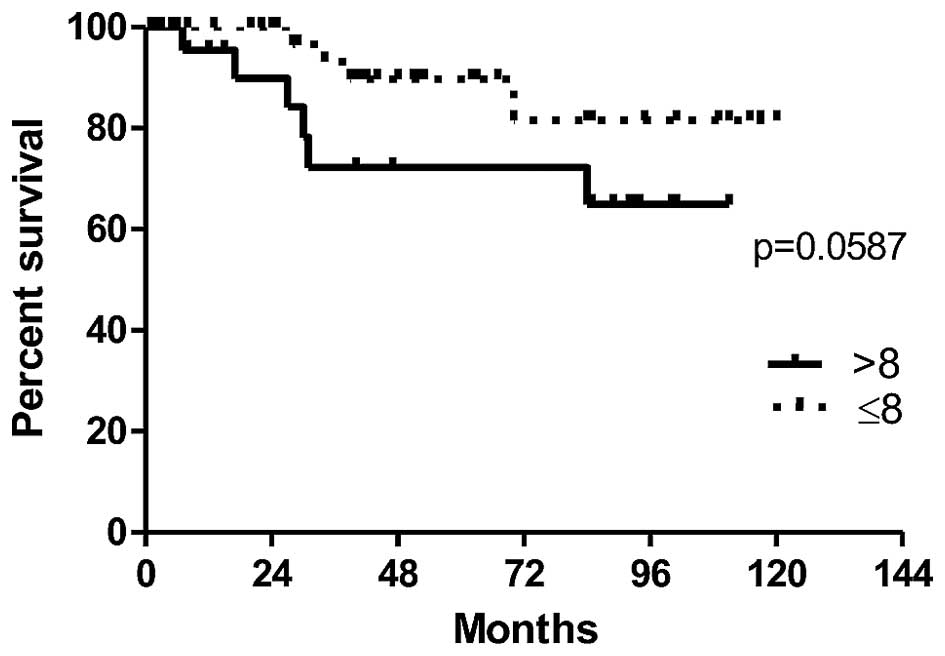
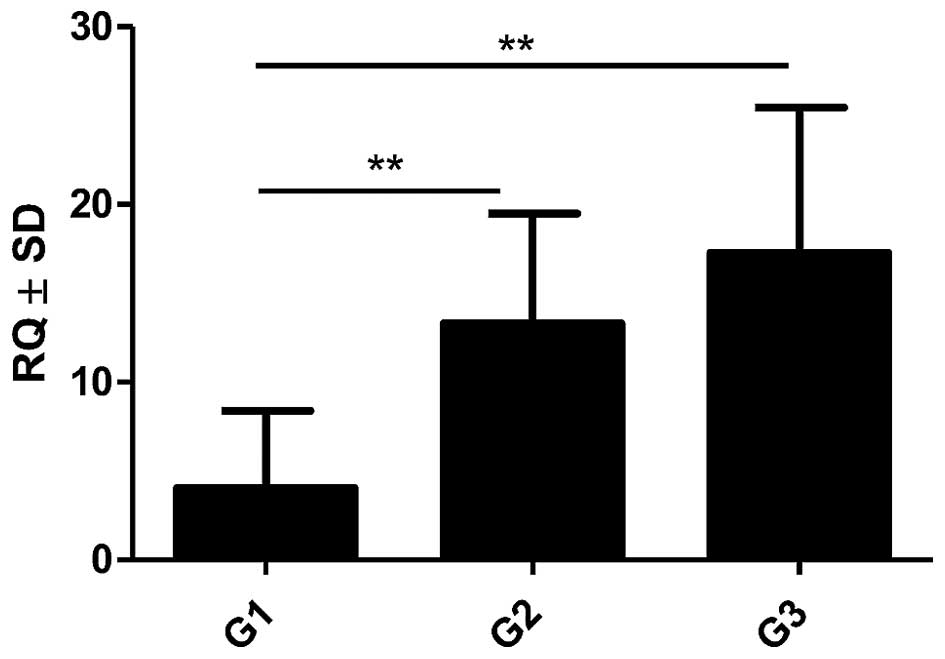
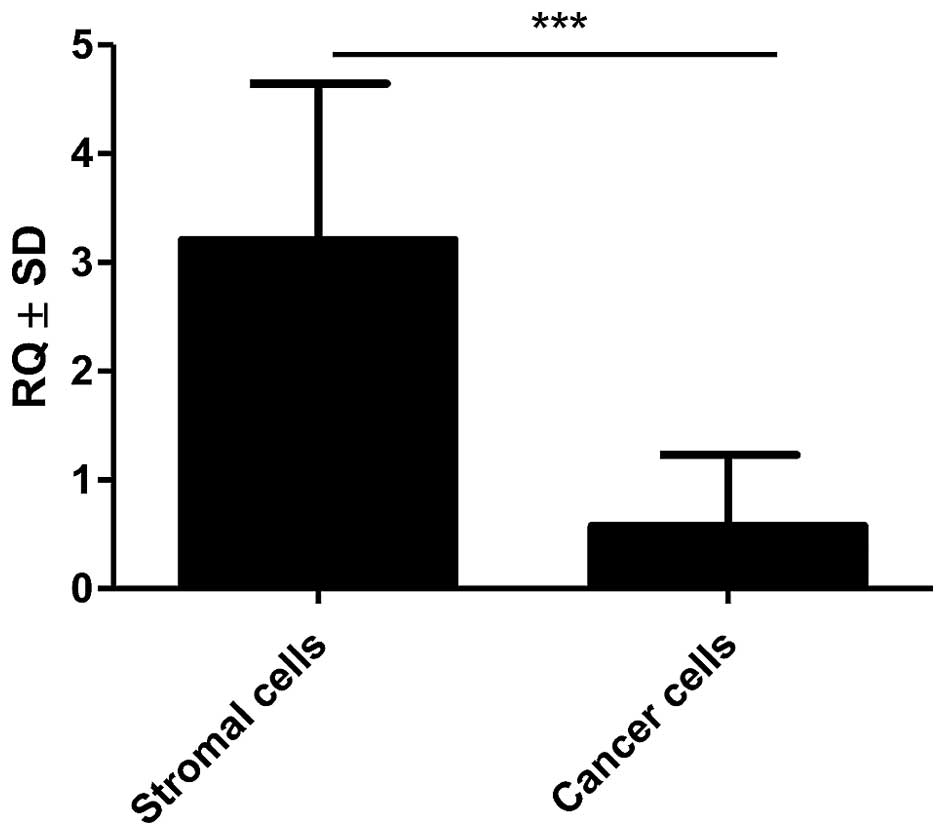
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Takeshita S, Kikuno R, Tezuka K and Amann
E: Osteoblast-specific factor 2: Cloning of a putative bone
adhesion protein with homology with the insect protein fasciclin I.
Biochem J. 294:271–278. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nuzzo PV, Buzzatti G, Ricci F, Rubagotti
A, Argellati F, Zinoli L and Boccardo F: Periostin: A novel
prognostic and therapeutic target for genitourinary cancer? Clin
Genitourin Cancer. 12:301–311. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ruan K, Bao S and Ouyang G: The
multifaceted role of periostin in tumorigenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci.
66:2219–2230. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Horiuchi K, Amizuka N, Takeshita S,
Takamatsu H, Katsuura M, Ozawa H, Toyama Y, Bonewald LF and Kudo A:
Identification and characterization of a novel protein, periostin,
with restricted expression to periosteum and periodontal ligament
and increased expression by transforming growth factor beta. J Bone
Miner Res. 14:1239–1249. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Morra L and Moch H: Periostin expression
and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer: A review and an
update. Virchows Arch. 459:465–475. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Norris RA, Damon B, Mironov V, Kasyanov V,
Ramamurthi A, Moreno-Rodriguez R, Trusk T, Potts JD, Goodwin RL,
Davis J, et al: Periostin regulates collagen fibrillogenesis and
the biomechanical properties of connective tissues. J Cell Biochem.
