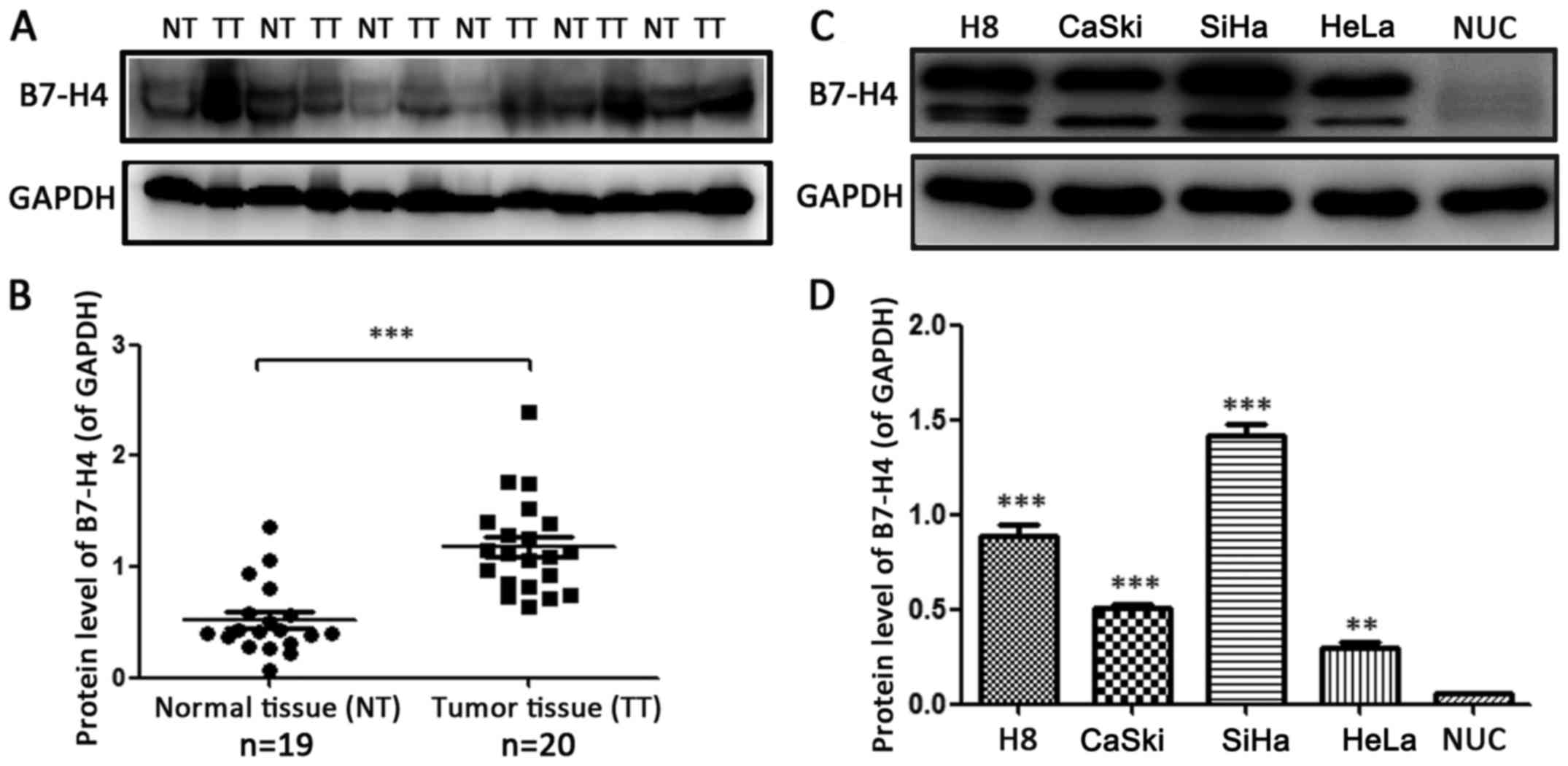
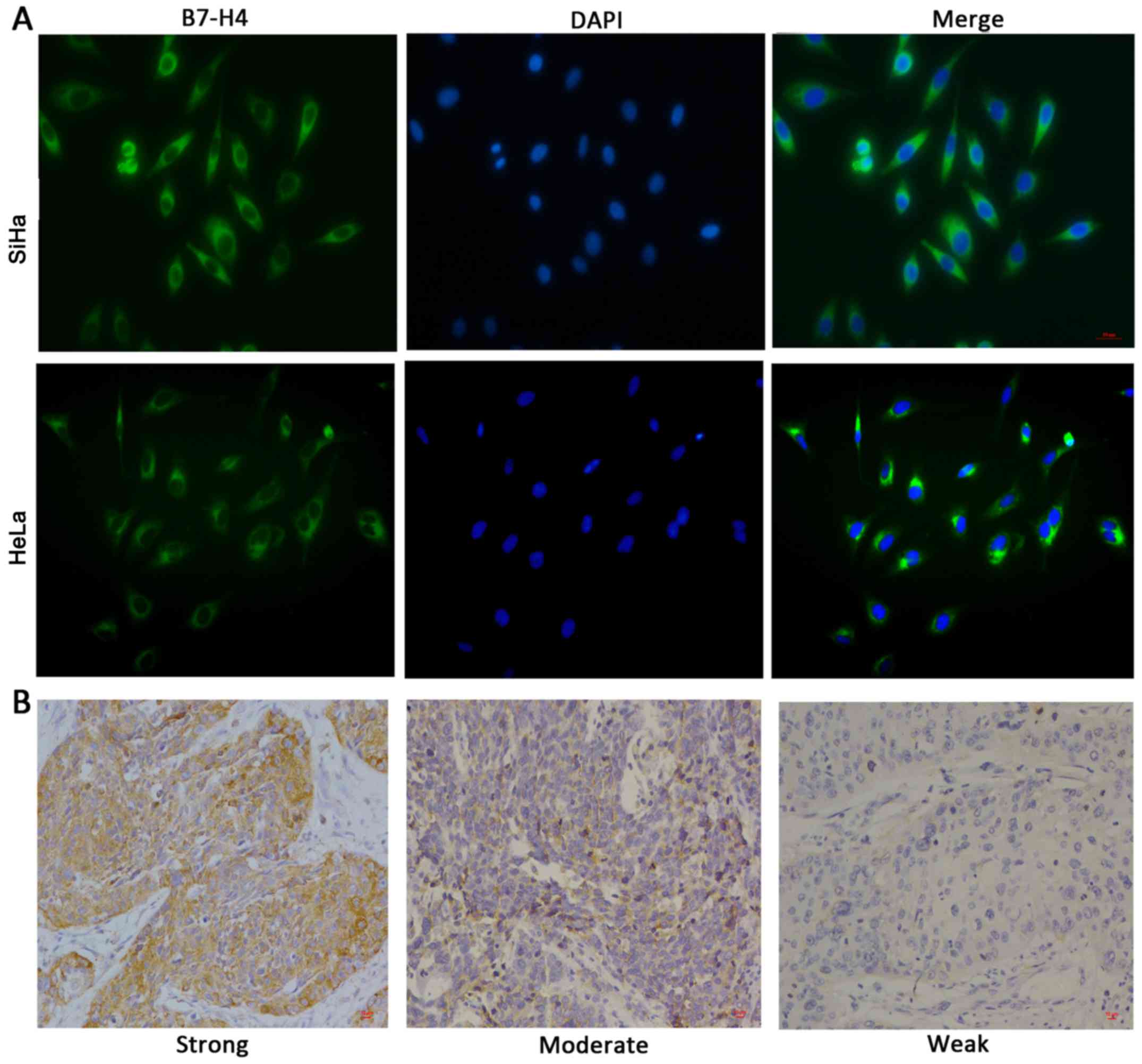
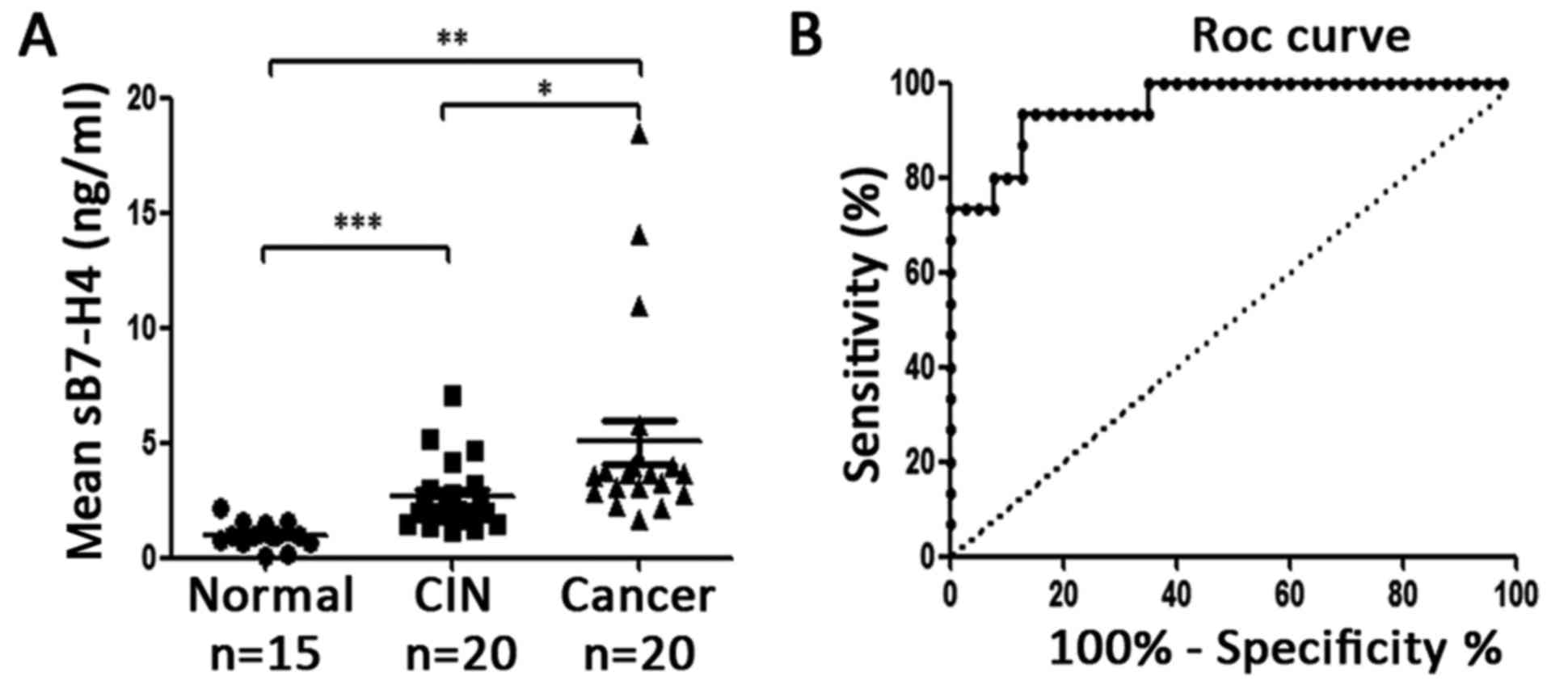
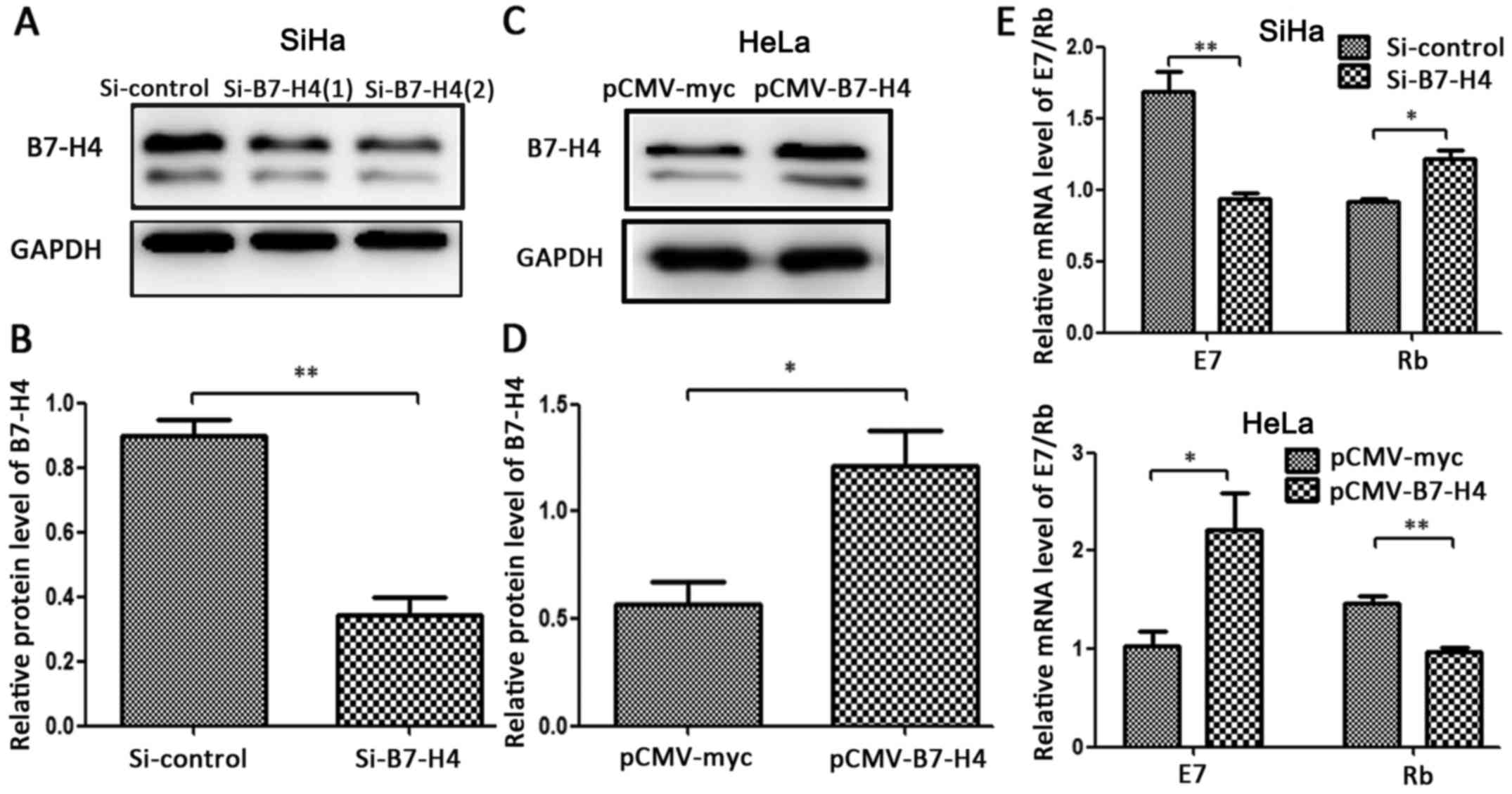
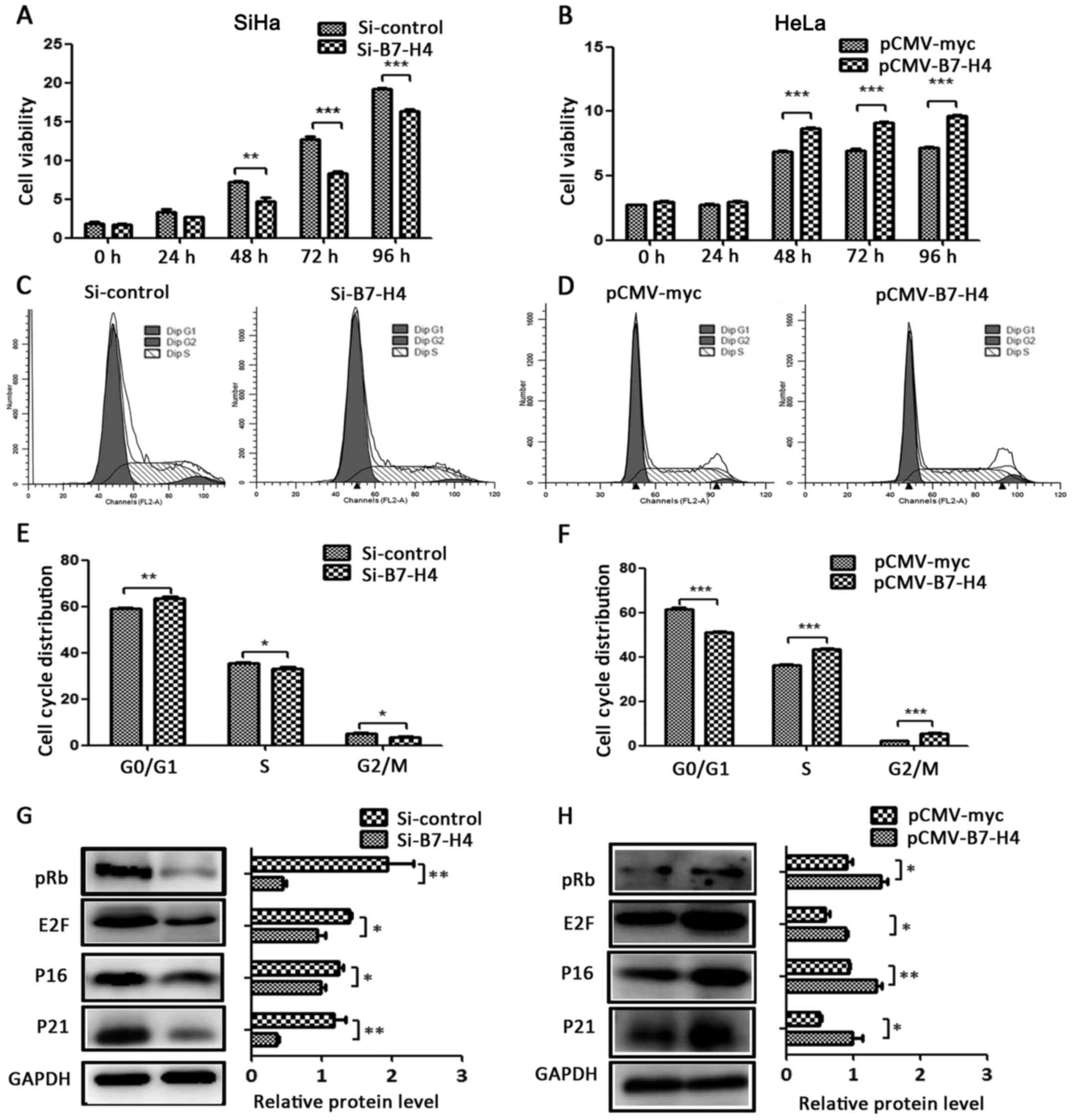
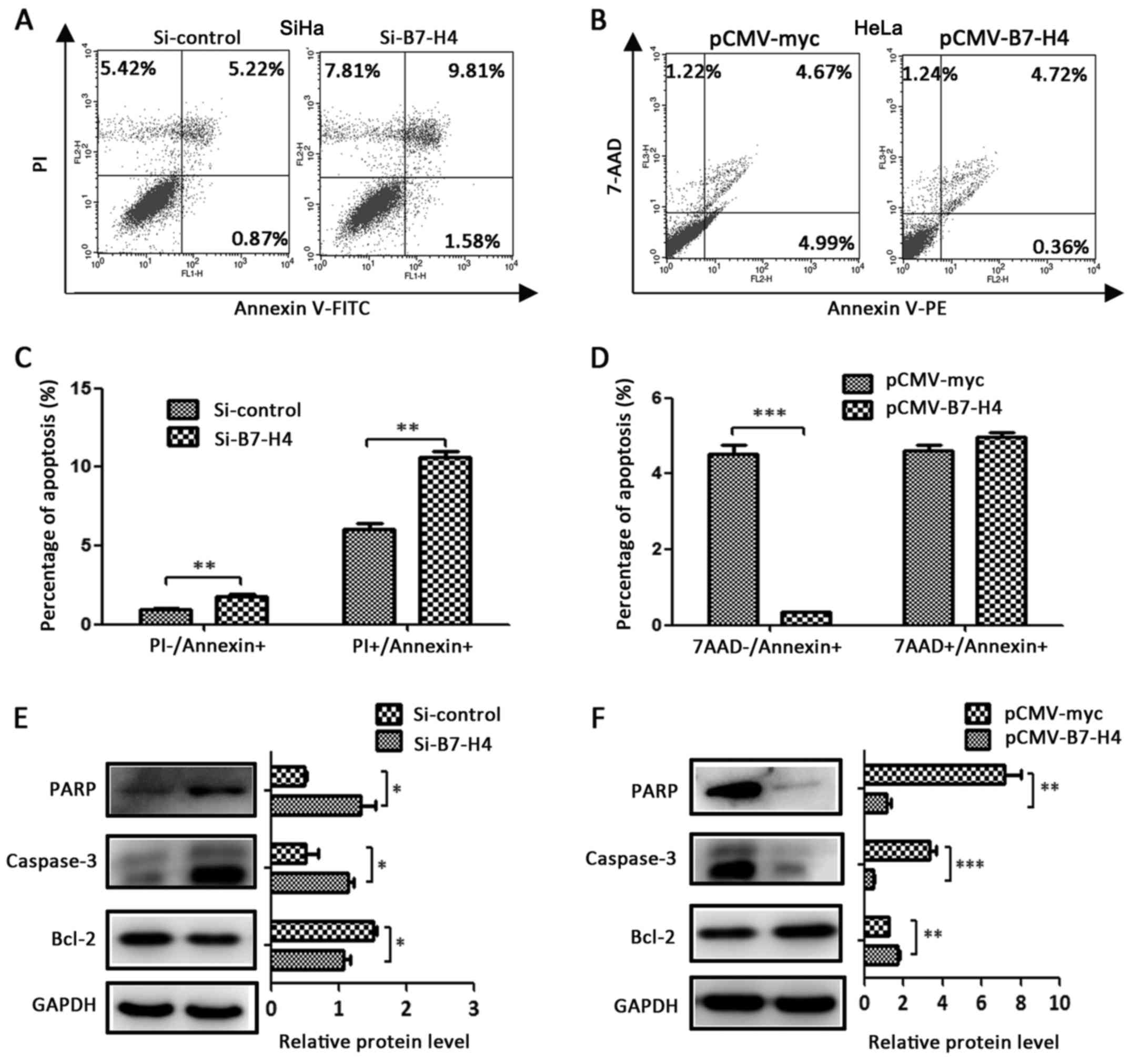
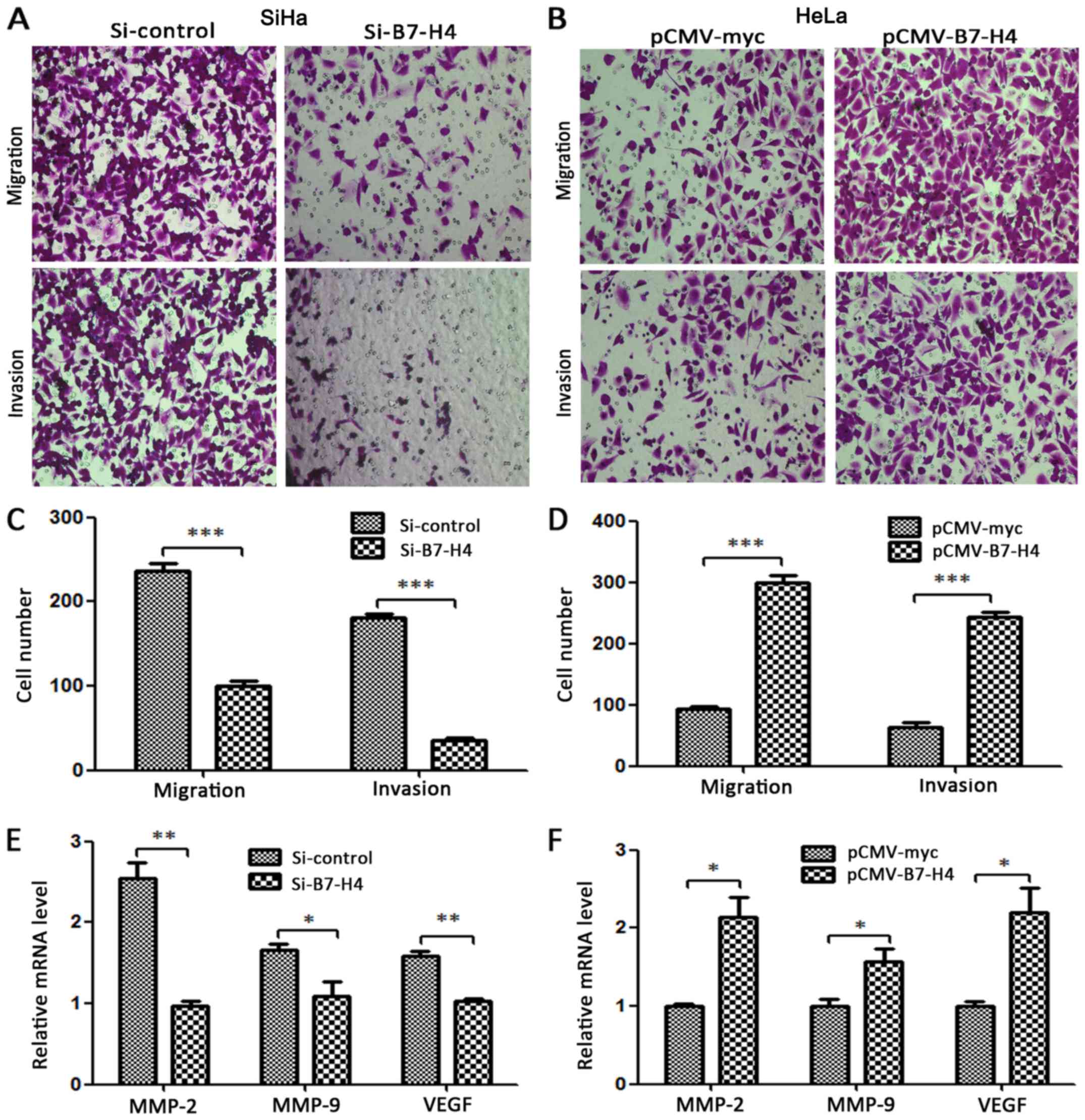
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zur Hausen H: Papillomaviruses causing
cancer: Evasion from host-cell control in early events in
carcinogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 92:690–698. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shi Y, Li L, Hu Z, Li S, Wang S, Liu J, Wu
