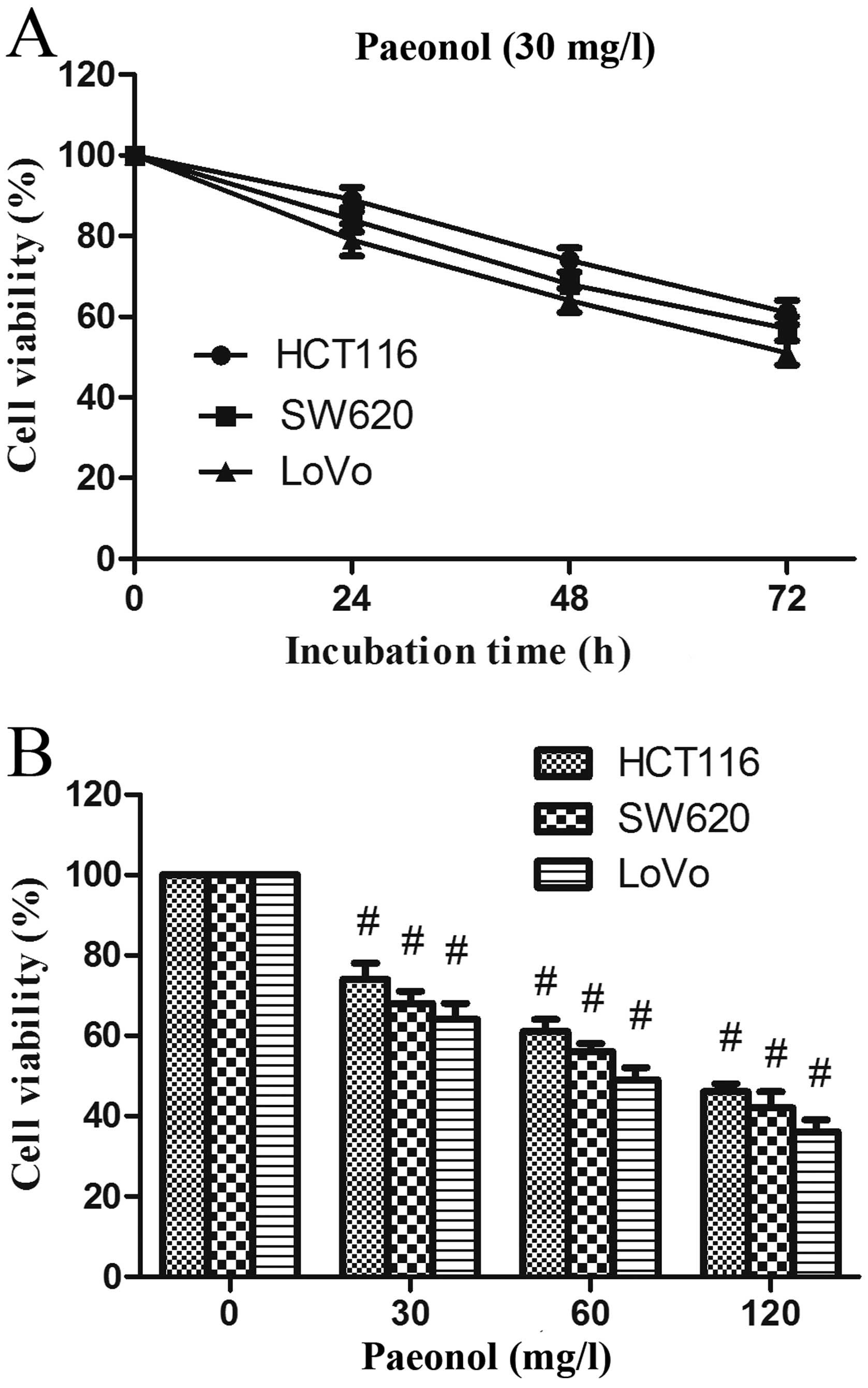
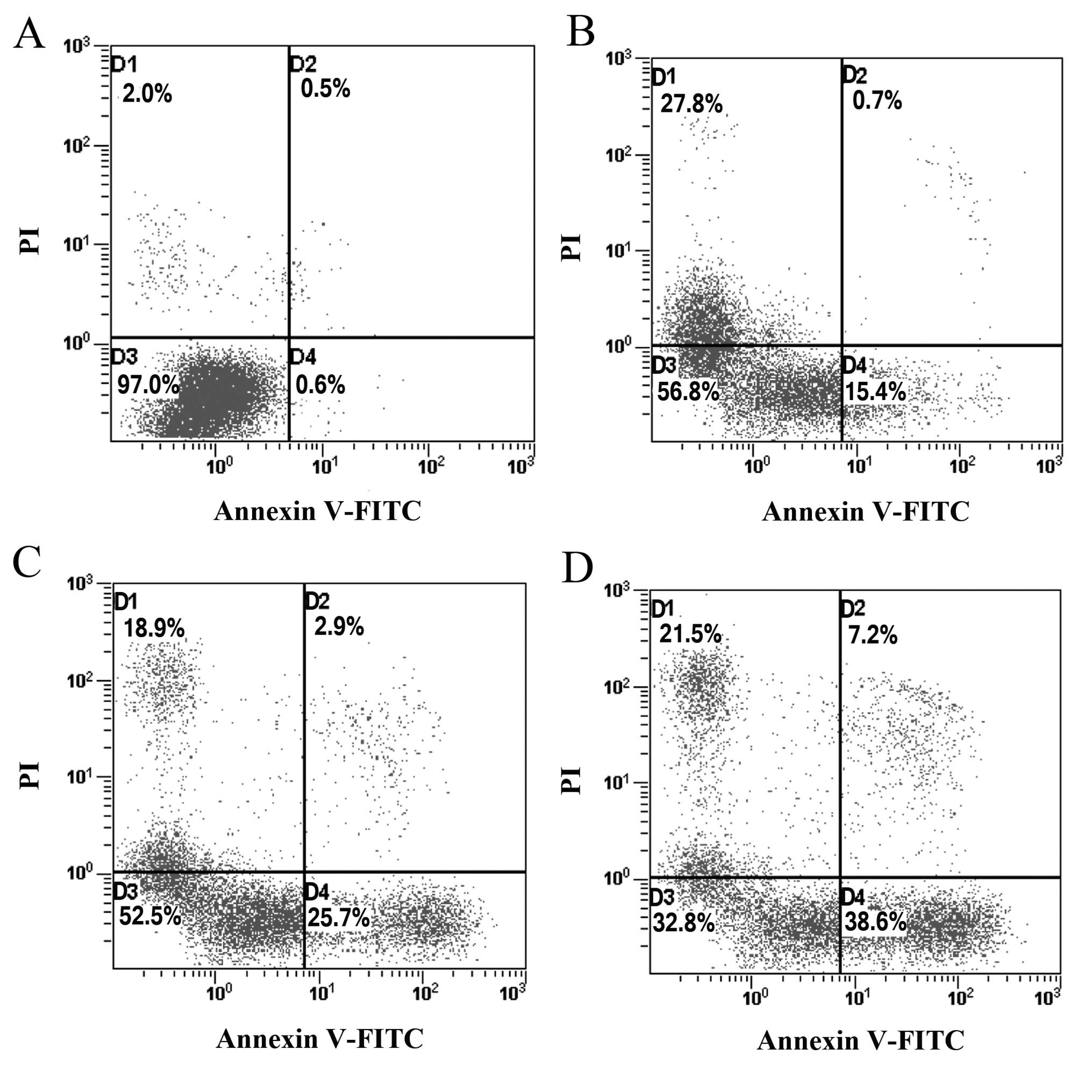
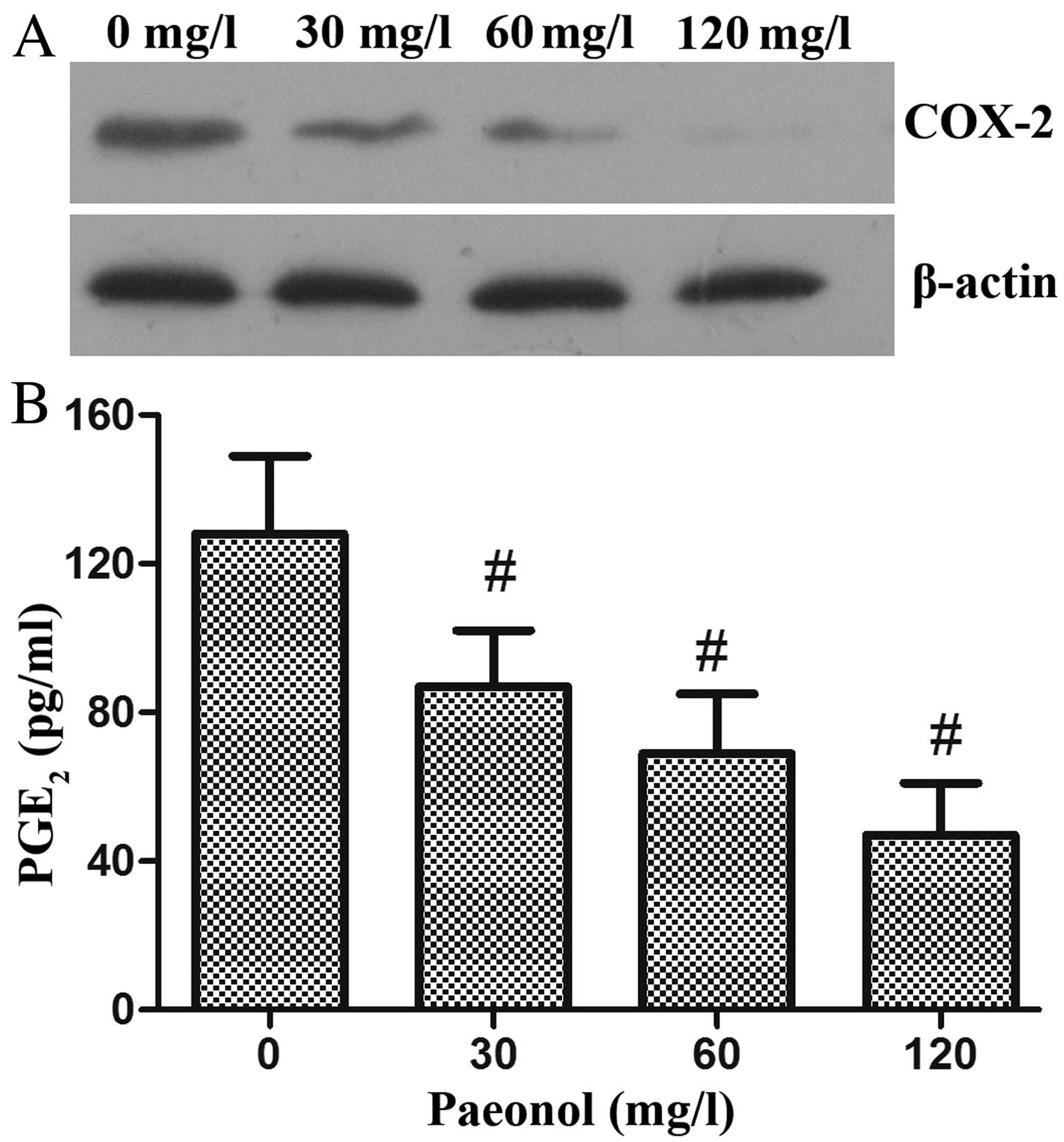
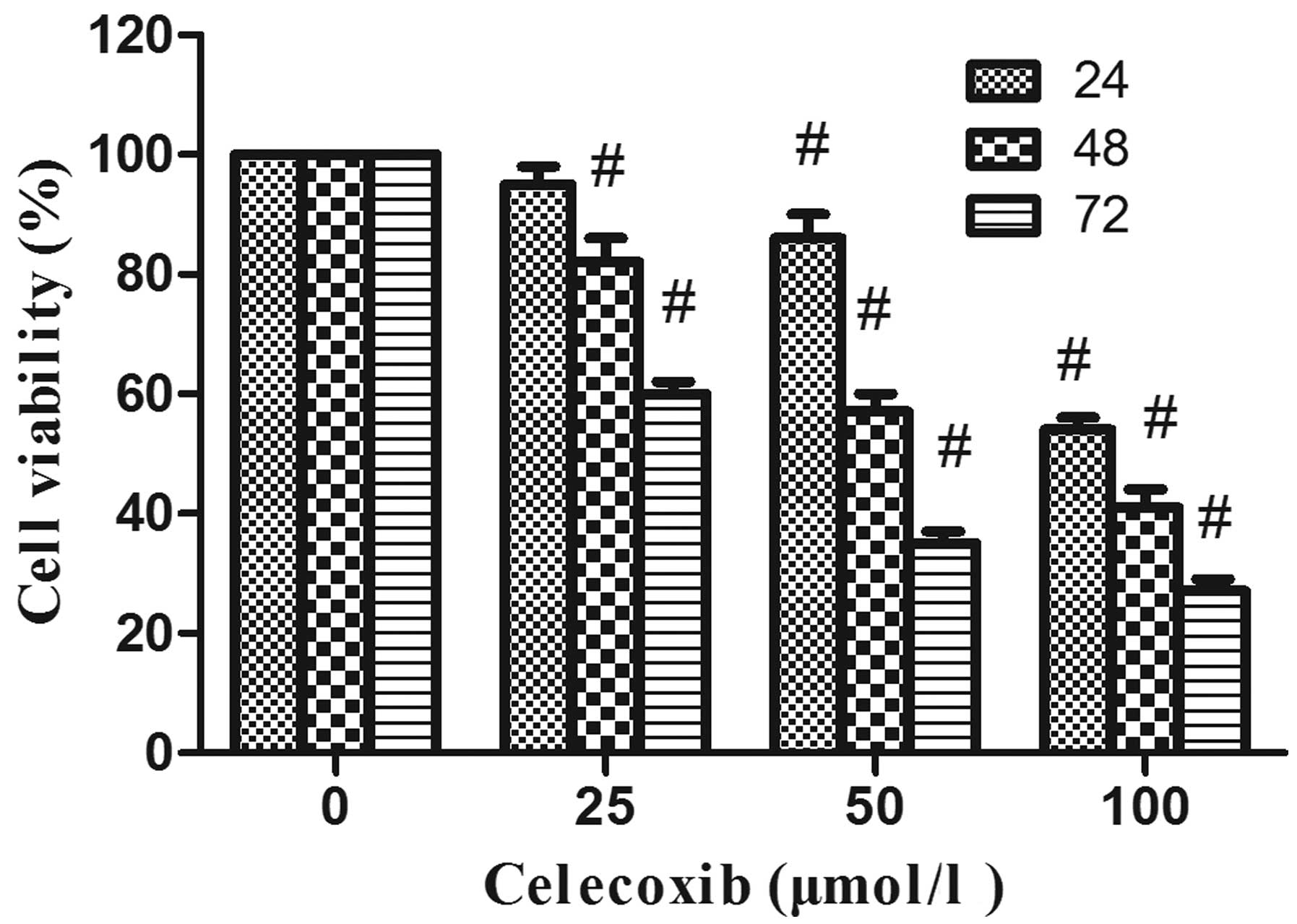
|
1
|
Strimpakos AS, Cunningham D, Mikropoulos
C, Petkar I, Barbachano Y and Chau I: The impact of
carcinoembryonic antigen flare in patients with advanced colorectal
cancer receiving first-line chemotherapy. Ann Oncol. 21:1013–1019.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Benamouzig R, Uzzan B, Martin A, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2 expression and recurrence of colorectal adenomas:
effect of aspirin chemoprevention. Gut. 59:622–629. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang R, Guo L, Wang P, Yang W, Lu Y, Huang
