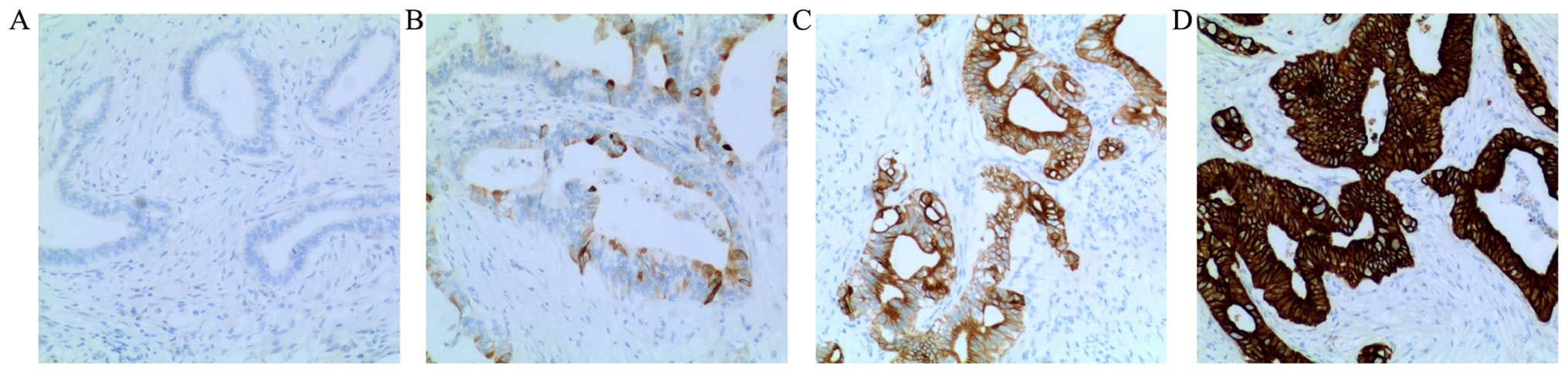
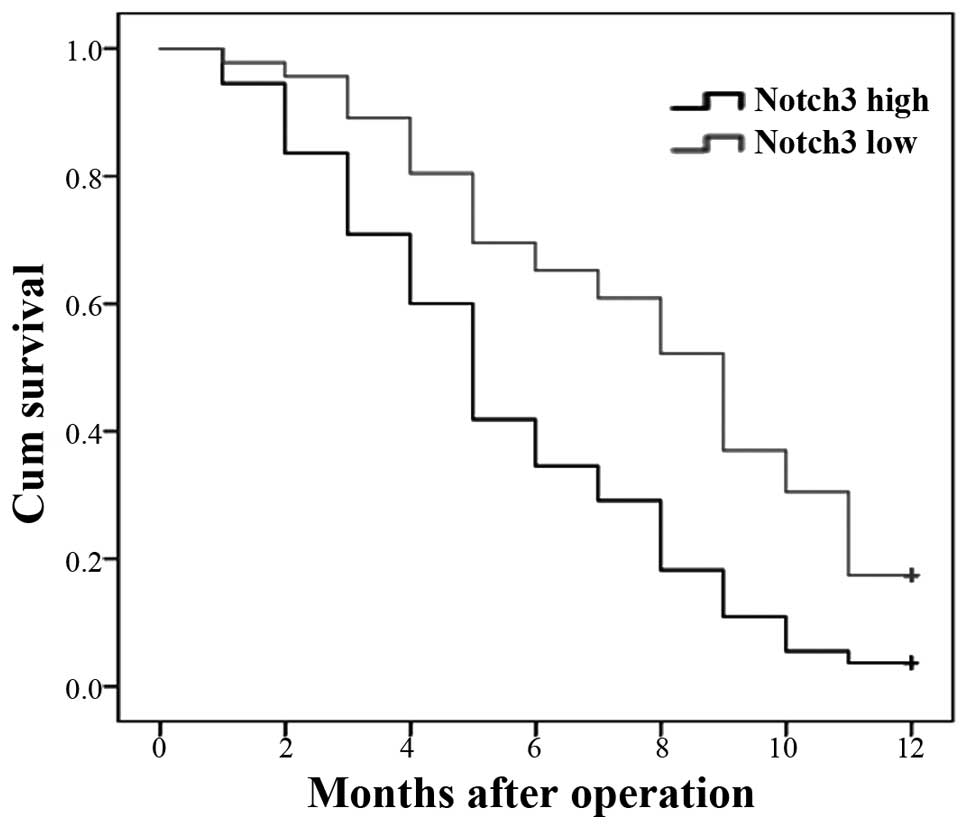
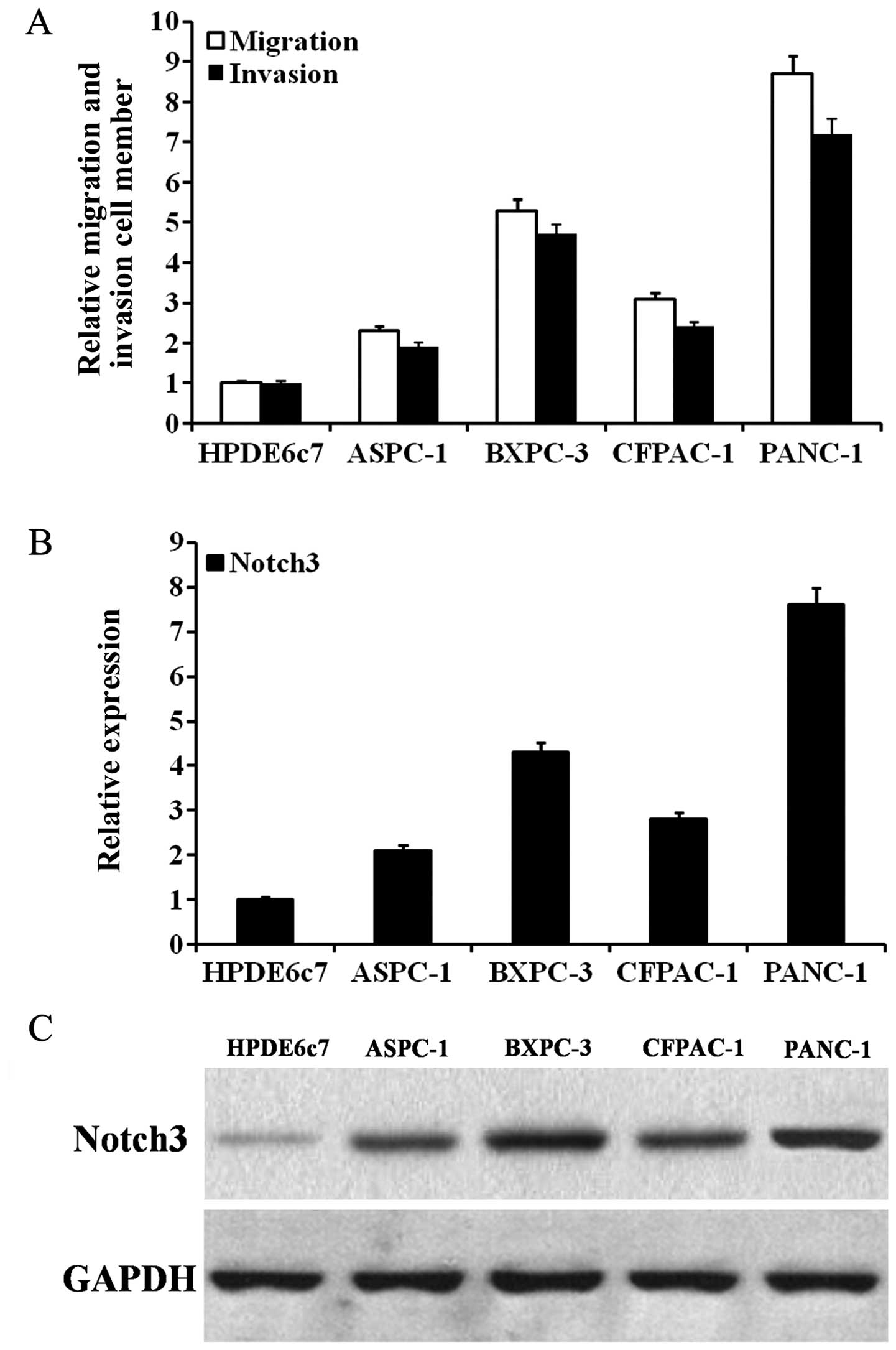
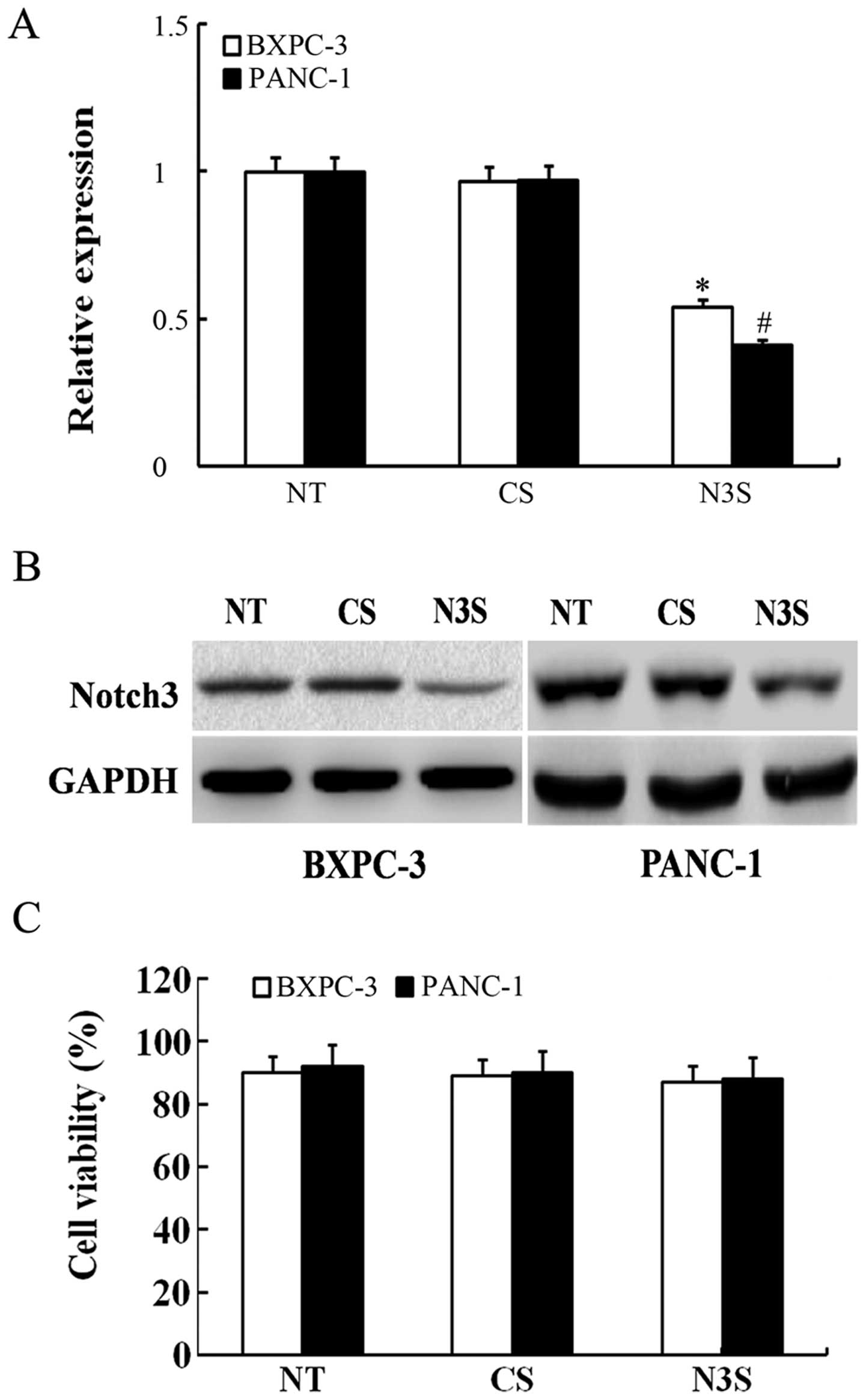
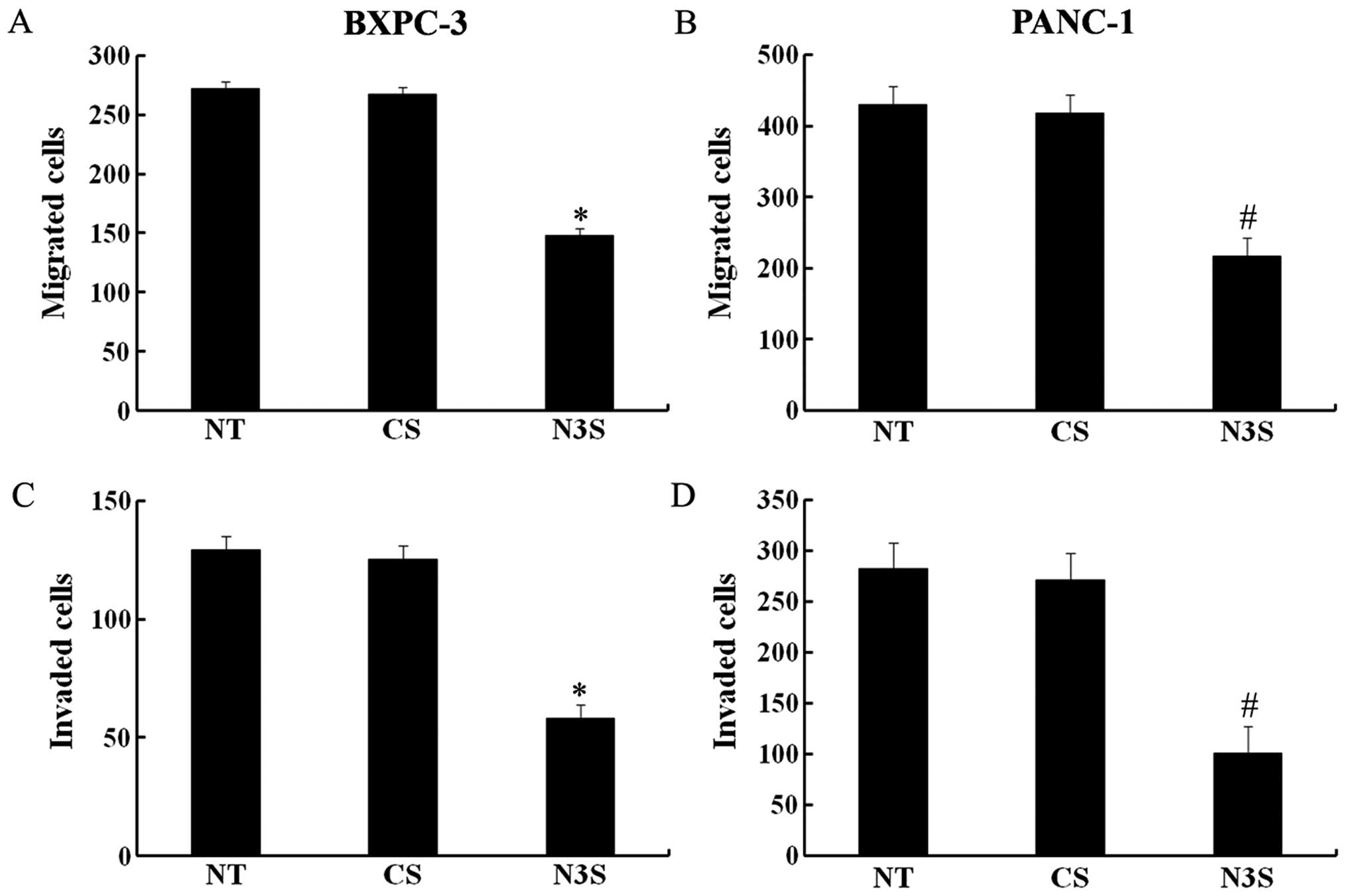
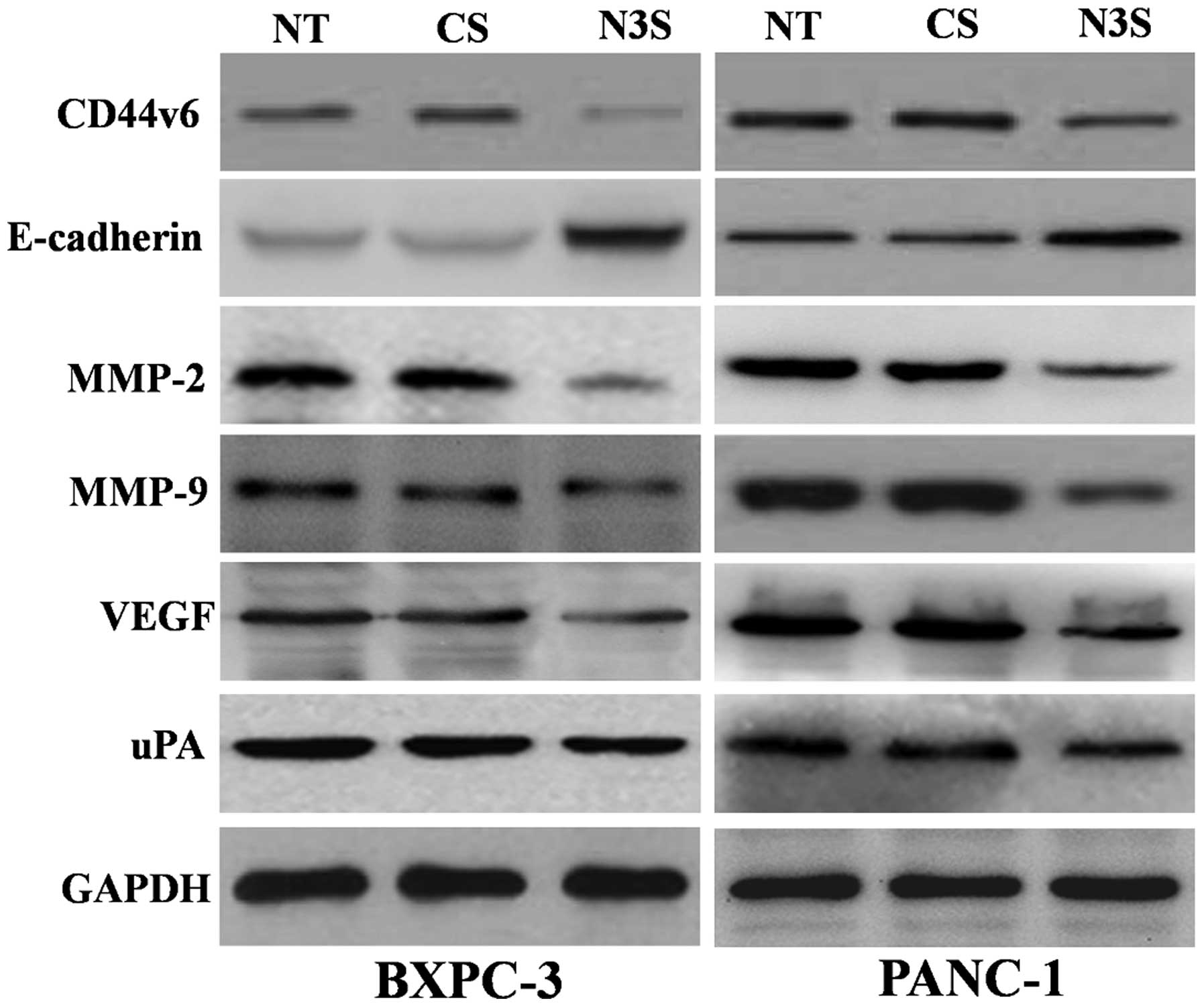
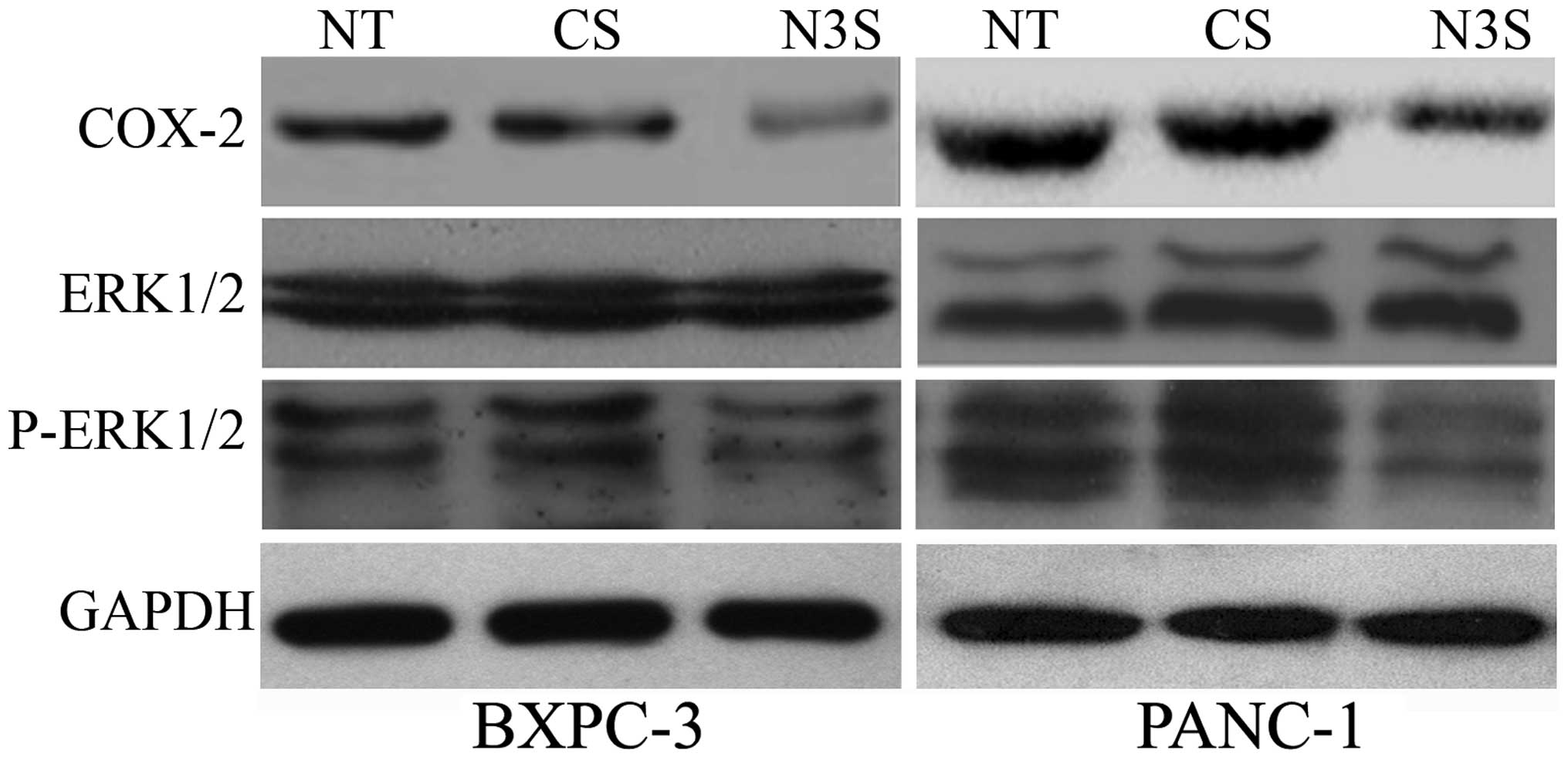
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vincent A, Herman J, Schulick R, Hruban RH
and Goggins M: Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 378:607–620. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hidalgo M: Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J
Med. 362:1605–1617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stathis A and Moore MJ: Advanced
pancreatic carcinoma: Current treatment and future challenges. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 7:163–172. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD and Lake RJ:
Notch signaling: Cell fate control and signal integration in
development. Science. 284:770–776. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Miele L and Osborne B: Arbiter of
differentiation and death: Notch signaling meets apoptosis. J Cell
Physiol. 181:393–409. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ohishi K, Katayama N, Shiku H,
Varnum-Finney B and Bernstein ID: Notch signalling in
hematopoiesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 14:143–150. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
You L, Chen G and Zhao YP: Core signaling
pathways and new therapeutic targets in pancreatic cancer. Chin Med
J. 123:1210–1215. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
De La O JP and Murtaugh LC: Notch
signaling: Where pancreatic cancer and differentiation meet?
