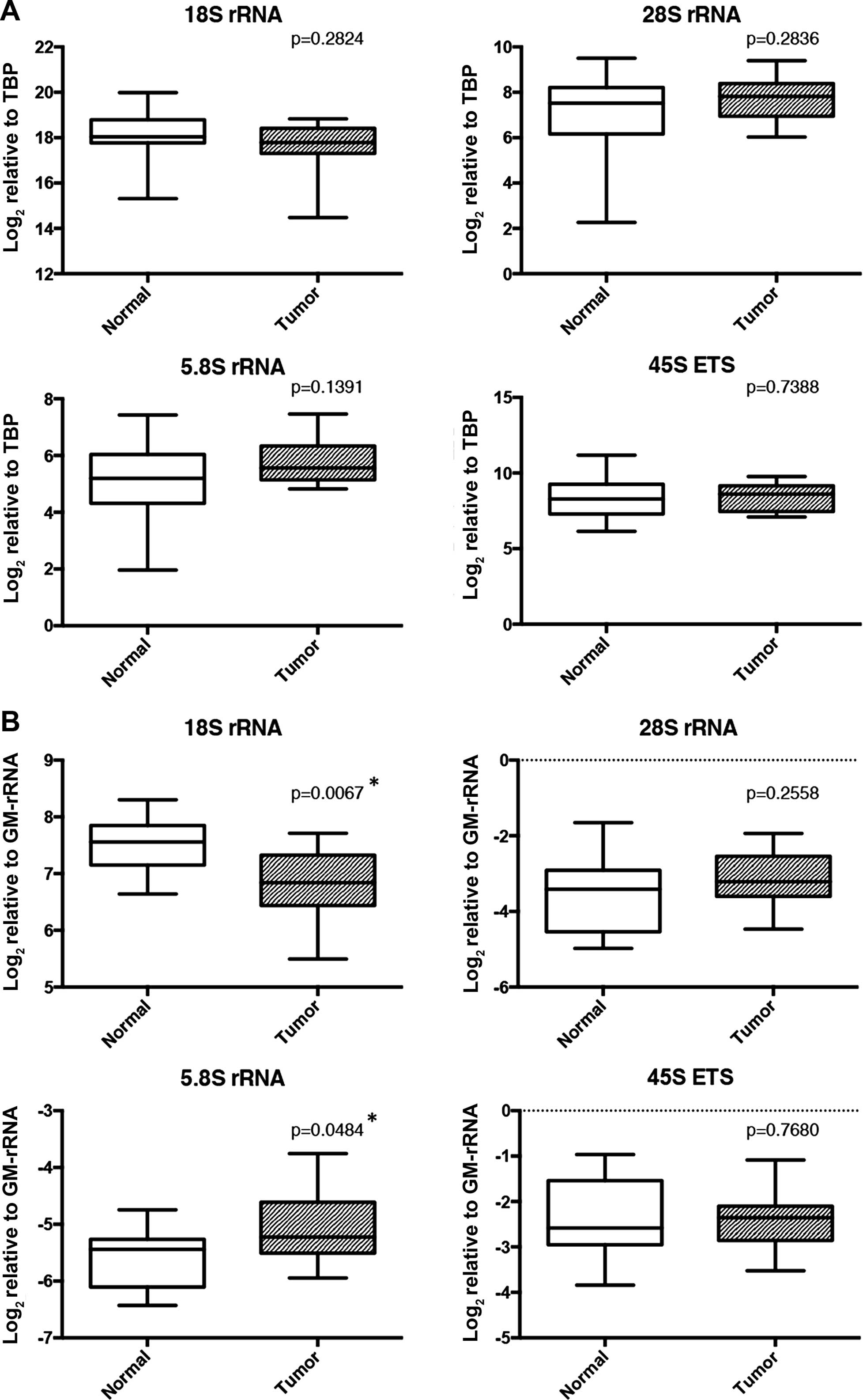
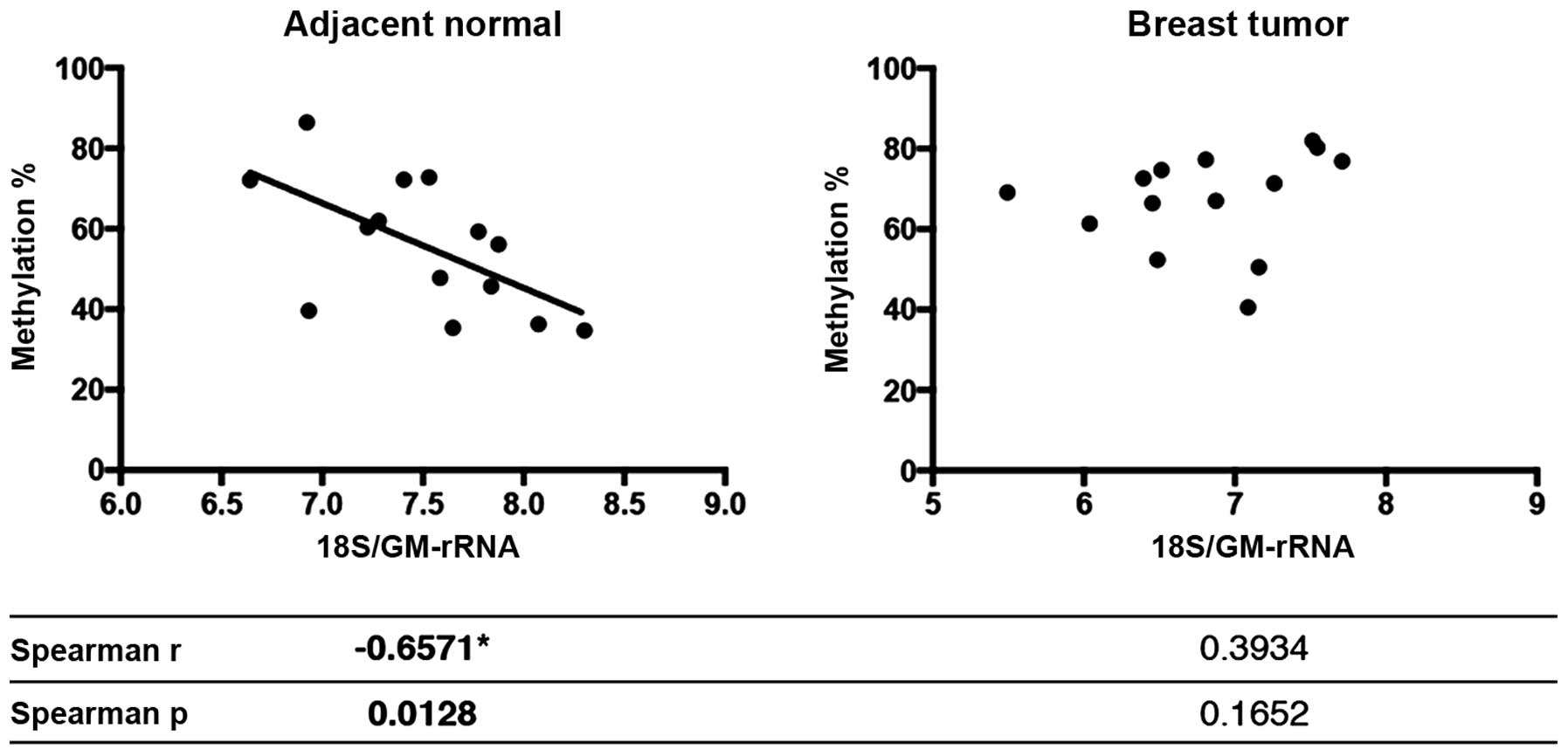
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M,
Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and
Bray F: GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality
Worldwide. (IARC CancerBase No. 11). http://globocan.iarc.fr.
