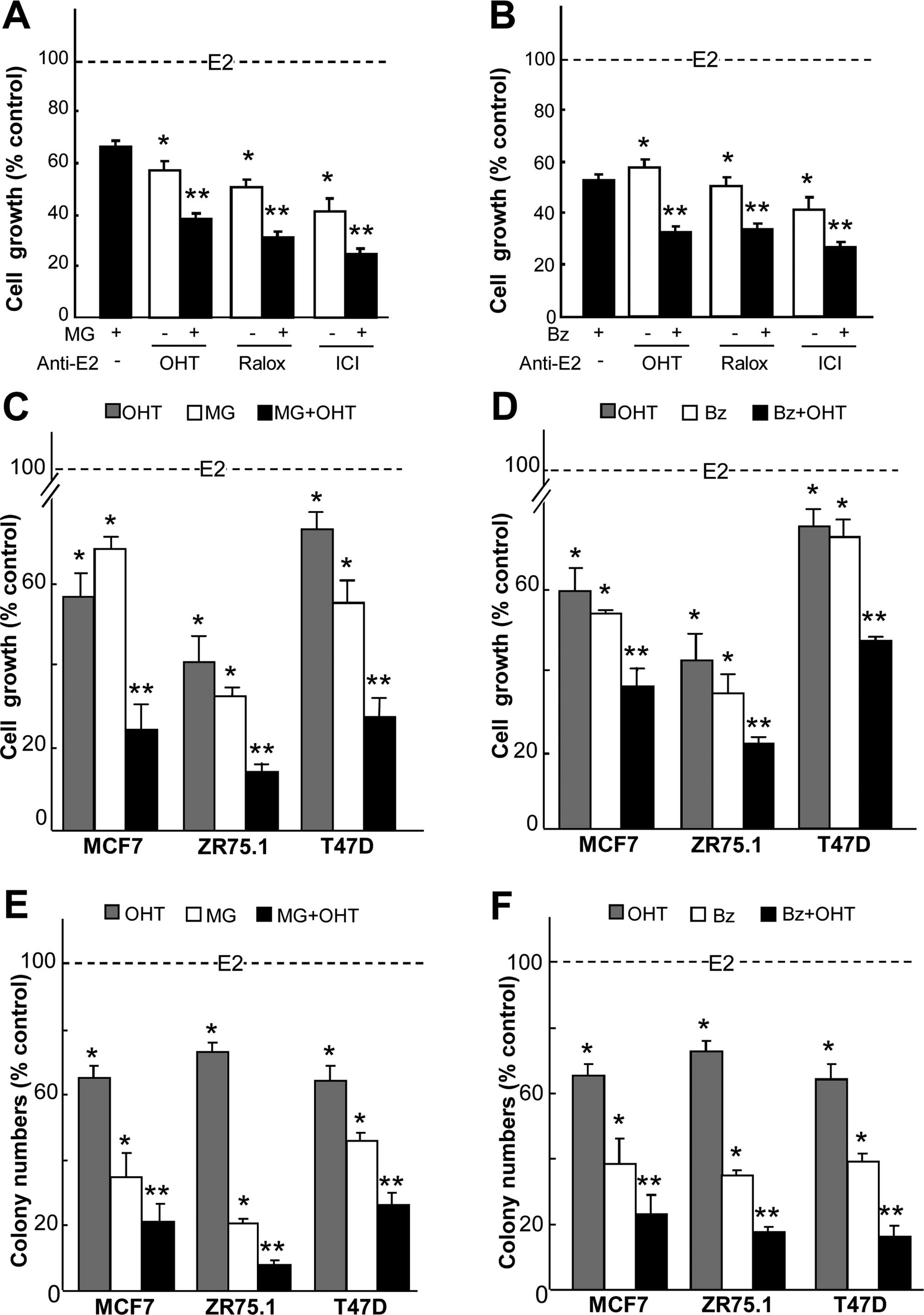
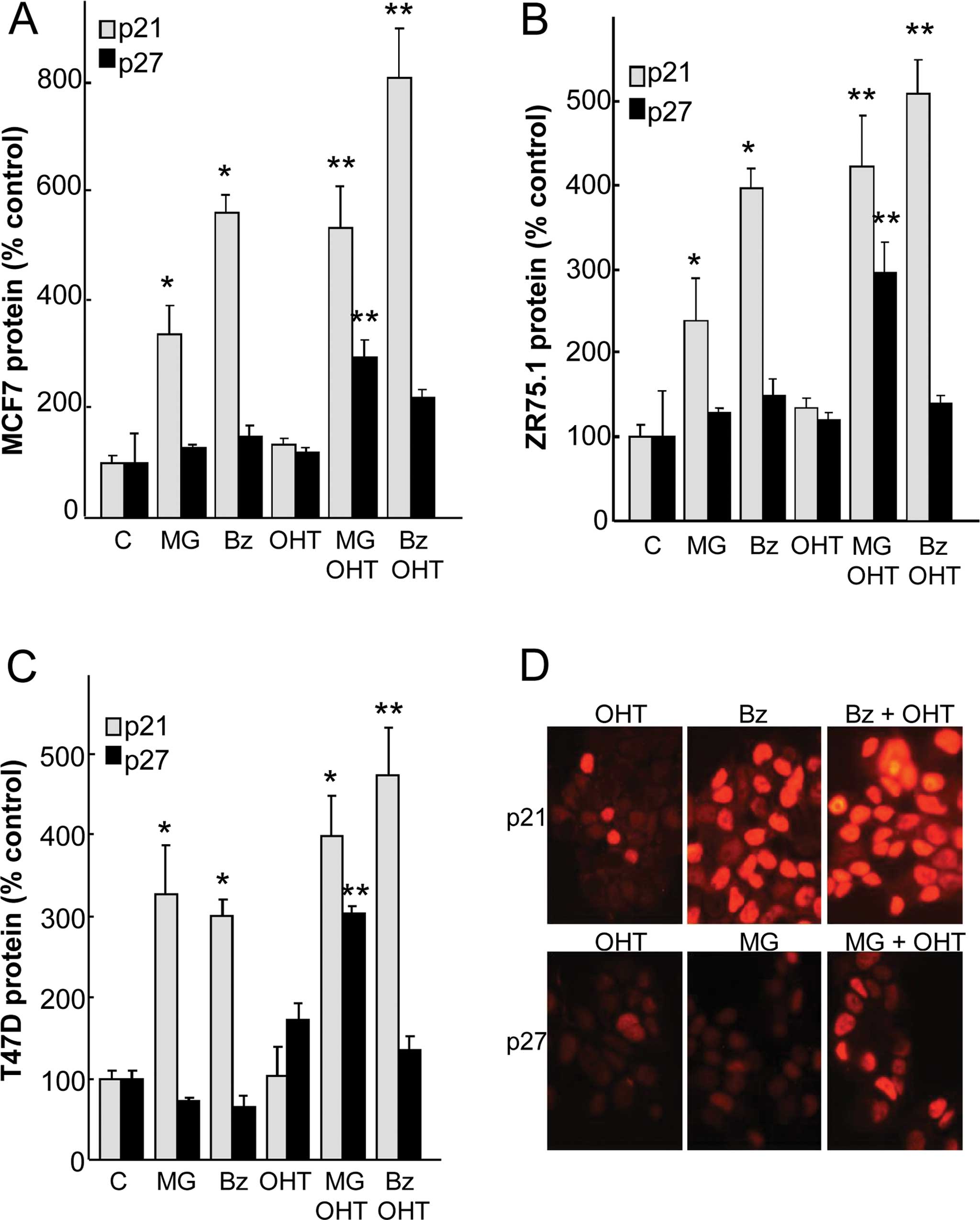
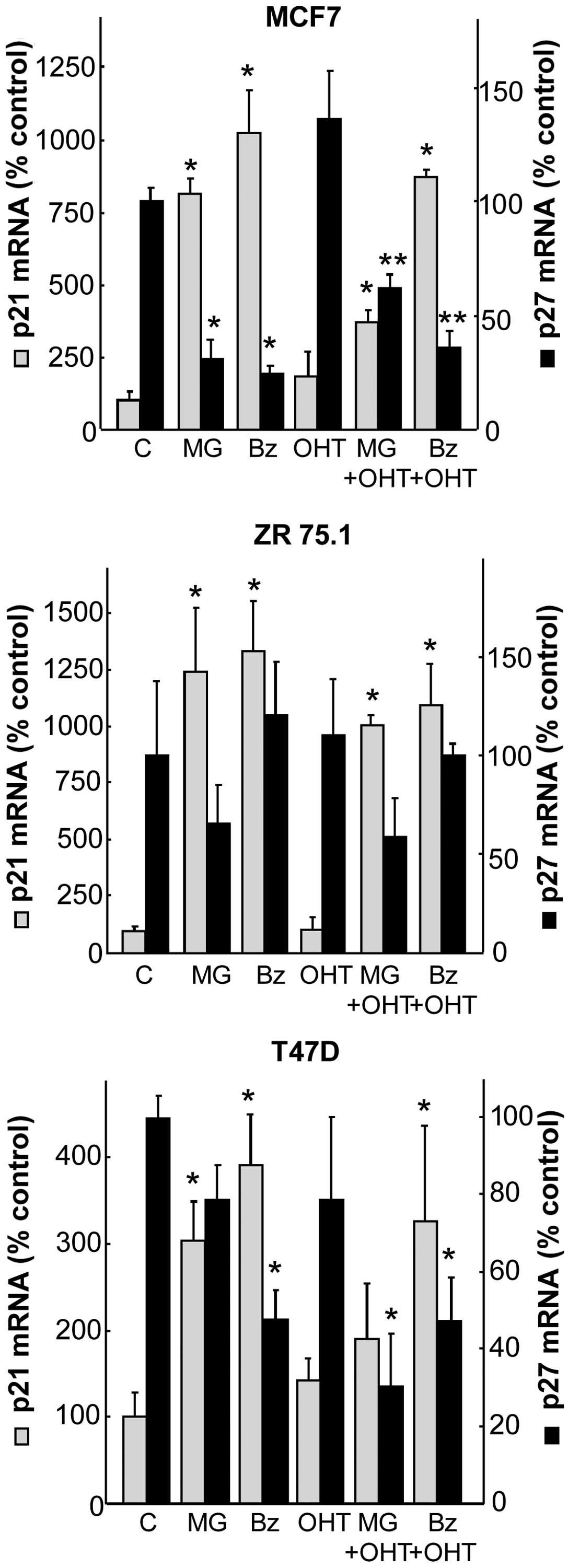
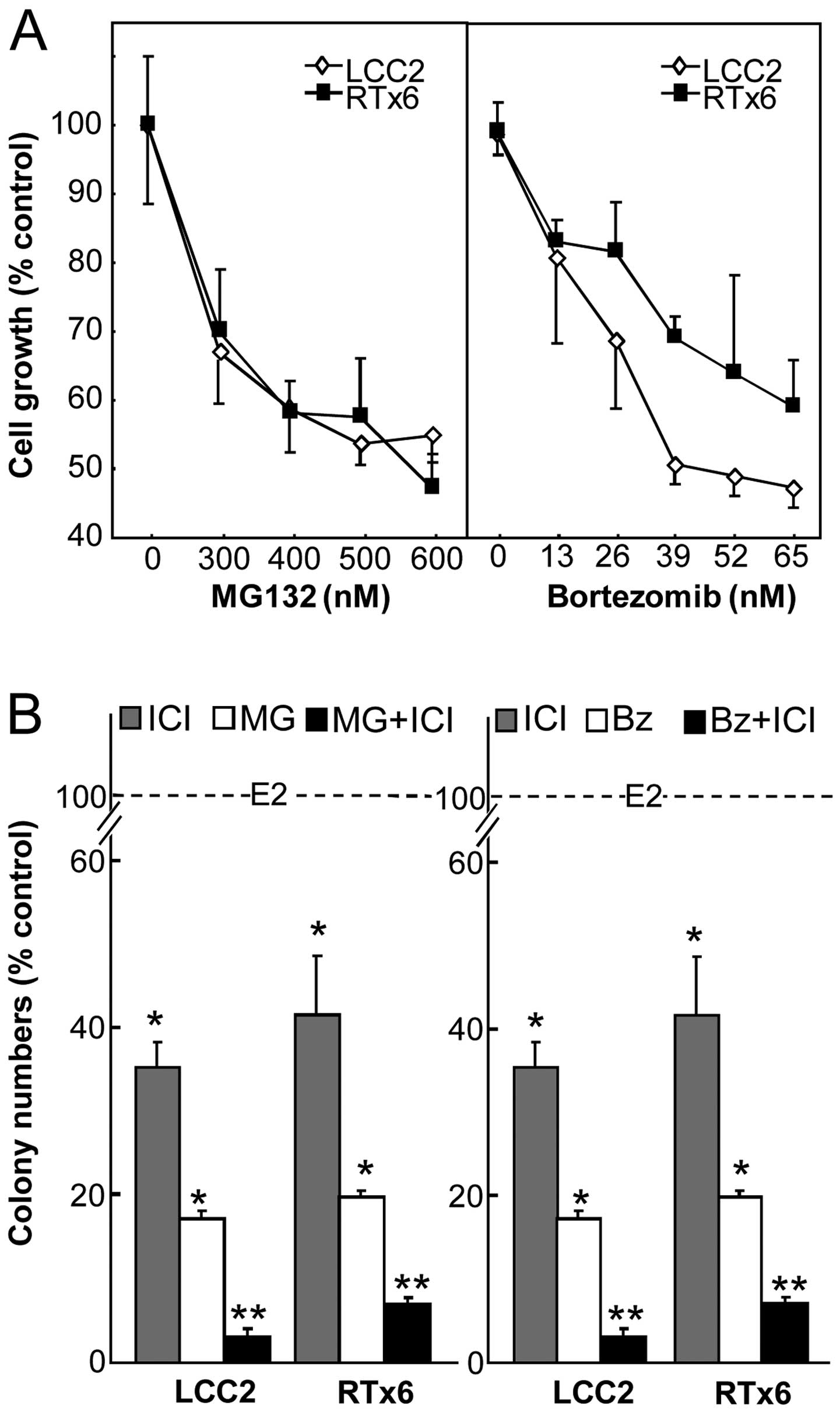
|
1
|
Henderson BE, Ross R and Bernstein L:
Estrogens as a cause of human cancer: The Richard and Hinda
Rosenthal Foundation award lecture. Cancer Res. 48:246–253.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Couse JF and Korach KS: Estrogen receptor
null mice: What have we learned and where will they lead us? Endocr
Rev. 20:358–417. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
McDonnell DP, Connor CE, Wijayaratne A,
Chang CY and Norris JD: Definition of the molecular and cellular
mechanisms underlying the tissue-selective agonist/antagonist
activities of selective estrogen receptor modulators. Recent Prog