101:695–711. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hamilton DW: Functional role of periostin
in development and wound repair: Implications for connective tissue
disease. J Cell Commun Signal. 2:9–17. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kudo Y, Siriwardena BS, Hatano H, Ogawa I
and Takata T: Periostin: Novel diagnostic and therapeutic target
for cancer. Histol Histopathol. 22:1167–1174. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Michaylira CZ, Wong GS, Miller CG,
Gutierrez CM, Nakagawa H, Hammond R, Klein-Szanto AJ, Lee JS, Kim
SB, Herlyn M, et al: Periostin, a cell adhesion molecule,
facilitates invasion in the tumor microenvironment and annotates a
novel tumor-invasive signature in esophageal cancer. Cancer Res.
70:5281–5292. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ratajczak-Wielgomas K and Dziegiel P: The
role of periostin in neoplastic processes. Folia Histochem
Cytobiol. 53:120–132. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Franco OE, Shaw AK, Strand DW and Hayward
SW: Cancer associated fibroblasts in cancer pathogenesis. Semin
Cell Dev Biol. 21:33–39. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Pennacchietti S, Michieli P, Galluzzo M,
Mazzone M, Giordano S and Comoglio PM: Hypoxia promotes invasive
growth by transcriptional activation of the met protooncogene.
Cancer Cell. 3:347–361. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim HM, Jung WH and Koo JS: Expression of
cancer-associated fibroblast related proteins in metastatic breast
cancer: An immunohistochemical analysis. J Transl Med. 13:2222015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Puglisi F, Puppin C, Pegolo E, Andreetta
C, Pascoletti G, D'Aurizio F, Pandolfi M, Fasola G, Piga A, Damante
G, et al: Expression of periostin in human breast cancer. J Clin
Pathol. 61:494–498. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang Y, Zhang G, Li J, Tao Q and Tang W:
The expression analysis of periostin in human breast cancer. J Surg
Res. 160:102–106. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Xu D, Xu H, Ren Y, Liu C, Wang X, Zhang H
and Lu P: Cancer stem cell-related gene periostin: A novel
prognostic marker for breast cancer. PLoS One. 7:e466702012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nuzzo PV, Rubagotti A, Zinoli L, Salvi S,
Boccardo S and Boccardo F: The prognostic value of stromal and
epithelial periostin expression in human breast cancer: Correlation
with clinical pathological features and mortality outcome. BMC
Cancer. 16:952016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sasaki H, Dai M, Auclair D, Fukai I,
Kiriyama M, Yamakawa Y, Fujii Y and Chen LB: Serum level of the
periostin, a homologue of an insect cell adhesion molecule, as a
prognostic marker in nonsmall cell lung carcinomas. Cancer.
92:843–848. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Morra L, Rechsteiner M, Casagrande S, von
Teichman A, Schraml P, Moch H and Soltermann A: Characterization of
periostin isoform pattern in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung
Cancer. 76:183–190. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hong LZ, Wei XW, Chen JF and Shi Y:
Overexpression of periostin predicts poor prognosis in non-small
cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 6:1595–1603. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kikuchi Y, Kunita A, Iwata C, Komura D,
Nishiyama T, Shimazu K, Takeshita K, Shibahara J, Kii I, Morishita
Y, et al: The niche component periostin is produced by
cancer-associated fibroblasts, supporting growth of gastric cancer
through ERK activation. Am J Pathol. 184:859–870. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lv H, Liu R, Fu J, Yang Q, Shi J, Chen P,
Ji M, Shi B and Hou P: Epithelial cell-derived periostin functions
as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer through stabilizing p53 and
E-cadherin proteins via the Rb/E2F1/p14ARF/Mdm2 signaling pathway.
Cell Cycle. 13:2962–2974. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li B, Wang L and Chi B: Upregulation of
periostin prevents P53-mediated apoptosis in SGC-7901 gastric
cancer cells. Mol Biol Rep. 40:1677–1683. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liu Y and Liu BA: Enhanced proliferation,
invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of
nicotine-promoted gastric cancer by periostin. World J
Gastroenterol. 17:2674–2680. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tai IT, Dai M and Chen LB: Periostin
induction in tumor cell line explants and inhibition of in vitro
cell growth by anti-periostin antibodies. Carcinogenesis.