2013
|
|
2
|
Lalloo F and Evans DG: Familial breast
cancer. Clin Genet. 82:105–114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jaenisch R and Bird A: Epigenetic
regulation of gene expression: How the genome integrates intrinsic
and environmental signals. Nat Genet. 33(Suppl): S245–S254. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Salozhin SV, Prokhorchuk EB and Georgiev
GP: Methylation of DNA - one of the major epigenetic markers.
Biochemistry. 70:525–532. 2005.
|
|
5
|
Nafee TM, Farrell WE, Carroll WD, Fryer AA
and Ismail KM: Epigenetic control of fetal gene expression. BJOG.
115:158–168. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Esteller M: Aberrant DNA methylation as a
cancer-inducing mechanism. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 45:629–656.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Karpinets TV and Foy BD: Tumorigenesis:
The adaptation of mammalian cells to sustained stress environment
by epigenetic alterations and succeeding matched mutations.
Carcinogenesis. 26:1323–1334. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baylin SB and Ohm JE: Epigenetic gene
silencing in cancer - a mechanism for early oncogenic pathway
addiction? Nat Rev Cancer. 6:107–116. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dez C and Tollervey D: Ribosome synthesis
meets the cell cycle. Curr Opin Microbiol. 7:631–637. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
McKnight SL and Miller OL Jr:
Ultrastructural patterns of RNA synthesis during early
embryogenesis of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 8:305–319. 1976.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schmickel RD: Quantitation of human
ribosomal DNA: Hybridization of human DNA with ribosomal RNA for
quantitation and fractionation. Pediatr Res. 7:5–12. 1973.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Warner JR: The economics of ribosome
biosynthesis in yeast. Trends Biochem Sci. 24:437–440. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Russell J and Zomerdijk JC:
RNA-polymerase-I-directed rDNA transcription, life and works.
Trends Biochem Sci. 30:87–96. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Paule MR and White RJ: Survey and summary:
Transcription by RNA polymerases I and III. Nucleic Acids Res.
28:1283–1298. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Learned RM, Learned TK, Haltiner MM and
Tjian RT: Human rRNA transcription is modulated by the coordinate
binding of two factors to an upstream control element. Cell.
45:847–857. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Clos J, Buttgereit D and Grummt I: A
purified transcription factor (TIF-IB) binds to essential sequences
of the mouse rDNA promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 83:604–608.
1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Eichler DC and Craig N: Processing of
eukaryotic ribosomal RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol.
49:197–239. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Trapman J, Retèl J and Planta RJ:
Ribosomal precursor particles from yeast. Exp Cell Res. 90:95–104.
1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Venema J and Tollervey D: Ribosome
synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Annu Rev Genet. 33:261–311.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Esteller M: Epigenetic gene silencing in
cancer: The DNA hypermethylome. Hum Mol Genet. 16:R50–R59. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Worton RG, Sutherland J, Sylvester JE,
Willard HF, Bodrug S, Dubé I, Duff C, Kean V, Ray PN and Schmickel
RD: Human ribosomal RNA genes: Orientation of the tandem array and
conservation of the 5′ end. Science. 239:64–68. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ghoshal K, Majumder S, Datta J, Motiwala
T, Bai S, Sharma SM, Frankel W and Jacob ST: Role of human
ribosomal RNA (rRNA) promoter methylation and of methyl-CpG-binding
protein MBD2 in the suppression of rRNA gene expression. J Biol
Chem. 279:6783–6793. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Raval A, Sridhar KJ, Patel S, Turnbull BB,
Greenberg PL and Mitchell BS: Reduced rRNA expression and increased
rDNA promoter methylation in CD34+ cells of patients
with myelodys-plastic syndromes. Blood. 120:4812–4818. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Uemura M, Zheng Q, Koh CM, Nelson WG,
Yegnasubramanian S and De Marzo AM: Overexpression of ribosomal RNA
in prostate cancer is common but not linked to rDNA promoter
hypomethylation. Oncogene. 31:1254–1263. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Gagnon-Kugler T, Langlois F, Stefanovsky
V, Lessard F and Moss T: Loss of human ribosomal gene CpG
methylation enhances cryptic RNA polymerase II transcription and
disrupts ribosomal RNA processing. Mol Cell. 35:414–425. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gur-Dedeoglu B, Konu O, Bozkurt B, Ergul
G, Seckin S and Yulug IG: Identification of endogenous reference
genes for qRT-PCR analysis in normal matched breast tumor tissues.