Gastroenterology. 136:1499–1502. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Z, Li Y and Sarkar FH: Notch
signaling proteins: Legitimate targets for cancer therapy. Curr
Protein Pept Sci. 11:398–408. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Z, Zhang Y, Li Y, Banerjee S, Liao J
and Sarkar FH: Down-regulation of Notch-1 contributes to cell
growth inhibition and apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 5:483–493. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang Z, Banerjee S, Li Y, Rahman KM, Zhang
Y and Sarkar FH: Down-regulation of notch-1 inhibits invasion by
inactivation of nuclear factor-kappaB, vascular endothelial growth
factor, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in pancreatic cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 66:2778–2784. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Plentz R, Park JS, Rhim AD, Abravanel D,
Hezel AF, Sharma SV, Gurumurthy S, Deshpande V, Kenific C,
Settleman J, et al: Inhibition of gamma-secretase activity inhibits
tumor progression in a mouse model of pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. 136:1741–1749.e6. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ristorcelli E and Lombardo D: Targeting
Notch signaling in pancreatic cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
14:541–552. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hanlon L, Avila JL, Demarest RM, Troutman
S, Allen M, Ratti F, Rustgi AK, Stanger BZ, Radtke F, Adsay V, et
al: Notch1 functions as a tumor suppressor in a model of
K-ras-induced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res.
70:4280–4286. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chu D, Li Y, Wang W, Zhao Q, Li J, Lu Y,
Li M, Dong G, Zhang H, Xie H, et al: High level of Notch1 protein
is associated with poor overall survival in colorectal cancer. Ann
Surg Oncol. 17:1337–1342. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Egan SE, St-Pierre B and Leow CC: Notch
receptors, partners and regulators: From conserved domains to
powerful functions. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 228:273–324.
1998.
|
|
18
|
Callahan R and Egan SE: Notch signaling in
mammary development and oncogenesis. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 9:145–163. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mazur PK, Einwächter H, Lee M, Sipos B,
Nakhai H, Rad R, Zimber-Strobl U, Strobl LJ, Radtke F, Klöppel G,
et al: Notch2 is required for progression of pancreatic
intraepithelial neoplasia and development of pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:13438–13443. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yao J and Qian C: Inhibition of Notch3
enhances sensitivity to gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer through an
inactivation of PI3K/Akt-dependent pathway. Med Oncol.
27:1017–1022. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Mullendore ME, Koorstra JB, Li YM,
Offerhaus GJ, Fan X, Henderson CM, Matsui W, Eberhart CG, Maitra A
and Feldmann G: Ligand-dependent Notch signaling is involved in
tumor initiation and tumor maintenance in pancreatic cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:2291–2301. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Doucas H, Mann CD, Sutton CD, Garcea G,
Neal CP, Berry DP and Manson MM: Expression of nuclear Notch3 in
pancreatic adenocarcinomas is associated with adverse clinical
features, and correlates with the expression of STAT3 and
phosphorylated Akt. J Surg Oncol. 97:63–68. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mann CD, Bastianpillai C, Neal CP, Masood
MM, Jones DJ, Teichert F, Singh R, Karpova E, Berry DP and Manson
MM: Notch3 and HEY-1 as prognostic biomarkers in pancreatic
adenocarcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e511192012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gramantieri L, Giovannini C, Lanzi A,
Chieco P, Ravaioli M, Venturi A, Grazi GL and Bolondi L: Aberrant
Notch3 and Notch4 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Liver Int. 27:997–1007. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hu L, Xue F, Shao M, Deng A and Wei G:
Aberrant expression of Notch3 predicts poor survival for
hepatocellular carcinomas. Biosci Trends. 7:152–156.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Günthert U, Hofmann M, Rudy W, Reber S,
Zöller M, Haussmann I, Matzku S, Wenzel A, Ponta H and Herrlich P:
A new variant of glycoprotein CD44 confers metastatic potential to
rat carcinoma cells. Cell. 65:13–24. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jijiwa M, Demir H, Gupta S, Leung C, Joshi
K, Orozco N, Huang T, Yildiz VO, Shibahara I, de Jesus JA, et al:
CD44v6 regulates growth of brain tumor stem cells partially through
the AKT-mediated pathway. PLoS One. 6:e242172011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu YJ, Yan PS, Li J and Jia JF:
Expression and significance of CD44s, CD44v6, and nm23 mRNA in
human cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 11:6601–6606. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kemler R: From cadherins to catenins:
Cytoplasmic protein interactions and regulation of cell adhesion.