26:908–915. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bao S, Ouyang G, Bai X, Huang Z, Ma C, Liu
M, Shao R, Anderson RM, Rich JN and Wang XF: Periostin potently
promotes metastatic growth of colon cancer by augmenting cell
survival via the Akt/PKB pathway. Cancer Cell. 5:329–339. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xiao ZM, Wang XY and Wang AM: Periostin
induces chemoresistance in colon cancer cells through activation of
the PI3K/Akt/survivin pathway. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 62:401–406.
2015. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhu M, Fejzo MS, Anderson L, Dering J,
Ginther C, Ramos L, Gasson JC, Karlan BY and Slamon DJ: Periostin
promotes ovarian cancer angiogenesis and metastasis. Gynecol Oncol.
119:337–344. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhu M, Saxton RE, Ramos L, Chang DD,
Karlan BY, Gasson JC and Slamon DJ: Neutralizing monoclonal
antibody to periostin inhibits ovarian tumor growth and metastasis.
Mol Cancer Ther. 10:1500–1508. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Choi KU, Yun JS, Lee IH, Heo SC, Shin SH,
Jeon ES, Choi YJ, Suh DS, Yoon MS and Kim JH: Lysophosphatidic
acid-induced expression of periostin in stromal cells: Prognostic
relevance of periostin expression in epithelial ovarian cancer. Int
J Cancer. 128:332–342. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Tian Y, Choi CH, Li QK, Rahmatpanah FB,
Chen X, Kim SR, Veltri R, Chia D, Zhang Z, Mercola D, et al:
Correction: Overexpression of periostin in stroma positively
associated with aggressive prostate cancer. PLoS One.
10:e01303332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nuzzo PV, Rubagotti A, Zinoli L, Ricci F,
Salvi S, Boccardo S and Boccardo F: Prognostic value of stromal and
epithelial periostin expression in human prostate cancer:
Correlation with clinical pathological features and the risk of
biochemical relapse or death. BMC Cancer. 12:6252012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Chen J, Xi J, Tian Y, Bova GS and Zhang H:
Identification, prioritization, and evaluation of glycoproteins for
aggressive prostate cancer using quantitative glycoproteomics and
antibody-based assays on tissue specimens. Proteomics.
13:2268–2277. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhou W, Ke SQ, Huang Z, Flavahan W, Fang
X, Paul J, Wu L, Sloan AE, McLendon RE, Li X, et al: Periostin
secreted by glioblastoma stem cells recruits M2 tumour-associated
macrophages and promotes malignant growth. Nat Cell Biol.
17:170–182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mikheev AM, Mikheeva SA, Trister AD,
Tokita MJ, Emerson SN, Parada CA, Born DE, Carnemolla B, Frankel S,
Kim DH, et al: Periostin is a novel therapeutic target that
predicts and regulates glioma malignancy. Neuro Oncol. 17:372–382.
2015.
|
|
37
|
Tian B, Zhang Y and Zhang J: Periostin is
a new potential prognostic biomarker for glioma. Tumour Biol.