Horm Res. 57:295–316. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ikeda H, Taira N, Nogami T, Shien K, Okada
M, Shien T, Doihara H and Miyoshi S: Combination treatment with
fulvestrant and various cytotoxic agents (doxorubicin, paclitaxel,
docetaxel, vinorelbine, and 5-fluorouracil) has a synergistic
effect in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Cancer Sci.
102:2038–2042. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cariou S, Donovan JC, Flanagan WM, Milic
A, Bhattacharya N and Slingerland JM: Down-regulation of
p21WAF1/CIP1 or p27Kip1 abrogates
antiestrogen-mediated cell cycle arrest in human breast cancer
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:9042–9046. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Maynadier M, Ramirez JM, Cathiard AM,
Platet N, Gras D, Gleizes M, Sheikh MS, Nirde P and Garcia M:
Unliganded estrogen receptor alpha inhibits breast cancer cell
growth through interaction with a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor
(p21WAF1). FASEB J. 22:671–681. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Planas-Silva MD and Weinberg RA:
Estrogen-dependent cyclin E-cdk2 activation through p21
redistribution. Mol Cell Biol. 17:4059–4069. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Varshochi R, Halim F, Sunters A, Alao JP,
Madureira PA, Hart SM, Ali S, Vigushin DM, Coombes RC and Lam EW:
ICI182,780 induces p21WAF1 gene transcription through
releasing histone deacetylase 1 and estrogen receptor alpha from
Sp1 sites to induce cell cycle arrest in MCF-7 breast cancer cell
line. J Biol Chem. 280:3185–3196. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Catzavelos C, Bhattacharya N, Ung YC,
Wilson JA, Roncari L, Sandhu C, Shaw P, Yeger H, Morava-Protzner I,
Kapusta L, et al: Decreased levels of the cell-cycle inhibitor
p27Kip1 protein: Prognostic implications in primary
breast cancer. Nat Med. 3:227–230. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tan P, Cady B, Wanner M, Worland P, Cukor
B, Magi-Galluzzi C, Lavin P, Draetta G, Pagano M and Loda M: The
cell cycle inhibitor p27 is an independent prognostic marker in
small (T1a,b) invasive breast carcinomas. Cancer Res.
57:1259–1263. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wakasugi E, Kobayashi T, Tamaki Y, Ito Y,
Miyashiro I, Komoike Y, Takeda T, Shin E, Takatsuka Y, Kikkawa N,
et al: p21(Waf1/Cip1) and p53 protein expression in breast cancer.