C, He L, Zhou J, Li Z, et al: A genome-wide association study
identifies two new cervical cancer susceptibility loci at 4q12 and
17q12. Nat Genet. 45:918–922. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Postow MA, Callahan MK and Wolchok JD:
Immune checkpoint blockade in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol.
33:1974–1982. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zou W and Chen L: Inhibitory B7-family
molecules in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol.
8:467–477. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zang X, Loke P, Kim J, Murphy K, Waitz R
and Allison JP: B7x: A widely expressed B7 family member that
inhibits T cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:10388–10392. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Prasad DV, Richards S, Mai XM and Dong C:
B7S1, a novel B7 family member that negatively regulates T cell
activation. Immunity. 18:863–873. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sica GL, Choi IH, Zhu G, Tamada K, Wang
SD, Tamura H, Chapoval AI, Flies DB, Bajorath J and Chen L: B7-H4,
a molecule of the B7 family, negatively regulates T cell immunity.
Immunity. 18:849–861. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rahbar R, Lin A, Ghazarian M, Yau HL,
Paramathas S, Lang PA, Schildknecht A, Elford AR, Garcia-Batres C,
Martin B, et al: B7-H4 expression by nonhematopoietic cells in the
tumor microenvironment promotes antitumor immunity. Cancer Immunol
Res. 3:184–195. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rahbar R and Ohashi PS: B7-H4 is a
positive regulator of antitumor immunity. OncoImmunology.
5:e10505752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sun Y, Wang Y, Zhao J, Gu M, Giscombe R,