Z and Tang C: Chemoprevention of cancers in gastrointestinal tract
with cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors. Curr Pharm Des. 19:115–125.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cheng J and Fan XM: Role of
cyclooxygenase-2 in colorectal cancer development and progression.
World J Gastroenterol. 19:7361–7318. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bocca C, Ievolella M, Autelli R, et al:
Expression of Cox-2 in human breast cancer cells as a critical
determinant of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and
invasiveness. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 18:121–135. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Singh B and Lucci A: Role of
cyclooxygenase-2 in breast cancer. J Surg Res. 108:173–179. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Harris RE: Cyclooxygenase-2 (cox-2)
blockade in the chemoprevention of cancers of the colon, breast,
prostate, and lung. Inflammopharmacology. 17:55–67. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Méric JB, Rottey S, Olaussen K, Soria JC,
Khayat D, Rixe O and Spano JP: Cyclooxygenase-2 as a target for
anticancer drug development. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 59:51–64.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dannenberg AJ and Subbaramaiah K:
Targeting cyclooxygenase-2 in human neoplasia: rationale and
promise. Cancer Cell. 4:431–436. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Elder DJ, Halton DE, Crew TE and Paraskeva
C: Apoptosis induction and cyclooxygenase-2 regulation in human
colorectal adenoma and carcinoma cell lines by the
cyclooxygenase-2-selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
NS-398. Int J Cancer. 86:553–560. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rostom A, Dubé C, Lewin G, et al:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and cyclooxygenase-2
inhibitors for primary prevention of colorectal cancer: a
systematic review prepared for the U.S. Preventive Services Task
Force. Ann Intern Med. 146:376–389. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Solomon SD, Wittes J, Finn PV, et al:
Cardiovascular risk of celecoxib in 6 randomized placebo-controlled
trials: the cross trial safety analysis. Circulation.