Oncol Res. 17:353–365. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tricarico C, Pinzani P, Bianchi S,
Paglierani M, Distante V, Pazzagli M, Bustin SA and Orlando C:
Quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain
reaction: Normalization to rRNA or single housekeeping genes is
inappropriate for human tissue biopsies. Anal Biochem. 309:293–300.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
de Kok JB, Roelofs RW, Giesendorf BA,
Pennings JL, Waas ET, Feuth T, Swinkels DW and Span PN:
Normalization of gene expression measurements in tumor tissues:
Comparison of 13 endogenous control genes. Lab Invest. 85:154–159.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chan MW, Wei SH, Wen P, Wang Z, Matei DE,
Liu JC, Liyanarachchi S, Brown R, Nephew KP, Yan PS, et al:
Hypermethylation of 18S and 28S ribosomal DNAs predicts
progression-free survival in patients with ovarian cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 11:7376–7383. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yan PS, Rodriguez FJ, Laux DE, Perry MR,
Standiford SB and Huang TH: Hypermethylation of ribosomal DNA in
human breast carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 82:514–517. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Powell MA, Mutch DG, Rader JS, Herzog TJ,
Huang TH and Goodfellow PJ: Ribosomal DNA methylation in patients
with endometrial carcinoma: An independent prognostic marker.
Cancer. 94:2941–2952. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bacalini MG, Pacilli A, Giuliani C, Penzo
M, Treré D, Pirazzini C, Salvioli S, Franceschi C, Montanaro L and
Garagnani P: The nucleolar size is associated to the methylation
status of ribosomal DNA in breast carcinomas. BMC Cancer.
14:3612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kumaki Y, Oda M and Okano M: QUMA:
Quantification tool for methylation analysis. Nucleic Acids Res.
36:W170–W175. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Haltiner MM, Smale ST and Tjian R: Two
distinct promoter elements in the human rRNA gene identified by
linker scanning mutagenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 6:227–235.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Brown SE and Szyf M: Dynamic epigenetic
states of ribosomal RNA promoters during the cell cycle. Cell
Cycle. 7:382–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guo C, Liu S, Wang J, Sun MZ and Greenaway
FT: ACTB in cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 417:39–44. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Guo C, Liu S and Sun MZ: Novel insight
into the role of GAPDH playing in tumor. Clin Transl Oncol.
15:167–172. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Esteller M, Corn PG, Baylin SB and Herman
JG: A gene hyper-methylation profile of human cancer. Cancer Res.
61:3225–3229. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ballestar E and Esteller M: Epigenetic
gene regulation in cancer. Adv Genet. 61:247–267. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Eden S and Cedar H: Role of DNA
methylation in the regulation of transcription. Curr Opin Genet
Dev. 4:255–259. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sentenac A: Eukaryotic RNA polymerases.
CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 18:31–90. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sharp PA: TATA-binding protein is a
classless factor. Cell. 68:819–821. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Comai L, Tanese N and Tjian R: The
TATA-binding protein and associated factors are integral components
of the RNA polymerase I transcription factor, SL1. Cell.
68:965–976. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kochanek S, Hosokawa K, Schiedner G, Renz
D and Doerfler W: DNA methylation in the promoter of ribosomal RNA
genes in human cells as determined by genomic sequencing. FEBS
Lett. 388:192–194. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Németh A, Guibert S, Tiwari VK, Ohlsson R
and Längst G: Epigenetic regulation of TTF-I-mediated
promoter-terminator interactions of rRNA genes. EMBO J.
27:1255–1265. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Brown SE and Szyf M: Epigenetic
programming of the rRNA promoter by MBD3. Mol Cell Biol.