Lefvert AK and Wang X: B7-H3 and B7-H4 expression in non-small-cell
lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 53:143–151. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Salceda S, Tang T, Kmet M, Munteanu A,
Ghosh M, Macina R, Liu W, Pilkington G and Papkoff J: The
immunomodulatory protein B7-H4 is overexpressed in breast and
ovarian cancers and promotes epithelial cell transformation. Exp
Cell Res. 306:128–141. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Krambeck AE, Thompson RH, Dong H, Lohse
CM, Park ES, Kuntz SM, Leibovich BC, Blute ML, Cheville JC and Kwon
ED: B7-H4 expression in renal cell carcinoma and tumor vasculature:
Associations with cancer progression and survival. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 103:10391–10396. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Peng HX, Wu WQ, Yang DM, Jing R, Li J,
Zhou FL, Jin YF, Wang SY and Chu YM: Role of B7-H4 siRNA in
proliferation, migration, and invasion of LOVO colorectal carcinoma
cell line. BioMed Res Int. 2015:3269812015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cheng L, Jiang J, Gao R, Wei S, Nan F, Li
S and Kong B: B7-H4 expression promotes tumorigenesis in ovarian
cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 19:1481–1486. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Simon I, Liu Y, Krall KL, Urban N, Wolfert
RL, Kim NW and McIntosh MW: Evaluation of the novel serum markers
B7-H4, Spondin 2, and DcR3 for diagnosis and early detection of
ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 106:112–118. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang W, Xu C, Wang Y, Yu L and Zhang X:
Prognostic values of B7-H4 in non-small cell lung cancer.
