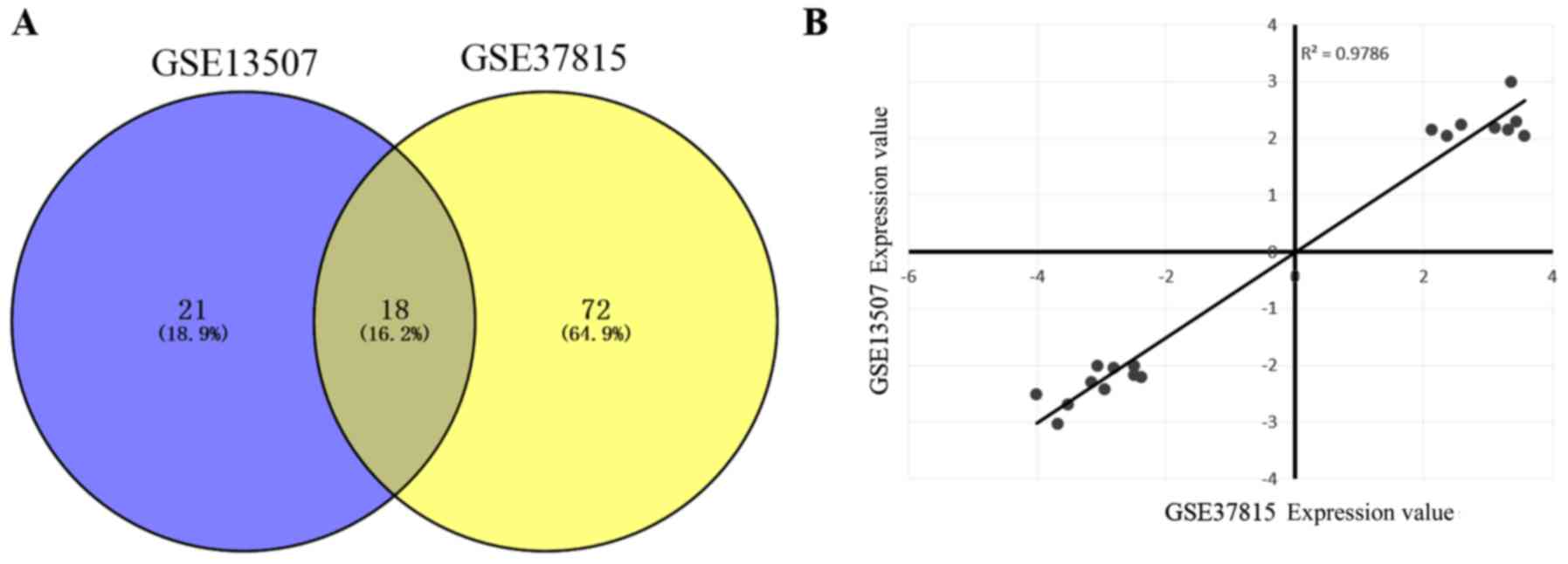
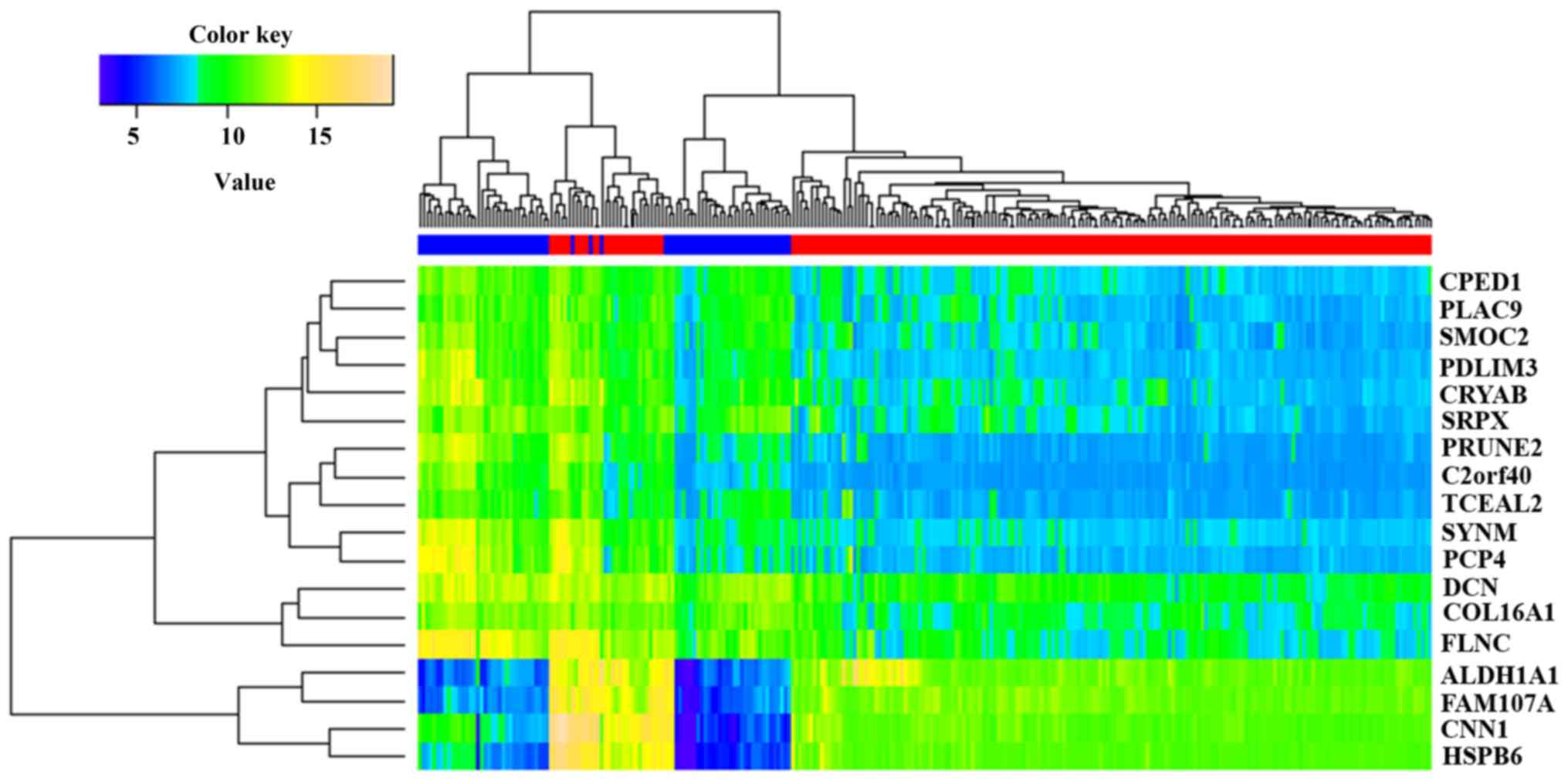
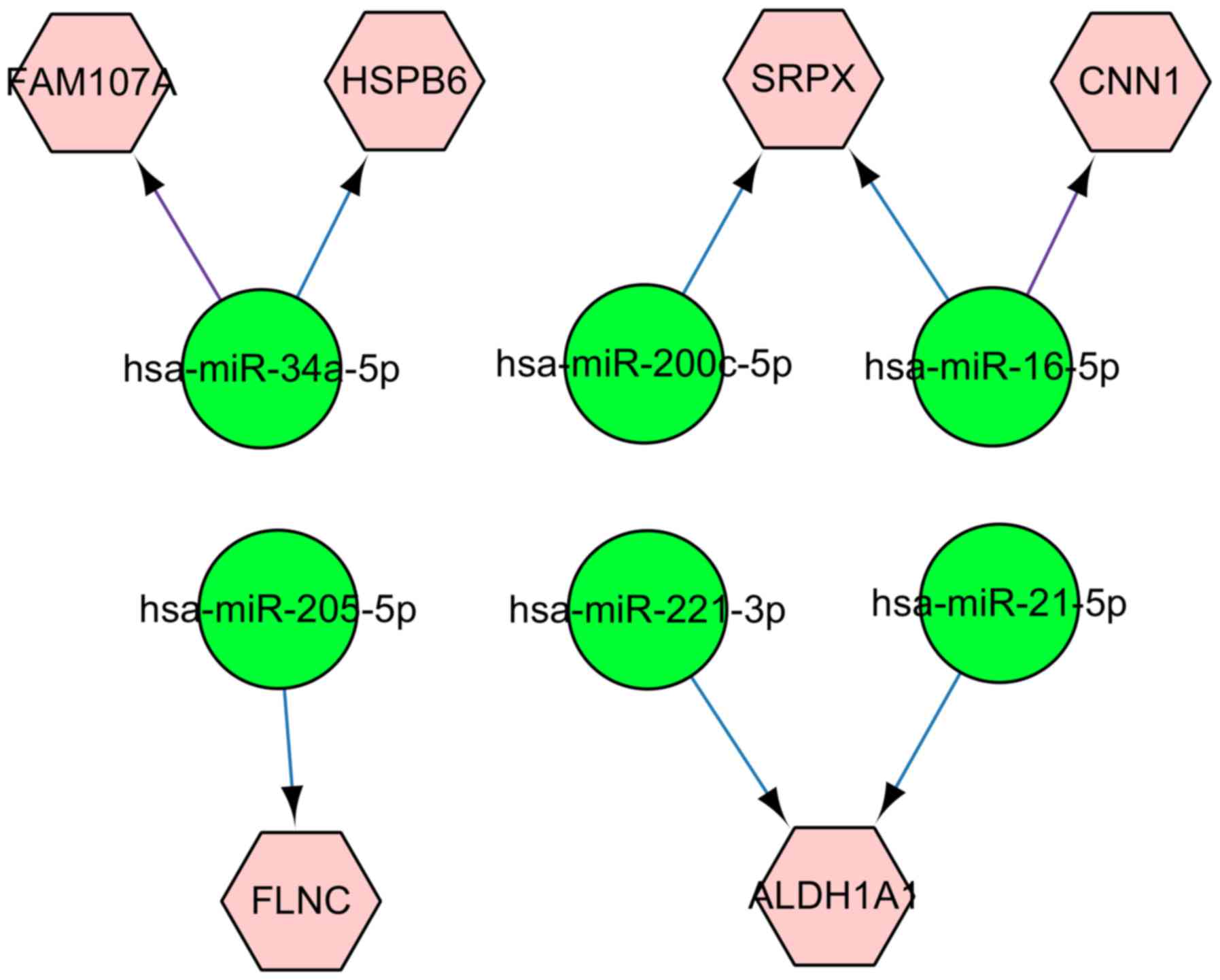
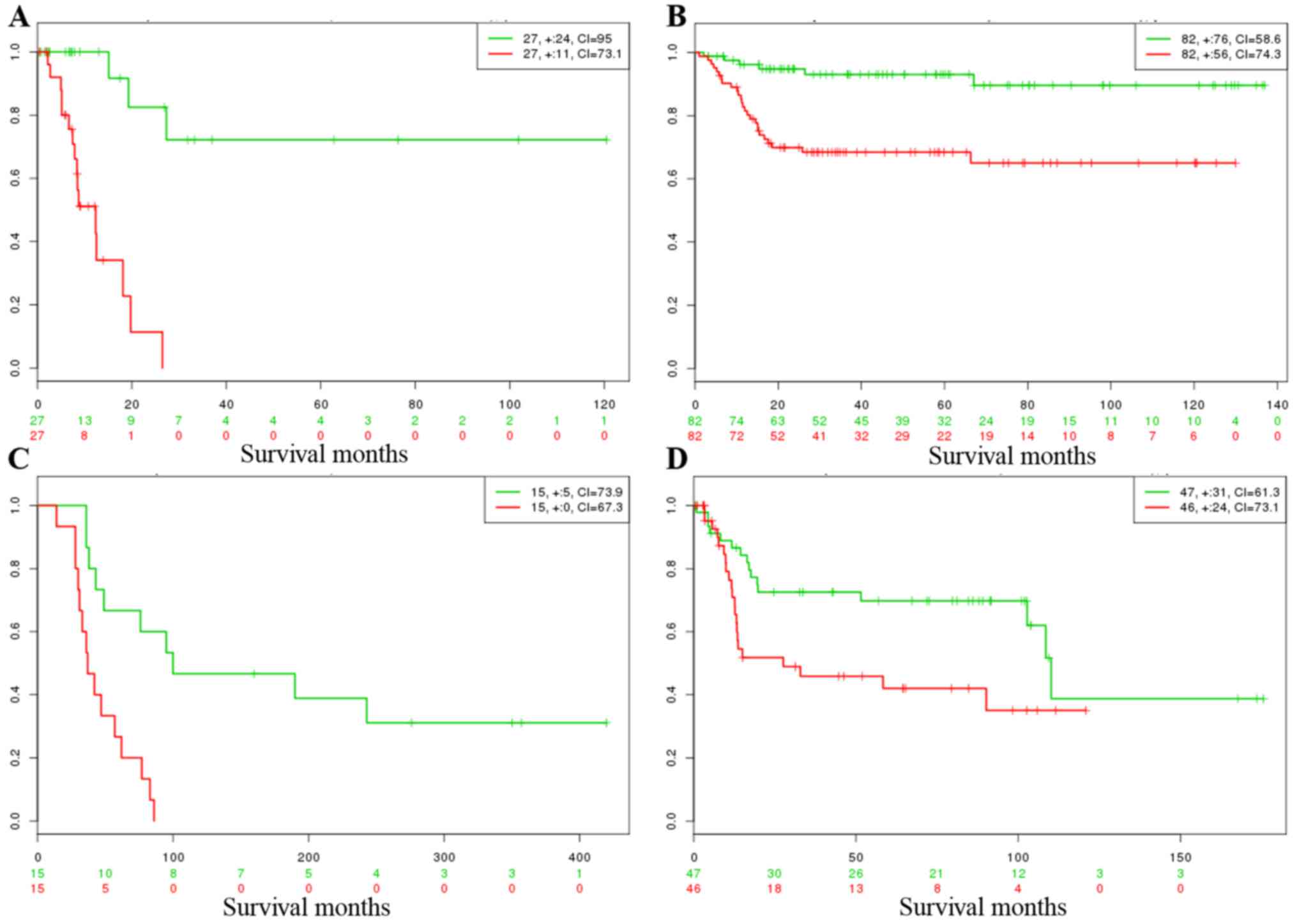
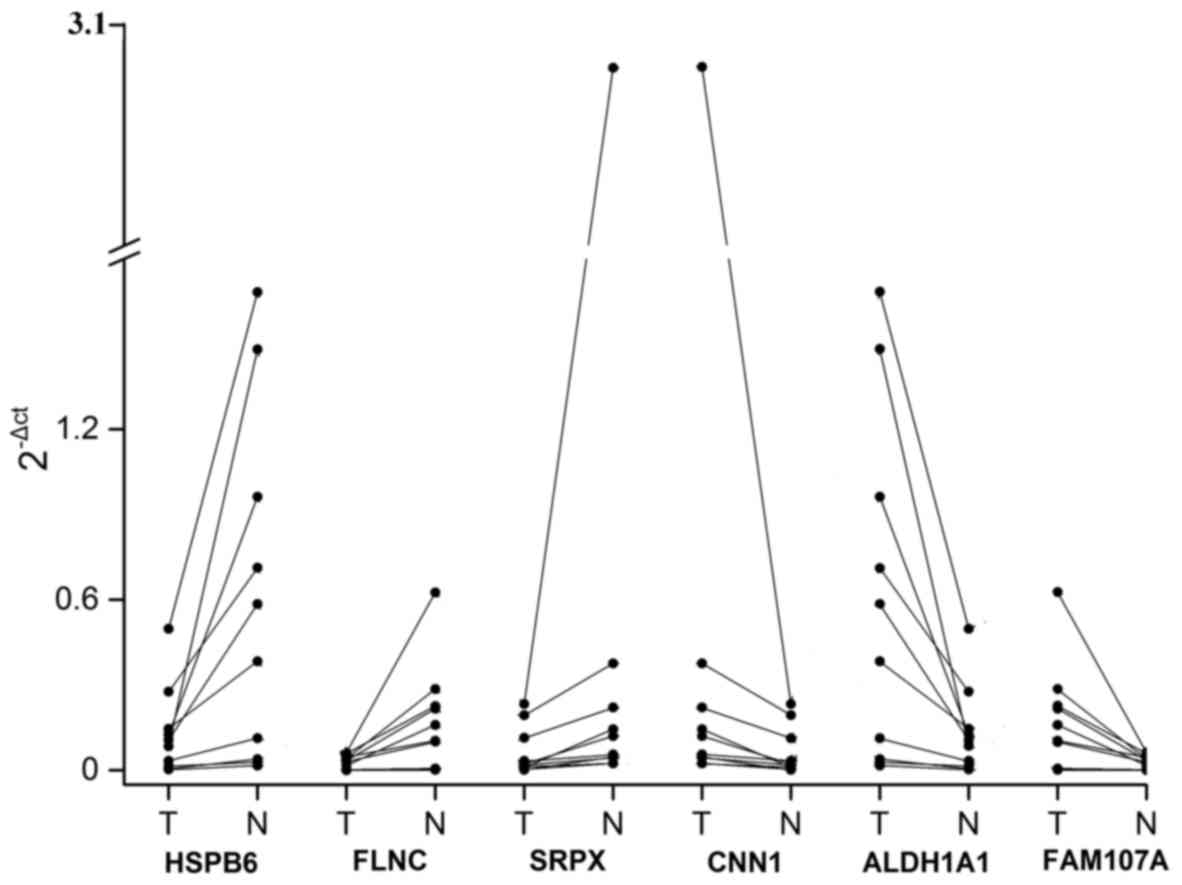
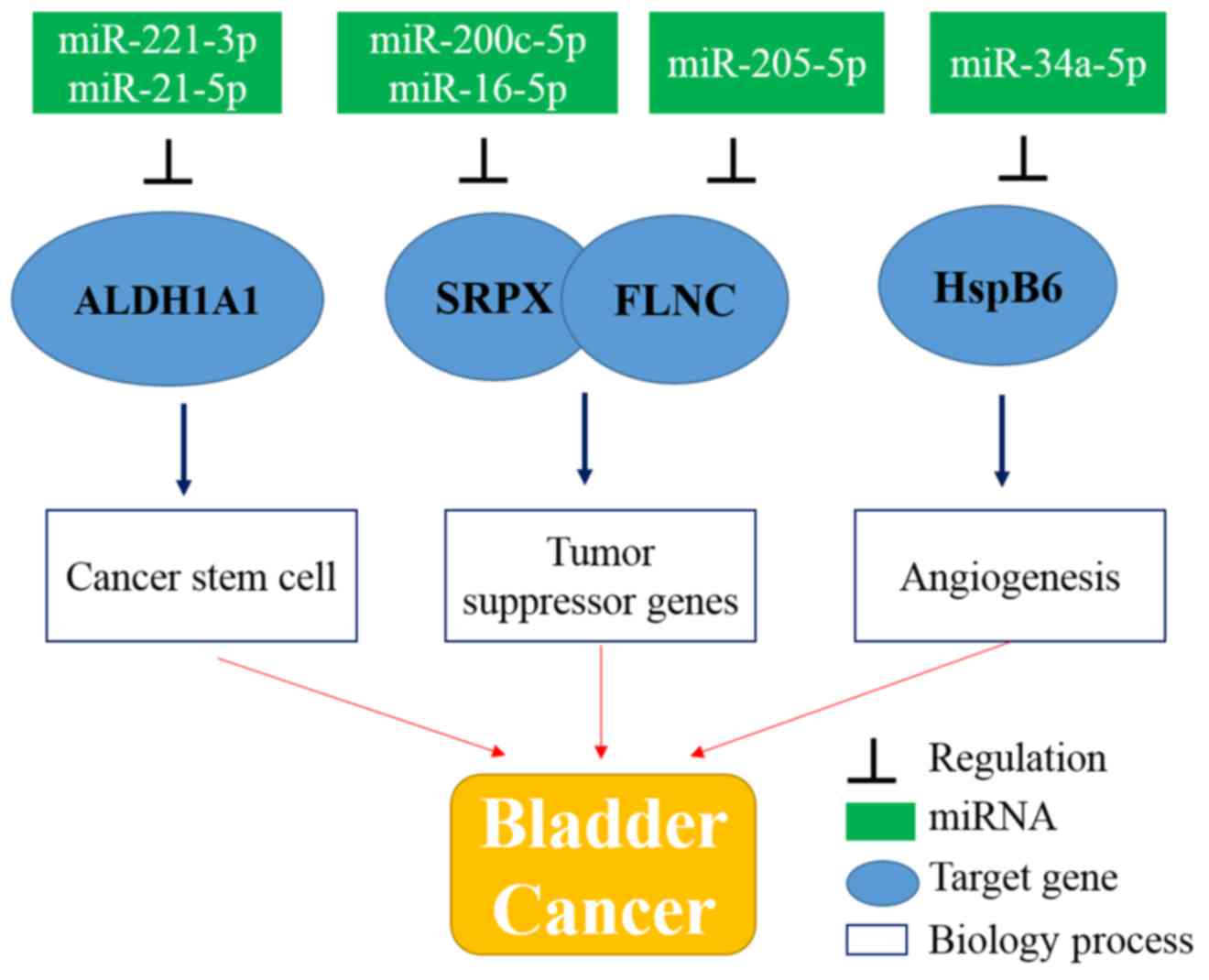
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S,
Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, et
al: Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20