27:4938–4952. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Oakes CC, Smiraglia DJ, Plass C, Trasler
JM and Robaire B: Aging results in hypermethylation of ribosomal
DNA in sperm and liver of male rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:1775–1780. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Macleod D and Bird A: Transcription in
oocytes of highly methylated rDNA from Xenopus laevis sperm.
Nature. 306:200–203. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Richards EJ and Elgin SC: Epigenetic codes
for heterochro-matin formation and silencing: Rounding up the usual
suspects. Cell. 108:489–500. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Muangsub T, Samsuwan J, Tongyoo P,
Kitkumthorn N and Mutirangura A: Analysis of methylation microarray
for tissue specific detection. Gene. 553:31–41. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chan MW, Wei SH, Wen P, Wang Z, Matei DE,
Liu JC, Liyanarachchi S, Brown R, Nephew KP, Yan PS, et al:
Hypermethylation of 18S and 28S ribosomal DNAs predicts
progression-free survival in patients with ovarian cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 11:7376–7383. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Egner JR: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. JAMA
J Am Med Assoc. 304:17262010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Jia F and Rock CD: MIR846 and MIR842
comprise a cistronic MIRNA pair that is regulated by abscisic acid
by alternative splicing in roots of Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol.
81:447–460. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Malik Ghulam M, Courtois F, Lerbs-Mache S
and Merendino L: Complex processing patterns of mRNAs of the large
ATP synthase operon in Arabidopsis chloroplasts. PLoS One.
8:e782652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Li SS, Yu SL and Singh S: Epigenetic
states and expression of imprinted genes in human embryonic stem
cells. World J Stem Cells. 2:97–102. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Gray TA, Saitoh S and Nicholls RD: An
imprinted, mammalian bicistronic transcript encodes two independent
proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:5616–5621. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kiss T, Fayet E, Jády BE, Richard P and
Weber M: Biogenesis and intranuclear trafficking of human box C/D
and H/ACA RNPs. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 71:407–417. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Terns M and Terns R: Noncoding RNAs of the
H/ACA family. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 71:395–405. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Dong XY, Rodriguez C, Guo P, Sun X, Talbot
JT, Zhou W, Petros J, Li Q, Vessella RL, Kibel AS, et al: SnoRNA
U50 is a candidate tumor-suppressor gene at 6q14.3 with a mutation
associated with clinically significant prostate cancer. Hum Mol
Genet. 17:1031–1042. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Dong XY, Guo P, Boyd J, Sun X, Li Q, Zhou
W and Dong JT: Implication of snoRNA U50 in human breast cancer. J
Genet Genomics. 36:447–454. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Tanaka R, Satoh H, Moriyama M, Satoh K,
Morishita Y, Yoshida S, Watanabe T, Nakamura Y and Mori S: Intronic
U50 small-nucleolar-RNA (snoRNA) host gene of no protein-coding
potential is mapped at the chromosome breakpoint t(3;6) (q27;q15)
of human B-cell lymphoma. Genes Cells. 5:277–287. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Pacilli A, Ceccarelli C, Treré D and
Montanaro L: SnoRNA U50 levels are regulated by cell proliferation
and rRNA transcription. Int J Mol Sci. 14:14923–14935. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Mourtada-Maarabouni M, Pickard MR, Hedge
VL, Farzaneh F and Williams GT: GAS5, a non-protein-coding RNA,
controls apoptosis and is downregulated in breast cancer. Oncogene.
28:195–208. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Kobayashi T: Ribosomal RNA gene repeats,
their stability and cellular senescence. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys
Biol Sci. 90:119–129. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Peng JC and Karpen GH: H3K9 methylation
and RNA interference regulate nucleolar organization and repeated
DNA stability. Nat Cell Biol. 9:25–35. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Kobayashi T: A new role of the rDNA and
nucleolus in the nucleus - rDNA instability maintains genome
integrity. Bioessays. 30:267–272. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|