Biomarkers. 1–16. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Pecorelli S, Zigliani L and Odicino F:
Revised FIGO staging for carcinoma of the cervix. Int J Gynaecol
Obstet. 105:107–108. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McMurray HR, Nguyen D, Westbrook TF and
McAnce DJ: Biology of human papillomaviruses. Int J Exp Pathol.
82:15–33. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kaur P, McDougall JK and Cone R:
Immortalization of primary human epithelial cells by cloned
cervical carcinoma DNA containing human papillomavirus type 16
E6/E7 open reading frames. J Gen Virol. 70:1261–1266. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen J, Lai L, Liu S, Zhou C, Wu C, Huang
M and Lin Q: Targeting HIF-1α and VEGF by lentivirus-mediated RNA
interference reduces liver tumor cells migration and invasion under
hypoxic conditions. Neoplasma. 63:934–940. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lu X, Duan L, Xie H, Lu X, Lu D, Lu D,
Jiang N and Chen Y: Evaluation of MMP-9 and MMP-2 and their
suppressor TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 in adenocarcinoma of esophagogastric
junction. Onco Targets Ther. 9:4343–4349. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xie B, Zhang Z, Wang H, Chen Z, Wang Y,
Liang H, Yang G, Yang X and Zhang H: Genetic polymorphisms in MMP
2, 3, 7, and 9 genes and the susceptibility and clinical outcome of
cervical cancer in a Chinese Han population. Tumour Biol.
37:4883–4888. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fauci JM, Straughn JM Jr, Ferrone S and
Buchsbaum DJ: A review of B7-H3 and B7-H4 immune molecules and
their role in ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 127:420–425. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang X, Wang T, Xu M, Xiao L, Luo Y, Huang
W, Zhang Y and Geng W: B7-H4 overexpression impairs the immune
response of T cells in human cervical carcinomas. Hum Immunol.
75:1203–1209. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang L, Wu H, Lu D, Li G, Sun C, Song H,
Li J, Zhai T, Huang L, Hou C, et al: The costimulatory molecule
B7-H4 promote tumor progression and cell proliferation through
translocating into nucleus. Oncogene. 32:5347–5358. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu H, Lin A, Shao X, Shi W, Zhang Y and
Yan W: Diagnostic accuracy of high-risk HPV genotyping in women
with high-grade cervical lesions: Evidence for improving the
cervical cancer screening strategy in China. Oncotarget.
7:83775–83783. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Park IU, Wojtal N, Silverberg MJ, Bauer
HM, Hurley LB and Manos MM: Cytology and human papillomavirus
co-test results preceding incident high-grade cervical
intraepithelial neoplasia. PLoS One. 10:e01189382015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang L, Cao NN, Wang S, Man HW, Li PF and
Shan BE: Roles of coinhibitory molecules B7-H3 and B7-H4 in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 37:2961–2971.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Balsitis S, Dick F, Dyson N and Lambert
PF: Critical roles for non-pRb targets of human papillomavirus type
16 E7 in cervical carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 66:9393–9400. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
van der Watt PJ, Ngarande E and Leaner VD:
Overexpression of Kpnβ1 and Kpnα2 importin proteins in cancer
derives from deregulated E2F activity. PLoS One. 6:e277232011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Crosbie EJ, Einstein MH, Franceschi S and
Kitchener HC: Human papillomavirus and cervical cancer. Lancet.
382:889–899. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|