age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the Global
Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 380:2095–2128. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
National Cancer Institute Surveillance, .
Epidemiology, and End Results Program: SEER stat fact sheets.
Bladder Cancer; 2014, http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/urinb.html
|
|
4
|
Knowles MA and Hurst CD: Molecular biology
of bladder cancer: New insights into pathogenesis and clinical
diversity. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:25–41. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network:
Comprehensive molecular characterization of urothelial bladder
carcinoma. Nature. 507:315–322. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Berger B, Peng J and Singh M:
Computational solutions for omics data. Nat Rev Genet. 14:333–346.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim WJ, Kim EJ, Kim SK, Kim YJ, Ha YS,
Jeong P, Kim MJ, Yun SJ, Lee KM, Moon SK, et al: Predictive value
of progression-related gene classifier in primary non-muscle
invasive bladder cancer. Mol Cancer. 9:32010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim YJ, Yoon HY, Kim JS, Kang HW, Min BD,
Kim SK, Ha YS, Kim IY, Ryu KH, Lee SC, et al: HOXA9, ISL1 and
ALDH1A3 methylation patterns as prognostic markers for nonmuscle
invasive bladder cancer: Array-based DNA methylation and expression
profiling. Int J Cancer. 133:1135–1142. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee JS, Leem SH, Lee SY, Kim SC, Park ES,
Kim SB, Kim SK, Kim YJ, Kim WJ and Chu IS: Expression signature of
E2F1 and its associated genes predict superficial to invasive
progression of bladder tumors. J Clin Oncol. 28:2660–2667. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gentleman RC, Carey VJ, Bates DM, Bolstad
B, Dettling M, Dudoit S, Ellis B, Gautier L, Ge Y, Gentry J, et al:
Bioconductor: Open software development for computational biology
and bioinformatics. Genome Biol. 5:R802004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kerr MK: Linear models for microarray data
analysis: Hidden similarities and differences. J Comput Biol.