Am J Clin Pathol. 107:684–691. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tiezzi DG, Andrade JM, Ribeiro-Silva A,
Zola FE, Marana HR and Tiezzi MG: HER-2, p53, p21 and hormonal
receptors proteins expression as predictive factors of response and
prognosis in locally advanced breast cancer treated with
neoadjuvant docetaxel plus epirubicin combination. BMC Cancer.
7:362007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sáez A, Sánchez E, Sánchez-Beato M, Cruz
MA, Chacón I, Muñoz E, Camacho FI, Martínez-Montero JC, Mollejo M,
García JF, et al: p27Kip1 is abnormally expressed in
diffuse large B-cell lymphomas and is associated with an adverse
clinical outcome. Br J Cancer. 80:1427–1434. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tsihlias J, Kapusta L and Slingerland J:
The prognostic significance of altered cyclin-dependent kinase
inhibitors in human cancer. Annu Rev Med. 50:401–423. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Adams J, Palombella VJ, Sausville EA,
Johnson J, Destree A, Lazarus DD, Maas J, Pien CS, Prakash S and
Elliott PJ: Proteasome inhibitors: A novel class of potent and
effective antitumor agents. Cancer Res. 59:2615–2622.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Uddin S, Ahmed M, Bavi P, El-Sayed R,
Al-Sanea N, AbdulJabbar A, Ashari LH, Alhomoud S, Al-Dayel F,
Hussain AR, et al: Bortezomib (Velcade) induces p27Kip1
expression through S-phase kinase protein 2 degradation in
colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 68:3379–3388. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dulić V, Stein GH, Far DF and Reed SI:
Nuclear accumulation of p21Cip1 at the onset of mitosis:
A role at the G2/M-phase transition. Mol Cell Biol.
18:546–557. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hideshima T, Richardson P, Chauhan D,
Palombella VJ, Elliott PJ, Adams J and Anderson KC: The proteasome
inhibitor PS-341 inhibits growth, induces apoptosis, and overcomes
drug resistance in human multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Res.
61:3071–3076. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ludwig H, Khayat D, Giaccone G and Facon
T: Proteasome inhibition and its clinical prospects in the
treatment of hematologic and solid malignancies. Cancer.
104:1794–1807. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen F and Harrison LE:
Ciglitazone-induced cellular anti-proliferation increases
p27Kip1 protein levels through both increased
transcriptional activity and inhibition of proteasome degradation.
Cell Signal. 17:809–816. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Maynadier M, Shi J, Vaillant O, Gary-Bobo
M, Basile I, Gleizes M, Cathiard AM, Wah JL, Sheikh MS and Garcia
M: Roles of estrogen receptor and p21Waf1 in
bortezomib-induced growth inhibition in human breast cancer cells.
Mol Cancer Res. 10:1473–1481. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Richardson PG, Barlogie B, Berenson J,
Singhal S, Jagannath S, Irwin D, Rajkumar SV, Srkalovic G, Alsina
M, Alexanian R, et al: A phase 2 study of bortezomib in relapsed,
refractory myeloma. N Engl J Med. 348:2609–2617. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Orlowski RZ, Stinchcombe TE, Mitchell BS,
Shea TC, Baldwin AS, Stahl S, Adams J, Esseltine DL, Elliott PJ,
Pien CS, et al: Phase I trial of the proteasome inhibitor PS-341 in
patients with refractory hematologic malignancies. J Clin Oncol.
20:4420–4427. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Powers GL, Ellison-Zelski SJ, Casa AJ, Lee
AV and Alarid ET: Proteasome inhibition represses ERalpha gene
expression in ER+ cells: A new link between proteasome
activity and estrogen signaling in breast cancer. Oncogene.
29:1509–1518. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Brünner N, Frandsen TL, Holst-Hansen C,
Bei M, Thompson EW, Wakeling AE, Lippman ME and Clarke R:
MCF7/LCC2: A 4-hydroxytamoxifen resistant human breast cancer
variant that retains sensitivity to the steroidal antiestrogen ICI
182,780. Cancer Res. 53:3229–3232. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Faye JC, Jozan S, Redeuilh G, Baulieu EE
and Bayard F: Physicochemical and genetic evidence for specific
antiestrogen binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 80:3158–3162.