117:2104–2113. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chou TC: Anti-inflammatory and analgesic
effects of paeonol in carrageenan-evoked thermal hyperalgesia. Br J
Pharmacol. 139:1146–1152. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang H, Chang EJ, Lee Y, Kim JS, Kang SS
and Kim HH: A genome-wide microarray analysis reveals
anti-inflammatory target genes of paeonol in macrophages. Inflamm
Res. 57:189–198. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hsieh CL, Cheng CY, Tsai TH, et al:
Paeonol reduced cerebral infarction involving the superoxide anion
and microglia activation in ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. J
Ethnopharmacol. 106:208–215. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim SA, Lee HJ, Ahn KS, et al: Paeonol
exerts anti-angiogenic and anti-metastatic activities through
downmodulation of Akt activation and inactivation of matrix
metalloproteinases. Biol Pharm Bull. 32:1142–1147. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim SH, Kim SA, Park MK, et al: Paeonol
inhibits anaphylactic reaction by regulating histamine and
TNF-alpha. Int Immunopharmacol. 4:279–287. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun YC, Shen YX and Sun GP: Advances in
the studies of major pharmacological activity of paeonol. Zhong
Cheng Yao Zazhi. 26:579–582. 2004.(In Chinese).
|
|
19
|
Cai J, Chen S, Zhang W, Hu S, Lu J, Xing J
and Dong Y: Paeonol reverses paclitaxel resistance in human breast
cancer cells by regulating the expression of transgelin 2.
Phytomedicine. 21:984–991. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fan L, Song B, Sun G, Ma T, Zhong F and
Wei W: Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced resistance to
doxorubicin is reversed by paeonol treatment in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 8:e626272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li M, Tan SY, Zhang J and You HX: Effects
of paeonol on intracellular calcium concentration and expression of
RUNX3 in LoVo human colon cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 7:1425–1430.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kindler HL and Shulman KL: Metastatic
colorectal cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2:459–471. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tang D, Lotze MT, Kang R and Zeh HJ:
Apoptosis promotes early tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 30:1851–1854.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Masferrer JL, Leahy KM, Koki AT, et al:
Antiangiogenic and antitumor activities of cyclooxygenase-2
inhibitors. Cancer Res. 60:1306–1311. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sheng H, Shao J, Kirkland SC, et al:
Inhibition of human colon cancer cell growth by selective
inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2. J Clin Invest. 99:2254–2259. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Singh T, Vaid M, Katiyar N, Sharma S and
Katiyar SK: Berberine, an isoquinoline alkaloid, inhibits melanoma
cancer cell migration by reducing the expressions of
cyclooxygenase-2, prostaglandin E2 and prostaglandin
E2 receptors. Carcinogenesis. 32:86–92. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Reich R and Martin GR: Identification of
arachidonic acid pathways required for the invasive and metastatic
activity of malignant tumor cells. Prostaglandins. 51:1–17. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dubois RN, Abramson SB, Crofford L, et al:
Cyclooxygenase in biology and disease. FASEB J. 12:1063–1073.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Arber N, Eagle CJ, Spicak J, et al:
Celecoxib for prevention of colorectal adenomas. N Engl J Med.
355:885–895. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Baron JA, Sandler RS, Bresalier RS, et al:
A randomized trial of rofecoxib for the chemoprevention of
colorectal adenomas. Gastroenterology. 131:1674–1682. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bertagnolli MM, Eagle CJ, Zauber AG, et
al: Celecoxib for the prevention of sporadic colorectal adenomas. N
Engl J Med. 355:873–884. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Enders GA: Cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression
abrogates the antiproliferative effects of TGF-beta. Br J Cancer.
97:1388–1392. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen XL, Su BS, Sun RQ, Zhang J and Wang
YL: Relationship between expression and distribution of
cyclooxygenase-2 and bcl-2 in human gastric adenocarcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 11:1228–1231. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Han JA, Kim JI, Ongusaha PP, et al:
p53-mediated induction of Cox-2 counteracts p53- or genotoxic
stress-induced apoptosis. EMBO J. 21:5635–5644. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ghosh S, May MJ and Kopp EB: NF-kappa B
and Rel proteins: evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune
responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 16:225–260. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Barkett M and Gilmore TD: Control of
apoptosis by Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene.
18:6910–6924. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Karin M and Lin A: NF-kappaB at the
crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol. 3:221–227. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|