10:891–901. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for Annotation,
Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Acunzo M and Croce CM: MicroRNA in cancer
and cachexia - a mini-review. J Infect Dis. 212 Suppl 1:S74–S77.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sapre N, Macintyre G, Clarkson M, Naeem H,
Cmero M, Kowalczyk A, Anderson PD, Costello AJ, Corcoran NM and
Hovens CM: A urinary microRNA signature can predict the presence of
bladder urothelial carcinoma in patients undergoing surveillance.
Br J Cancer. 114:454–462. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kutmon M, Kelder T, Mandaviya P, Evelo CT
and Coort SL: CyTargetLinker: A cytoscape app to integrate
regulatory interactions in network analysis. PLoS One.
8:e821602013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Aguirre-Gamboa R, Gomez-Rueda H,
Martínez-Ledesma E, Martínez-Torteya A, Chacolla-Huaringa R,
Rodriguez-Barrientos A, Tamez-Peña JG and Treviño V: SurvExpress:
An online biomarker validation tool and database for cancer gene
expression data using survival analysis. PLoS One. 8:e742502013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhuang J, Lu Q, Shen B, Huang X, Shen L,
Zheng X, Huang R, Yan J and Guo H: TGFβ1 secreted by
cancer-associated fibroblasts induces epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of bladder cancer cells through lncRNA-ZEB2NAT. Sci Rep.
5:119242015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hung TT, Wang H, Kingsley EA, Risbridger
GP and Russell PJ: Molecular profiling of bladder cancer:
Involvement of the TGF-beta pathway in bladder cancer progression.
Cancer Lett. 265:27–38. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jebar AH, Hurst CD, Tomlinson DC, Johnston
C, Taylor CF and Knowles MA: FGFR3 and Ras gene mutations are
mutually exclusive genetic events in urothelial cell carcinoma.
Oncogene. 24:5218–5225. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kreso A and Dick JE: Evolution of the
cancer stem cell model. Cell Stem Cell. 14:275–291. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Keymoosi H, Gheytanchi E, Asgari M,
Shariftabrizi A and Madjd Z: ALDH1 in combination with CD44 as
putative cancer stem cell markers are correlated with poor
prognosis in urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Asian Pac
J Cancer Prev. 15:2013–2020. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Steg AD, Bevis KS, Katre AA, Ziebarth A,
Dobbin ZC, Alvarez RD, Zhang K, Conner M and Landen CN: Stem cell
pathways contribute to clinical chemoresistance in ovarian cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 18:869–881. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Marcato P, Dean CA, Giacomantonio CA and
Lee PW: Aldehyde dehydrogenase: Its role as a cancer stem cell
marker comes down to the specific isoform. Cell Cycle.