35:5877–5883. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tavassoli FA, Ortiz-Hidalgo C,
Baquera-Heredia J and Grassi P: Images in pathology: The hearts of
a breast pathologist, a hematopathologist, and of a
cytotechnologist. Int J Surg Pathol. 10:2952002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Remmele W and Stegner HE: Recommendation
for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for
immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast
cancer tissue. Pathologe. 8:138–140. 1987.In German. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mueller-Holzner E, Fink V, Frede T and
Marth C: Immunohistochemical determination of HER2 expression in
breast cancer from core biopsy specimens: A reliable predictor of
HER2 status of the whole tumor. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 69:13–19.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Hugo H, Ackland ML, Blick T, Lawrence MG,
Clements JA, Williams ED and Thompson EW: Epithelial-mesenchymal
and mesenchymal-epithelial transitions in carcinoma progression. J
Cell Physiol. 213:374–383. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Guarino M: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and tumour invasion. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
39:2153–2160. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Baril P, Gangeswaran R, Mahon PC, Caulee
K, Kocher HM, Harada T, Zhu M, Kalthoff H, Crnogorac-Jurcevic T and
Lemoine NR: Periostin promotes invasiveness and resistance of
pancreatic cancer cells to hypoxia-induced cell death: Role of the
beta4 integrin and the PI3k pathway. Oncogene. 26:2082–2094. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Gillan L, Matei D, Fishman DA, Gerbin CS,
Karlan BY and Chang DD: Periostin secreted by epithelial ovarian
carcinoma is a ligand for alpha(V)beta(3) and alpha(V)beta(5)
integrins and promotes cell motility. Cancer Res. 62:5358–5364.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Siriwardena BS, Kudo Y, Ogawa I, Kitagawa
M, Kitajima S, Hatano H, Tilakaratne WM, Miyauchi M and Takata T:
Periostin is frequently overexpressed and enhances invasion and
angiogenesis in oral cancer. Br J Cancer. 95:1396–1403. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shao R, Bao S, Bai X, Blanchette C,
Anderson RM, Dang T, Gishizky ML, Marks JR and Wang XF: Acquired
expression of periostin by human breast cancers promotes tumor
angiogenesis through up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth
factor receptor 2 expression. Mol Cell Biol. 24:3992–4003. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kudo Y, Ogawa I, Kitajima S, Kitagawa M,
Kawai H, Gaffney PM, Miyauchi M and Takata T: Periostin promotes
invasion and anchorage-independent growth in the metastatic process
of head and neck cancer. Cancer Res. 66:6928–6935. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Pula B, Jethon A, Piotrowska A,
Gomulkiewicz A, Owczarek T, Calik J, Wojnar A, Witkiewicz W, Rys J,
Ugorski M, et al: Podoplanin expression by cancer-associated
fibroblasts predicts poor outcome in invasive ductal breast
carcinoma. Histopathology. 59:1249–1260. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kikuchi Y, Kashima TG, Nishiyama T,
Shimazu K, Morishita Y, Shimazaki M, Kii I, Horie H, Nagai H, Kudo
A, et al: Periostin is expressed in pericryptal fibroblasts and
cancer-associated fibroblasts in the colon. J Histochem Cytochem.
56:753–764. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Underwood TJ, Hayden AL, Derouet M, Garcia
E, Noble F, White MJ, Thirdborough S, Mead A, Clemons N, Mellone M,
et al: Cancer-associated fibroblasts predict poor outcome and
promote periostin-dependent invasion in oesophageal adenocarcinoma.
J Pathol. 235:466–477. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
51
|
Ryner L, Guan Y, Firestein R, Xiao Y, Choi
Y, Rabe C, Lu S, Fuentes E, Huw LY, Lackner MR, et al: Upregulation
of periostin and reactive stroma is associated with primary
chemoresistance and predicts clinical outcomes in epithelial
ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21:2941–2951. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li M, Li C, Li D, Xie Y, Shi J, Li G, Guan
Y, Li M, Zhang P, Peng F, et al: Periostin, a stroma-associated
protein, correlates with tumor invasiveness and progression in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis. 29:865–877. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Reddy LA, Mikesh L, Moskulak C, Harvey J,
Sherman N, Zigrino P, Mauch C and Fox JW: Host response to human
breast Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC) as observed by changes in
the stromal proteome. J Proteome Res. 13:4739–4751. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ishiba T, Nagahara M, Nakagawa T, Sato T,
Ishikawa T, Uetake H, Sugihara K, Miki Y and Nakanishi A: Periostin
suppression induces decorin secretion leading to reduced breast
cancer cell motility and invasion. Sci Rep. 4:70692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yamaguchi Y, Mann DM and Ruoslahti E:
Negative regulation of transforming growth factor-beta by the
proteoglycan decorin. Nature. 346:281–284. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bi X, Pohl NM, Qian Z, Yang GR, Gou Y,
Guzman G, Kajdacsy-Balla A, Iozzo RV and Yang W: Decorin-mediated
inhibition of colorectal cancer growth and migration is associated
with E-cadherin in vitro and in mice. Carcinogenesis. 33:326–330.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
57
|
Ben QW, Jin XL, Liu J, Cai X, Yuan F and
Yuan YZ: Periostin, a matrix specific protein, is associated with
proliferation and invasion of pancreatic cancer. Oncol Rep.
25:709–716. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|