Trends Genet. 9:317–321. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bremnes RM, Veve R, Gabrielson E, Hirsch
FR, Baron A, Bemis L, Gemmill RM, Drabkin HA and Franklin WA:
High-throughput tissue microarray analysis used to evaluate biology
and prognostic significance of the E-cadherin pathway in
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 20:2417–2428. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tsujii M and DuBois RN: Alterations in
cellular adhesion and apoptosis in epithelial cells overexpressing
prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase 2. Cell. 83:493–501. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu D, Huang C, Kameyama K, Hayashi E,
Yamauchi A, Kobayashi S and Yokomise: E-cadherin expression
associated with differentiation and prognosis in patients with
non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 71:949–954. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wells A, Yates C and Shepard CR:
E-cadherin as an indicator of mesenchymal to epithelial reverting
transitions during the metastatic seeding of disseminated
carcinomas. Clin Exp Metastasis. 25:621–628. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dohadwala M, Batra RK, Luo J, Lin Y,
Krysan K, Pold M, Sharma S and Dubinett SM: Autocrine/paracrine
prostaglandin E2 production by non-small cell lung cancer cells
regulates matrix metalloproteinase-2 and CD44 in
cyclooxygenase-2-dependent invasion. J Biol Chem. 277:50828–50833.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dohadwala M, Yang SC, Luo J, Sharma S,
Batra RK, Huang M, Lin Y, Goodglick L, Krysan K, Fishbein MC, et
al: Cyclooxygenase-2-dependent regulation of E-cadherin:
Prostaglandin E2 induces transcriptional repressors ZEB1
and snail in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 66:5338–5345.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dubinett SM, Sharma S, Huang M, Dohadwala
M, Pold M and Mao JT: Cyclooxygenase-2 in lung cancer. Prog Exp
Tumor Res. 37:138–162. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dannenberg AJ and Subbaramaiah K:
Targeting cyclooxy-genase-2 in human neoplasia: Rationale and
promise. Cancer Cell. 4:431–436. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Park K, Han S, Shin E, Kim HJ and Kim JY:
Cox-2 expression on tissue microarray of breast cancer. Eur J Surg
Oncol. 32:1093–1096. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yeh TS, Wu CW, Hsu KW, Liao WJ, Yang MC,
Li AF, Wang AM, Kuo ML and Chi CW: The activated Notch1 signal
pathway is associated with gastric cancer progression through
cyclooxy-genase-2. Cancer Res. 69:5039–5048. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Itoh Y and Nagase H: Matrix
metalloproteinases in cancer. Essays Biochem. 38:21–36. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zeng ZS, Cohen AM and Guillem JG: Loss of
basement membrane type IV collagen is associated with increased
expression of metalloproteinases 2 and 9 (MMP-2 and MMP-9) during
human colorectal tumorigenesis. Carcinogenesis. 20:749–755. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Komatsu K, Nakanishi Y, Nemoto N, Hori T,
Sawada T and Kobayashi M: Expression and quantitative analysis of
matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in human gliomas. Brain Tumor
Pathol. 21:105–112. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Shimizu M, Cohen B, Goldvasser P, Berman
H, Virtanen C and Reedijk M: Plasminogen activator uPA is a direct
transcriptional target of the JAG1-Notch receptor signaling pathway
in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 71:277–286. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wey JS, Fan F, Gray MJ, Bauer TW, McCarty
MF, Somcio R, Liu W, Evans DB, Wu Y, Hicklin DJ, et al: Vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor-1 promotes migration and
invasion in pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Cancer. 104:427–438.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Takahashi Y, Kitadai Y, Bucana CD, Cleary
KR and Ellis LM: Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor
and its receptor, KDR, correlates with vascularity, metastasis, and
proliferation of human colon cancer. Cancer Res. 55:3964–3968.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chan-Hui PY and Weaver R: Human
mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase mediates the
stress-induced activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase
cascades. Biochem J. 336:599–609. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Trusolino L and Comoglio PM:
Scatter-factor and semaphorin receptors: Cell signalling for
invasive growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:289–300. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Arai K, Lee SR and Lo EH: Essential role
for ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase in matrix
metalloproteinase-9 regulation in rat cortical astrocytes. Glia.
43:254–264. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cheng YC, Chen LM, Chang MH, Chen WK, Tsai
FJ, Tsai CH, Lai TY, Kuo WW, Huang CY and Liu CJ:
Lipopolysaccharide upregulates uPA, MMP-2 and MMP-9 via ERK1/2
signaling in H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells. Mol Cell Biochem.
325:15–23. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|