10:1378–1384. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Meng E, Mitra A, Tripathi K, Finan MA,
Scalici J, McClellan S, da Silva L Madeira, Reed E, Shevde LA,
Palle K, et al: ALDH1A1 maintains ovarian cancer stem cell-like
properties by altered regulation of cell cycle checkpoint and DNA
repair network signaling. PLoS One. 9:e1071422014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mukaisho K, Suo M, Shimakage M, Kushima R,
Inoue H and Hattori T: Down-regulation of drs mRNA in colorectal
neoplasms. Jpn J Cancer Res. 93:888–893. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim CJ, Shimakage M, Kushima R, Mukaisho
K, Shinka T, Okada Y and Inoue H: Down-regulation of drs mRNA in
human prostate carcinomas. Hum Pathol. 34:654–657. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tambe Y, Isono T, Haraguchi S,
Yoshioka-Yamashita A, Yutsudo M and Inoue H: A novel apoptotic
pathway induced by the drs tumor suppressor gene. Oncogene.
23:2977–2987. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Duff RM, Tay V, Hackman P, Ravenscroft G,
McLean C, Kennedy P, Steinbach A, Schöffler W, van der Ven PF,
Fürst DO, et al: Mutations in the N-terminal actin-binding domain
of filamin C cause a distal myopathy. Am J Hum Genet. 88:729–740.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vanaja DK, Ehrich M, van den Boom D,
Cheville JC, Karnes RJ, Tindall DJ, Cantor CR and Young CY:
Hypermethylation of genes for diagnosis and risk stratification of
prostate cancer. Cancer Invest. 27:549–560. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mahapatra S, Klee EW, Young CY, Sun Z,
Jimenez RE, Klee GG, Tindall DJ and Donkena KV: Global methylation
profiling for risk prediction of prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
18:2882–2895. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Imura M, Yamashita S, Cai LY, Furuta J,
Wakabayashi M, Yasugi T and Ushijima T: Methylation and expression
analysis of 15 genes and three normally-methylated genes in 13
Ovarian cancer cell lines. Cancer Lett. 241:213–220. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zeller C, Dai W, Steele NL, Siddiq A,
Walley AJ, Wilhelm-Benartzi CS, Rizzo S, van der Zee A, Plumb JA
and Brown R: Candidate DNA methylation drivers of acquired
cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer identified by methylome and
expression profiling. Oncogene. 31:4567–4576. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kaneda A, Kaminishi M, Yanagihara K,
Sugimura T and Ushijima T: Identification of silencing of nine
genes in human gastric cancers. Cancer Res. 62:6645–6650.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Oue N, Mitani Y, Motoshita J, Matsumura S,
Yoshida K, Kuniyasu H, Nakayama H and Yasui W: Accumulation of DNA
methylation is associated with tumor stage in gastric cancer.
Cancer. 106:1250–1259. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Qiao J, Cui SJ, Xu LL, Chen SJ, Yao J,
Jiang YH, Peng G, Fang CY, Yang PY, Liu F and Filamin C: A
dysregulated protein in cancer revealed by label-free quantitative
proteomic analyses of human gastric cancer cells. Oncotarget.
6:1171–1189. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell.
141:52–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nishida N, Yano H, Nishida T, Kamura T and
Kojiro M: Angiogenesis in cancer. Vasc Health Risk Manag.
2:213–219. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Latchman DS: Heat shock proteins and
cardiac protection. Cardiovasc Res. 51:637–646. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Willis MS and Patterson C: Hold me tight:
Role of the heat shock protein family of chaperones in cardiac
disease. Circulation. 122:1740–1751. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen S, Huang H, Yao J, Pan L and Ma H:
Heat shock protein B6 potently increases non-small cell lung cancer
growth. Mol Med Rep. 10:677–682. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang X, Zhao T, Huang W, Wang T, Qian J,
Xu M, Kranias EG, Wang Y and Fan GC: Hsp20-engineered mesenchymal
stem cells are resistant to oxidative stress via enhanced
activation of Akt and increased secretion of growth factors. Stem
Cells. 27:3021–3031. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang X, Wang X, Zhu H, Kranias EG, Tang
Y, Peng T, Chang J and Fan GC: Hsp20 functions as a novel
cardiokine in promoting angiogenesis via activation of VEGFR2. PLoS
One. 7:e327652012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|