1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gary-Bobo M, Hocine O, Brevet D, Maynadier
M, Raehm L, Richeter S, Charasson V, Loock B, Morère A, Maillard P,
et al: Cancer therapy improvement with mesoporous silica
nanoparticles combining targeting, drug delivery and PDT. Int J
Pharm. 423:509–515. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Prud'homme GJ, Glinka Y, Toulina A, Ace O,
Subramaniam V and Jothy S: Breast cancer stem-like cells are
inhibited by a non-toxic aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist. PloS
One. 5:e138312010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Maynadier M, Chambon M, Basile I, Gleizes
M, Nirde P, Gary-Bobo M and Garcia M: Estrogens promote cell-cell
adhesion of normal and malignant mammary cells through increased
desmosome formation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 364:126–133. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pérez-Tenorio G, Berglund F, Esguerra
Merca A, Nordenskjöld B, Rutqvist LE, Skoog L and Stål O:
Cytoplasmic p21WAF1/CIP1 correlates with Akt activation
and poor response to tamoxifen in breast cancer. Int J Oncol.
28:1031–1042. 2006.
|
|
31
|
Shah MH, Young D, Kindler HL, Webb I,
Kleiber B, Wright J and Grever M: Phase II study of the proteasome
inhibitor bortezomib (PS-341) in patients with metastatic
neuroendocrine tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 10:6111–6118. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Papandreou CN, Daliani DD, Nix D, Yang H,
Madden T, Wang X, Pien CS, Millikan RE, Tu SM, Pagliaro L, et al:
Phase I trial of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in patients
with advanced solid tumors with observations in
androgen-independent prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 22:2108–2121.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Blaney SM, Bernstein M, Neville K,
Ginsberg J, Kitchen B, Horton T, Berg SL, Krailo M and Adamson PC:
Phase I study of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib in pediatric
patients with refractory solid tumors: A Children's Oncology Group
study (ADVL0015). J Clin Oncol. 22:4804–4809. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Awada A, Albanell J, Canney PA, Dirix LY,
Gil T, Cardoso F, Gascon P, Piccart MJ and Baselga J:
Bortezomib/docetaxel combination therapy in patients with
anthracycline-pretreated advanced/metastatic breast cancer: A phase
I/II dose-escalation study. Br J Cancer. 98:1500–1507. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim JE, Yoon DH, Jang G, Lee DH, Kim S,
Park CS, Huh J, Kim WS, Park J, Lee JH, et al: A phase I/II study
of bortezomib plus CHOP every 2 weeks (CHOP-14) in patients with
advanced-stage diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Korean J Hematol.
47:53–59. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Houot R, Le Gouill S, Ojeda Uribe M,
Mounier C, Courby S, Dartigeas C, Bouabdallah K, Alexis Vigier M,
Moles MP, Tournilhac O, et al French GOELAMS group: Combination of
rituximab, bortezomib, doxorubicin, dexamethasone and chlorambucil
(RiPAD+C) as first-line therapy for elderly mantle cell lymphoma
patients: Results of a phase II trial from the GOELAMS. Ann Oncol.
23:1555–1561. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Periyasamy-Thandavan S, Jackson WH,
Samaddar JS, Erickson B, Barrett JR, Raney L, Gopal E, Ganapathy V,
Hill WD, Bhalla KN, et al: Bortezomib blocks the catabolic process
of autophagy via a cathepsin-dependent mechanism, affects
endoplasmic reticulum stress and induces caspase-dependent cell
death in antiestrogen-sensitive and resistant ER+ breast
cancer cells. Autophagy. 6:19–35. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lu Z and Hunter T: Ubiquitylation and
proteasomal degradation of the p21Cip1,
p27Kip1 and p57Kip2 CDK inhibitors. Cell
Cycle. 9:2342–2352. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhou Y, Yau C, Gray JW, Chew K, Dairkee
SH, Moore DH, Eppenberger U, Eppenberger-Castori S and Benz CC:
Enhanced NF kappa B and AP-1 transcriptional activity associated
with antiestrogen resistant breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 7:592007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
O'Regan RM, Osipo C, Ariazi E, Lee ES,
Meeke K, Morris C, Bertucci A, Sarker MA, Grigg R and Jordan VC:
Development and therapeutic options for the treatment of
raloxifene-stimulated breast cancer in athymic mice. Clin Cancer
Res. 12:2255–2263. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fox EM, Arteaga CL and Miller TW:
Abrogating endocrine resistance by targeting ERα and PI3K in breast
cancer. Front Oncol. 2:1452012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Shaw LE, Sadler AJ, Pugazhendhi D and
Darbre PD: Changes in oestrogen receptor-alpha and -beta during
progression to acquired resistance to tamoxifen and fulvestrant
(Faslodex, ICI 182,780) in MCF7 human breast cancer cells. J
Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 99:19–32. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|